实验报告2
实验结果:
实验4代码如下:info.hpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; class info { private: string nickname; string contact; string city; int n; static int mebers_reserved; public: info(){ n = 0; cout << "initialized without any parameter!\n"; } info(string a, string b, string c, int d) : nickname(a), contact(b), city(c), n(d) { mebers_reserved += d;} info(const info& a) : nickname(a.nickname), contact(a.contact), city(a.city), n(a.n) { mebers_reserved += a.n;} void print() const; int current_audience_number() { return mebers_reserved; } }; int info::mebers_reserved = 0; void info::print() const { cout << "the name of the member is: " << nickname << endl; cout << "contact :" << contact << endl; cout << "city:" << city << endl; cout << "the number of is group:" << n << endl; }
main.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include "info.hpp" #include <vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector<info> audience_info_list; const int max_audience = 100; cout << "please print the data of audience on the screen! and type end to end this programme!\n"; string nickname; string contact; string city; int n; while (cin >> nickname) { cin >> contact; cin >> city; cin >> n; audience_info_list.push_back(info(nickname, contact, city, n)); if (audience_info_list[0].current_audience_number() > max_audience) { cout << "oop! too more audience ! error , the programme is finished!\n"; audience_info_list.pop_back(); break; } } cout << "untile now , there are " << audience_info_list[0].current_audience_number() << " members in this group!\n"; for (auto i = audience_info_list.begin(); i != audience_info_list.end(); ++i) (*i).print(); return 0; }
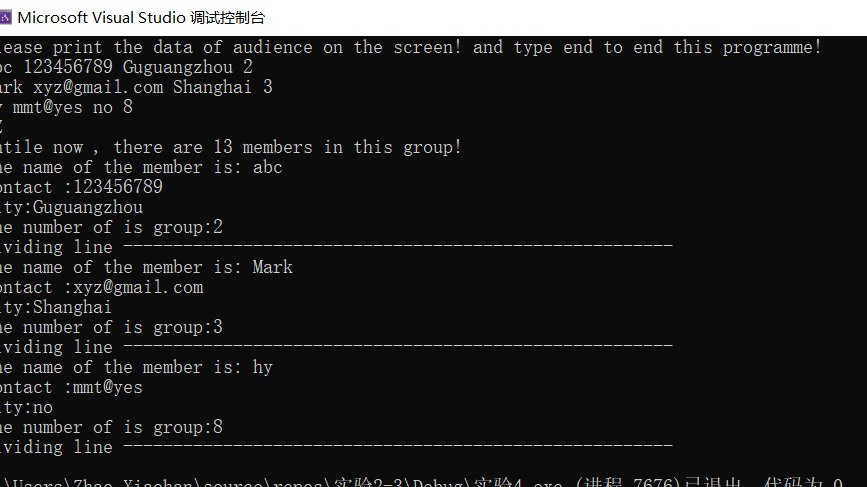
测试1:输入control + z 自动结束,打印
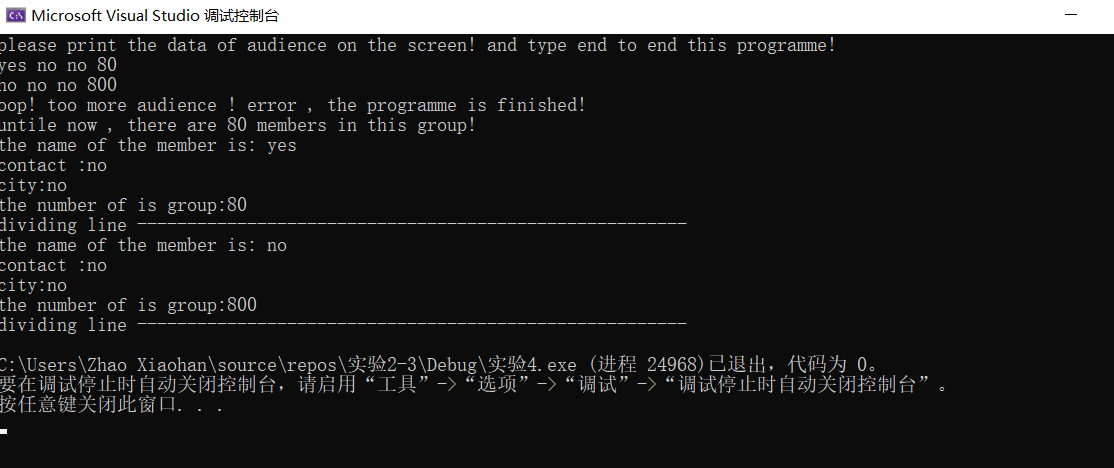
测试2:当人数输入超过最大上线的人数时,程序结束,打印当前信息
实验5代码如下:
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; class TextCoder { private: string text; public: TextCoder() { cout << "initialized without any input!\n"; } TextCoder(string a) : text(a) {} TextCoder(TextCoder& a) :text(a.text) {} string encoder(); string decoder(); }; string TextCoder::encoder() { string temp = text; for (auto &ch : temp) { if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'U') ch += 5; else if (ch >= 'V' && ch <= 'Z') ch = 'A' + ch - 'V'; else if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'u') ch += 5; else if (ch >= 'v' && ch < 'z') ch = 'a' + ch - 'v'; } return temp; } string TextCoder::decoder() { string temp = text; for (auto &ch : temp) { if (ch >= 'f' && ch <= 'z') ch -= 5; else if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'e') ch = 'z' + ch - 'e'; if (ch >= 'F' && ch <= 'Z') ch -= 5; else if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'E') ch = 'Z' + ch - 'E' ; } return temp; }
实验5测试:
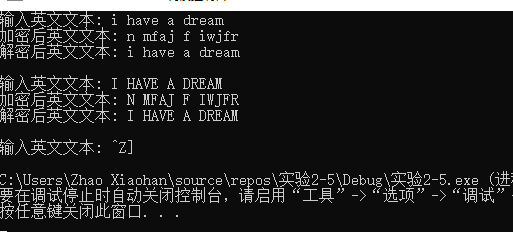
大小写转化正常,输入contr z退出
实验总结:
1、语法层面:
(1)类数组的模板类构造使用是默认构造函数以及复制构造函数,所以,在处理人数的时候,如果在构造的时候已经将总人数自增了,那么在传参数给模板类,让模板类压栈的时候,就不应该再一次增加人数,也就是复制构造函数不应该有member += d 这一句,因为这样人数会变成原来的两倍。
(2)auto for循环的语法,for(auto xx : temp)自动选取temp里面的序列,有点像是python里面的for i in {sequence},但是这个sequence是由auto自动取得的,注意,如果想要修改xx,则应该为&xx,表示xx为temp序列的一个引用,如果是xx,那么诸如x += 5,就是相当于将这个指针往后跳五个序列长度,这里要注意。
2、开发层面:
(1)要学会用新版本的新特性,这样可以节省生命,让编程更轻松一点。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号