双端栈
关于双端栈
为了节省数组空间并增加栈的个数,可以使用双端栈。
双端栈的基本操作都和栈没太大区别,因此不再赘述。
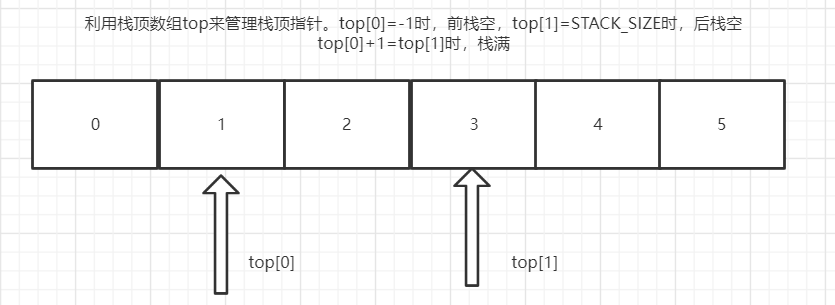
此外,如果真的需要管理多个栈,使用数组+链栈是一个不错的选择
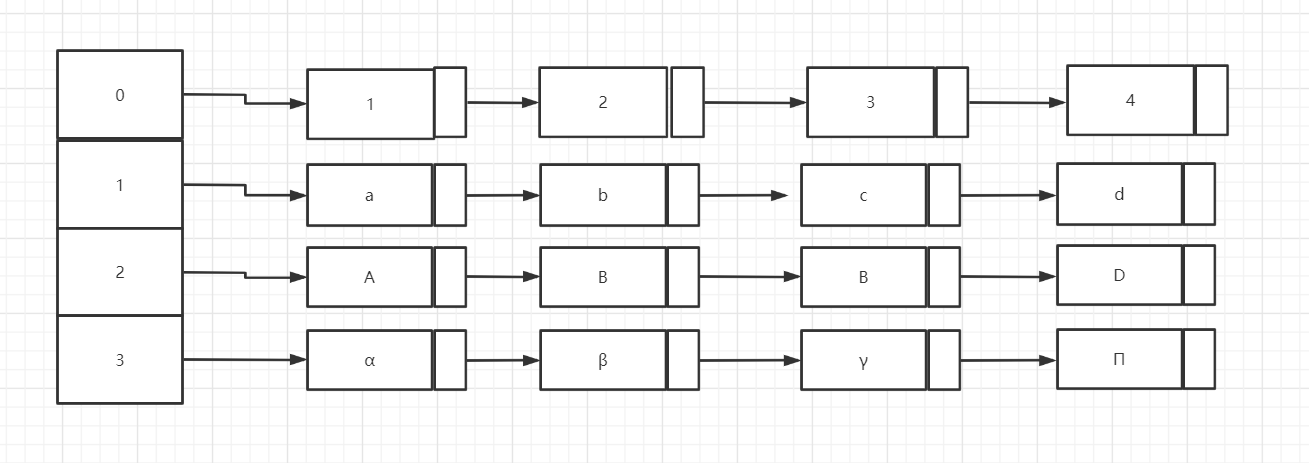
这种多栈形式仅仅是用数组管理链栈而已,不再赘述
实现
仅实现双端栈的插入删除初始化操作。
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#define STACK_SIZE 100
template <typename ElementType>
struct DoubleSideStack
{
int top[2];
ElementType Stack[STACK_SIZE];
DoubleSideStack(); //初始化(构造函数)
bool push(ElementType x, int i); //压栈
bool pop(ElementType *x, int i); //出栈
};
template <typename ElementType>
DoubleSideStack<ElementType>::DoubleSideStack()
{//初始化
top[0] = -1;
top[1] = STACK_SIZE;
}
template <typename ElementType>
bool DoubleSideStack<ElementType>::push(ElementType x, int i)
{//压栈
if (this->top[0] + 1 == this->top[1])
{ //判断栈满与否
std::cout << "栈满";
return false;
}
switch (i)
{
case 0:
{
this->top[0]++;
this->Stack[this->top[0]] = x;
return true;
break;
}
case 1:
{
this->top[1]--;
this->Stack[this->top[1]] = x;
return true;
break;
}
default:
{
std::cout << "out of range" << std::endl;
return false;
break;
}
}
}
template <typename ElementType>
bool DoubleSideStack<ElementType>::pop(ElementType *x, int i)
{//出栈
switch (i)
{
case 0:
{
if (this->top[0] == -1)
{//判断栈空与否
std::cout << "out of range" << std::endl;
return false;
}
*x = this->Stack[this->top[0]];
this->top[0]--;
return true;
break;
}
case 1:
{
if (this->top[1] == STACK_SIZE)
{//判断栈空与否
std::cout << "out of range" << std::endl;
return false;
}
*x = this->Stack[this->top[1]];
this->top[1]++;
return true;
break;
}
default:
{
return false;
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
DoubleSideStack<std::string> testStack;
testStack.push("this is a test", 0);
testStack.push("this is a end test", 1);
std::string newString;
testStack.pop(&newString, 1);
testStack.pop(&newString, 1);
std::cout << newString;
}
使用数组管理多栈仅仅是加一个数组而已,其余与链栈别无二致。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号