BLOG-3_JavaHomework_Summary
前言
小总结
第六次PTA作业开始了新的篇章----电信计费系列,由于吸取了之前的教训,所以每次的作业都要考虑可拓展性,虽然这个系列也用到了正则表达式,但是有之前的铺垫,已经能从容面对了,总的来说,相对之前的作业而言,有了更多的思考,更深入的理解了OO。
设计与分析
多态测试
题目简述:
输入立方体或圆柱体的信息,输出所有图形的表面积之和、体积之和
代码
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static int cnt; public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String s; Container[] containers = new Container[1000]; cnt = in.nextInt(); for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) { s = in.next(); if ("cube".equals(s)) { containers[i] = new Cube(in.nextDouble()); } else { containers[i] = new Cylinder(in.nextDouble(), in.nextDouble()); } } System.out.printf("%.2f\n", Container.sumofArea(containers)); System.out.printf("%.2f\n", Container.sumofVolume(containers)); } } interface Container { double pi = 3.1415926; double area(); double volume(); static double sumofArea(Container[] c) { double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < Main.cnt; i++) sum += c[i].area(); return sum; } static double sumofVolume(Container[] c) { double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < Main.cnt; i++) sum += c[i].volume(); return sum; } } class Cylinder implements Container { private final double radius; private final double high; public Cylinder(double radius, double high) {this.radius = radius;this.high = high;} @Override public double area() {return 2 * pi * radius * radius + high * 2.0 * pi * radius;} @Override public double volume() {return pi * radius * radius * high;} } class Cube implements Container { private final double sideLength; public Cube(double sideLength) {this.sideLength = sideLength;} @Override public double area() {return sideLength * sideLength * 6.0;} @Override public double volume() {return sideLength * sideLength * sideLength;} }
分析
既然题目已经提醒要用多态了,那么就要考虑什么时候可以用到多态,很明显,题目有两种图形,但是输出却是两种图形数据的和
所以我们考虑有让两个图形都实现一个共同的Container接口,使得Container在遍历容器求和时,通过多态可以让两种图形分别报出自己的数据。
sdut-Collection-sort--C~K的班级(II)
题目简述:
输入若干学生信息,输出去重后的学生信息
代码
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); HashSet<Stud> studs = new HashSet<>(); int t = in.nextInt(); for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) { studs.add(new Stud(in.next(), in.next(), in.next(), in.next())); } System.out.println(studs.size()); ArrayList<Stud> studsArr = new ArrayList<>(studs); Collections.sort(studsArr); for (Stud s : studsArr) System.out.println(s); } } class Stud implements Comparable<Stud>{ String id, name, age, sex; public Stud(String id, String name, String age, String sex) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; this.sex = sex; } @Override public int hashCode() {return Integer.parseInt(id);} @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) {return id.equals(((Stud) obj).id);} @Override public String toString() {return id + " " + name + " " + age + " " + sex;} @Override public int compareTo(Stud o) {return Integer.compare(Integer.parseInt(id), Integer.parseInt(o.id));} }
分析
说到去重,很明显,可以用
HashSet来完成使用
HashSet需要重写hashCode()和equals()@Override public int hashCode() { return Integer.parseInt(id); } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { return id.equals(((Stud) obj).id); }由于每个学生的学号是唯一的,那么我们可以将学号作为每个学生的
HashCode,那么equals也同理题目还提到排序
这需要让学生的类实现
Comparable接口,将HashSet放入到链表,然后调用Collections.sort()对链表进行排序后,遍历输出,便是有序的
编写一个类Shop(商店)、内部类InnerCoupons(内部购物券)
题目简述:
商店类有内部类购物券,商店有面额为100,50的购物券,输入牛奶箱数,输出使用什么购物券买牛奶,以及牛奶剩余
代码
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); Shop myshop = new Shop(in.nextInt(), 50, 100); myshop.buy(); } } class Shop { private int milkCount; private InnerCoupons coupons50; private InnerCoupons coupons100; class InnerCoupons { public int value; public InnerCoupons(int value) {this.value = value;} public void buy() { System.out.println("使用了面值为" + value + "的购物券进行支付"); setMilkCount(getMilkCount() - value / 50); System.out.println("牛奶还剩" + getMilkCount() + "箱"); } } public void buy(){ coupons50.buy(); coupons100.buy(); } public Shop(int milkCount, int coupons50, int coupons100) { this.milkCount = milkCount; this.coupons50 = new InnerCoupons(coupons50); this.coupons100 = new InnerCoupons(coupons100); } public int getMilkCount() {return milkCount;} public void setMilkCount(int milkCount) {this.milkCount = milkCount;} }
