
TestInherits.java
package Test;
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("Grandparent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("Grandparent Created.String:"+string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Child c=new Child();
}
}
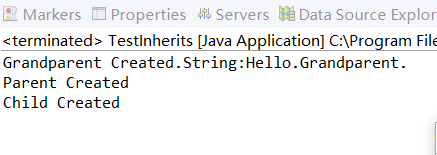
但是如果将其中一段改成
public Parent()
{
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
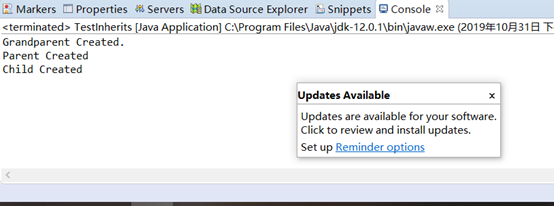
将super("Hello.Grandparent.");注释后,调用的是GrandParent类的第一个构造函数了。这说明运行子类前必须先运行父类的构造函数,且super方法只能放在子类构造函数的第一句。


因为子类继承了父类的属性与方法,要想初始化子类的对象,首先便需要父类的属性和方法,所以需要先调用父类的属性和方法,然后再在构造自己在父类基础上增加的属性和方法。
2.

真相是神马?
ExplorationJDKSource.Java
public class ExplorationJDKSource {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
class A{}
