java 线程池(重点)
基本概念 使用线程池的好处

阿里巴巴开发手册建议
但是出于学习目的我们还是会先使用Executors
Executors的三大创建方法
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//创建单个线程
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//创建一个固定线程池大小
Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//可伸缩 遇强则强
单个线程使用例子
package com.jie.pool;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadpool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//创建单个线程
// Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//创建一个固定线程池大小
// Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//可伸缩 遇强则强
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//使用了线程池后 通过线程池创建线程
threadpool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" run");
});
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//线程池使用完后 要关闭
finally {
threadpool.shutdown();
}
}
}
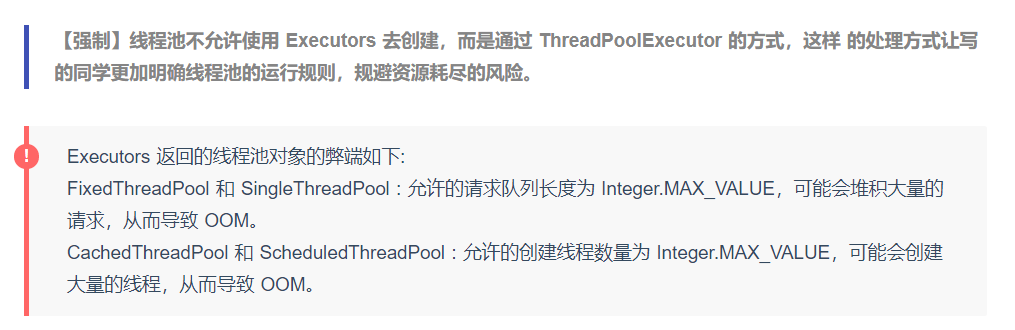
程序结果可以看到运行的是同一个线程
我们使用长度为5的线程池运行看看
package com.jie.pool;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ExecutorService threadpool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//创建单个线程
ExecutorService threadpool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//创建一个固定线程池大小
// Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//可伸缩 遇强则强
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//使用了线程池后 通过线程池创建线程
threadpool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" run");
});
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//线程池使用完后 要关闭
finally {
threadpool.shutdown();
}
}
}
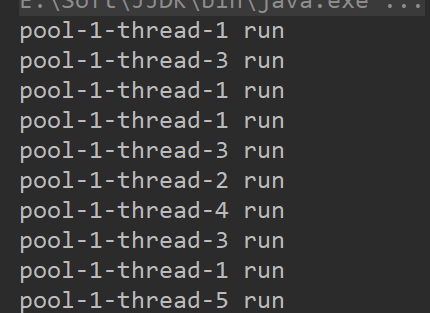
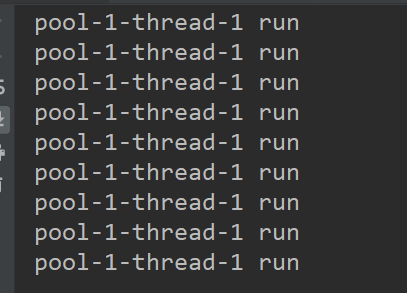
可以看到有5个线程就执行
而第3种 就是遇强则强 最多可能出现10线程就执行
7大参数
查看3大创建方法的源码 可以看到它们本质都是ThreadPoolExecutor
源代码如下
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}

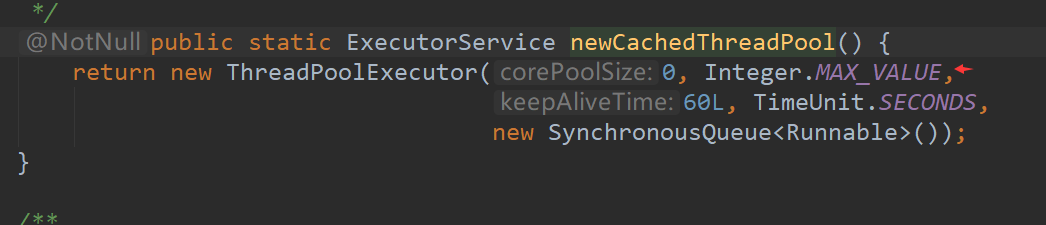
我们可以得知newCachedThreadPool在设置最大值时使用的Integer.MAX_VALUE 这也是为什么阿里巴巴不推荐使用的原因
可能会出现OOM形象(内存溢出)
4中拒绝策略
查看参数拒绝策略的源码 找到4种拒绝策略
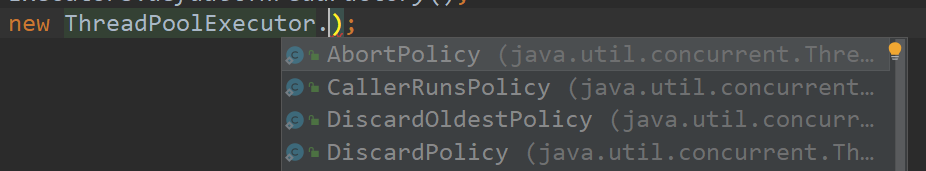
AbortPolicy

