概念学习笔记
一个对概念学习很好的理解:https://blog.csdn.net/firparks/article/details/50678027
一个经典例子:
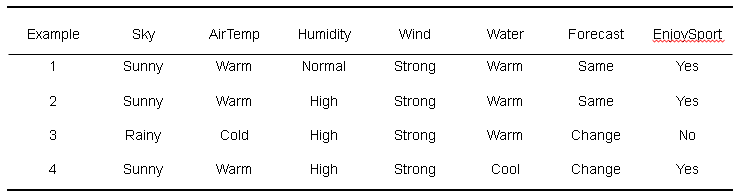
find-s 算法:
1 def find_s(): 2 x1 = ['sunny', 'warm', 'nurmal', 'strong', 'warm', 'same', 1] 3 x2 = ['sunny', 'warm', 'high', 'strong', 'warm', 'same', 1] 4 x3 = ['rainy', 'cold', 'high', 'strong', 'warm', 'change', 0] 5 x4 = ['sunny', 'warm', 'high', 'strong', 'cool', 'change', 1] 6 7 h = [None, None, None, None, None, None] 8 h1 = ['sunny', 'warm', 'nurmal', 'strong', 'warm', 'same'] //初始化 9 10 xa = [x1, x2, x3, x4] 11 12 xb = [x1, x2, x4, x3] 13 14 for i in xb: 15 if i[6] == 1: 16 index = 0 17 for j in i[:-1]: 18 if (h1[index] == None): 19 h1[index] = j 20 elif (h1[index] != j): 21 h1[index] = '?' 22 index += 1 23 print(h1) 24 25 if __name__ == "__main__": 26 find_s()
候选消除算法:
1 class Holder: 2 factors = {} # Initialize an empty dictionary 3 attributes = () # declaration of dictionaries parameters with an arbitrary length 4 5 ''' 6 Constructor of class Holder holding two parameters, 7 self refers to the instance of the class 8 ''' 9 10 def __init__(self, attr): # 11 self.attributes = attr 12 for i in attr: 13 self.factors[i] = [] 14 15 def add_values(self, factor, values): 16 self.factors[factor] = values 17 18 19 class CandidateElimination: 20 Positive = {} # Initialize positive empty dictionary 21 Negative = {} # Initialize negative empty dictionary 22 23 def __init__(self, data, fact): 24 self.num_factors = len(data[0][0]) 25 self.factors = fact.factors 26 self.attr = fact.attributes 27 self.dataset = data 28 29 # print self.attr 30 31 def run_algorithm(self): 32 # print self.dataset 33 ''' 34 Initialize the specific and general boundaries, and loop the dataset against the algorithm 35 ''' 36 G = self.initializeG() 37 S = self.initializeS() 38 39 ''' 40 Programmatically populate list in the iterating variable trial_set 41 ''' 42 count = 0 43 for trial_set in self.dataset: 44 if self.is_positive(trial_set): # if trial set/example consists of positive examples 45 G = self.remove_inconsistent_G(G, trial_set[0]) # remove inconsitent data from the general boundary 46 S_new = S[:] # initialize the dictionary with no key-value pair 47 print(S_new) 48 for s in S: 49 if not self.consistent(s, trial_set[0]): 50 S_new.remove(s) 51 generalization = self.generalize_inconsistent_S(s, trial_set[0]) 52 generalization = self.get_general(generalization, G) 53 if generalization: 54 S_new.append(generalization) 55 S = S_new[:] 56 S = self.remove_more_general(S) 57 58 print(S) 59 else: # if it is negative 60 S = self.remove_inconsistent_S(S, trial_set[0]) # remove inconsitent data from the specific boundary 61 G_new = G[:] # initialize the dictionary with no key-value pair (dataset can take any value) 62 print(G_new) 63 for g in G: 64 if self.consistent(g, trial_set[0]): 65 G_new.remove(g) 66 specializations = self.specialize_inconsistent_G(g, trial_set[0]) 67 specializationss = self.get_specific(specializations, S) 68 if specializations != []: 69 G_new += specializations 70 G = G_new[:] 71 print(G) 72 G = self.remove_more_specific(G) 73 74 print(S) 75 print(G) 76 77 def initializeS(self): 78 ''' Initialize the specific boundary ''' 79 S = tuple(['-' for factor in range(self.num_factors)]) # 6 constraints in the vector 80 return [S] 81 82 def initializeG(self): 83 ''' Initialize the general boundary ''' 84 G = tuple(['?' for factor in range(self.num_factors)]) # 6 constraints in the vector 85 return [G] 86 87 def