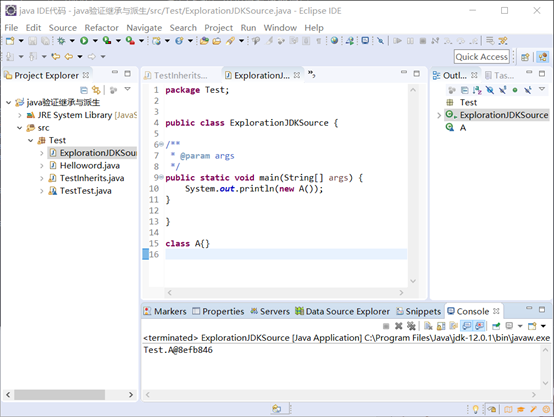
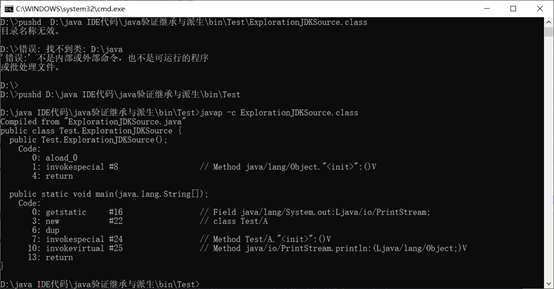
会发现输出的是object类,然而object类转换成字符串时会变成 类名@地址 的格式。
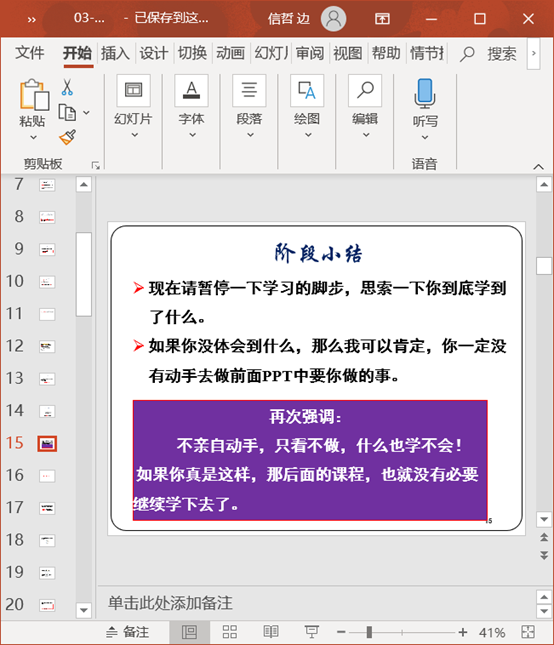
3.
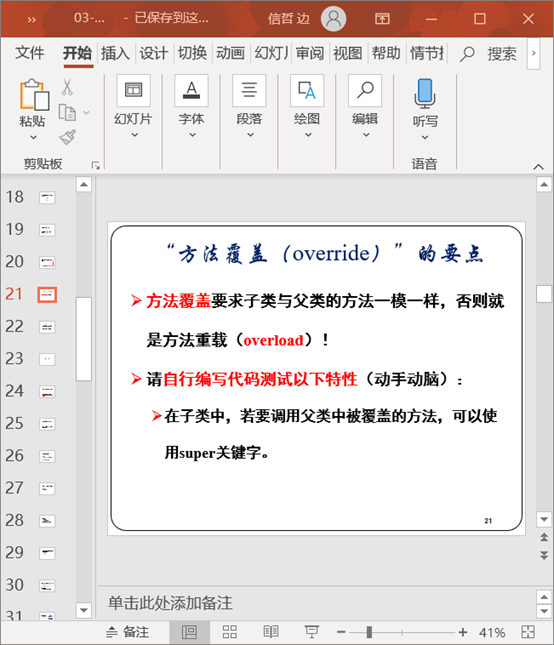
在子类中,要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字。
package Test;
public class TestOverWrite {
public static void main(String args[])
{
B b=new B();
b.bFunction();
b.bFunction2();
}
}
class A
{
public void aFunction()
{
System.out.println("A!");
}
}
class B extends A
{
public void bFunction()
{
System.out.println("B!");
}
public void bFunction2()
{
super.aFunction();
}
}
运行结果如下:
B!
A!
4.
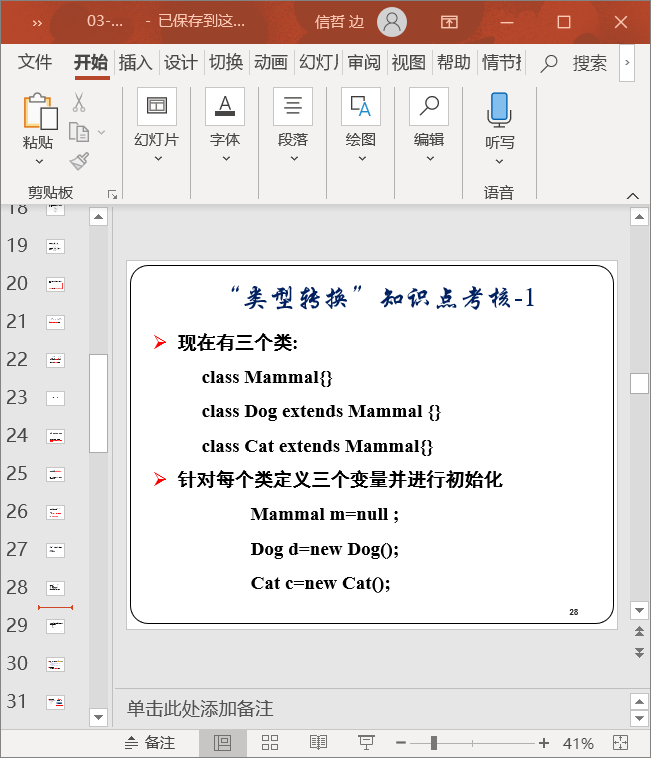
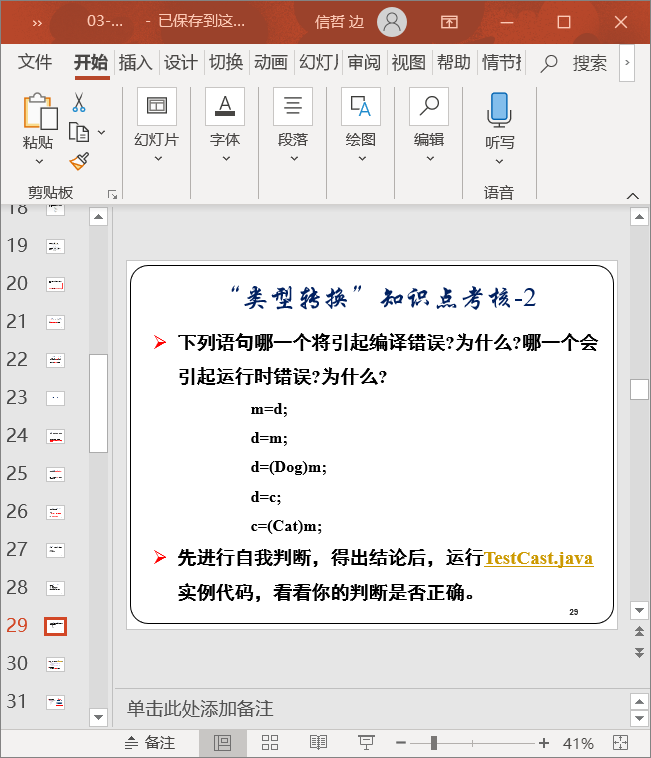




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号