线索二叉树
基本概念
线索二叉树是为了得到结点在遍历序列中的前驱和后继信息而设计的一种数据结构
在一颗有n个结点的二叉树中,有2n个链域,但是有n-1个链域是有用的,有n+1个链域并没有使用,所以使用这n+1个结点来表示前驱和后继。
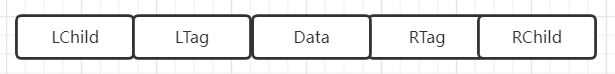
为此,为结点结构增设两个标志域Ltag与Rtag:

在这种存储结构中,指向前驱和后继结点的指针称为线索,以这种结构组成的二叉链表作为二叉树的存储结构,称为线索链表。
对于树:
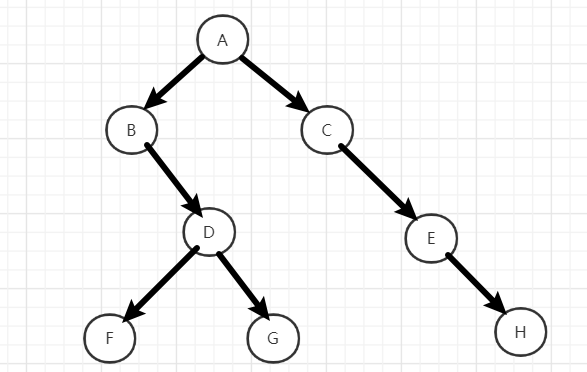
其中序遍历序列为:
BFDGACEH
则B的LChid为空,而F的LChild应指向B。
以下介绍中序线索二叉树的相关操作
线索二叉树的相关操作
线索二叉树的结点结构
struct Node{
char data;
int LTag = 0;
Node* LChild = nullptr ;
int RTag = 0;
Node* RChild = nullptr ;
};
线索二叉树的结构以及需要实现的操作
struct ThreadedBinaryTree
{
Node* root = nullptr ;
//创建一个二叉树,使用扩展的先序遍历
Node* createBinaryTree(Node* root); //不再细说,就建立一颗普通的二叉树
//建立中序线索树,或者说二叉树的线索化
void inThread();
//在中序线索树中查找结点的前驱结点
Node* inPre(Node* p);
//在中序线索树中寻找结点的后继结点
Node* inNext(Node* p);
//在中序线索树中求中序遍历的第一个结点
Node* inFirst(Node* root);
//遍历中序二叉线索树
void traverseInOrder(Node* root);
};
①使用扩展的先序遍历创建一个二叉树
不用再多说了。
Node *ThreadedBinaryTree::createBinaryTree()
{
char ch = cin.get();
if (ch == '#' )
{
return nullptr ;
}
else
{
Node* newNode = new Node;
newNode->data = ch;
newNode->LChild = createBinaryTree();
newNode->RChild = createBinaryTree();
return newNode;
}
}
②二叉树的线索化
static Node *pre = nullptr;
void ThreadedBinaryTree::inThread(Node *root)
{
/*
线索化一颗二叉树的过程就是逐个访问结点的过程
加线索操作需要利用刚访问的结点的当前结点的关系,因此设置一个指针pre
始终记录刚访问的结点,其初值为nullptr
*/
if (root != nullptr)
{
inThread(root->LChild); //线索化左子树
if (root->LChild == nullptr) //置前驱线索
{
root->LChild = pre;
root->LTag = 1;
}
if (pre != NULL && pre->RChild == nullptr) //置后继线索
{
pre->RChild = root;
pre->RTag = 1;
}
pre = root;
inThread(root->RChild); //线索化右子树
}
}
③在线索二叉树中查找前驱
Node *ThreadedBinaryTree::inPre(Node *p)
{
Node *pre = nullptr;
if (p->LTag == 1)
{
pre = p->LChild;
}
else
{
// 寻找p左子树最右下端结点
Node* q;
for(q = p->LChild; q->RTag == 0; q = q->RChild);
pre = q;
}
return pre;
}
④在线索二叉树中查找后继
Node *ThreadedBinaryTree::inNext(Node *p)
{
Node *next;
if (p->RTag == 1)
{
next = p->RChild;
}
else //在右子树中查找最左下端结点
{
Node* q;
for(q = p->RChild; p->LTag == 0; p = p->LChild);
next = q;
}
return next;
}
⑤在中序线索树中求中序遍历的第一个结点
Node *ThreadedBinaryTree::inFirst(Node *root)
{
if (!root)
{
return nullptr;
}
while (root->LTag == 0)
{
root = root->LChild;
}
return root;
}
⑥遍历中序二叉线索树
void ThreadedBinaryTree::traverseInOrder(Node *root)
{
Node *p;
p = this->inFirst(root);
while (p)
{
cout << p->data;
