七大排序——C实现

#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #include<time.h> #define MAX_NUM_SIZE 20000000 #define MAX_RANDOM_NUM 100 #define SWAP(a,b){int temp; temp = a; a = b; b = temp;}

//冒泡排序 void bubbleSort(int a[]) { for (int x = 0; x < MAX_NUM_SIZE; x++) { for (int y = MAX_NUM_SIZE - 1; y >= x; y--) { if (a[x] > a[y]) { a[x] = a[x] + a[y]; a[y] = a[x] - a[y]; a[x] = a[x] - a[y]; } } } }

//选择排序 void selectSort(int a[]) { for (int i = 0; i < MAX_NUM_SIZE - 1; i++) { int min = i; //min记录的是最小值的下标 for (int j = i + 1; j < MAX_NUM_SIZE; j++) { if (a[min] > a[j]) { min = j; } } if (min != i) { SWAP(a[min],a[i]); } } }

//插入排序 void insertSort(int a[]) { for (int i = 0; i < MAX_NUM_SIZE; i++) { int indexInsertedLast; int insertValue = a[i]; for (indexInsertedLast = i - 1; indexInsertedLast >= 0 && a[indexInsertedLast] > insertValue;indexInsertedLast--) { a[indexInsertedLast + 1] = a[indexInsertedLast]; } a[indexInsertedLast + 1] = insertValue; } }

//希尔排序 void shellSort(int a[], int length) { for (int gap = length / 2; gap > 0; gap /= 2) { for (int i = gap; i < MAX_NUM_SIZE; i++) { int insertValue = a[i]; int indexInsertedLast; for (indexInsertedLast = i - gap; indexInsertedLast >= 0 && a[indexInsertedLast] > insertValue; indexInsertedLast -= gap) { a[indexInsertedLast + gap] = a[indexInsertedLast]; } a[indexInsertedLast + gap] = insertValue; } } }

//快速排序 int partition(int *a, int left, int right) { int start, end; //start是大于pivot的区间的开始位置的下标,end是该区间结束位置的下标 for (start = left, end = left; end < right; end++) {//扩大小于pivot的数的区间 if (a[end] < a[right]) { SWAP(a[start], a[end]); start++; } } SWAP(a[start], a[right]); //将pivot移到两个区间的交界处,分隔完成 return start; //返回pivot } void quickSort(int *a, int left, int right) { if (left < right) { //即元素个数至少为2 int pivot = partition(a,left,right); quickSort(a, left, pivot - 1); quickSort(a, pivot + 1, right); } }

//计数排序(多用于去除重复数字) void countSort(int *a) { int count[MAX_RANDOM_NUM] = { 0 }; //统计a中的元素出现次数到count中 for (int i = 0; i < MAX_NUM_SIZE; i++) { count[ a[i] ] ++; } for (int index_count = 0, index_a = 0; index_count < MAX_RANDOM_NUM; index_count++) { for (int i = 0; i < count[index_count]; i++) { //i是循环重复a中元素的次数 a[index_a++] = index_count; //重复输出到a[]中 } } }

//堆排序(出现频率高) void adjustMaxHeap(int *a, int originalFather, int lengthHeap) { int dad = originalFather; //当前的父节点 int son = 2 * (originalFather + 1) - 1; //当前的子节点 while (son < lengthHeap) { //son < lengthHeap即子节点存在,子节点的下标范围在堆的大小以内 //循环的效果是不断地执行循环,将左右子树比较,再将较大的子树与父比较,选出父与子树中最大的节点作最终的父节点 //随着son++,会不断地向数的下方调整堆 if (son + 1 < lengthHeap&&a[son] < a[son + 1]) { //son+1为右子树的下标,这里是比较左右子树的大小,较大的将来要与父节点比较 ++son; } if (a[son] > a[dad]) { //子树节点比父节点大,则交换子与父 SWAP(a[son], a[dad]); dad = son; son = 2 * dad + 1; } else { break; //子树节点比父节点小,则父节点位置稳定,结束这次调整堆 } } } void heapSort(int *a) { //从最后一个父节点(MAX_NUM_SIZE / 2 - 1)开始,回头遍历父节点,初步调整堆 for (int i = MAX_NUM_SIZE / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //i为每个父节点的下标 adjustMaxHeap(a, i, MAX_NUM_SIZE); } SWAP(a[0], a[MAX_NUM_SIZE - 1]); //初步调整完成后,不断将堆顶最大元素与堆的最后一个元素交换,再在下一次循环建堆时排除最后一个元素,以此缩小堆的规模 for (int i = MAX_NUM_SIZE - 1; i > 1; i--) { //i为堆的规模大小 adjustMaxHeap(a, 0, i); SWAP(a[0], a[i - 1]); } } int compare(const void *pleft, const void *pright) { int *pa = (int *)pleft; int *pb = (int *)pright; return *pa - *pb; }

