实验5 继承和多态
四、实验结论
实验任务3
pets.hpp
#pragma once #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class MachinePets { public: MachinePets(const string &s = " "); string get_nickname() const; public: virtual string talk() = 0; protected: string nickname; }; MachinePets::MachinePets(const string &s):nickname{s}{} string MachinePets::get_nickname() const { return nickname; } class PetCats :public MachinePets { public: PetCats(const string &s =" "); public: string talk() override; }; PetCats::PetCats(const string& s):MachinePets{s}{} string PetCats::talk() { string talk_cats = " miao wu~ "; return talk_cats; } class PetDogs :public MachinePets { public: PetDogs(const string& s = " "); public: string talk() override; }; PetDogs::PetDogs(const string& s) :MachinePets{ s } {} string PetDogs::talk() { string talk_dogs = " wang wang~"; return talk_dogs; };
task3.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "pets.hpp" void play(MachinePets& obj) { std::cout << obj.get_nickname() << " says " << obj.talk() << std::endl; } void test() { PetCats cat("miku"); PetDogs dog("da huang"); play(cat); play(dog); } int main() { test(); }
运行测试截图:

实验任务4
Person.hpp
#pragma once #include<limits> #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class Person { public: Person(const string& s1 = " ", const string& s2 = " ", const string& s3 = " "); Person(const Person &p); public: void update_telephone(); void update_email(); friend std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& os, const Person& p); friend std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& is, Person& p); friend bool operator==(const Person& p1, const Person& p2); private: string name, telephone, email; }; Person::Person(const string& s1 , const string& s2 , const string& s3 ):name{s1},telephone{s2},email{s3}{} Person::Person(const Person& p):name{p.name},telephone{p.telephone},email{p.email}{} void Person::update_telephone() { cin.clear(); cout << "输入电话号码:"; string new_telephone; getline(cin,new_telephone); telephone = new_telephone; cout << "电话号码已更新..." << endl; } void Person::update_email() { cout << "输入email地址:"; string new_email; getline(cin,new_email); email = new_email; cout << "email地址已更新..." << endl; } std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& os, const Person& p) { os << p.name << endl << p.telephone << endl << p.email << endl; return os; } std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& is, Person& p) { getline(is, p.name); getline(is, p.telephone); getline(is, p.email); cin.ignore(numeric_limits<streamsize>::max(), '\n'); return is; } bool operator==(const Person& p1, const Person& p2) { return ((p1.name == p2.name) && (p1.telephone == p2.telephone)); }
task4.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include "Person.hpp" void test() { using namespace std; vector<Person> phone_book; Person p; cout << "输入一组联系人的联系方式,E直至按下Ctrl+Z终止\n"; while (cin >> p) { phone_book.push_back(p); } cout << "\n更新phone_book中索引为0的联系人的手机号、邮箱:\n"; phone_book.at(0).update_telephone(); phone_book.at(0).update_email(); cout << "\n测试两个联系人是否是同一个:\n"; cout << boolalpha << (phone_book.at(0) == phone_book.at(1)) << endl; } int main() { test(); }
运行测试截图:
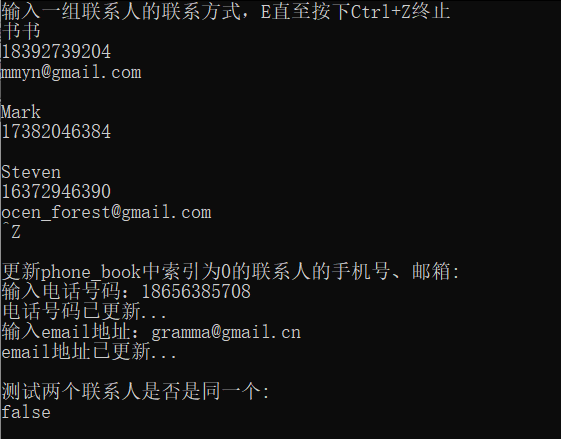
实验任务5
date.h
#pragma once #include<iostream> class Date { private: int year; int month; int day; int totalDays; public: Date(int year, int month, int day); int getYear() const { return year; } int getMonth() const { return month; } int getDay() const { return day; } int getMaxDay() const; bool isLeapYear() const { return year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0; } void show() const; int operator-(const Date& date)const { return totalDays - date.totalDays; } };
date.cpp
