Java模拟生产者消费者程序
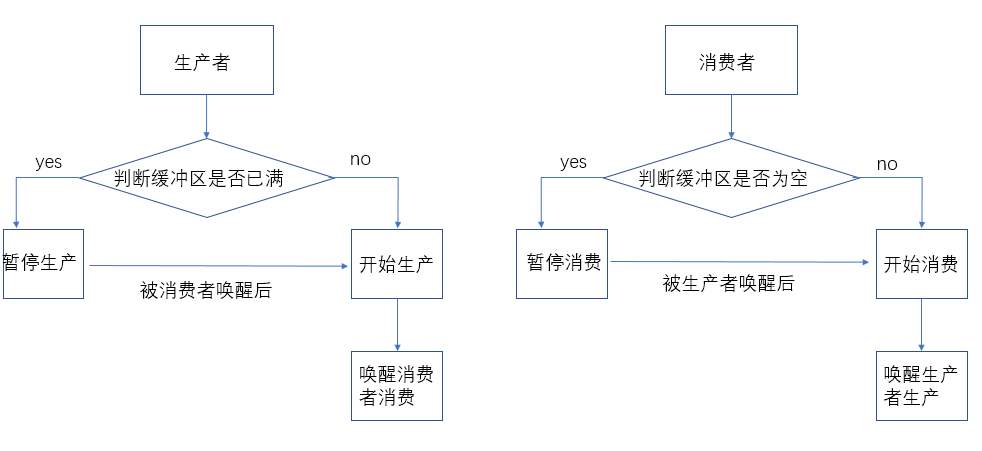
生产者消费者问题是操作系统课程中一个经典的同步问题。它描绘了这样一种场景:有一个最大容量为n的商店,有一个或多个生产者不断生产产品并放入商店中,同时有一个或多个消费者从商店中取出产品。当商店容量已满时,要生产产品的生产者暂停放入产品,等待消费者消费后继续生产;当商店产品耗尽时,消费者暂停取出商品,等待生产者放入产品后继续消费。
1.产品类Product
public class Product{ int num; // 产品编号 public Product(int num) { this.num = num; } public int getNum() { return num; } public void setNum(int num) { this.num = num; } }
2.商店类Store
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Store { int max; //商店最大容量 ArrayList<Product> list; //商店存储的货物 //构造方法 public Store(int max) { this.max = max; list = new ArrayList<Product>(); } //商店添加货物 public synchronized void add(Product product) { //如果容量已经满,则等待 if(list.size() == max) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } list.add(product); notify(); } //商店取出货物 public synchronized Product pop() { //如果没有产品了,则等待 if(list.size() == 0) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } Product p = list.remove(0); notify(); return p; } }
3.生产者类Producer
//生产者类继承Thread类,每一个生产者都可视为一个线程 public class Producer extends Thread { String name; //生产者名称 Store store; //生产的产品所放入的商店 public Producer( String name,Store store) { this.name = name; this.store = store; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { //每次生产一个产品,编号随机为0~100 Product product = new Product((int) (Math.random()*100)); store.add(product); System.out.println(name + "生产了" + product.num); } } }
4.消费者Consumer类
//继承Thread类,每一个Consumer对象都可视为一个线程 public class Consumer extends Thread { String name; //消费者名 Store store; //取走商品的商店 public Consumer(String s,Store t) { name = s; store = t; } @Override public void run() { while (true){ Product product = store.pop(); System.out.println(name + "取走了" +product.num); } } }
5.main函数
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Store store = new Store(100); Producer producer = new Producer("A",store); Consumer consumer = new Consumer("B",store); producer.start(); consumer.start(); } }
运行结果(前10行)
A生产了75
B取走了75
A生产了57
B取走了57
B取走了84
A生产了84
A生产了50
A生产了65
B取走了50
B取走了65
问题:在A还未生产84号产品时,就被B取走了。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号