【第九周】单链有序线性表+后羿采集器
1 .h 2 // 单链有序线性表基本操作介面 3 typedef int ElemType; // 定义线性表元素类型为整数 int. 4 5 typedef struct node { // 定义链结表节点 6 ElemType elem; // 节点数据,整数 7 struct node* next; // 节点的链,递归定义。 8 } Node; // 节点型态 9 10 typedef Node* Link; // 节点的链,是节点的指针。 11 12 typedef Link List; // 有序线性表是一个节点指针,指向链结表的头节点 (head node)。 13 14 // 初始化线性表,将 size 设为 0。 15 void initial(List *); 16 17 // 线性表的大小。 18 int getSize(List); 19 20 // 取出线性表的第 i 个元素, 返回该元素的值; 21 // 若 i 大于线性表的元素个数,返回 -1。 22 ElemType getElem(List, int); 23 // 搜寻线性表的元素,返回该元素的位置。若成功,返回该元素的位置; 24 // 否则,返回 -1。 25 int search(List, ElemType); 26 27 // 将一个元素插入到线性表适当的位置。若成功,返回该元素的位置; 28 // 否则,返回 -1。 29 int insert(List *, ElemType); 30 31 // 从线性表删除一个元素。若成功,返回该元素原来的位置;否则,返回 -1。 32 int delete(List *, ElemType); 33 34 // 将线性表清空。 35 void clear(List *); 36 37 // 檢查线性表是否為空表。若是空,返回 1;否则,返回 0。 38 int is_empty(List); 39 40 // 打印线性表元素。 41 // 我们增加这个函数,因为它的必要性。 42 void printlst(List); 43 44 45 .c 46 // 单链有序线性表基本操作介面 47 #include <stdio.h> 48 #include <stdlib.h> 49 #include "sorted_list_single_list.h" 50 51 // 初始化线性表 L。 52 void initial(List *L) { 53 *L = NULL; // 将线性表的指针设为空值。 54 } 55 56 // 取得线性表 L 的大小,返回元素个数。 57 int getSize(List L) { 58 Link link = L; // 节点指针。 59 int size = 0; // 线性表个数初始值设为 0. 60 61 while (link!=NULL) { 62 link = link->next; // 下一个节点。 63 size++; 64 } 65 return size; // 线性表 L 的大小。 66 } 67 // 取出线性表的第 i 个元素, 返回该元素的值; 68 // 若 i 大于线性表的元素个数,返回 -1。 69 ElemType getElem(List L, int inx) { 70 Link current = L; // 节点指针。 71 int i; // 循环变量。 72 73 for (i=0; i<inx; i++) 74 if (current==NULL) return -1; // 第 i 个元素不存在。 75 else current = current->next; // 移到下一个元素。 76 return current->elem; // 返回节点的元素值。 77 } 78 79 // 搜寻元素 e 在 L 中的位置。若成功,返回 e 的索引;否则,返回 -1。 80 int search(List L, ElemType e) { 81 Link link = L; // 节点指针。 82 int position=0; // 元素位置,设定初始值为 0。 83 84 while (link!=NULL) { 85 if (link->elem==e) return position; // 搜寻成功,返回元素 e 的位置。 86 else if (link->elem<e) { // 还有其它节点,继续搜寻。 87 link = link->next; // 移到下一个节点。 88 position++; // 位置加 1。 89 } 90 else return -1; // 节点的值已超过,搜寻失败。 91 } 92 return -1; // 已经超过线性表的最后一个节点,搜寻失败。 93 } 94 95 // 将元素 e 插入到 L 适当的位置。插入完成时,返回 e 的位置。 96 int insert(List *L, ElemType e) { 97 Link current = *L; // 指向目前的节点。 98 Link previous = NULL; // 指向前一个节点,开始时为空。 99 Link newNode; // 新节点的指针。 100 int position = 0; // 目前节点位置。 101 102 if (*L==NULL) { // Case 1:线性表是空的。 103 newNode = (Link) malloc(sizeof(Node)); // 要求一个新节点的内存。 104 newNode->elem = e; // 设定头节点的数据。 105 newNode->next = NULL; // 设定头节点的链。 106 *L = newNode; // 线性表指向第一个节点。 107 return 0; // 返回头节点位置。 108 } 109 110 do { // 检查目前的节点。 if (current->elem>=e) { // Cases 2 & 3: 找到插入位置,插在这个节点之前。 111 newNode = (Link) malloc(sizeof(Node)); // 要求一个新节点的内存。 