哈夫曼编/译码器【NOJ实验第7题】
前言
在造哈夫曼树的时候用了不少时间,因为之前写的哈夫曼树是错的(没错,不过上一篇文章已经重投了)
这道题思路很简单,但实现起来感觉还是有点麻烦。。。
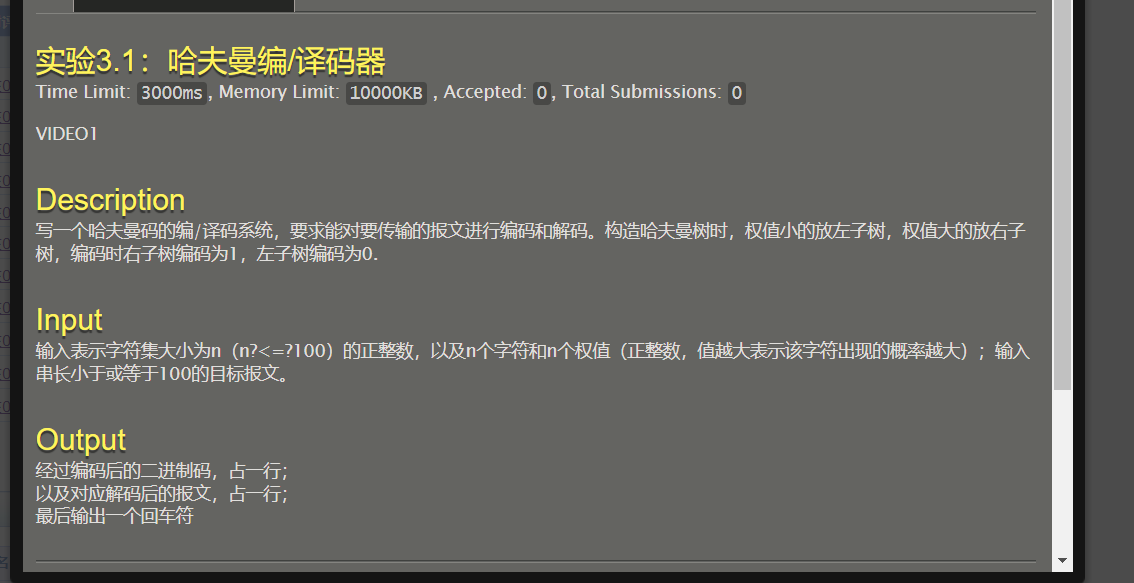
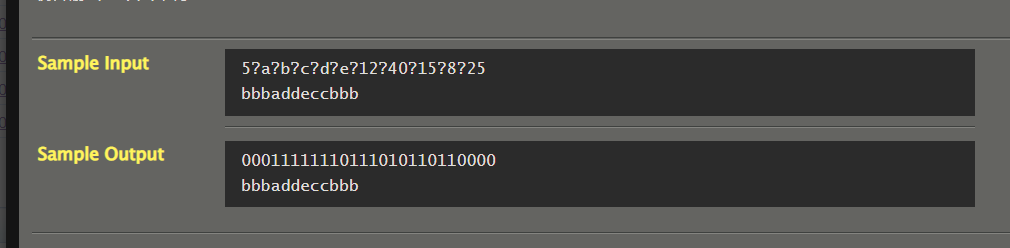
题目描述
思路详解
先来看看解决方案的结构
struct HuffmanTreeNode
{
bool hasChecked; // 检查该结点是否在森林中,true表示不在
int weight; // 权值
int LChild; // 左孩子下标
int RChild; // 右孩子下标
int parent; // 双亲下标
};
class HuffmanTree
{
private:
HuffmanTreeNode *tree; // 哈夫曼树结点数组
int n; // 结点数组的长度
public:
void init(int weight[], int n, char character[]); // 创建并初始化一颗哈夫曼树
void search(int max, int &s1, int &s2); // 寻找森林里权值最小的两棵树
void sort(int weight[], char character[]); // 对输入的权值序列以及其对应的字母顺序进行排序
void createCode(char **result, int *weight); // 创造字母对应的哈夫曼编码
void printCode(char *input, char **result, char *character, char *code); // 输出字母转换的哈夫曼编码,并将其保存于code中
void paresCodeAndPrint(char *code, char **result, char *character); // 将code中的哈夫曼编码转化为字母并打印输出
};
题目要求我们输入长度$n$,$n$个字符,$n$个权值以及原始码序列,但我们首先需要创建哈夫曼树的一个实例,因此在main函数中
int main(){
HuffmanTree aTree; // 实例化的树
int n; // 输入长度n
int weight[100] = {0}; // 权值序列
char character[100] = {0}; // 对应的字母序列
char input[100] = {0}; // 输入的原始字符串
char **result = new char *[100]; //每个字母对应的哈夫曼编码数组
char code[100] = {'\0'}; // 转换成的哈夫曼编码
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
result[i] = new char[100];
}
std::cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
std::cin >> character[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
std::cin >> weight[i];
}
std::cin >> input;
这下输入完成了,那么接下来我们应该创建哈夫曼树,也就是初始化。
void HuffmanTree::init(int weight[], int n, char character[])
{
this->n = n;
tree = new HuffmanTreeNode[2 * n];
sort(weight, character);
//初始化前1~n个
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
tree[i] = {false, weight[i - 1], 0, 0, 0};
}
//初始化后n + 1~2n - 1个
for (int i = n + 1; i <= 2 * n - 1; i++)
{
tree[i] = {false, 100, 0, 0, 0};
}
int s1, s2;
for (int i = n + 1; i <= 2 * n - 1; i++)
{
search(i - 1, s1, s2);
// 找出权值最小的两颗子树
// 由于需要让权值小的在左子树,因此我们让权值s1 < s2
tree[i].weight = tree[s1].weight + tree[s2].weight;
tree[i].LChild = s1;
tree[i].RChild = s2;
tree[s1].parent = i;
tree[s2].parent = i;
}
}
而其中的search函数实现如下
void HuffmanTree::search(int max, int &s1, int &s2)
{
int i, min = 999, k = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= max; i++)
{
if (tree[i].hasChecked) // 如果该树不在森林中则跳过
{
continue;
}
if (tree[i].weight < min)
{
min = tree[i].weight;
k = i;
}
}
s1 = k;
tree[s1].hasChecked = true; // 将找到的最小权值的树移出森林再寻找最小的树
k = 1;
min = 999;
for (i = 1; i <= max; i++)
{
if (tree[i].hasChecked)
{
continue;
}
if (tree[i].weight < min)
{
min = tree[i].weight;
k = i;
}
}
s2 = k;
tree[k].hasChecked = true;
}
其中为了保证有序还对输入权值序列进行了排序(可能非必要)
void HuffmanTree::sort(int *weight, char character[])
{ // 选择排序
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int min = weight[i];
k = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (weight[j] < min)
{
min = weight[j];
k = j;
}
}
if (k != i)
{
// 字母数组与权值序列同时进行排序以保持对应关系
int t = weight[k];
weight[k] = weight[i];
weight[i] = t;
char m = character[k];
character[k] = character[i];
character[i] = m;
}
}
}
