C++ STL摘记
1. string类补充
1.1. 函数-find/rfind
find和rfind函数,返回的是下标或者string::npos
index=ss.find(s1,pos,num)
find从pos(包括)开始往右查找(num的作用待补充)
index=ss.rfind(s1,poss,num)
rfind从pos(包括)开始往左查找(num的作用待补充)
代码示例:
//>>>>Qiansui
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int maxm=1e4+5;
string ss[3]{"123asd123","a123gh123","ea123s123"},s1="123";
int main(){
int index;
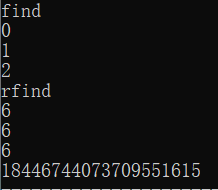
cout<<"find\n";
for(int i=0;i<3;++i){
index=ss[i].find(s1);
if(index!=string::npos) cout<<index<<endl;
else cout<<"Error\n";
}
cout<<"rfind\n";
for(int i=0;i<3;++i){
index=ss[i].rfind(s1,6);
if(index!=string::npos) cout<<index<<endl;
else cout<<"Error\n";
}
cout<<string::npos;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1.2. 遍历
代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
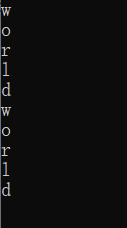
string s1{"world"};
for(int i=0;i<s1.size(); ++i)
cout<<s1[i]<<endl;
for(auto c : s1)
cout<<c<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1.3. string的修改器
push_back()和pop_back()实现string类对象的前后的单个字符的改变
string ss;
char ch='a';
ss.push_back(ch);//Append character to string (public member function)
cout<<ss<<"\n";
ss.push_back('b');
cout<<ss<<"\n";
ss.pop_back();//Delete last character (public member function)
cout<<ss<<'\n';
/*
a
ab
a
*/
2. STL函数
头文件:#include<algorithm>
2.1. copy, copy_backward, copy_n, copyif 函数
copy_backward(begin(from), end(from), end(to)):从后往前,将 from[begin, end) 拷贝到 to(...,end) 中去,函数返回 end 的起始位置的迭代器
代码示例
int n = 5;
vector<int> a;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i) a.push_back(i);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i) cout << a[i] << " \n"[i == n - 1];
copy_backward(a.begin(), a.begin() + 2, a.end());
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i) cout << a[i] << " \n"[i == n - 1];
参考链接: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/597481245
2.2. fill 函数
用于对容器的值进行填充,可以填充普通数组、vector等
fill(a.begin(),a.end(),10);
int arr[10];
fill(arr, arr + 10, 2);
相关资料:
2.3. lower_bound() 和 upper_bound() 函数
这里暂时摘记这两个二分排序自定义排序的相关内容
lower_bound comp(element, value) [](const Product& elem, double val)
upper_bound comp(value, element) [](double val, const Product& elem)
- 一道可以用到自定义排序的题:Leetcode 2106. 摘水果
// 自定义排序代码示例 Leetcode 2106. 摘水果
// 先左后右
int res = k, pos = s;
for(int l = p - 1; l >= 0; -- l){
res -= abs(f[l][0] - pos);
pos = f[l][0];
if(res < 0) break;
int r = upper_bound(f.begin(), f.end(), pos + res, [](int y, auto& x){
return y < x[0];
}) - f.begin() - 1;
r = max(r, p - 1);
ans = max(ans, sum[r + 1] - sum[l]);
}
// 先右后左
res = k;
pos = s;
for(int r = p; r < n; ++ r){
res -= abs(f[r][0] - pos);
pos = f[r][0];
if(res < 0) break;
int l = lower_bound(f.begin(), f.end(), pos - res, [](auto& x, int y){
return x[0] < y;
}) - f.begin();
l = min(l, p);
ans = max(ans, sum[r + 1] - sum[l]);
}
2.4. reverse 函数
https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/algorithm/reverse
可以翻转数组、字符串、容器等
reverse函数用于反转在[first,last)范围内的顺序[first,last)(左闭右开),reverse函数没有返回值
例题:
简单的翻转 https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc284/tasks/abc284_a?lang=en vector<string>
2.5. unique 函数
该函数的作用是“去除”容器或者数组中相邻元素的重复出现的元素
返回值是一个迭代器,它指向的是去重后容器中不重复序列的最后一个元素的下一个元素。
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
ans.erase(unique(ans.begin(), ans.end()), ans.end());
相关资料:
https://www.cnblogs.com/wangkundentisy/p/9033782.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36561697/article/details/82356053
3. priority_queue 优先队列
头文件#include<queue>
3.1. 相关资料
https://blog.csdn.net/c20182030/article/details/70757660
3.2. 摘记
- 默认从大到小,如:
priority_queue<int> a;
a.push(1);
cout<<a.top()<<'\n';
a.push(10);
cout<<a.top()<<'\n';
a.push(8);
cout<<a.top()<<'\n';
a.push(3);
cout<<a.top()<<'\n';
while(a.size()){
cout<<a.size()<<" "<<a.top()<<'\n';
a.pop();
}
return ;