分析
题目要求用内部类,根据题目要求完成即可
动物发声模拟器(多态)
题目简述:
用多态输出猫、狗、山羊的类型以及叫声
代码
//动物发生模拟器. 请在下面的【】处添加代码。 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Cat cat = new Cat(); Dog dog = new Dog(); Goat goat = new Goat(); speak(cat); speak(dog); speak(goat); } //定义静态方法speak() public static void speak(Animal animal) { System.out.print(animal.getAnimalClass() + "的叫声:"); animal.shout(); } } //定义抽象类Animal abstract class Animal { abstract String getAnimalClass(); abstract void shout(); } //基于Animal类,定义猫类Cat,并重写两个抽象方法 class Cat extends Animal { @Override String getAnimalClass() {return "猫";} @Override void shout() {System.out.println("喵喵");} } //基于Animal类,定义狗类Dog,并重写两个抽象方法 class Dog extends Animal { @Override String getAnimalClass() {return "狗";} @Override void shout() {System.out.println("汪汪");} } //基于Animal类,定义山羊类Goat,并重写两个抽象方法 class Goat extends Animal { @Override String getAnimalClass() {return "山羊";} @Override void shout() {System.out.println("咩咩");} }
分析
题目要求用到多态,根据题目提示完成即可
电信计费系列1、系列2-手机+座机计费、系列3-短信计费
题目简述:
输入若干用户和其通讯记录,输出用户话费余额
代码
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/*
* Main程序入口
* 职责:输入数据,将正确的信息存入InputData,*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
HashSet<User> userSet = new HashSet<>();
ArrayList<CommunicationRecord> communicationRecords = new ArrayList<>();
String Line;
do {
Line = in.nextLine();
if (Line.equals("")) continue;
if (Line.charAt(0) == 'u') {
String[] uData = InputFormat.input_u_Format(Line);
if (uData != null) userSet.add(new User(uData[1], uData[2].charAt(0) - '0'));
} else if (Line.charAt(0) == 't') {
CallRecord tempCallRecord = InputFormat.input_t_Format(Line);
if (tempCallRecord != null) communicationRecords.add(tempCallRecord);
} else if (Line.charAt(0) == 'm') {
String[] mData = InputFormat.input_m_Format(Line);
if (mData != null) communicationRecords.add(new MessageRecord(mData[0], mData[1], mData[2]));
}
} while (!"end".equals(Line));
ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>(userSet);
DataCentre dataCentre = new DataCentre(users, communicationRecords);
dataCentre.printUserCosts();
}
}
/*
* CommunicationRecord通讯记录
* 由主动用户与应答用户为基本,电话,短信等方式构成*/
abstract class CommunicationRecord {
String callingNumber, answerNumber;
public CommunicationRecord(String callingNumber, String answerNumber) {
this.callingNumber = callingNumber;
this.answerNumber = answerNumber;
}
public CommunicationRecord() {
}
public String getCallingNumber() {
return callingNumber;
}
public String getAnswerNumber() {
return answerNumber;
}
}
class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode {
public LandlinePhoneCharging() {
getChargeRules().add(new LandPhoneInCityRule());
getChargeRules().add(new LandPhoneInProvinceRule());
getChargeRules().add(new LandPhoneInLandRule());
}
@Override
double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
double cost = 0;
for (ChargeRule chargeRule : getChargeRules())
cost += (chargeRule instanceof CallChargeRule) ? ((CallChargeRule) chargeRule).calCost(userRecords) : 0;
return cost;
}
@Override
double getMonthlyRent() {
return 20;
}
}
class PhoneMessage extends ChargeMode {
private double monthlyRent = 0;
public PhoneMessage() {
getChargeRules().add(new SendMessageRule());
}
@Override
double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
double cost = 0;
for (ChargeRule chargeRule : getChargeRules())
cost += (chargeRule instanceof SendMessageRule) ? ((SendMessageRule) chargeRule).calCost(userRecords) : 0;
return cost;
}
@Override
double getMonthlyRent() {
return monthlyRent;
}
}
class PhoneCharging extends ChargeMode {
private double monthlyRent = 15;
public PhoneCharging() {
getChargeRules().add(new PhoneInCityRule());
getChargeRules().add(new PhoneInProvinceRule());
getChargeRules().add(new PhoneInLandRule());
getChargeRules().add(new PhoneAnsInLandRule());
getChargeRules().add(new SendMessageRule());
}
@Override
double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
double cost = 0;
for (ChargeRule chargeRule : getChargeRules())