创建完哈夫曼树后,即是根据哈夫曼树来创造哈夫曼编码
void HuffmanTree::createCode(char **result, int *weight)
{
// 自树的叶子结点(即前1~n个结点)向上进行编码
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int k = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < 2 * n; j++) // 寻找在树节点数组里对应的权值
{
// 若不是叶子结点
if (tree[j].LChild || tree[j].RChild)
{
continue;
}
else
{
if (tree[j].weight == *weight)
{
k = j;
weight++;
break;
}
}
}
char *temp = *result; // 记录字符串开始位置
if (k == 0)
return;
while (tree[k].parent != 0) // 找到之后开始从下网上进行编码
{
if (tree[tree[k].parent].LChild == k)
{
**result = '0';
(*result)++;
}
else if (tree[tree[k].parent].RChild == k)
{
**result = '1';
(*result)++;
}
k = tree[k].parent;
}
**result = '\0'; // 补全字符串
(*result) = temp; // 找回原字符串位置
// 对数组进行翻转
for (int m = 0, j = (strlen((*result)) - 1); m < j; m++, j--)
{
char temp = (*result)[m];
(*result)[m] = (*result)[j];
(*result)[j] = temp;
}
result++;
}
}
现在每一个字母对应的哈夫曼编码已经得到了,保存于result中,那么下面就是根据编码输出了,这里为了方便下一步操作,还将输出的哈夫曼编码保存在了code中
void HuffmanTree::printCode(char *input, char **result, char *character, char *code)
{
while (*input != '\0')
{
// 寻找result中对应的结果
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (*input == character[i])
{
break;
}
}
std::cout << result[i];
strcat(code, result[i]); // 构造code
input++;
}
}
最后一步便是根据哈夫曼编码输出原始字符串了
void HuffmanTree::paresCodeAndPrint(char *code, char **result, char *character)
{
while (*code != '\0')
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (strncmp(code, result[i], strlen(result[i])) == 0)
{
std::cout << character[i];
code += strlen(result[i]);
break;
}
}
}
}
到此这道题结束
完整代码实现
/**
* @file 7.cpp
* @author zh(帝皇の惊)(RickSchanze)
* @brief 哈夫曼编/译码器
* @date 2022-04-19
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
struct HuffmanTreeNode
{
bool hasChecked; // 检查该结点是否在森林中,true表示不在
int weight; // 权值
int LChild; // 左孩子下标
int RChild; // 右孩子下标
int parent; // 双亲下标
};
class HuffmanTree
{
private:
HuffmanTreeNode *tree; // 哈夫曼树结点数组
int n; // 结点数组的长度
public:
void init(int weight[], int n, char character[]); // 创建并初始化一颗哈夫曼树
void search(int max, int &s1, int &s2); // 寻找森林里权值最小的两棵树
void sort(int weight[], char character[]); // 对输入的权值序列以及其对应的字母顺序进行排序
void createCode(char **result, int *weight); // 创造字母对应的哈夫曼编码
void printCode(char *input, char **result, char *character, char *code); // 输出字母转换的哈夫曼编码,并将其保存于code中
void paresCodeAndPrint(char *code, char **result, char *character); // 将code中的哈夫曼编码转化为字母并打印输出
};
void HuffmanTree::init(int weight[], int n, char character[])
{
this->n = n;
tree = new HuffmanTreeNode[2 * n];
sort(weight, character);
//初始化前1~n个
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
tree[i] = {false, weight[i - 1], 0, 0, 0};
}
//初始化后n + 1~2n - 1个
for (int i = n + 1; i <= 2 * n - 1; i++)
{
tree[i] = {false, 100, 0, 0, 0};
}
int s1, s2;
for (int i = n + 1; i <= 2 * n - 1; i++)
{
search(i - 1, s1, s2);
// 找出权值最小的两颗子树
// 由于需要让权值小的在左子树,因此我们让权值s1 < s2
tree[i].weight = tree[s1].weight + tree[s2].weight;
tree[i].LChild = s1;
tree[i].RChild = s2;
tree[s1].parent = i;
tree[s2].parent = i;
}
}
void HuffmanTree::search(int max, int &s1, int &s2)
{
