2023秋季地大北京算法课
- pta 习题摘记
- 7 - 1 GPA
- 7 - 2 小伍的升序数组
- 7 - 3 两数之和
- 7 - 4 归并排序
- 7 - 5 棋盘覆盖问题
- 快速幂
- 7 - 6 最大字段和问题(分治版)
- 国王的奖励(分治版)
- 7 - 7 平面最近点对(分治版)
- 7 - 8 寻找第 k 小(分治版)
- 7 - 9 铺设油井管道plus
- 7-10 两个序列的中位数(减治法)
- 7-11 淘汰赛冠军(减治法)
- 7-12 数塔
- 7-13 最短路径
- 7-14 旅行商问题
- 7-15 最长有序子序列
- 7-16 最长公共子序列长度
- 7-17 0-1背包
- 7-18 h0145. 会议安排
- 7-19 小伍的背包问题
- 7-20 Prim算法
- 7-21 批处理作业调度
- 7-22 八皇后问题(*)
- 7-23 图着色问题
- 7-24 素数环
pta 传送门
不贴完整代码防止 CV 做题
pta 习题摘记
7 - 1 GPA
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> s(n), v(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i) cin >> s[i];
double sum = 0, vsum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
cin >> v[i];
vsum += v[i];
if(s[i] >= 90) sum += 4.0 * v[i];
else if(s[i] >= 85) sum += 3.5 * v[i];
else if(s[i] >= 80) sum += 3.0 * v[i];
else if(s[i] >= 75) sum += 2.5 * v[i];
else if(s[i] >= 70) sum += 2.0 * v[i];
else if(s[i] >= 65) sum += 1.5 * v[i];
else if(s[i] >= 60) sum += 1.0 * v[i];
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << sum / vsum << '\n';
return ;
}
7 - 2 小伍的升序数组
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
bool f = true;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; ++ i){
cin >> a[i];
if(i && a[i] < a[i - 1]) f = false;
}
if(f) cout << "Yes\n";
else cout << "No\n";
return ;
}
7 - 3 两数之和
void solve(){
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
vector<int> a(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
cin >> a[i];
}
map<int, int> q;
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; -- i){
if(q.count(k - a[i])){
ans += q[k - a[i]];
}
++ q[a[i]];
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return ;
}
void solve(){
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
vector<int> a(n);
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
cin >> a[i];
for(int j = 0; j < i; ++ j)
if(a[i] + a[j] == k) ++ ans;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return ;
}
7 - 4 归并排序
//>>>Qiansui
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define mem(x,y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define debug(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define debug2(x,y) cout << #x << " = " << x << " " << #y << " = "<< y << '\n'
//#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<ull, ull> pull;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
/*
*/
const int maxm = 2e5 + 5, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f, mod = 998244353;
ll n;
vector<ll> r(maxm + 1, 0), r1(maxm, 0);
void Merge(int s, int m, int t){//合并两个升序数组为一个升序数组
int i = s, j = m + 1, k = s;
while(i <= m && j <= t){
if(r[i] <= r[j]) r1[k ++] = r[i ++];
else r1[k ++] = r[j ++];
}
while(i <= m) r1[k ++] = r[i ++];
while(j <= t) r1[k ++] = r[j ++];
return ;
}
void Merge_Sort(int s, int t){//归并排序
if(s != t){//可以划分
int m = (s + t) / 2;
Merge_Sort(s, m);//求解子问题1
Merge_Sort(m + 1, t);//求解子问题2
Merge(s, m, t);//合并两个序列
for(int i = s; i <= t; ++ i)//结果复制到r数组中
r[i] = r1[i];
}
return ;
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> r[i];
Merge_Sort(1, n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cout << r[i] << " \n"[i == n];
return ;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
7 - 5 棋盘覆盖问题
//>>>Qiansui
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define mem(x,y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define debug(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define debug2(x,y) cout << #x << " = " << x << " " << #y << " = "<< y << '\n'
//#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<ull, ull> pull;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
/*
*/
const int maxm = 2e2 + 5, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f, mod = 998244353;
int idx = 0, board[maxm][maxm];
