四丶人生苦短,我用python【第四篇】
1 基本数据类型
- 数字 int
- 字符串 str
- 布尔值 bool
- 列表 list
- 元组 tuple
- 字典 dict
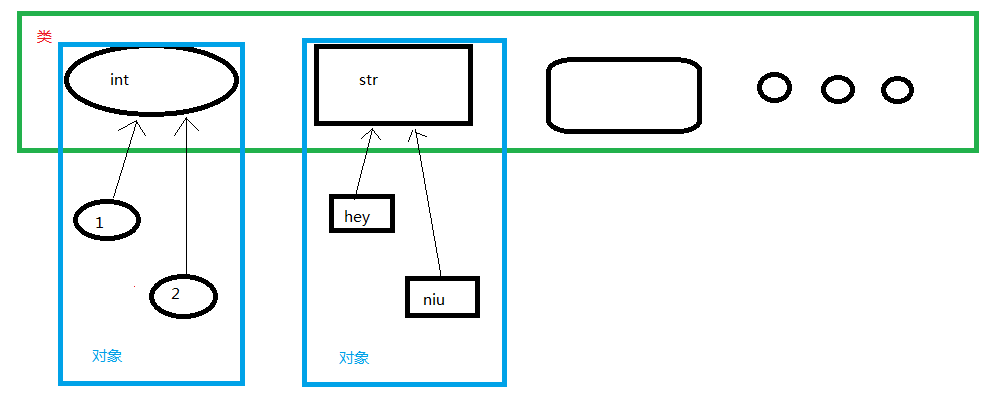
》》》type() 一个参数时返回对象类型。
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- temp = "hey" lei = type(temp) print(lei) 输出: C:\Users\msi\Desktop\python\venv\Scripts\python.exe "C:/Users/msi/Desktop/python/one day.py" <type 'str'> Process finished with exit code 0
注:所有数字、字符串、字典等所具备的方法都存在相对应的类里。
》》》查看对象的类,或对象所具备的功能
第一种:
ctrl+鼠标左键,找到对应的类,以及内部所有的方法
第二种:dir() 快速看对象具有的功能
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- temp = "hey" lei = dir(temp) print(lei) #显示 C:\Users\msi\Desktop\python\venv\Scripts\python.exe "C:/Users/msi/Desktop/python/one day.py" ['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__getslice__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '_formatter_field_name_split', '_formatter_parser', 'capitalize', 'center', 'count', 'decode', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isdigit', 'islower', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill'] Process finished with exit code 0
第三种:help()
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- temp = "hey" lei = help(type(temp)) print(lei)
1.1 int
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # a.加法 同n1+n2 n1 = 123 n2 = 456 print(n1.__add__(n2)) #b.获取可表示的二进制最短位数 ret = n1.bit_length() print(ret)
1.2 str
字符串常用功能:
- a.移除空白
lstrip() 移除左侧空白 rstrip() 移除右侧空白 strip() 移除左右两侧空白
- b.连接
# join(self, iterable) 连接 lb = ["sn","fn","ww"] s = "--".join(lb) #循环lb的每一个元素,通过--连接起来 print(s) #输出>>> sn--fn--ww
- c.分割
#partition(self, sep) 分割,前,中,后三部分 s = "sada afqw qwfrqw" ret = s.partition("af") #根据af将字符串分割成三部分,添加到一个元组中 print(ret) #输出>>> ('sada ', 'af', 'qw qwfrqw')
- d.替换
# replace(self, old, new, count=None) 替换 s = "abc cde afa faf" ret = s.replace("a","**",3) #从左往右将3个a替换成** print(ret) #输出>>> **bc cde **f** faf

#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # 1 capitalize()首字母大写 a1 = "sn" ret = a1.capitalize() print(ret) # >>>输出Sn # 2 center(self, width, fillchar=None) 内容居中,width:总长度;fillchar:空白处填充内容,默认无 rat = a1.center(10,'*') print(rat) #输出>>> ****sn**** # 3 count(self, sub, start=None, end=None) 子序列个数 c1 = "sn is sn" rct = c1.count("s",0,5) #s在大于等于0小于5的位置出现了几次 print(rct) #输出>>> 2 # 4 decode()解码 encode()编码 # 5 endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None) 是否以 xxx 结束 temp = "hello" print(temp.endswith('o',4,5)) #o在大于等于4小于5的位置出 #输出>>> True # 6 expandtabs(self, tabsize=None) 将tab转换成空格,默认一个tab转换成8个空格 # 7 find(self, sub, start=None, end=None)寻找子序列位置,如果没找到,返回 -1 s = "faqfasq" print(s.find("q")) #输出>>> 2 # 8 format(*args, **kwargs) 字符串格式化,动态参数 p = "hello {0},age {1}" #{0}占位符 new = p.format("sn",20) print(new) #输出>>> hello sn,age 20

#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # 1 isalnum(self) 检查所有内容是否是字母和数字 # 2 isalpha(self) 是否是字母 # 3 isdigit(self) 是否是数字 # 4 islower(self) 是否小写 # 5 isspace() 是否是空格 # 6 istitle() 是否是标题 所有首字母是大写 # 7 isupper() 是否大写 a = "wafa" print(a.islower()) #输出>>> True # 8 ljust(self, width, fillchar=None) 内容左对齐,右侧填充 #9 lower()变小写 upper()变大写 print("dasf".upper())



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号