int i, min = 999, k = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= max; i++)
{
if (tree[i].hasChecked) // 如果该树不在森林中则跳过
{
continue;
}
if (tree[i].weight < min)
{
min = tree[i].weight;
k = i;
}
}
s1 = k;
tree[s1].hasChecked = true; // 将找到的最小权值的树移出森林再寻找最小的树
k = 1;
min = 999;
for (i = 1; i <= max; i++)
{
if (tree[i].hasChecked)
{
continue;
}
if (tree[i].weight < min)
{
min = tree[i].weight;
k = i;
}
}
s2 = k;
tree[k].hasChecked = true;
}
void HuffmanTree::sort(int *weight, char character[])
{ // 选择排序
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int min = weight[i];
k = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (weight[j] < min)
{
min = weight[j];
k = j;
}
}
if (k != i)
{
// 字母数组与权值序列同时进行排序以保持对应关系
int t = weight[k];
weight[k] = weight[i];
weight[i] = t;
char m = character[k];
character[k] = character[i];
character[i] = m;
}
}
}
void HuffmanTree::createCode(char **result, int *weight)
{
// 自树的叶子结点(即前1~n个结点)向上进行编码
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int k = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < 2 * n; j++) // 寻找在树节点数组里对应的权值
{
// 若不是叶子结点
if (tree[j].LChild || tree[j].RChild)
{
continue;
}
else
{
if (tree[j].weight == *weight)
{
k = j;
weight++;
break;
}
}
}
char *temp = *result; // 记录字符串开始位置
if (k == 0)
return;
while (tree[k].parent != 0) // 找到之后开始从下网上进行编码
{
if (tree[tree[k].parent].LChild == k)
{
**result = '0';
(*result)++;
}
else if (tree[tree[k].parent].RChild == k)
{
**result = '1';
(*result)++;
}
k = tree[k].parent;
}
**result = '\0'; // 补全字符串
(*result) = temp; // 找回原字符串位置
// 对数组进行翻转
for (int m = 0, j = (strlen((*result)) - 1); m < j; m++, j--)
{
char temp = (*result)[m];
(*result)[m] = (*result)[j];
(*result)[j] = temp;
}
result++;
}
}
void HuffmanTree::printCode(char *input, char **result, char *character, char *code)
{
while (*input != '\0')
{
// 寻找result中对应的结果
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (*input == character[i])
{
break;
}
}
std::cout << result[i];
strcat(code, result[i]); // 构造code
input++;
}
}
void HuffmanTree::paresCodeAndPrint(char *code, char **result, char *character)
{
while (*code != '\0')
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (strncmp(code, result[i], strlen(result[i])) == 0)
{
std::cout << character[i];
code += strlen(result[i]);
break;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
HuffmanTree aTree; // 实例化的树
int n; // 输入长度n
int weight[100] = {0}; // 权值序列
char character[100] = {0}; // 对应的字母序列
char input[100] = {0}; // 输入的原始字符串
char **result = new char *[100]; //每个字母对应的哈夫曼编码数组
char code[100] = {'\0'}; // 转换成的哈夫曼编码
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
result[i] = new char[100];
}
std::cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
std::cin >> character[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
std::cin >> weight[i];
}
std::cin >> input;
aTree.init(weight, n, character);
aTree.createCode(result, weight);
aTree.printCode(input, result, character, code);
std::cout << std::endl;
aTree.paresCodeAndPrint(code, result, character);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号