p = this->inNext(p);
}
}
完整测试代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
char data;
int LTag = 0;
Node *LChild = nullptr;
int RTag = 0;
Node *RChild = nullptr;
};
struct ThreadedBinaryTree
{
Node *root = nullptr;
ThreadedBinaryTree() : root(createBinaryTree()) {}
//创建一个二叉树,使用扩展的先序遍历
Node *createBinaryTree(); //不再细说,就建立一颗普通的二叉树
//建立中序线索树,或者说二叉树的线索化
void inThread(Node *root);
//在中序线索树中查找结点的前驱结点
Node *inPre(Node *p);
//在中序线索树中寻找结点的后继结点
Node *inNext(Node *p);
//在中序线索树中求中序遍历的第一个结点
Node *inFirst(Node *root);
//遍历中序二叉线索树
void traverseInOrder(Node *root);
};
Node *ThreadedBinaryTree::createBinaryTree()
{
char ch = cin.get();
if (ch == '#')
{
return nullptr;
}
else
{
Node *newNode = new Node;
newNode->data = ch;
newNode->LChild = createBinaryTree();
newNode->RChild = createBinaryTree();
return newNode;
}
}
static Node *pre = nullptr;
void ThreadedBinaryTree::inThread(Node *root)
{
/*
线索化一颗二叉树的过程就是逐个访问结点的过程
加线索操作需要利用刚访问的结点的当前结点的关系,因此设置一个指针pre
始终记录刚访问的结点,其初值为nullptr
*/
if (root != nullptr)
{
inThread(root->LChild); //线索化左子树
if (root->LChild == nullptr) //置前驱线索
{
root->LChild = pre;
root->LTag = 1;
}
if (pre != NULL && pre->RChild == nullptr) //置后继线索
{
pre->RChild = root;
pre->RTag = 1;
}
pre = root;
inThread(root->RChild); //线索化右子树
}
}
Node *ThreadedBinaryTree::inPre(Node *p)
{
Node *pre = nullptr;
if (p->LTag == 1)
{
pre = p->LChild;
}
else
{
// 寻找p左子树最右下端结点
Node *q;
for (q = p->LChild; q->RTag == 0; q = q->RChild)
;
pre = q;
}
return pre;
}
Node *ThreadedBinaryTree::inNext(Node *p)
{
Node *next = nullptr;
if (p->RTag == 1)
{
next = p->RChild;
}
else //在右子树中查找最左下端结点
{
if (p->RChild)
{
Node *q;
for (q = p->RChild; q->LTag == 0; q = q->LChild)
;
next = q;
}
}
return next;
}
Node *ThreadedBinaryTree::inFirst(Node *root)
{
if (!root)
{
return nullptr;
}
while (root->LTag == 0)
{
root = root->LChild;
}
return root;
}
void ThreadedBinaryTree::traverseInOrder(Node *root)
{
Node *p;
p = this->inFirst(root);
while (p)
{
cout << p->data;
p = this->inNext(p);
}
}
int main()
{
ThreadedBinaryTree aTree;
aTree.inThread(aTree.root);
cout << aTree.inPre(aTree.root->RChild)->data << "\n";
cout << aTree.inNext(aTree.root->RChild)->data << "\n";
cout << aTree.inFirst(aTree.root)->data << "\n";
aTree.traverseInOrder(aTree.root);
cout << 1;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号