// 棋盘左上坐标[tr, tc],棋盘边长为 size,特殊方格位置为 [dr, dc]
void ChessBoard(int tr, int tc, int size, int dr, int dc){
if(size == 1) return ;// 只有一个特殊方格时
int id = ++ idx, s = size / 2;
if(dr < tr + s && dc < tc + s){// 特殊方格在左上子棋盘中
ChessBoard(tr, tc, s, dr, dc);
}else{
board[tr + s - 1][tc + s - 1] = id;
ChessBoard(tr, tc, s, tr + s - 1, tc + s - 1);
}
if(dr < tr + s && dc >= tc + s){// 特殊方格在右上子棋盘中
ChessBoard(tr, tc + s, s, dr, dc);
}else{
board[tr + s - 1][tc + s] = id;
ChessBoard(tr, tc + s, s, tr + s - 1, tc + s);
}
if(dr >= tr + s && dc < tc + s){// 特殊方格在左下子棋盘中
ChessBoard(tr + s, tc, s, dr, dc);
}else{
board[tr + s][tc + s - 1] = id;
ChessBoard(tr + s, tc, s, tr + s, tc + s - 1);
}
if(dr >= tr + s && dc >= tc + s){// 特殊方格在右下子棋盘中
ChessBoard(tr + s, tc + s, s, dr, dc);
}else{
board[tr + s][tc + s] = id;
ChessBoard(tr + s, tc + s, s, tr + s, tc + s);
}
return ;
}
void solve(){
int n, x, y;
cin >> n >> x >> y;
ChessBoard(1, 1, n, x, y);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++ j)
cout << setw(5) << left << board[i][j];
cout << '\n';
}
return ;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
快速幂
//>>>Qiansui
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define mem(x,y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define debug(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define debug2(x,y) cout << #x << " = " << x << " " << #y << " = "<< y << '\n'
//#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<ull, ull> pull;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
/*
*/
const int maxm = 2e5 + 5, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
// ll qpow(ll a, ll x, ll p){
// a %= p;
// ll res = 1;
// while(x){
// if(x & 1) res = res * a % p;
// x >>= 1; a = a * a % p;
// }
// return res;
// }
ll qpow(ll x, ll y, ll m) {
// cout << x << " " << y << " " << m << endl;
if(y == 0) {
return 1;
}
if(y % 2 == 1) {
return x * qpow(x, y - 1, m) % m;
} else {
ll temp = qpow(x, y / 2, m) % m;
return temp * temp % m;
}
}
void solve(){
ll a, n, m;
cin >> a >> n >> m;
cout << qpow(a, n, m) << '\n';
return ;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
7 - 6 最大字段和问题(分治版)
const int maxm = 1e5 + 5, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f, mod = 998244353;
ll n, a[maxm];
ll calc(int l, int r){
if(l == r) return a[l];
int m = l + r >> 1;
ll max1 = calc(l, m), max2 = calc(m + 1, r), max3;
ll maxl = 0, maxr = 0, t;
t = 0;
for(int i = m; i >= l; -- i){
t += a[i];
maxl = max(maxl, t);
}
t = 0;
for(int i = m + 1; i <= r; ++ i){
t += a[i];
maxr = max(maxr, t);
}
max3 = maxl + maxr;
return max(max1, max(max2, max3));
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> a[i];
cout << calc(1, n);
return ;
}
国王的奖励(分治版)
题意
国际象棋是很久以前由一个印度人Shashi发明的,当他把该发明献给国王的时候,国王很高兴,就许诺可以给这个发明人任何他想要的奖赏。Shashi要求以这种方式给他一些粮食:棋盘的第1个方格里只放\(1\)粒麦粒,第2格\(q\)个,第三格\(q^2\)个,第四格\(q^3\)个⋯,直到n个格子全部放满。这个奖赏最终会是什么样子的呢?Shashi已经有算法了,请你算一算吧。
当然Shashi并不关心具体的数有多少了,他有一个检验你的答案是否与他心意相通的办法:把你求出的答案对100000007取模看看和Shashi算的是否一样就行了。
注:\(1 \le n, q \le 10^{18}\)
思路
代码
法一:等比数列求和公式
//>>>Qiansui
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define mem(x,y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define debug(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define debug2(x,y) cout << #x << " = " << x << " " << #y << " = "<< y << '\n'
//#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<ull, ull> pull;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
/*
*/
const int maxm = 2e5 + 5, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f, mod = 100000007;
ll n, q, ans;
ll qpow(ll a, ll x, ll p){
a %= p;
ll res = 1;
while(x){
if(x & 1) res = res * a % p;
x >>= 1; a = a * a % p;
}
return res;
}
void solve(){
cin >> q >> n;
q %= mod;// 精彩的处理!!!