#include"date.h" #include<iostream> #include<cstdlib> using namespace std; namespace { const int DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[] = { 0,31,59,90,120,151,181,212,243,273,304,334,365 }; } Date::Date(int year, int month, int day) :year(year), month(month), day(day) { if (day <= 0 || day > getMaxDay()) { cout << "Invalid date: "; show(); cout << endl; exit(1); } int years = year - 1; totalDays= years * 365 + years / 4 - years / 100 + years / 400 + DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[month - 1] + day; if (isLeapYear() && month > 2)totalDays++; } int Date::getMaxDay() const { if (isLeapYear() && month == 2) return 29; else return DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[month] - DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[month - 1]; } void Date::show()const { cout << getYear() << "-" << getMonth() << "-" << getDay(); }
accumulator.h
#pragma once #include"date.h" #include<iostream> class Accumulator { private: Date lastDate; double value; double sum; public: Accumulator(const Date&date,double value):lastDate{date},value{value},sum{0}{} double getSum(const Date& date)const { return sum + value * (date - lastDate); } void change(const Date& date, double value) { sum = getSum(date); lastDate = date; this->value = value; } void reset(const Date& date, double value) { lastDate = date; this->value = value; sum = 0; } };
account.h
#pragma once #include"accumulator.h" #include"date.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class Account { private: string id; double balance; static double total; protected: Account(const Date& date, const string& id); void record(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc); void error(const string& msg) const; public: const string getId() const { return id; } double getBalance() const { return balance; } static double getTotal() { return total; } virtual void deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) = 0; virtual void withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) = 0; virtual void settle(const Date& date) = 0; virtual void show() const; }; class SavingsAccount :public Account { private: Accumulator acc; double rate; public: SavingsAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double rate); double getRate()const { return rate; } void deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc); void withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc); void settle(const Date& date); }; class CreditAccount :public Account { private: Accumulator acc; double credit; double rate; double fee; double getDebt()const { double balance = getBalance(); return (balance < 0 ? balance : 0); } public: CreditAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double credit, double rate, double fee); double getCredit() const { return credit; } double getRate() const { return rate; } double getFee() const { return fee; } double getAvailableCredit() const { if (getBalance() < 0) return credit + getBalance(); else return credit; } void deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc); void withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc); void settle(const Date& date); void show()const; };
account.cpp
#include"account.h" #include<cmath> #include<iostream> using namespace std; double Account::total = 0; Account::Account(const Date& date, const string& id) :id{ id }, balance{ 0 } { date.show(); cout << "\t#" << id << "created" << endl; } void Account::record(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { amount = floor(amount * 100 + 0.5) / 100; balance += amount; total += amount; date.show(); cout << "\t#" << id << "\t" << amount << "\t" << balance << "\t" << desc << endl; } void Account::show() const { cout << id << "\tBalance: " << balance; } void Account::error(const string& msg)const { cout << "Error(#" << id << ")" << msg << endl; } //SavingsAccount 类相关成员函数的实现 SavingsAccount::SavingsAccount(const Date&date,const string &id,double rate):Account {date,id},rate{rate},acc{date,0}{} void