二叉树
前言
关于树是什么和一些术语我就不解释了,相信各位能用自己的力量找到
下面的内容大部分取自课本
介绍
二叉树的结构有如下特点:
- 每个结点的度都不能大于2
- 每个孩子结点次序不可颠倒
因此,对于二叉树的每一个结点而言,只有三种情况:
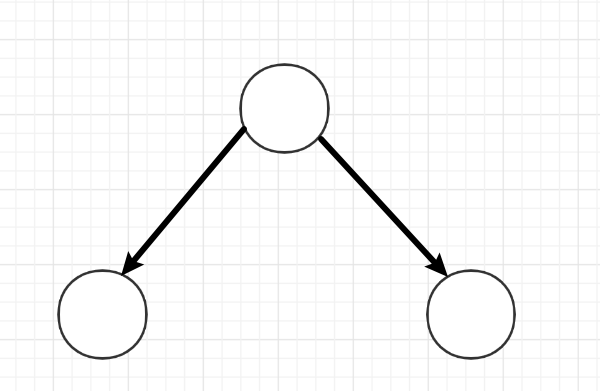
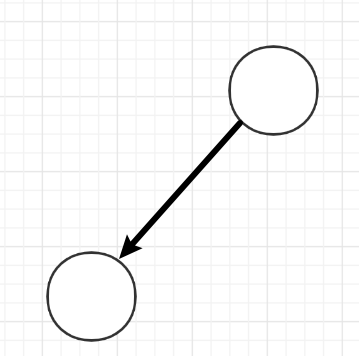
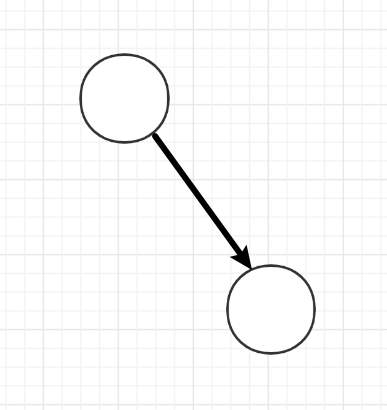
两种特殊的二叉树
满二叉树:在满二叉树中,每层结点都是满的,即每层结点都有最大节点数,如:
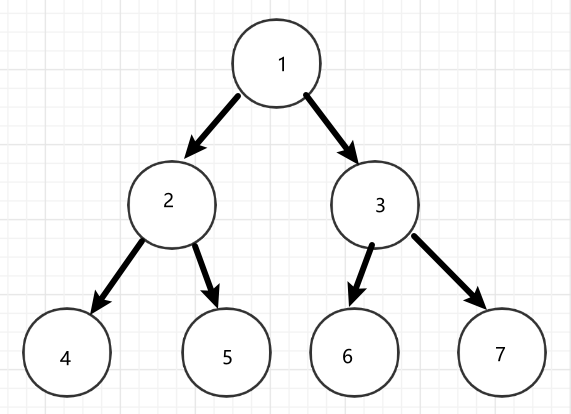
满二叉树的顺序表示:即从二叉树根开始,从上到下从左到右依次逐层进行编号
完全二叉树
对于深度为k,结点为n的二叉树,如果其结点1~n的位置序号与等高满二叉树1~n的位置序号一一对应,则为完全二叉树,如图
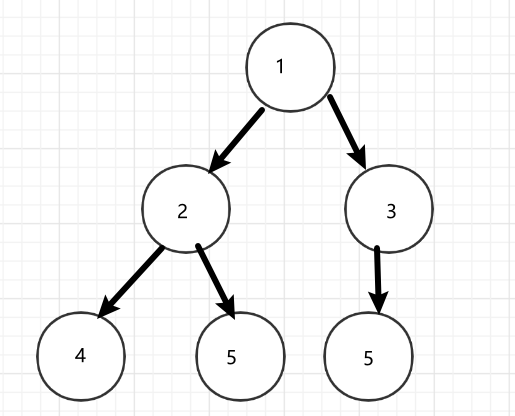
对于完全二叉树:
- 叶子结点只可能出现在最后层
- 度为1的结点个数为0或1
性质
- 二叉树的第 i 层上至多有
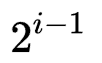 个结点
个结点 -
深度为k的二叉树之多有
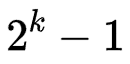 个结点
个结点 -
对任意二叉树,若终端结点数为
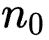 ,而其度数为2的结点数为
,而其度数为2的结点数为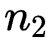 ,则
,则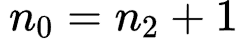
-
具有 n 个结点的完全二叉树的深度为
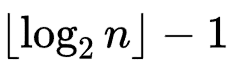
-
对于具有n个结点的完全二叉树 ,如果按从上到下,从左到右的顺序对二叉树中所有结点从1开始编号,则对于任意序号为i的结点有:
-
- 若 i = 1 ,则序号i的结点就是根节点, 若 i > 1,则序号为 i 的结点的双亲结点序号为
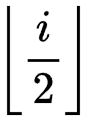
- 若 2i > n,则序号为i的结点无左孩子;若2i<=n,则序号为i的结点的左孩子结点序号为2i。
- 若2i+1>n,则序号为i的结点无有孩子,若2i+1<=n,则序号为i的结点的右孩子结点的序号为2i+1