112 newNode->elem = e; // 设定新节点的数据。 113 newNode->next = current; // 设定新节点的链。 114 if (previous==NULL) *L = newNode; // Case 2: 插入线性表的头节点。 115 else previous->next = newNode; // Case3:修改前一节点的链。 116 return position; // 返回位置。 117 } 118 else { 119 previous = current; // 将目前的节点设为前一个节点。 120 current = current->next; // 将下一个节点设为下一步骤的目前节点。 121 position++; // 位置加 1。 122 } 123 } while (current!=NULL); // 若线性表还有节点,继续。 124 125 // Case 4:while 循环结束,没有执行返回,移到链结表的最后节点。 126 newNode = (Link) malloc(sizeof(Node)); // 要求一个新节点的内存。 127 newNode->elem = e; // 设定新节点的数据。 128 newNode->next = NULL; // 最后的节点,将其下一个节点设为空值。 129 previous->next = newNode; // 将新增节点放在线性表的最后。 130 return position; // 返回位置。 131 } 132 133 // 从 L 删除元素 e。若成功,返回 e 原来的位置;否则,返回 -1。 134 int delete(List *L, ElemType e) { 135 Link current = *L; // 指向目前的节点。 136 Link previous; // 指向前一个节点。 137 int position = 0; // 目前节点位置。 138 139 while (current!=NULL) { // 当线性表还有节点。 140 if (current->elem==e) { // 找到要删除的节点。 141 if (position==0) { // 删除的节点是头节点。 142 *L = current->next; // 设定下一个节点为头节点。 143 free(current); // 释放删除的节点。 144 return position; // 返回删除节点的原来位置。 145 } 146 else { 147 previous->next = current->next; // 将前一个节点的链指向目前的下一个节点。 148 free(current); // 释放删除的节点。 149 return position; // 返回删除节点的原来位置。 150 } 151 } 152 else if (current->elem<e) { 153 previous = current; // 将目前的节点设为前一个节点。 154 current = current->next; // 将下一个节点设为下一步骤的目前节点。 155 position++; // 位置加 1。 156 } 157 else return -1; // 目前节点数据已超过删除的值;删除失败。 158 } 159 return -1; // 已经没有节点,删除失败。 160 } 161 162 // 将线性表 L 清空。 163 void clear(List *L) { 164 Link current; // 指向目前的节点。 165 166 while (*L!=NULL) { // 还有节点要清除。 167 current = *L; // 目前的节点。 168 *L = current->next; // 剩余的链结表。 169 free(current); // 释放目前的节点。 170 } 171 } 172 173 // 檢查线性表 L 是否為空表。若是空,返回 1;否则,返回 0。 174 int is_empty(List L) { 175 return L==NULL; // 若 L 为空值,返回 1,否则,返回 0。 } 176 177 // 打印线性表元素。 178 // 我们增加这个函数,因为它的必要性。 179 void printlst(List L) { 180 List current = L; // 指向目前的节点。 181 int position = 0; // 目前节点的位置。 182 183 printf("线性表元素个数:%3d 元素\n", getSize(L)); 184 185 while (current!=NULL) { // 还有节点要打印。 186 printf("%3d ", current->elem); // 打印节点数据。 187 if ((position+1)%20==0) printf("\n"); // 满 20 个元素,打印换行。 188 current = current->next; // 移到下一个节点。 189 position++; // 下一个位置。 190 } 191 if ((position%20)!=0) printf("\n"); // 若不足 20 个元素,打印一个换行。 192 printf("\n"); // 打印一个换行。 193 } 194 195 196 main.c 197 #include <stdio.h> 198 #include <stdlib.h> 199 #include <time.h> 200 #include "sorted_list_single_list.h" 201 202 // 合并 (merge) 两个线性表 L1 和 L2。 203 // 返回合并后的线性表。 204 List merge_list(List L1, List L2) { 205 List L; // 合并的线性表。 206 int size1=getSize(L1), size2=getSize(L2); // 线性表 L1,和 L2 的大小。 207 ElemType e1, e2; // 线性表 L1 和 L2 的元素。 