is_positive(self, trial_set): 88 ''' Check if a given training trial_set is positive ''' 89 if trial_set[1] == 'Y': 90 return True 91 elif trial_set[1] == 'N': 92 return False 93 else: 94 raise TypeError("invalid target value") 95 96 def is_negative(self, trial_set): 97 ''' Check if a given training trial_set is negative ''' 98 if trial_set[1] == 'N': 99 return False 100 elif trial_set[1] == 'Y': 101 return True 102 else: 103 raise TypeError("invalid target value") 104 105 def match_factor(self, value1, value2): 106 ''' Check for the factors values match, 107 necessary while checking the consistency of 108 training trial_set with the hypothesis ''' 109 if value1 == '?' or value2 == '?': 110 return True 111 elif value1 == value2: 112 return True 113 return False 114 115 def consistent(self, hypothesis, instance): 116 ''' Check whether the instance is part of the hypothesis ''' 117 for i, factor in enumerate(hypothesis): 118 if not self.match_factor(factor, instance[i]): 119 return False 120 return True 121 122 def remove_inconsistent_G(self, hypotheses, instance): 123 ''' For a positive trial_set, the hypotheses in G 124 inconsistent with it should be removed ''' 125 G_new = hypotheses[:] 126 for g in hypotheses: 127 if not self.consistent(g, instance): 128 G_new.remove(g) 129 return G_new 130 131 def remove_inconsistent_S(self, hypotheses, instance): 132 ''' For a negative trial_set, the hypotheses in S 133 inconsistent with it should be removed ''' 134 S_new = hypotheses[:] 135 for s in hypotheses: 136 if self.consistent(s, instance): 137 S_new.remove(s) 138 return S_new 139 140 def remove_more_general(self, hypotheses): 141 ''' After generalizing S for a positive trial_set, the hypothesis in S 142 general than others in S should be removed ''' 143 S_new = hypotheses[:] 144 for old in hypotheses: 145 for new in S_new: 146 if old != new and self.more_general(new, old): 147 S_new.remove[new] 148 return S_new 149 150 def remove_more_specific(self, hypotheses): 151 ''' After specializing G for a negative trial_set, the hypothesis in G 152 specific than others in G should be removed ''' 153 G_new = hypotheses[:] 154 for old in hypotheses: 155 for new in G_new: 156 if old != new and self.more_specific(new, old): 157 G_new.remove[new] 158 return G_new 159 160 def generalize_inconsistent_S(self, hypothesis, instance): 161 ''' When a inconsistent hypothesis for positive trial_set is seen in the specific boundary S, 162 it should be generalized to be consistent with the trial_set ... we will get one hypothesis''' 163 hypo = list(hypothesis) # convert tuple to list for mutability 164 for i, factor in enumerate(hypo): 165 if factor == '-': 166 hypo[i] = instance[i] 167 elif not self.match_factor(factor, instance[i]): 168 hypo[i] = '?' 169 generalization = tuple(hypo) # convert list back to tuple for immutability 170 return generalization 171 172 def specialize_inconsistent_G(self, hypothesis, instance): 173 ''' When a inconsistent hypothesis for negative trial_set is seen in the general boundary G 174 should be specialized to be consistent with the trial_set.. we will get a set of hypotheses ''' 175 specializations = [] 176 hypo = list(hypothesis) # convert tuple to list for mutability 177 for i, factor in enumerate(hypo): 178 if factor == '?': 179 values = self.factors[self.attr[i]] 180 for j in values: 181 if instance[i] != j: 182 hyp = hypo[:] 183 hyp[i] = j 184 hyp = tuple(hyp) # convert list back to tuple for immutability 185 