cost += (chargeRule instanceof CallChargeRule) ? ((CallChargeRule) chargeRule).calCost(userRecords) : (chargeRule instanceof SendMessageRule) ? ((SendMessageRule) chargeRule).calCost(userRecords) : 0;
return cost;
}
@Override
double getMonthlyRent() {
return monthlyRent;
}
}
class UserRecords {
private ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<MessageRecord> sendMessageRecords = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<MessageRecord> receiveMessageRecords = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords() {
return callingInCityRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords() {
return callingInProvinceRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords() {
return callingInLandRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInCityRecords() {
return answerInCityRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInProvinceRecords() {
return answerInProvinceRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInLandRecords() {
return answerInLandRecords;
}
public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getSendMessageRecords() {
return sendMessageRecords;
}
public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getReceiveMessageRecords() {
return receiveMessageRecords;
}
}
abstract class ChargeMode {
ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules = new ArrayList<>();
abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords);
abstract double getMonthlyRent();
public ArrayList<ChargeRule> getChargeRules() {
return chargeRules;
}
}
class MessageRecord extends CommunicationRecord {
private String message;
public MessageRecord(String callingNumber, String answerNumber, String message) {
super(callingNumber, answerNumber);
this.message = message;
}
public boolean isSendUser(User user) {
return callingNumber.equals(user.getNumber());
}
public boolean isAnsUser(User user) {
return answerNumber.equals(user.getNumber());
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
/*
* DataCentre
* 职责:将记录与用户匹配,存用户数据*/
class DataCentre {
private ArrayList<User> users; //所有用户
private ArrayList<CommunicationRecord> communicationRecords; //所有记录
public DataCentre(ArrayList<User> users, ArrayList<CommunicationRecord> communicationRecords) {
this.users = users;
this.communicationRecords = communicationRecords;
matchingRecords();
}
/*根据拨出号码匹配其记录*/
private void matchingRecords() {
for (User user : users) {
ArrayList<CommunicationRecord> communicationRecords = new ArrayList<>();
for (CommunicationRecord communicationRecord : this.communicationRecords) {
//所有拨的记录匹配到用户
if (communicationRecord instanceof CallRecord && (user.getNumber().equals(communicationRecord.getCallingNumber())))
communicationRecords.add(communicationRecord);
else if (communicationRecord instanceof MessageRecord)
communicationRecords.add(communicationRecord);
}
user.getCallRecords().addAll(communicationRecords);
}
for (User user : users) {
ArrayList<CommunicationRecord> communicationRecords = new ArrayList<>();
for (CommunicationRecord communicationRecord : this.communicationRecords) {
//所有接的记录匹配到用户
if (communicationRecord instanceof CallRecord && (user.getNumber().equals(communicationRecord.getAnswerNumber())))
communicationRecords.add(communicationRecord);
else if (communicationRecord instanceof MessageRecord)
communicationRecords.add(communicationRecord);
}
user.getAnsRecords().addAll(communicationRecords);
}
}
// 按序输出用户的当月费用
public void printUserCosts() {
Collections.sort(users);
for (User user : users) {
user.classifyRecords();
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
/*
* ChargeRule计费规则类
* */
class ChargeRule {
}
class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule {
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
double cost = 0;
for (CallRecord callRecord : userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) {
int a = callRecord.getSecMinus() / 60 + callRecord.getSecMinus() % 60 > 0 ? 1 : 0;
cost += placePerCost(callRecord) * a;
}
return cost;
}
public double placePerCost(CallRecord callRecord) {
String ansAddress = callRecord.getAnswerAddressAreaCode();