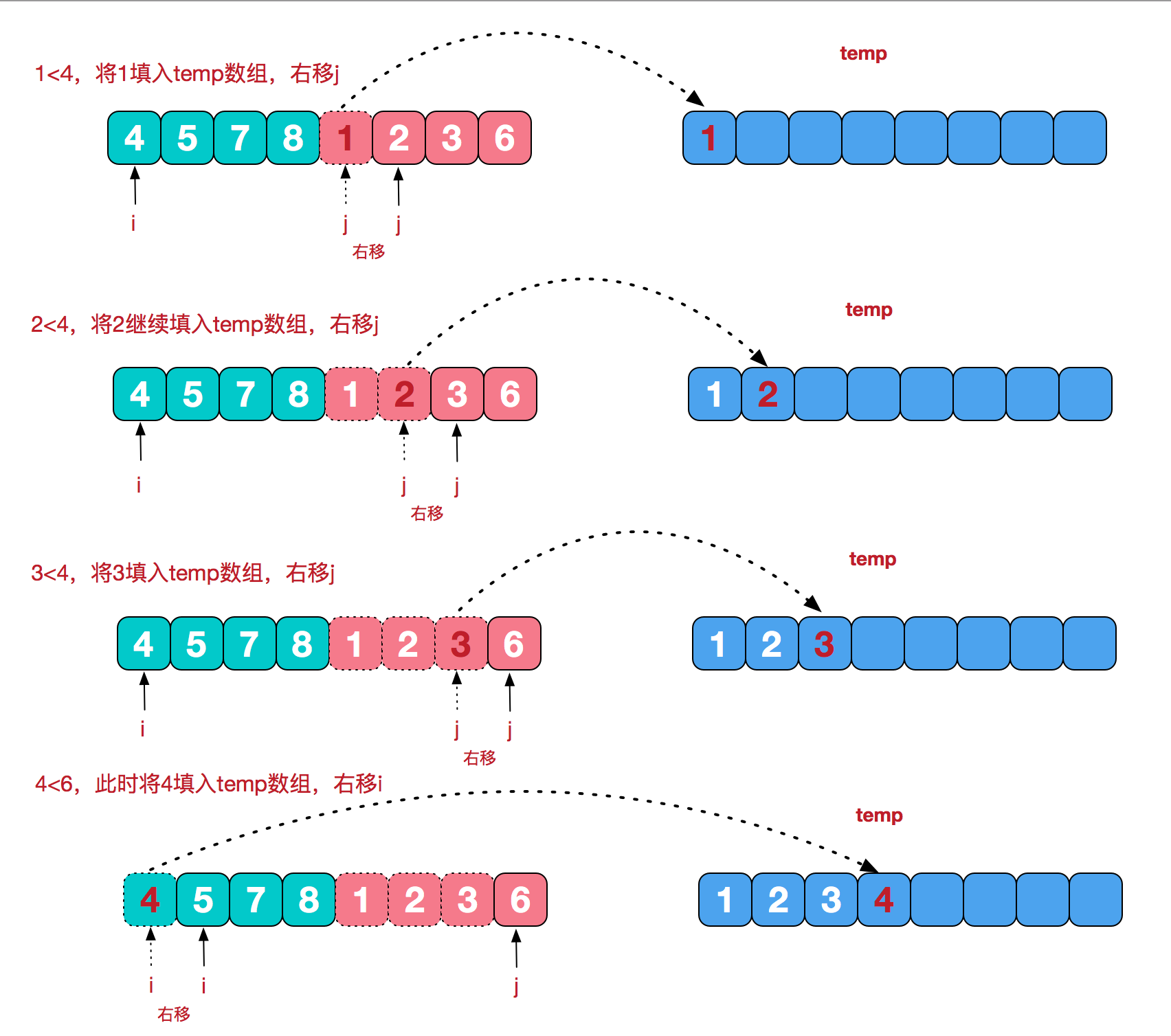
//归并排序 void merge(int *a, int left, int mid, int right) { int *b = (int *)malloc(MAX_NUM_SIZE * sizeof(int)); memcpy(b, a, MAX_NUM_SIZE * sizeof(int)); //leftPartP是左半边数组的当前下标,rightPartP是右半边的下标,destP是合并后的目标数组的当前下标 int leftPartP = left, rightPartP = mid + 1, destinationP = left; while (leftPartP <= mid && rightPartP <= right) { if (b[leftPartP] < b[rightPartP]) { a[destinationP] = b[leftPartP]; leftPartP++; destinationP++; } else { a[destinationP] = b[rightPartP]; rightPartP++; destinationP++; } } while (leftPartP <= mid) { a[destinationP] = b[leftPartP]; leftPartP++; destinationP++; } while (rightPartP <= right) { a[destinationP] = b[rightPartP]; rightPartP++; destinationP++; } free(b); b = NULL; } void mergeSort(int *a, int left, int right) { if (left < right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2; //mid是中间的下标 mergeSort(a, left, mid); //左半边归并排序 mergeSort(a, mid + 1, right); //右半边归并排序 merge(a, left, mid, right); //合并左右两边 } }

//快排的非递归的compare函数,原型类似于qsort(a, MAX_NUM_SIZE, sizeof(int), compare); int compare(const void *pleft, const void *pright) { int *pa = (int *)pleft; int *pb = (int *)pright; return *pa - *pb; //降序输出,如果要逆序输出就*pb - *pa }
归并排序的图解,from——https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6194356.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号