specializations.append(hyp) 186 return specializations 187 188 def get_general(self, generalization, G): 189 ''' Checks if there is more general hypothesis in G 190 for a generalization of inconsistent hypothesis in S 191 in case of positive trial_set and returns valid generalization ''' 192 193 for g in G: 194 if self.more_general(g, generalization): 195 return generalization 196 return None 197 198 def get_specific(self, specializations, S): 199 ''' Checks if there is more specific hypothesis in S 200 for each of hypothesis in specializations of an 201 inconsistent hypothesis in G in case of negative trial_set 202 and return the valid specializations''' 203 valid_specializations = [] 204 for hypo in specializations: 205 for s in S: 206 if self.more_specific(s, hypo) or s == self.initializeS()[0]: 207 valid_specializations.append(hypo) 208 return valid_specializations 209 210 def exists_general(self, hypothesis, G): 211 '''Used to check if there exists a more general hypothesis in 212 general boundary for version space''' 213 214 for g in G: 215 if self.more_general(g, hypothesis): 216 return True 217 return False 218 219 def exists_specific(self, hypothesis, S): 220 '''Used to check if there exists a more specific hypothesis in 221 general boundary for version space''' 222 223 for s in S: 224 if self.more_specific(s, hypothesis): 225 return True 226 return False 227 228 def get_version_space(self, specific, general): 229 ''' Given the specific and the general boundary of the 230 version space, evaluate the version space in between ''' 231 while get_order(VS): 232 for hypothesis in VS[:]: 233 hypo = list(hypothesis) # convert tuple to list for mutability 234 for i, factor in enumerate(hypo): 235 if factor != '?': 236 hyp = hypo[:] 237 hyp[i] = '?' 238 if self.exists_general(hyp, general) and self.exists_specific(hyp, specific): 239 VS.append(tuple(hyp)) 240 241 return VS 242 243 def get_order(self, hypothesis): 244 pass 245 246 def more_general(self, hyp1, hyp2): 247 ''' Check whether hyp1 is more general than hyp2 ''' 248 hyp = zip(hyp1, hyp2) 249 for i, j in hyp: 250 if i == '?': 251 continue 252 elif j == '?': 253 if i != '?': 254 return False 255 elif i != j: 256 return False 257 else: 258 continue 259 return True 260 261 def more_specific(self, hyp1, hyp2): 262 ''' hyp1 more specific than hyp2 is 263 equivalent to hyp2 being more general than hyp1 ''' 264 return self.more_general(hyp2, hyp1) 265 266 267 dataset = [(('sunny', 'warm', 'normal', 'strong', 'warm', 'same'), 'Y'), 268 (('sunny', 'warm', 'high', 'strong', 'warm', 'same'), 'Y'), 269 (('rainy', 'cold', 'high', 'strong', 'warm', 'change'), 'N'), 270 (('sunny', 'warm', 'high', 'strong', 'cool', 'change'), 'Y')] 271 attributes = ('Sky', 'Temp', 'Humidity', 'Wind', 'Water', 'Forecast') 272 273 f = Holder(attributes) 274 f.add_values('Sky', ('sunny', 'rainy', 'cloudy')) # sky can be sunny rainy or cloudy 275 f.add_values('Temp', ('cold', 'warm')) # Temp can be sunny cold or warm 276 f.add_values('Humidity', ('normal', 'high')) # Humidity can be normal or high 277 f.add_values('Wind', ('weak', 'strong')) # wind can be weak or strong 278 f.add_values('Water', ('warm', 'cold')) # water can be warm or cold 279 f.add_values('Forecast', ('same', 'change')) # Forecast can be same or change 280 a = CandidateElimination(dataset, f) # pass the dataset to the algorithm class and call the run algoritm method 281 a.run_algorithm()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号