return InCity(ansAddress) ? 0.1 : InProvince(ansAddress) ? 0.3 : 0.6;
}
}
class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule {
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
return 0;
}
}
class LandPhoneInLandRule extends CallChargeRule {
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
return 0;
}
}
class PhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule {
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
double cost = 0;
for (CallRecord callRecord : userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) {
int a = callRecord.getSecMinus() / 60 + callRecord.getSecMinus() % 60 > 0 ? 1 : 0;
cost += placePerCost(callRecord) * a;
}
return cost;
}
public double placePerCost(CallRecord callRecord) {
String ansAddress = callRecord.getAnswerAddressAreaCode();
return InCity(ansAddress) ? 0.1 : InProvince(ansAddress) ? 0.2 : 0.3;
}
}
class PhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule {
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
double cost = 0;
for (CallRecord callRecord : userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) {
int a = callRecord.getSecMinus() / 60 + callRecord.getSecMinus() % 60 > 0 ? 1 : 0;
cost += placePerCost() * a;
}
return cost;
}
public double placePerCost() {
return 0.3;
}
}
class PhoneInLandRule extends CallChargeRule {
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
double cost = 0;
for (CallRecord callRecord : userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()) {
int a = callRecord.getSecMinus() / 60 + callRecord.getSecMinus() % 60 > 0 ? 1 : 0;
cost += placePerCost(callRecord) * a;
}
return cost;
}
public double placePerCost(CallRecord callRecord) {
return 0.6;
}
}
class PhoneAnsInLandRule extends CallChargeRule {
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
double cost = 0;
for (CallRecord callRecord : userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords()) {
int a = callRecord.getSecMinus() / 60 + callRecord.getSecMinus() % 60 > 0 ? 1 : 0;
cost += placePerCost(callRecord) * a;
}
return cost;
}
public double placePerCost(CallRecord callRecord) {
return 0.3;
}
}
class InputFormat {
public static String[] input_u_Format(String str) {
Matcher m = Pattern.compile("([ut])-([0-9]{11,12}) ([0-3])").matcher(str);//(u)-(0\\d{9,11}) ([0-2])
if (m.find()) {
// if (!numTypeLegal(m.group(2), m.group(3))) return null;
return new String[]{m.group(1), m.group(2), m.group(3)};
} else return null;
}
private static boolean numTypeLegal(String num, String type) {
if (num.charAt(0) == '0') return num.charAt(0) == type.charAt(0);
else if (num.charAt(0) == '1') return num.length() == 11 && (type.charAt(0) == '1' || type.charAt(0) == '2');
else return false;
}
public static CallRecord input_t_Format(String str) {
return (input_00_Format(str) != null) ? input_00_Format(str) : (input_01_Format(str) != null) ? input_01_Format(str) : (input_10_Format(str) != null) ? input_10_Format(str) : (input_11_Format(str) != null) ? input_11_Format(str) : null;
}
private static CallRecord input_00_Format(String str) {
if (!input_t00_RightFormat(str)) return null;
String[] nums = new String[2];
int numbSplit = str.indexOf(" ", str.indexOf(" ") + 1) + 1;
String Nums = str.substring(0, numbSplit);
Matcher m = Pattern.compile("([ut])-([0-9]{10,12}) ([0-9]{10,12}) ").matcher(Nums);
if (m.find()) {
nums[0] = m.group(2);
nums[1] = m.group(3);
} else return null;
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss");
simpleDateFormat.setLenient(false);
int dateSplit = str.indexOf(" ", str.indexOf(" ", numbSplit) + 1);
String Time1 = str.substring(numbSplit, dateSplit);
String Time2 = str.substring(dateSplit + 1);
Date date1, date2;
try {
date1 = simpleDateFormat.parse(Time1);
date2 = simpleDateFormat.parse(Time2);
} catch (ParseException e) {
return null;
}
if (date1.compareTo(date2) > 0) return null;
return new CallRecord(nums[0], nums[1], date1, date2);
}
private static CallRecord input_01_Format(String str) {
if (!input_t01_RightFormat(str)) return null;
String[] nums = new String[3];
// int numbSplit = str.indexOf(" ", str.indexOf(" ") + 1) + 1;
int numbSplit = blankIdx(str, 3);