SavingsAccount::deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { record(date, amount, desc); acc.change(date, getBalance()); } void SavingsAccount::withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { if (amount > getBalance()) { error("not enough money"); }else{ record(date, -amount, desc); acc.change(date, getBalance()); } } void SavingsAccount::settle(const Date& date) { if (date.getMonth() == 1) { double interest = acc.getSum(date) * rate / (date - Date(date.getYear() - 1, 1, 1)); if (interest != 0) record(date, interest, "interest"); acc.reset(date, getBalance()); } } //CreditAccount 类相关成员函数的实现 CreditAccount::CreditAccount(const Date&date,const string &id,double credit,double rate,double fee): Account{date,id},credit{credit},rate{rate},fee{fee},acc{date,0}{} void CreditAccount::deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { record(date, amount, desc); acc.change(date, getDebt()); } void CreditAccount::withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { if (amount - getBalance() > credit) { error("not enough credit"); } else { record(date, -amount, desc); acc.change(date, getDebt()); } } void CreditAccount::settle(const Date& date) { double interest = acc.getSum(date) * rate; if (interest != 0)record(date, interest, "interest"); if (date.getMonth() == 1) record(date, -fee, "annual fee"); acc.reset(date, getDebt()); } void CreditAccount::show() const { Account::show(); cout << "\tAvailable credit:" << getAvailableCredit(); }
8_8.cpp
#include"account.h" #include<iostream> using namespace std; void test() { Date date(2008, 11, 1); //建立几个账户 SavingsAccount sa1(date, "S3755217", 0.015); SavingsAccount sa2(date, "02342342", 0.015); CreditAccount ca(date, "C5392394", 10000, 0.0005, 50); Account* accounts[] = { &sa1,&sa2,&ca }; const int n = sizeof(accounts) / sizeof(Account*); cout << "(d)deposit (w)withdraw (s)show (c)change day (n)next month (e)exit" << endl; char cmd; do { date.show(); cout << "\tTotal: " << Account::getTotal() << "\tcommand>"; int index, day; double amount; string desc; cin >> cmd; switch (cmd) { case 'd': cin >> index >> amount; getline(cin, desc); accounts[index]->deposit(date, amount, desc); break; case 'w': cin >> index >> amount; getline(cin, desc); accounts[index]->withdraw(date, amount, desc); break; case 's': for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cout << "[" << i << "]"; accounts[i]->show(); cout << endl; } break; case 'c': cin >> day; if (day < date.getDay()) cout << "You cannot specify a previous day"; else if (day > date.getMaxDay()) cout << "Invalid day"; else date = Date(date.getYear(), date.getMonth(), day); break; case 'n': if (date.getMonth() == 12) date = Date(date.getYear() + 1, 1, 1); else date = Date(date.getYear(), date.getMonth() + 1, 1); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) accounts[i]->settle(date); break; } } while (cmd != 'e'); } int main() { test(); return 0; }
运行测试截图:
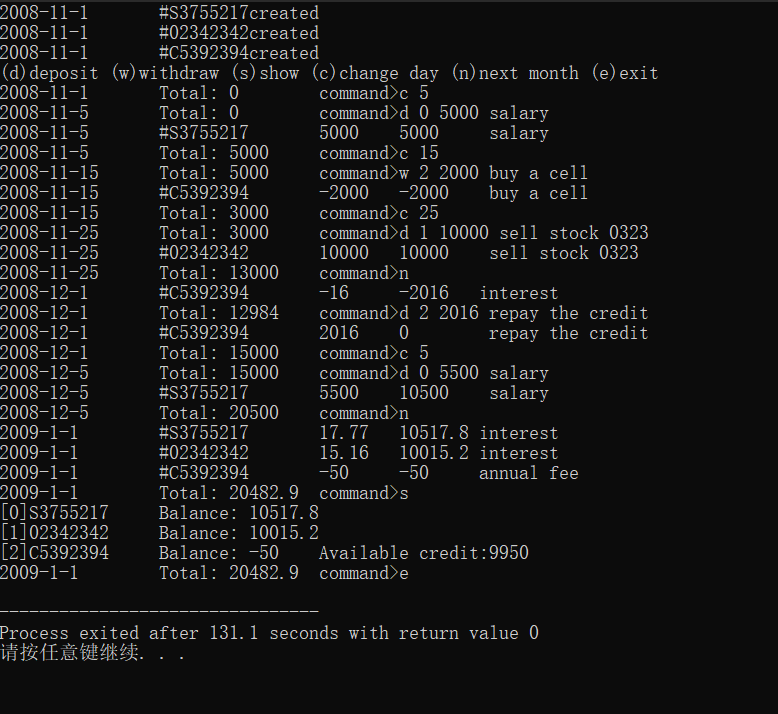
五、实验总结
实现类的继承与多态化,有助于我们更好地使用C++这门语言:
-
代码重用性(Code Reusability):
- 基类功能重用: 通过继承,子类可以继承基类的成员函数和数据成员,从而避免了重复编写相似的代码。
- 派生类扩展: 派生类可以在基类的基础上添加新的功能,从而使得代码更加灵活和可扩展。
-
抽象与封装(Abstraction and Encapsulation):
- 抽象: 通过基类定义共同的接口和行为,实现了对对象的抽象描述,使得程序员可以专注于对象的高层次概念而不必关注底层的实现细节。
- 封装: 派生类可以隐藏其实现的细节,只暴露出与外部交互的接口,提高了代码的安全性和可维护性。
-
多态性(Polymorphism):
- 运行时多态: 通过虚函数和动态绑定,可以在运行时决定调用哪个函数,从而实现了多态性。这使得可以用基类指针或引用来操作派生类对象,提高了代码的灵活性。
- 函数重载: 在同一个类中可以定义多个同名函数,通过参数的不同来区分它们,提供了静态多态性的实现。
-
易维护性和扩展性(Maintainability and Extensibility):
- 易维护性: 通过将相关的功能放在一个类中,代码的组织更加清晰,容易理解和维护。
- 易扩展性: 可以通过添加新的派生类来扩展系统的功能,而无需修改现有的代码,从而降低了引入新功能的风险。
-
代码结构和组织(Code Structure and Organization):
- 层次结构: 类的继承可以形成层次结构,使得代码的组织更加有序,更容易理解。
- 模块化: 每个类可以看作是一个独立的模块,有助于将代码分解成更小、更易管理的单元。
-
接口和协议(Interfaces and Contracts):
- 接口定义: 通过纯虚函数(抽象类)或虚函数,可以定义类的接口,规定了派生类需要实现的功能。
- 协议遵循: 派生类必须遵循基类的接口,这种强制性的约束有助于确保系统的一致性和可靠性。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号