设计模式 桥模式
简单概念
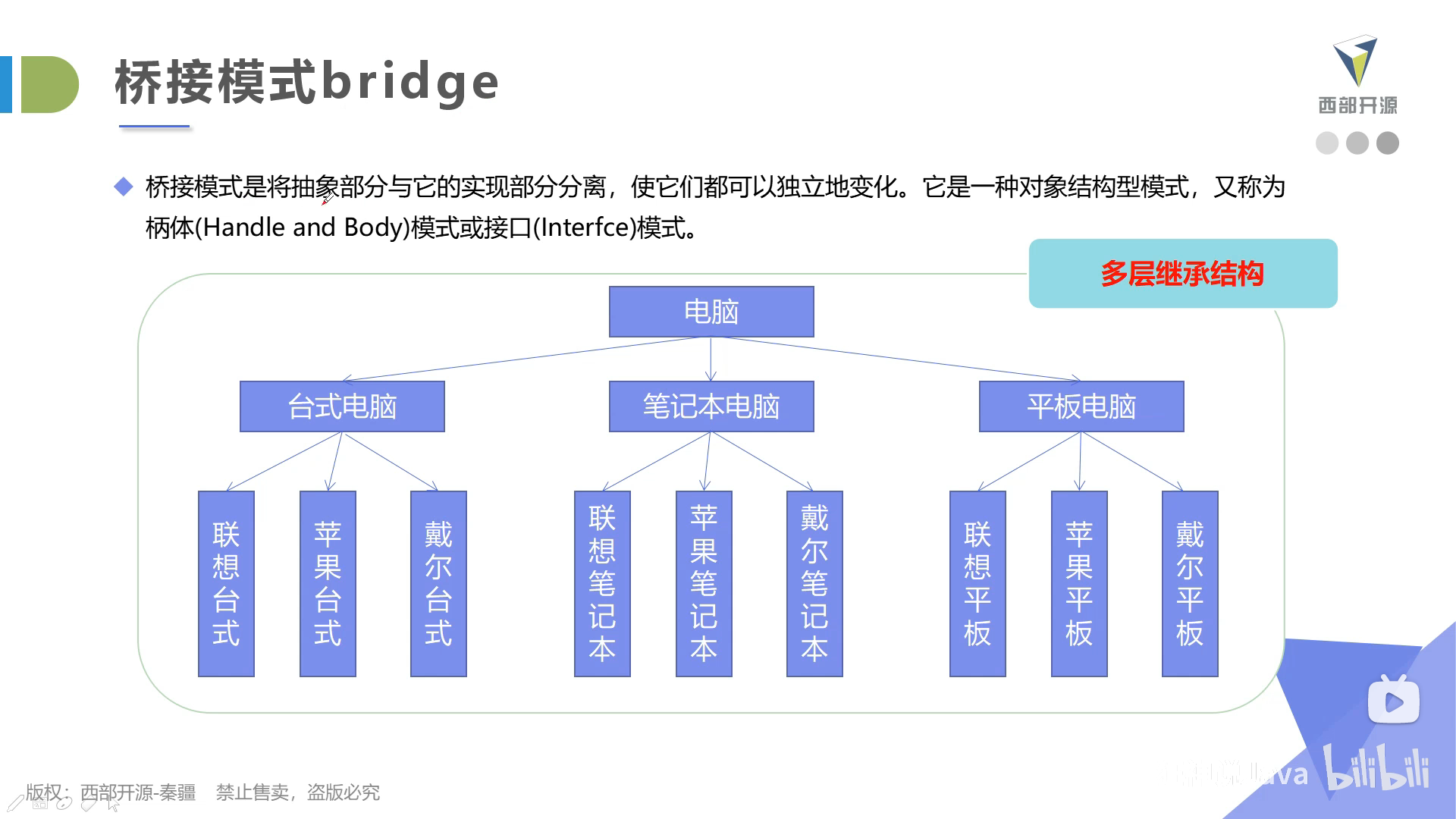
下图的结构违反了单一职责原则 一个产品有两个变化的维度(产品类型和产品品牌)
对于有多个变化维度的情景我们可以使用桥模式
简单例子
桥模式的核心思想就是将变化的维度分开来 然后在你想要具体的某一个类时 组装起来
我们吧上面的例子分为品牌和类型两个维度
首先定义一个品牌接口
package demo1;
//品牌
public interface Brand {
void info();
}
实现苹果品牌和联想品牌
public class Apple implements Brand{
public void info() {
System.out.println("苹果");
}
}
//联想品牌
public class Lenvo implements Brand {
public void info() {
System.out.println("联想");
}
}
创建类别抽象类
同时我们通过组合 在创建类时需要一个品牌赋值这样就可以做到拼装
//抽象的电脑类型
public abstract class Computer {
//组合 品牌
protected Brand brand;
public Computer(Brand brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public void info(){
brand.info();
}
}
实现台式机和笔记本的品牌具体实现类
class Desktop extends Computer{
public Desktop(Brand brand) {
super(brand);
}
@Override
public void info() {
super.info();
System.out.println("台式机");
}
}
class Laptop extends Computer{
public Laptop(Brand brand) {
super(brand);
}
@Override
public void info() {
super.info();
System.out.println("笔记本");
}
}
测试使用
假设我想要苹果台式机 那么我就给出两个维度对应的类然后拼接上即可
package demo1;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer computer=new Desktop(new Apple());
computer.info();
}
}
总结




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号