String Nums = str.substring(0, numbSplit);
Matcher m = Pattern.compile("([ut])-([0-9]{10,12}) ([0-9]{11,12}) (\\d+) ").matcher(Nums);
if (m.find()) {
nums[0] = m.group(2);
nums[1] = m.group(3);
nums[2] = m.group(4);
} else return null;
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss");
simpleDateFormat.setLenient(false);
int dateSplit = str.indexOf(" ", str.indexOf(" ", numbSplit) + 1);
String Time1 = str.substring(numbSplit, dateSplit);
String Time2 = str.substring(dateSplit + 1);
Date date1, date2;
try {
date1 = simpleDateFormat.parse(Time1);
date2 = simpleDateFormat.parse(Time2);
} catch (ParseException e) {
return null;
}
// if (isDate(Time1) || isDate(Time2))return null;
if (date1.compareTo(date2) > 0) return null;
return new CallRecord(nums[0], nums[1], nums[2], date1, date2, 1);
}
private static CallRecord input_10_Format(String str) {
if (!input_t10_RightFormat(str)) return null;
String[] nums = new String[3];
// int numbSplit = str.indexOf(" ", str.indexOf(" ") + 1) + 1;
int numbSplit = blankIdx(str, 3);
String Nums = str.substring(0, numbSplit);
Matcher m = Pattern.compile("([ut])-([0-9]{11,12}) (\\d+) ([0-9]{10,12}) ").matcher(Nums);
if (m.find()) {
nums[0] = m.group(2);
nums[1] = m.group(3);
nums[2] = m.group(4);
} else return null;
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss");
simpleDateFormat.setLenient(false);
int dateSplit = str.indexOf(" ", str.indexOf(" ", numbSplit) + 1);
String Time1 = str.substring(numbSplit, dateSplit);
String Time2 = str.substring(dateSplit + 1);
Date date1, date2;
try {
date1 = simpleDateFormat.parse(Time1);
date2 = simpleDateFormat.parse(Time2);
} catch (ParseException e) {
return null;
}
if (date1.compareTo(date2) > 0) return null;
return new CallRecord(nums[0], nums[1], nums[2], date1, date2, 2);
}
private static CallRecord input_11_Format(String str) {
if (!input_t11_RightFormat(str)) return null;
String[] nums = new String[4];
// int numbSplit = str.indexOf(" ", str.indexOf(" ") + 1) + 1;
int numbSplit = blankIdx(str, 4);
String Nums = str.substring(0, numbSplit);
Matcher m = Pattern.compile("([ut])-([0-9]{11,12}) (\\d+) ([0-9]{11,12}) (\\d+) ").matcher(Nums);
if (m.find()) {
nums[0] = m.group(2);
nums[1] = m.group(3);
nums[2] = m.group(4);
nums[3] = m.group(5);
} else return null;
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss");
simpleDateFormat.setLenient(false);
int dateSplit = str.indexOf(" ", str.indexOf(" ", numbSplit) + 1);
String Time1 = str.substring(numbSplit, dateSplit);
String Time2 = str.substring(dateSplit + 1);
Date date1, date2;
try {
date1 = simpleDateFormat.parse(Time1);
date2 = simpleDateFormat.parse(Time2);
} catch (ParseException e) {
return null;
}
if (date1.compareTo(date2) > 0) return null;
return new CallRecord(nums[0], nums[1], nums[2], nums[3], date1, date2);
}
private static int blankIdx(String str, int cnt) {
for (int i = 0, t = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if (t == cnt) return i;
if (str.charAt(i) == ' ') t++;
}
return str.length();
}
public static String[] input_m_Format(String str) {
Matcher m = Pattern.compile("(m)-(1[0-9]{10}) (1[0-9]{10}) ([a-z 0-9,.]+)").matcher(str);
if (m.matches()) {
return new String[]{m.group(2), m.group(3), m.group(4)};
} else return null;
}
private static boolean input_t00_RightFormat(String str) {
return str.matches("t-0\\d{9,11} 0\\d{9,11}( [0-9]{4}\\.(([1-9])|(1[0-2]))\\.(([1-9])|(([1|2])[0-9])|30|31) ((([0|1])[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])){2}");
}
private static boolean input_t01_RightFormat(String str) {
return str.matches("t-0\\d{9,11} 1\\d{10} 0\\d{2,3}( [0-9]{4}\\.(([1-9])|(1[0-2]))\\.(([1-9])|(([1|2])[0-9])|30|31) ((([0|1])[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])){2}");
}
private static boolean input_t10_RightFormat(String str) {
return str.matches("t-1\\d{10} 0\\d{2,3} 0\\d{9,11}( [0-9]{4}\\.(([1-9])|(1[0-2]))\\.(([1-9])|(([1|2])[0-9])|30|31) ((([0|1])[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])){2}");
}
private static boolean input_t11_RightFormat(String str) {