- 若 i = 1 ,则序号i的结点就是根节点, 若 i > 1,则序号为 i 的结点的双亲结点序号为
注:符号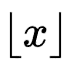 指不大于 x 的最大整数
指不大于 x 的最大整数
二叉树的存储结构
采用链式存储,因为顺序存储在某些情况下浪费太大。
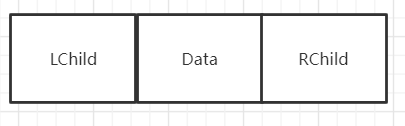
二叉树单节点的结构:
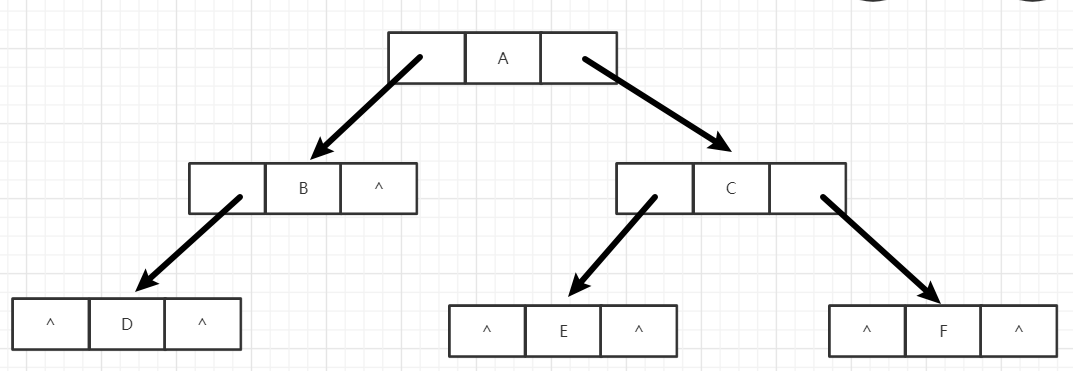
一个二叉链表的结构:
二叉树的遍历
因为课本上二叉树的建立用到了遍历里面的东西,因此先说二叉树的遍历
先序遍历
操作有三:
- 访问根节点
- 按先序遍历左子树
- 按先序遍历后字数
代码描述
void preOrder(BinaryTree root)
{
if (root != nullptr)
{
visit(root->data);
preOrder(root->LChild);
preOrder(root->RChild);
}
}
中序遍历
操作有三:
- 按中序遍历左子树
- 访问根节点
- 按中序遍历右子树
代码描述
void inOrder(BinaryTree root)
{
if (root != nullptr)
{
inOrder(root->LChild);
visit(root->data);
inOrder(root->RChild);
}
}
后序遍历
操作:
- 后序遍历左子树
- 后序遍历右子树
- 访问根节点
代码描述
void postOrder(BinaryTree root)
{
if (root != nullptr)
{
postOrder(root->LChild);
postOrder(root->RChild);
visit(root->data);
}
}
遍历算法的应用
1.建立二叉链表方式存储的二叉树
给定一颗二叉树的遍历序列,可以相应的创建二叉链表。这里所说的遍历序列是一种“扩展的遍历序列”,在扩展的遍历序列中,必须用特定元素表示空子树
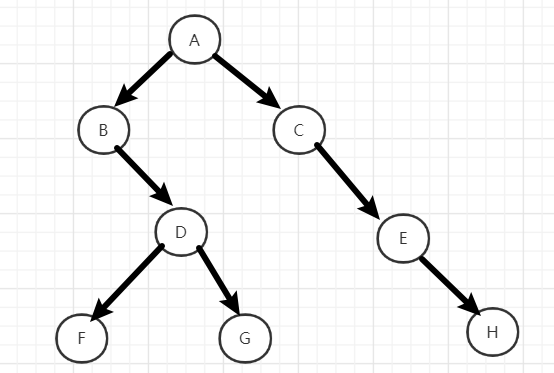
例如:对于扩展的先序遍历序列
AB.DF..G..C.E.H..
其二叉树结构为:
代码描述:
void createBinaryTree(BinaryTree* root) //使用二重指针是为了能改变root的指向
{
char ch;
ch = cin.get();
if (ch == '.')