if(q == 1) ans = n % mod;
else{
ans = (mod + qpow(q, n, mod) - 1) % mod * qpow(q - 1, mod - 2, mod) % mod;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return ;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
7 - 7 平面最近点对(分治版)
//>>>Qiansui
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define mem(x,y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define debug(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define debug2(x,y) cout << #x << " = " << x << " " << #y << " = "<< y << '\n'
//#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<ull, ull> pull;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
/*
*/
const int N = 2e5 + 5, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f, mod = 998244353;
ll n;
pdd p[N], t[N];
double dis(pdd & i, pdd & j){
double dx = i.first - j.first, dy = i.second - j.second;
return sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
double closedots(int l, int r){
if(l == r) return 2e9;
if(r == l + 1) return dis(p[l], p[r]);
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
double d1, d2, d;
d1 = closedots(l, mid); d2 = closedots(mid + 1, r);
d = min(d1, d2);
int id = 0;
for(int i = l; i <= r; ++ i)
if(fabs(p[i].first - p[mid].first) < d) t[++ id] = p[i];
sort(t + 1, t + 1 + id, [](pdd& a, pdd& b){
return a.second < b.second;
});
for(int i = 1; i < id; ++ i)
for(int j = i + 1; j <= id && t[j].second - t[i].second < d; ++ j)
d = min(d, dis(t[i], t[j]));
return d;
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> p[i].first >> p[i].second;
sort(p + 1, p + 1 + n, [](pdd& a, pdd& b){
return a.first < b.first || a.first == b.first && a.second < b.second;
});
double ans = closedots(1, n);
cout << fixed << setprecision(4) << ans << '\n';
return ;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
7 - 8 寻找第 k 小(分治版)
C++ 函数:nth_element(first, k, last);
或者
利用快速排序的划分思想找第 k 个元素
快速排序的划分会将所有比数 i 小的元素放在其前面,比其大的元素放在后面,那么数 i 在数组中的排名就知道了,那么再比较排名与 k 的值,相等即找到,不等则递归左右序列找第 k 大的元素
//>>>Qiansui
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define mem(x,y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define debug(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define debug2(x,y) cout << #x << " = " << x << " " << #y << " = "<< y << '\n'
//#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<ull, ull> pull;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
/*
*/
const int N = 2e6 + 5, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f, mod = 998244353;
int n, k, a[N];
int partition(int begin, int end){// 划分
int i = begin, j = end;
while(i < j){
while(i < j && a[i] <= a[j]) -- j;// 右侧扫描
if(i < j){// 将小元素放在前面
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
++ i;
}
while(i < j && a[i] <= a[j]) ++ i;// 左侧扫描
if(i < j){// 将大元素放在后面
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
-- j;
}
}
return i;
}
int find_kth(int l, int r, int k){
int p = partition(l, r);
if(p == k) return p;
else if(p < k) return find_kth(p + 1, r, k);
else return find_kth(l, p, k);
}
void solve(){
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> a[i];
cout << a[find_kth(1, n, k)] << '\n';
return ;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
7 - 9 铺设油井管道plus
题面
某石油公司有 n 口油井,为方便输送石油,计划修建输油管道。根据设计要求,水平方向有一条主管道,每口油井修一条垂直方向的支线管道通向主管道。请设计一种算法确定主管道的位置,使得所有油井到主管道之间的支线管道长度的总和最小。提示:复杂度为 O(n) 能通过所有测试用例。
每个输入文件为一个测试用例,每个文件的第一行给出一个正整数 n \((1\le n \le 2·10^6)\),表示油井数量,从第二行起的 n 行数据,表示每口油井的位置,每行包含以空格分隔的两个整数,分别表示每口油井的横坐标 x \((-10^9 \le x \le 10^9)\)和纵坐标 y \((-10^9 \le y \le 10^9)\)。
输出各油井到主管道之间的支管道最小长度总和。
思路
思路就是利用 7 - 8 的代码找中位数即为主管道的 y 坐标,之后遍历求解
快读可过,关流 cin 目前过不了300 ms
//>>>Qiansui
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define mem(x,y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define debug(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define debug2(x,y) cout << #x << " = " << x << " " << #y << " = "<< y << '\n'