208 int i1=0, i2=0; // 线性表 L1 和 L2 的索引。 209 210 initial(&L); // 初始化 L。 211 212 // i1<L1.size: l1 还有元素待合并。 213 // i2<L2.size: l2 还有元素待合并。 214 while (i1<size1 && i2<size2) { 215 e1 = getElem(L1, i1); // 取得 L1 的元素。 216 e2 = getElem(L2, i2); // 取得 L2 的元素。 217 // 将 L1 和 L2 较小的元素放到 L 中,并移到下一个元素的位置。 218 if (e1<=e2) {insert(&L, e1); i1++;} 219 else {insert(&L, e2); i2++;} 220 } 221 222 // L1 还有元素,继续复制 L1 的元素。 223 while (i1<size1) insert(&L, getElem(L1, i1++)); 224 225 // L2 还有元素,继续复制 L2 的元素。 226 while (i2<size2) insert(&L, getElem(L2, i2++)); 227 228 return L; // 返回合并后的线性表。 229 } 230 231 // 合自 L1 中移除 (remove) 所有 L2 的元素。 232 // 返回移除后的线性表。 233 List remove_list(List L1, List L2) { 234 List L; // 移除的线性表。 235 int size1=getSize(L1), size2=getSize(L2); // 线性表 L1,和 L2 的大小。 236 ElemType e1, e2; // 线性表 L1 和 L2 的元素。 237 int i1=0, i2=0; // 线性表 L1 和 L2 的索引。 238 239 initial(&L); // 初始化 L。 240 // i1<size1: l1 还有元素待移除。 241 // i2<size2: l2 还有元素待移除。 242 while (i1<size1 && i2<size2) { 243 e1 = getElem(L1, i1); // 取得 L1 的元素。 244 e2 = getElem(L2, i2); // 取得 L2 的元素。 245 // 若 L1 和 L2 的元素相同,移除 L1 的元素,不储存。 246 if (e1==e2) i1++; 247 // 若 L1 的元素小于 L2 的元素,将 L1 的元素放到 L 中。 248 else if (e1<e2) {insert(&L, e1); i1++;} 249 // 若 L1 的元素大于 L2 的元素,检查下一个 L2 的元素。 250 else i2++; 251 } 252 253 // L2 已经没有元素;但是,L1 还有元素,继续将 L1 的元素放到 L 中。 254 while (i1<size1) insert(&L, getElem(L1, i1++)); 255 256 return L; // 返回移除后的线性表。 257 } 258 259 int main(void) { 260 List L, L1, L2; // 声明线性表。 261 int leng1, leng2; // 两个线性表的长度。 int i; // 循环变量。 262 263 initial(&L1); // 初始化 L1。 264 initial(&L2); // 初始化 L2。 265 266 srand(time(NULL)); // 随机数生成器的种子。 267 268 // 输入线性表 L1 的元素个数。 269 do { 270 printf("输入线性表 L1 的元素个数 (1 与 100 (含)之间):"); 271 scanf("%d", &leng1); 272 } while (leng1<0 || leng1>100); 273 274 // 输入线性表 L2 的元素个数。 275 do { 276 printf("输入线性表 L2 的元素个数 (1 与 100 (含)之间):"); 277 scanf("%d", &leng2); 278 } while (leng2<0 || leng2>100); 279 printf("-------------------------------------------\n"); 280 281 // 随机产生 L1 的元素。 282 for (i=0; i<leng1; i++) insert(&L1, rand() % 100); // 插入 L1 的元素。 283 printf("线性表 L1:\n"); 284 printlst(L1); // 打印线性表 L1。 285 286 // 随机产生 L2 的元素。 287 for (i=0; i<leng2; i++) insert(&L2, rand() % 100); // 插入 L2 的元素。 288 printf("线性表 L2:\n"); 289 printlst(L2); // 打印线性表 L2。 290 291 L = merge_list(L1, L2); // 合并 L1 和 L2。 292 printf("合并 L1 和 L2 的线性表:\n"); 293 printlst(L); // 打印合并的线性表。 294 295 L = remove_list(L1, L2); // 从 L1 移除 L2。 296 printf("从 L1 移除 L2 的线性表:\n"); 297 printlst(L); // 打印移除的线性表。 298 299 return 0; 300 }
学习思考以上老师代码
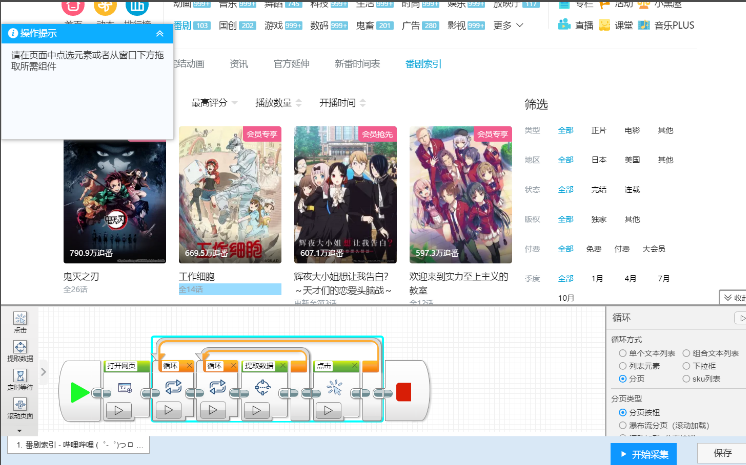
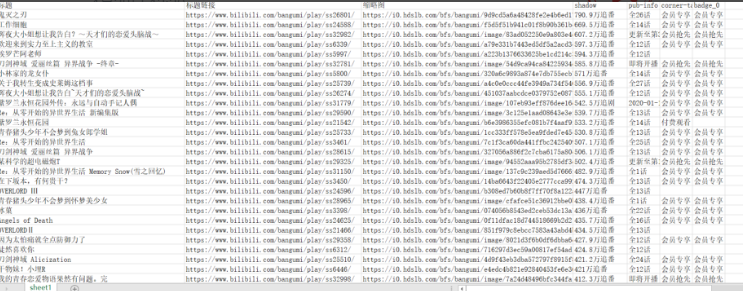
自主学习后羿采集器的用法提取数据



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号