greater<int>——从小到大——priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> a
less<int>——从大到小——priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int>> a
top返回第一个,pop删除第一个,即队列头
3.3. 自定义排序
struct node{
ll val,id,c;
// operator() 返回 true 时,p1 的优先级被认为低于 p2
bool operator <(const node &a)const{
return a.val<val;//必须重载小于号和使用小于号
}
};
priority_queue<node> q;//此处为最小堆
4. set
4.1. 基本用法
set.erase()
| 形式 | 函数原型 | 返回值 | 复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 按位置删除 | iterator erase(const_iterator pos) | 返回指向被删元素之后的迭代器 | 摊还常数 O(1) |
| 按值删除 | size_type erase(const key_type& key) | 返回删除的元素个数(set 中只能是 0 或 1) | 对数级别 O(logn) |
| 按范围删除 | "iterator erase(const_iterator first, const_iterator last)" | 返回指向最后一个被删元素之后的迭代器 | O(logn+m), m 为区间长度 |
set 的 lower_bound 和 upper_bound
4.2. 4.2 multiset
c++语言中,multiset是set库中一个非常有用的类型,它可以看成一个序列,插入一个数,删除一个数都能够在O(logn)的时间内完成,而且他能时刻保证序列中的数是有序的,而且序列中可以存在重复的数。
4.2.1. 操作
c.erase(elem) 删除与elem相等的所有元素,返回被移除的元素个数。
4.2.2. 4.2.2 相关资料
multiset用法总结 https://blog.csdn.net/sodacoco/article/details/84798621
4.2.3. 例题
双multiset维护数组的k个最大值Best Performances做法见提交和题解
4.3. unordered_set
使用介绍:https://blog.csdn.net/tilblackout/article/details/134172656
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45031801/article/details/141651611
5. map
map 由红黑树实现,插入、查找、删除的时间复杂度近似为 \(O(log N)\)
unordered_map 由哈希表实现,插入、查找的时间复杂度为 \(O(常数)\)
5.1. unordered_map
- 自定义哈希函数
struct custom_hash {
static uint64_t splitmix64(uint64_t x) {
x += 0x9e3779b97f4a7c15;
x = (x ^ (x >> 30)) * 0xbf58476d1ce4e5b9;
x = (x ^ (x >> 27)) * 0x94d049bb133111eb;
return x ^ (x >> 31);
}
size_t operator()(uint64_t x) const {
static const uint64_t FIXED_RANDOM = chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();
return splitmix64(x + FIXED_RANDOM);
}
};
unordered_map<int, int, custom_hash> c;
5.2. map
- 自定义排序:一个示例
auto cmp = [](const int& x, const int& y){
return y < x;
};
map<int, int, decltype(cmp)> cnt;
5.3. 相关资料
map的默认排序和自定义排序 https://www.cnblogs.com/stay-alive/p/8215400.html
6. vector
类似于数组的容器,但是动态扩容(细节不清楚,日后摘记)
6.1. 相关方法
resize(): https://blog.csdn.net/JMW1407/article/details/108785448
- void resize(std::size_t __new_size)
- void resize(std::size_t __new_size, const int &__x)
resize 方法支持两种形式的调用,改变的是 vector 的元素个数 size()。缩小时基本不会重新分配内存,只有扩大且超出预分配空间时才会扩容
7. std::function
类模版std::function是一种通用、多态的函数封装器
例如:
void solve(){
function <void(int, int)> output = [](int x, int y) -> void {
cout << x + y << '\n';
};
auto output2 = [](int x, int y){
return x + y;
};
output(1, 2);
cout << output2(2, 34) << '\n';
return ;
}
// c++ 23 支持? 显式对象参数
auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, int i, int j) -> int {
if(i + 1 == j) return 0;
int& res = m[i][j];
if(res != inf) return res;
for(int k = i + 1; k < j; ++ k){
res = min(res, dfs(i, k) + dfs(k, j) + v[i] * v[j] * v[k]);
}
return res;
};
8. 末尾 - 杂项(此处不一定都是STL的内容)
8.1. STL 自定义排序
参考链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/600531550
远古图片,保留一下哈哈哈~

8.2. memset 函数
头文件:C 中 #include<string.h> ,C++ 中 #include<cstring>
memset 是按字节赋值,而 int 有 4 个字节,所以 memset(a, 127, sizeof(a)) 不是将 a 全赋 127,而是赋了一个很大很大的数($ > 2^{30} $)
8.3. __lg() 函数和 log2() 函数
__lg() 函数接受一个整数,返回一个整数,表示该数二进制表示下最高一位 1 的位置。事实上这个数就是 \(\lfloor \log_2 n \rfloor\) 的准确值。
log2() 函数接受一个浮点数,返回一个浮点数,表示该数以 2 为底的对数的具体值。由于是浮点数,因此精度有限。当输入的数绝对值很大时,很可能最终结果与准确值相差 eps。
8.4. sort函数相关
// 自定义比较函数
// 如果 a 应该排在 b 前面,则返回 true
bool compare_desc(int a, int b) {
return a > b;
}
一个例子,用于理解默认的排序方式:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
// 辅助函数,用于打印 vector<vector<int>>
void printVectorOfVectors(const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& vec) {
std::cout << "{ ";
for (const auto& inner_vec : vec) {
std::cout << "{ ";
for (int x : inner_vec) {
std::cout << x << " ";
}
std::cout << "} ";
}
std::cout << "}" << std::endl;
}
int main() {
std::vector<std::vector<int>> m = {
{1, 3, 5},
{1, 2},
{2, 1},
{1, 3, 2}
};
std::cout << "排序前: ";
printVectorOfVectors(m);
sort(m.begin(), m.end());
std::cout << "排序后: ";
printVectorOfVectors(m);
return 0;
}
/* 输出:
排序前: { { 1 3 5 } { 1 2 } { 2 1 } { 1 3 2 } }
排序后: { { 1 2 } { 1 3 2 } { 1 3 5 } { 2 1 } }
*/
8.5. id iota 排序
vector<int> id(n);
iota(id.begin(), id.end(), 0);
sort(id.begin(), id.end(), [&](int& x, int& y){
return h[x] < h[y];
});


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号