//#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<ull, ull> pull;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
/*
*/
const int N = 2e6 + 5, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f, mod = 998244353;
int n, k, a[N];
template<typename T>inline void read(T &x) {
int f = 1;
x = 0;
char ch = getchar();
for(; ch < '0' || ch > '9'; ch = getchar()) if(ch == '-') f = -1;
for(; ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'; ch = getchar()) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48);
x *= f;
}
int partition(int begin, int end){// 划分
int i = begin, j = end;
while(i < j){
while(i < j && a[i] <= a[j]) -- j;// 右侧扫描
if(i < j){// 将小元素放在前面
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
++ i;
}
while(i < j && a[i] <= a[j]) ++ i;// 左侧扫描
if(i < j){// 将大元素放在后面
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
-- j;
}
}
return i;
}
int find_kth(int l, int r, int k){
int p = partition(l, r);
if(p == k) return p;
else if(p < k) return find_kth(p + 1, r, k);
else return find_kth(l, p, k);
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
read(a[i]); read(a[i]);
}
int pos = find_kth(1, n, (n + 1) / 2);
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) ans += abs(a[i] - a[pos]);
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return ;
}
signed main(){
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
7-10 两个序列的中位数(减治法)
此题为求解两个等长升序数组的中位数
算法的基本思想如下:
(1)分别求出两个序列的中位数 a, b
(2)比较 a 和 b,会有如下三种情况:
- a = b,则 a 即为两个序列的中位数
- a < b,则中位数出现在 a 和 b 之间,在序列 A 中舍弃前半段,序列 B 中舍弃后半段
- a > b,则中位数出现在 b 和 a 之间,在序列 B 中舍弃前半段,序列 A 中舍弃后半段
(3)再新序列 A,B 中分别求出中位数,重复上诉操作,直到两个序列中只有一个元素,则较小者即为所求
整体的时间复杂度为 \(O(\log_2n)\)
int search_mid(vector<int> & a, vector<int> & b, int n){
int l[2] = {1, 1}, r[2] = {n, n}, mid[2];
while(l[0] < r[0] && l[1] < r[1]){
mid[0] = l[0] + r[0] >> 1;
mid[1] = l[1] + r[1] >> 1;
if(a[mid[0]] == b[mid[1]]) return a[mid[0]];
if(a[mid[0]] < b[mid[1]]){
if((r[0] + l[0]) % 2) l[0] = mid[0] + 1;
else l[0] = mid[0];
r[1] = mid[1];
}else{
if((r[0] + l[0]) % 2) l[1] = mid[1] + 1;
else l[1] = mid[1];
r[0] = mid[0];
}
}
if(a[l[0]] < b[l[1]]) return a[l[0]];
else return b[l[1]];
}
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1), b(n + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> b[i];
cout << search_mid(a, b, n) << '\n';
return ;
}
7-11 淘汰赛冠军(减治法)
假设有 \(n = 2^k\) 个选手进行竞技淘汰赛,最后决出冠军的选手
规则如下:
开始时将所有选手分成 n/2 组,每组两个选手进行比赛,被淘汰者不参加以后的比赛,然后再将剩余选手分成 n/4 组,每组两个选手进行比赛,......直到剩余最后两个选手,进行一次比赛即可选出最后的冠军。下图(减治法求解淘汰赛冠军问题示例图)给出了一个减治技术解决淘汰赛冠军问题的过程示例(假设按照字符编码进行比较)。
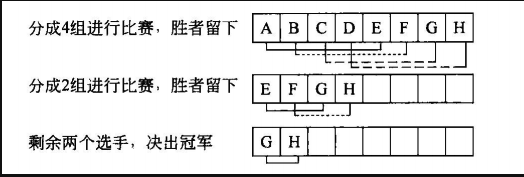
时间复杂度为 \(O(n)\)
pta 给出的题每一轮选手的能力值需乘权重取余,基本思想还是上面的思想
const int N = (1 << 19) + 5, M = 20 + 5, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f, mod = 998244353;
ll n, k, a[N], b[M], r[N];
int comp(int x, int y, int c){
ll l = a[x] * b[c] % mod, r = a[y] * b[c] % mod;
if(l < r || l == r && y < x) return true;
else return false;
}
int Game(){
int i = n, c = 1;
while(i > 1){
i /= 2;
for(int j = 1; j <= i; ++ j){
if(comp(r[j], r[j + i], c))
r[j] = r[j + i];
}
++ c;
}
return r[1];
}
void solve(){
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= k; ++ i) cin >> b[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> a[i], r[i] = i;
cout << Game() << '\n';
return ;
}
7-12 数塔
简单动态规划,洛谷传送门
从下往上
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector a(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
for(int j = 1; j <= i; ++ j){
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 1; -- i){
for(int j = 1; j <= i; ++ j){
a[i][j] += max(a[i + 1][j], a[i + 1][j + 1]);
}
}
cout << a[1][1] << '\n';
return ;
}
从上往下
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector a(2, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
int p = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
for(int j = 1; j <= i; ++ j){
cin >> a[p][j];
a[p][j] += max(a[1 - p][j], a[1 - p][j - 1]);
}
p = 1 - p;
}
cout << *max_element(a[1 - p].begin(), a[1 - p].end()) << '\n';