return str.matches("t-1\\d{10} 0\\d{2,3} 1\\d{10} 0\\d{2,3}( [0-9]{4}\\.(([1-9])|(1[0-2]))\\.(([1-9])|(([1|2])[0-9])|30|31) ((([0|1])[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])){2}");
}
}
/*******************************************************************
* User调用通话记录和计费模式,
* 通话记录只将记录分类,整理,
* 计费模式是计费规则类的集合,计费规则只需将所有计费规则进行整理,统一计费
* 职责:将用户按终端、记录整合
* */
class User implements Comparable<User> {
private UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords();
private ArrayList<CommunicationRecord> callRecords = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<CommunicationRecord> ansRecords = new ArrayList<>();
private double balance = 100;
private ChargeMode chargeMode;
private String number;
public User(String number, int mod) {
this.number = number;
switch (mod) {
case 0: {
chargeMode = new LandlinePhoneCharging();
break;
}
case 1: {
chargeMode = new PhoneCharging();
}
case 2: {
}
case 3: {
chargeMode = new PhoneMessage();
}
default:
}
}
// 话费
public double calCost() {
return chargeMode.calCost(userRecords);
}
// 余额
public double calBalance() {
return balance - chargeMode.getMonthlyRent();
}
/*将用户的所有记录分类,存于userRecords
* */
public void classifyRecords() {
//拨的
for (CommunicationRecord communicationRecord : callRecords) {
if (communicationRecord instanceof CallRecord) {
if (((CallRecord) communicationRecord).callInCity())
userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords().add((CallRecord) communicationRecord);
else if (((CallRecord) communicationRecord).callInProvince())
userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords().add((CallRecord) communicationRecord);
else if (((CallRecord) communicationRecord).callInLand())
userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords().add((CallRecord) communicationRecord);
} else if (communicationRecord instanceof MessageRecord) {
if (((MessageRecord) communicationRecord).isSendUser(this))
userRecords.getSendMessageRecords().add((MessageRecord) communicationRecord);
}
}
//接的
for (CommunicationRecord communicationRecord : ansRecords) {
if (communicationRecord instanceof CallRecord) {
if (((CallRecord) communicationRecord).ansInCity())
userRecords.getAnswerInCityRecords().add((CallRecord) communicationRecord);
else if (((CallRecord) communicationRecord).ansInProvince())
userRecords.getAnswerInProvinceRecords().add((CallRecord) communicationRecord);
else if (((CallRecord) communicationRecord).ansInLand())
userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords().add((CallRecord) communicationRecord);
} else if (communicationRecord instanceof MessageRecord) {
if (((MessageRecord) communicationRecord).isAnsUser(this))
userRecords.getSendMessageRecords().add((MessageRecord) communicationRecord);
}
}
}
public UserRecords getUserRecords() {
return userRecords;
}
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public ArrayList<CommunicationRecord> getCallRecords() {
return callRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CommunicationRecord> getAnsRecords() {
return ansRecords;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(User o) {
return number.compareTo(o.getNumber());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return 1;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return obj instanceof User && number.equals(((User) obj).number);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
double cost = calCost();
double balance = calBalance() - cost;
return getNumber() + " " + OutFormat.doubleFormat(cost) + " " + OutFormat.doubleFormat(balance);
}
}
class CallRecord extends CommunicationRecord {
private Date startTime, endTime;
private String callingAddressAreaCode, answerAddressAreaCode;
//座机互打
public CallRecord(String callingNumber, String answerNumber, Date startTime, Date endTime) {
super(callingNumber, answerNumber);
this.startTime = startTime;
this.endTime = endTime;
callingAddressAreaCode = callingNumber.substring(0, 4);
answerAddressAreaCode = answerNumber.substring(0, 4);
}
/* //座机打手机 1
public CallRecord(String callingNumber, String answerNumber, String answerAddressAreaCode, Date startTime, Date endTime) {
super(callingNumber, answerNumber);
this.startTime = startTime;