{
*root = nullptr;
}
else
{
*root = new Node;
(*root)->data = ch;
createBinaryTree(&((*root)->LChild)); //因为是二重指针
createBinaryTree(&((*root)->RChild)); //因为是二重指针
}
}
2.先序遍历输出二叉树中结点
代码描述
void preOrderPrint(BinaryTree root)
{
//先序遍历输出二叉树结点
if (root != nullptr)
{
cout << root->data << " ";
preOrder(root->LChild);
preOrder(root->RChild);
}
}
3.统计叶子结点数目
方法一:
int leafNum = 0;
void leafCount(BinaryTree root)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
leafCount(root->LChild);
leafCount(root->RChild);
if (root->LChild == nullptr && root->RChild == nullptr)
{
leafNum++;
}
}
}
方法二:
int leafCount2(BinaryTree root)
{
int leafCount = 0;
if (root == NULL)
{
leafCount = 0;
}
else if (root->LChild == NULL && root->RChild == NULL)
{
leafCount = 1;
}
else
leafCount = leafCount2(root->LChild) + leafCount2(root->RChild);
return leafCount;
}
4.二叉树高度
方法一:分治法
int postTreeDepth(BinaryTree root)
{
int hl, hr, max;
if (root != NULL)
{
hl = postTreeDepth(root->LChild);
hr = postTreeDepth(root->RChild);
max = hl > hr ? hl : hr;
return max + 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
方法二:先序遍历
int depth = 0;
void preTreeDepth(BinaryTree root, int h)
{
if (root != nullptr)
{
if (h > depth)
{
depth = h;
preTreeDepth(root->LChild, h + 1);
preTreeDepth(root->RChild, h + 1);
}
}
}
5.后续遍历的非递归算法
使用: std::stack
//后续遍历二叉树的非递归算法
void postOrderTree(BinaryTree root)
{
Node *p, *q;
stack<BinaryTree> aStack;
q = nullptr;
p = root;
while (p != nullptr || !aStack.empty())
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
aStack.push(p);
p = p->LChild; //遍历左子树
}
else
{
p = aStack.top();
if (p->RChild == nullptr || p->RChild == q) //无右孩子或右孩子已遍历过
{
visit(p->data); //访问根结点
q = p; //保存到q,作为下一次处理的前驱
aStack.pop();
p = nullptr;
}
else
p = p->RChild;
}
}
}
完整测试代码
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
char data;
Node *LChild = nullptr;
Node *RChild = nullptr;
};
typedef Node *BinaryTree;
void visit(char a)
{
cout << a << endl;
}
void preOrder(BinaryTree root)
{
if (root != nullptr)
{
visit(root->data);
preOrder(root->LChild);
preOrder(root->RChild);
}
}
void inOrder(BinaryTree root)
{
if (root != nullptr)
{
inOrder(root->LChild);
visit(root->data);
inOrder(root->RChild);
}
}
void postOrder(BinaryTree root)
{
if (root != nullptr)
{
postOrder(root->LChild);
postOrder(root->RChild);
visit(root->data);
}
}
void createBinaryTree(BinaryTree *root) //使用二重指针是为了能改变root的指向
{
char ch;
ch = cin.get();
if (ch == '.')
{
*root = nullptr;
}
else
{
*root = new Node;
(*root)->data = ch;
createBinaryTree(&((*root)->LChild)); //因为是二重指针
createBinaryTree(&((*root)->RChild)); //因为是二重指针
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void preOrderPrint(BinaryTree root)
{
//先序遍历输出二叉树结点
if (root != nullptr)
{
cout << root->data << " ";
preOrder(root->LChild);
preOrder(root->RChild);
}
}
int leafNum = 0;
void leafCount(BinaryTree root)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
leafCount(root->LChild);
leafCount(root->RChild);
if (root->LChild == nullptr && root->RChild == nullptr)
{
leafNum++;
}
}
}
// 2
int leafCount2(BinaryTree root)
{
int leafCount = 0;
if (root == NULL)
{
leafCount = 0;
}
else if (root->LChild == NULL && root->RChild == NULL)
{
leafCount = 1;
}
else
leafCount = leafCount2(root->LChild) + leafCount2(root->RChild);
return leafCount;
}
int postTreeDepth(BinaryTree root)
{
int hl, hr, max;
if (root != NULL)
{
hl = postTreeDepth(root->LChild);
hr = postTreeDepth(root->RChild);
max = hl > hr ? hl : hr;
return max + 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
void preTreeDepth(BinaryTree root, int h)
{
if (root != nullptr)
{
if (h > depth)
{
depth = h;
preTreeDepth(root->LChild, h + 1);
preTreeDepth(root->RChild, h + 1);
}
}
}
//后续遍历二叉树的非递归算法
void postOrderTree(BinaryTree root)
{
Node *p, *q;
stack<BinaryTree> aStack;
q = nullptr;
p = root;
while (p != nullptr || !aStack.empty())
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
aStack.push(p);
p = p->LChild; //遍历左子树
}
else
{
p = aStack.top();
if (p->RChild == nullptr || p->RChild == q) //无右孩子或右孩子已遍历过
{
visit(p->data); //访问根结点
q = p; //保存到q,作为下一次处理的前驱
aStack.pop();
p = nullptr;
}
else
p = p->RChild;
}
}
}
int main()
{
BinaryTree aTree;
createBinaryTree(&aTree);
postOrderTree(aTree);
cout << endl;
postOrder(aTree);
cout << endl;
preOrderPrint(aTree);
cout << endl;
leafCount(aTree);
cout << leafNum << endl;
cout << leafCount2(aTree) << endl;
cout << postTreeDepth(aTree) << endl;
preTreeDepth(aTree, 1);
cout << depth << endl;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号