return ;
}
7-13 最短路径
多段图最短路径问题,对于每个顶点,考虑其所有入边,从最小的起始距离转移而来
int n, m;
vector<pii> e[N];
void solve(){
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++ i){
int x, y, z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
e[x].push_back({y, z});
e[y].push_back({x, z});
}
vector<int> dis(n + 1, inf);
dis[1] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
for(auto & [v, w] : e[i]){
dis[v] = min(dis[v], dis[i] + w);
}
}
cout << dis[n];
return ;
}
7-14 旅行商问题
从某个城市出发,经过每个城市仅一次后返回出发城市,问你最小的路程之和
考虑状压DP求解该问题
状态
\(dp[i][j]\) 表示从城市 \(i\) 出发经过集合 \(j\) 中的所有城市并返回城市 \(s\) 的最小路程和
转移
利用二进制 1/0 来表示某个城市经过或者没经过
选择城市 0 作为出发城市(无论哪个城市出发都一样)
\(dp[i][0] = a[i][0]\)
\(dp[i][j] = \min{ \{a[i][k] + dp[k][j - \{ k \} \}}, (k \in j)\)
//>>>Qiansui
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define mem(x,y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define debug(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define debug2(x,y) cout << #x << " = " << x << " " << #y << " = "<< y << '\n'
//#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<ull, ull> pull;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
/*
*/
const int N = 20 + 5, M = (1 << 20), inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f, mod = 998244353;
int n, s, a[N][N], dp[N][M];
void tsp(){
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
dp[i][0] = a[i][0];
}
for(int j = 1; j < (1 << n); ++ j){
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
dp[i][j] = inf;
if(i && ((j >> (i - 1)) & 1) == 1) continue;// 如果后缀集合中包含 i,则跳过
for(int k = 1; k < n; ++ k){// 枚举剩下的 n - 1 个城市
if(((j >> (k - 1)) & 1) == 0) continue;
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], a[i][k] + dp[k][j ^ (1 << (k - 1))]);
}
}
}
return ;
}
void solve(){
cin >> n >> s;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++ j){
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
tsp();
cout << dp[0][(1 << (n - 1)) - 1] << '\n';
return ;
}
signed main(){
// freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
7-15 最长有序子序列
朴素的最长上升子序列 \(O(n^2)\) 或者 \(O(n \log_2 n)\) 都可以通过
- \(O(n^2)\)
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> dp(n, 1), a(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
cin >> a[i];
for(int j = 0; j < i; ++ j)
if(a[i] > a[j]) dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
cout << (*max_element(dp.begin(), dp.end()));
return ;
}
- \(O(n \log_2 n)\)
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> dp(n + 5, inf);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
int t;
cin >> t;
auto it = lower_bound(dp.begin() + 1, dp.end(), t) - dp.begin();
dp[it] = min(dp[it], t);
}
cout << lower_bound(dp.begin() + 1, dp.end(), inf) - dp.begin() - 1;
return ;
}
7-16 最长公共子序列长度
朴素的 \(O(n^2)\) 做法
void solve(){
string a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
a = '#' + a; b = '#' + b;
vector dp(a.size() + 5, vector<int>(b.size() + 5, 0));
for(int i = 1; i < a.size(); ++ i){
for(int j = 1; j < b.size(); ++ j){
if(a[i] == b[j]) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
cout << dp[a.size() - 1][b.size() - 1];
return ;
}
7-17 0-1背包
朴素的 \(O(NV)\) 做法
int n, c;
vector<int> dp(N, 0);
void solve(){
cin >> n >> c;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
int v, w;
cin >> v >> w;
for(int j = c; j >= v; -- j)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - v] + w);
}
cout << dp[c] << '\n';
return ;
}
7-18 h0145. 会议安排
贪心将所有活动按照结束时间非降序排序,再从前往后安排活动
void solve(){
int n, ans = 1;
cin >> n;
vector<pii> a(n);
for(auto & [x, y] : a) cin >> x >> y;
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), [&](pii x, pii y){
return x.second < y.second;
});
for(int i = 1, j = 0; i < n; ++ i){
if(a[i].first >= a[j].second){
++ ans;
j = i;
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return ;
}
7-19 小伍的背包问题
物品可以均匀切割的背包,贪心取价值重量比最大的一个一个放入背包即可
void solve(){
int n, c;
cin >> n >> c;
vector<pll> a(n);