this.endTime = endTime;
callingAddressAreaCode = callingNumber.substring(0, 4);
this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode;
}
//手机打座机 2
public CallRecord(String callingNumber, String callingAddressAreaCode, String answerNumber, Date startTime, Date endTime) {
super(callingNumber, answerNumber);
this.startTime = startTime;
this.endTime = endTime;
this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode;
}*/
public CallRecord(String callingNumber, String callingAreaCode_Or_AnsNumber, String ansNumber_Or_AnsAreaCode, Date startTime, Date endTime, int mod) {
if (mod == 1) {
this.callingNumber = callingNumber;
this.answerNumber = callingAreaCode_Or_AnsNumber;
this.startTime = startTime;
this.endTime = endTime;
callingAddressAreaCode = callingNumber.substring(0, 4);
answerAddressAreaCode = ansNumber_Or_AnsAreaCode;
} else {
this.callingNumber = callingNumber;
this.answerNumber = ansNumber_Or_AnsAreaCode;
this.startTime = startTime;
this.endTime = endTime;
callingAddressAreaCode = callingAreaCode_Or_AnsNumber;
answerAddressAreaCode = ansNumber_Or_AnsAreaCode.substring(0, 4);
}
}
//手机互打
public CallRecord(String callingNumber, String callingAddressAreaCode, String answerNumber, String answerAddressAreaCode, Date startTime, Date endTime) {
super(callingNumber, answerNumber);
this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode;
this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode;
this.startTime = startTime;
this.endTime = endTime;
}
/*南昌市内拨打*/
public boolean callInCity() {
return "0791".equals(callingAddressAreaCode);
}
/*非市内的省内拨打*/
public boolean callInProvince() {
if (callInCity() || callingAddressAreaCode.length() < 3) return false;
if ("0701".equals(callingAddressAreaCode)) return true;
return "079".equals(callingAddressAreaCode.substring(0, 3)) && (callingAddressAreaCode.charAt(3) >= '0' && callingAddressAreaCode.charAt(3) <= '9');
}
/*非省内拨打*/
public boolean callInLand() {
return !callInProvince();
}
/*南昌市内接听*/
public boolean ansInCity() {
return "0791".equals(answerAddressAreaCode);
}
/*非市内的省内接听*/
public boolean ansInProvince() {
if (ansInCity() || answerAddressAreaCode.length() < 3) return false;
if ("0701".equals(answerAddressAreaCode)) return true;
return "079".equals(answerAddressAreaCode.substring(0, 3)) && (answerAddressAreaCode.charAt(3) >= '0' && answerAddressAreaCode.charAt(3) <= '9');
}
/*非省内接听*/
public boolean ansInLand() {
return !ansInProvince();
}
public String getCallingAddressAreaCode() {
return callingAddressAreaCode;
}
public String getAnswerAddressAreaCode() {
return answerAddressAreaCode;
}
public int getSecMinus() {
return (int) ((endTime.getTime() - startTime.getTime()) / 1000);
}
}
/*
* CallChargeRule 电话计费
* 针对电话的不同的使用终端有不同的计费规则*/
abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule {
public abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords);
public boolean InCity(String callingAddressAreaCode) {
return "0791".equals(callingAddressAreaCode);
}
public boolean InProvince(String callingAddressAreaCode) {
if (InCity(callingAddressAreaCode) || callingAddressAreaCode.length() < 3) return false;
if ("0701".equals(callingAddressAreaCode)) return true;
return "079".equals(callingAddressAreaCode.substring(0, 3)) && (callingAddressAreaCode.charAt(3) >= '0' && callingAddressAreaCode.charAt(3) <= '9');
}
public boolean InLand(String callingAddressAreaCode) {
if (InCity(callingAddressAreaCode)) return false;
return !InProvince(callingAddressAreaCode);
}
}
abstract class MessageChargeRule extends ChargeRule {
public abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords);
}
class SendMessageRule extends MessageChargeRule {
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
int num = 0;
for (MessageRecord m : userRecords.getSendMessageRecords()) num += getMessageNum(m);
if (num > 5) return 0.7 + (num - 5) * 0.3;
else if (num > 3) return 0.3 + (num - 3) * 0.2;
else return num * 0.1;
}
private int getMessageNum(MessageRecord messageRecord) {
int len = messageRecord.getMessage().length();
int res = len / 10 ;
res += len % 10 != 0 ? 1 : 0;
return res;
}
}
class OutFormat {
