实验四 继承
实验二
task2.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <typeinfo> // definitation of Graph class Graph { public: virtual void draw() { std::cout << "Graph::draw() : just as an interface\n"; } }; // definition of Rectangle, derived from Graph class Rectangle : public Graph { public: void draw() { std::cout << "Rectangle::draw(): programs of draw a rectangle\n"; } }; // definition of Circle, derived from Graph class Circle : public Graph { public: void draw() { std::cout << "Circle::draw(): programs of draw a circle\n"; } }; // definitaion of fun(): as a call interface void fun(Graph *ptr) { std::cout << "pointer type: " << typeid(ptr).name() << "\n"; std::cout << "RTTI type: " << typeid(*ptr).name() << "\n"; ptr -> draw(); } // test int main() { Graph g1; Rectangle r1; Circle c1; // call by object name g1.draw(); r1.draw(); c1.draw(); std::cout << "\n"; // call by object name, and using the scope resolution operator:: r1.Graph::draw(); c1.Graph::draw(); std::cout << "\n"; // call by pointer to Base class fun(&g1); fun(&r1); fun(&c1); }
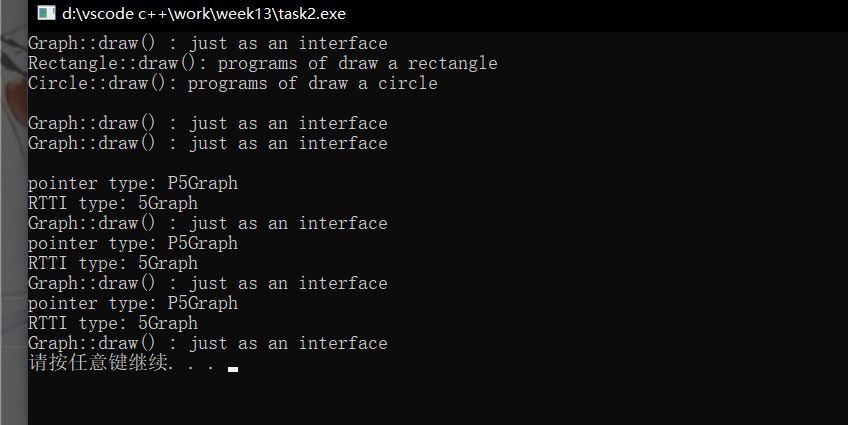
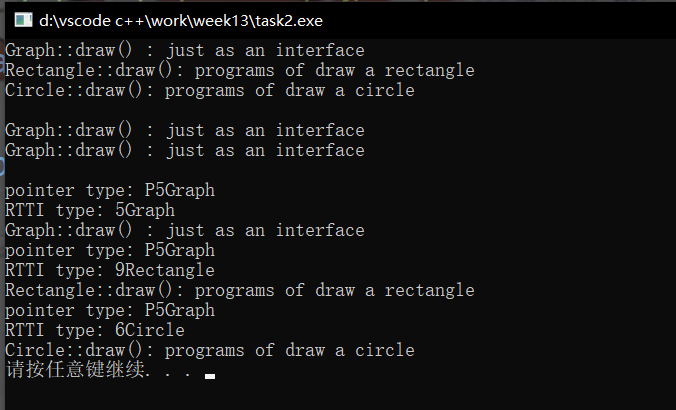
同名覆盖原则:由于基类和派生类的函数名一样,系统先基类,然后对象,最后派生类调用,就覆盖了。
二元作用域分辨符:可以通过派生类名和作用域分辨符来访问派生类中的同名成员。
类型兼容原则:类型兼容原则是指在需要基类对象的任何地方,都可以使用公有派生类的对象来替代。
实验三
task3.cpp
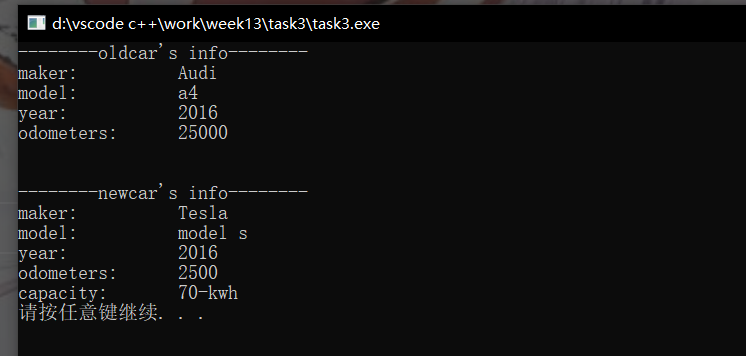
#include <iostream> #include "electricCar.hpp" int main() { using namespace std; // test class of Car Car oldcar("Audi", "a4", 2016); cout << "--------oldcar's info--------" << endl; oldcar.update_odometers(25000); oldcar.info(); cout << endl; // test class of ElectricCar ElectricCar newcar("Tesla", "model s", 2016); newcar.update_odometers(2500); cout << "\n--------newcar's info--------\n"; newcar.info(); system("pause"); }
car.hpp
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class Car { public: Car(string ma, string mo, int y ,int o = 0): maker(ma),model(mo),year(y),odo(o){} void info(){ cout << "maker:\t\t" << maker << endl; cout << "model:\t\t" << model << endl; cout << "year: \t\t" << year << endl; cout << "odometers:\t" << odo << endl; } void update_odometers(int o){ if(o < odo) cout << "---wearning---" << endl; else odo = o; } private: string maker, model; int year, odo; };
battery.hpp
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class Battery { public: Battery(int ca = 70):capacity(ca){} int get_capacity(){ return capacity; } private: int capacity; };
electricCar.hpp
#include<iostream> #include"car.hpp" #include"battery.hpp" using namespace std; class ElectricCar:public Car { public: ElectricCar(string a, string b,int c,int d = 0, int e = 70): Car(a,b,c,d), battery(e){} void info(){ Car::info(); cout << "capacity: \t" << battery.get_capacity() <<"-kwh"<<endl; } private: Battery battery; };
实验四
task4.cpp
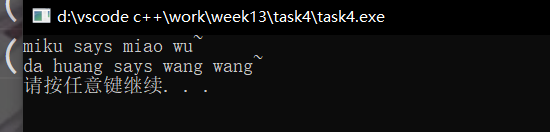
#include <iostream> #include "pets.hpp" void play(MachinePets *ptr) { std::cout << ptr->get_nickname() << " says " << ptr->talk() << std::endl; } int main() { PetCats cat("miku"); PetDogs dog("da huang"); play(&cat); play(&dog); system("pause"); }
pets.hpp
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class MachinePets { public: MachinePets(const string s):nickname(s){} ~MachinePets() = default; string get_nickname() const { return nickname; } virtual string talk(){} private: string nickname; }; class PetCats:public MachinePets { public: PetCats(const string name):MachinePets(name){} string talk(){ return "miao wu~"; } }; class PetDogs:public MachinePets { public: PetDogs(const string name):MachinePets(name){} string talk(){ return "wang wang~"; } };


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号