for(auto &[w, v] : a) cin >> v >> w;
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), [&](pll x, pll y){
return x.first * y.second > y.first * x.second;
});
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n && c; ++ i){
if(a[i].second <= c){
ans += a[i].first;
c -= a[i].second;
}else{
ans += 1.0 * a[i].first * c / a[i].second;
c = 0;
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return ;
}
7-20 Prim算法
Prim 算法板子题,注意 Prim 的写法,不然容易 TLE
ll n;
bool vis[N];
vector<pll> p(N);
ll getdis(int i, int j){
return abs(p[i].first - p[j].first) + abs(p[i].second - p[j].second);
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
p[i] = {x / 8, y / 8};
}
priority_queue<pll, vector<pll>, greater<pll>> q;
vector<ll> dis(n + 1, INF);
q.push({0, 0});
dis[0] = 0;
ll ans = 0;
while(q.size()){
auto [d, u] = q.top();
q.pop();
if(vis[u]) continue;
vis[u] = true;
dis[u] = d;
ans += d;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
if(!vis[i]){
ll len = getdis(i, u);
if(dis[i] > len){
dis[i] = len;
q.push({len, i});
}
}
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return ;
}
7-21 批处理作业调度
int n, a[N], b[N], sum[N][2];
ll ans = inf;
bool vis[N];
void dfs(int u){
if(u == n + 1){
ll t = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
t += sum[i][1];
ans = min(ans, t);
return ;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
if(!vis[i]){
vis[i] = true;
sum[u][0] = sum[u - 1][0] + a[i];
sum[u][1] = max(sum[u][0], sum[u - 1][1]) + b[i];
dfs(u + 1);
vis[i] = false;
}
}
return ;
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> b[i];
dfs(1);
cout << ans << '\n';
return ;
}
7-22 八皇后问题(*)
注意输出格式。。。
int n;
char ch[N][N];
bool c[N], l[N << 1], r[N << 1], flag;
void dfs(int u){
if(u == n + 1){
if(flag) cout << '\n';
flag = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++ j){
cout << ch[i][j] << " \n"[j == n];
}
}
return ;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
int x = u + i, y = n + 1 - i + u;
if(!c[i] && !l[x] && !r[y]){
c[i] = l[x] = r[y] = true;
ch[u][i] = 'Q';
dfs(u + 1);
c[i] = l[x] = r[y] = false;
ch[u][i] = '.';
}
}
return ;
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++ j)
ch[i][j] = '.';
dfs(1);
if(!flag) cout << "None\n";
return ;
}
7-23 图着色问题
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5 + 5;
int n, em, col[N];
vector<int> e[N];
bool check(int u){
for(auto v : e[u])
if(col[u] == col[v])
return false;
return true;
}
bool GraphColor(int m){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) col[i] = 0;
int k = 1;
while(k >= 1){
++ col[k];
while(col[k] <= m){
if(check(k)) break;
else ++ col[k];
}
if(col[k] <= m && k == n) return true;
if(col[k] <= m && k < n) ++ k;
else col[k --] = 0;
}
return false;
}
signed main(){
cin >> n >> em;
for(int i = 0; i < em; ++ i){
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
e[u].push_back(v);
e[v].push_back(u);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
if(GraphColor(i)){
cout << i << '\n';
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
7-24 素数环
bool flag = false, vis[N], isprime[N << 1];
int n, a[N];
void pre(){
for(int i = 2; i < (N << 1); ++ i){
isprime[i] = true;
for(int j = 2; j * j <= i; ++ j){
if(i % j == 0){
isprime[i] = false;
break;
}
}
}
return ;
}
bool check(int u){
bool f = true;
if(u > 1) f = f && isprime[a[u] + a[u - 1]];
if(u == n) f = f && isprime[a[u] + a[1]];
return f;
}
void dfs(int u){
if(u == n + 1){
flag = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
cout << a[i] << " \n"[i == n];
return ;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
a[u] = i;
if(!vis[i] && check(u)){
vis[i] = true;
dfs(u + 1);
vis[i] = false;
a[u] = 0;
}
}
return ;
}
void solve(){
pre();
cin >> n;
a[1] = 1;
vis[1] = true;
dfs(2);
if(!flag) cout << "No Answer\n";
return ;
}
本文来自博客园,作者:Qiansui,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Qiansui/p/17753596.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号