public static Double doubleFormat(double b) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.00");
return Double.valueOf(df.format(b));
}
}
代码类图
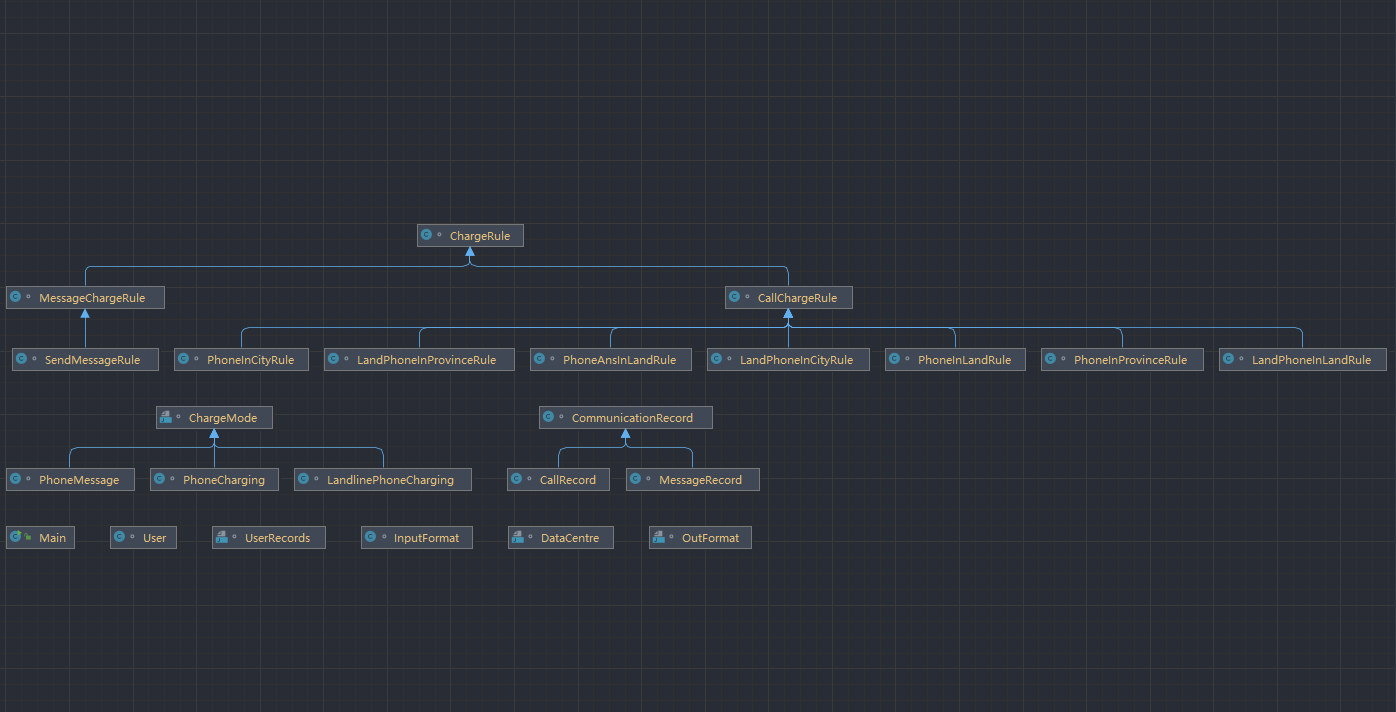
分析
个人的思路是将用户和记录读入后,分别存于容器,再将数据传到一个
DataCenter的类,此类的职责是将所有通讯记录匹配到用户
之后在用户得到所有自己的通讯记录后,将其分类存于不同的容器,从而让不同的Rule处理自己应处理的数据,分别计算费用并汇总;其实还有比较简单的思路,那就是将用户和记录分别存于容器,遍历每个用户,让每个用户遍历所有通讯记录,找到自己的通讯记录并将其按类型计费汇总,很明显,这样写出的代码性能会很差,所以没有采用这样的思路;
踩坑心得
关于
HashSet的使用疑惑代码:
import java.util.HashSet; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<User> users = new HashSet<>(); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); for(User u : users) System.out.println(u); } } class User{ String number; //*********************************************************************************// public User(String number) { this.number = number; } }输出:
User@5594a1b5 User@3b6eb2ec User@3ac3fd8b User@6a5fc7f7 User@1e643faf 进程已结束,退出代码0很明显,他们虽然放到了
HashSet中,但是HashSet并不认为他们是同一对象给
User重写了hashCode()import java.util.HashSet; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<User> users = new HashSet<>(); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); for(User u : users) System.out.println(u); } } class User{ String number; public User(String number) { this.number = number; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Integer.parseInt(number); } }输出
User@756b5b3 User@756b5b3 User@756b5b3 User@756b5b3 User@756b5b3 进程已结束,退出代码0虽然他们的地址是一样的,但是HashSet仍不觉的这是同一对象
给
User重写了equals()import java.util.HashSet; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<User> users = new HashSet<>(); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); users.add(new User("123123123")); for(User u : users) System.out.println(u); } } class User{ String number; public User(String number) { this.number = number; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Integer.parseInt(number); } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { return number.equals(((User)obj).number); } }输出
User@756b5b3 进程已结束,退出代码0成功对
User去重
改进建议
重载构造函数类型冲突
//座机打手机 1 public CallRecord(String callingNumber, String answerNumber, String answerAddressAreaCode, Date startTime, Date endTime) { super(callingNumber, answerNumber); this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; callingAddressAreaCode = callingNumber.substring(0, 4); this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } //手机打座机 2 public CallRecord(String callingNumber, String callingAddressAreaCode, String answerNumber, Date startTime, Date endTime) { super(callingNumber, answerNumber); this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; }解决方案1:
public CallRecord(String callingNumber, String callingAreaCode_Or_AnsNumber, String ansNumber_Or_AnsAreaCode, Date startTime, Date endTime, int mod) { if (mod == 1) { this.callingNumber = callingNumber; this.answerNumber = callingAreaCode_Or_AnsNumber; this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; callingAddressAreaCode = callingNumber.substring(0, 4); answerAddressAreaCode = ansNumber_Or_AnsAreaCode; } else { this.callingNumber = callingNumber; this.answerNumber = ansNumber_Or_AnsAreaCode; this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; callingAddressAreaCode = callingAreaCode_Or_AnsNumber; answerAddressAreaCode = ansNumber_Or_AnsAreaCode.substring(0, 4); } }利用一个mod来判断使用哪个重载
解决方案2:
class CallRecord{ //*********************************************************************************// public CallRecord(Number callingNumber, Number answerNumber, Date startTime, Date endTime) { super(callingNumber, answerNumber); this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; } //*********************************************************************************// } class Number{ String number,addressNumber; public Number(String number, String addressNumber) { this.number = number; this.addressNumber = addressNumber; } }用一个Number类来根治类型冲突的问题,思路也更清晰
总结
通过这几周的作业,克服了对正则表达式的恐惧,对程序的设计有了更开阔的思维,学会了用java.text.SimpleDateFormat格式化日期、用java.util.Date存储日期、还学会了用HashSet<>容器存储对象、以及用Collections.sort()对容器中实现Compareable<>接口的类的对象进行排序.....


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号