DiscardPolicy

DiscardOldestPolicy

CallerRunsPolicy

手动创建一个线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,//核心线程 永远都是在备战状态
5,//最大线程数 可以得知有3个线程是根据情况打开
3,//如果3秒内非核心线程没有被使用就关闭
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3),//阻塞队列长度 因此如果小等于5人 就会是核心线程2人处理加3人排队 超过就打开非核心线程
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),//记住是这个就好
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());//拒绝策略 如果人爆了 就默认拒绝新来的
我们运行5人 5人以下时只会最多允许两个线程
try{
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" run");
});
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
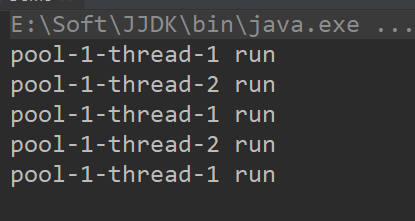
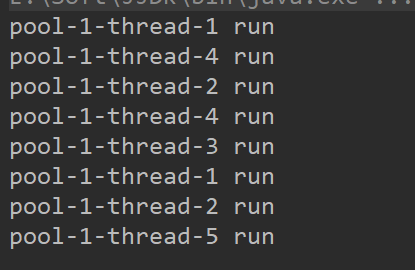
当我们超过5人 同时没有超出上限时就会开启非核心线程
try{
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++) {
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" run");
});
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
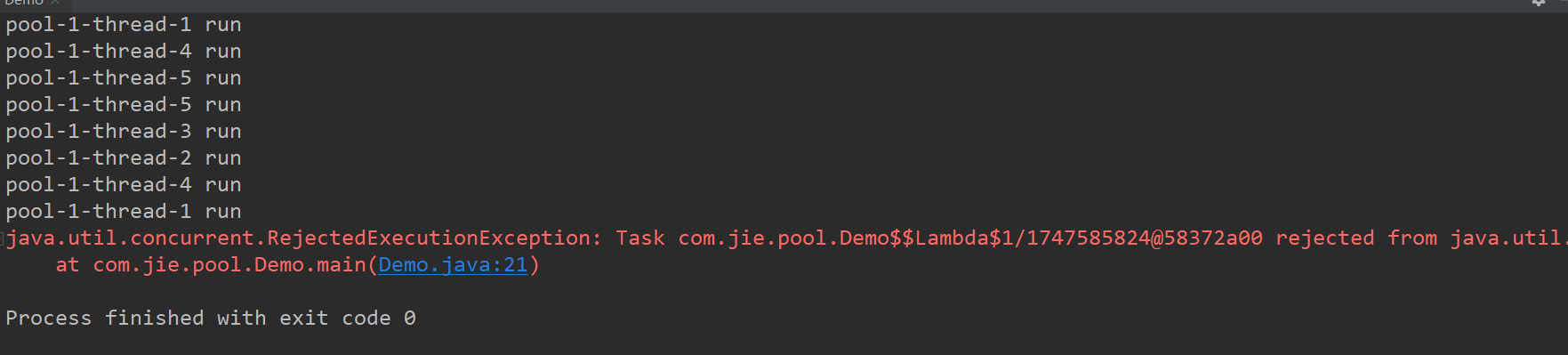
超出长度上限就会触发拒绝策略 使用的拒绝策略会不处理新进来的 并报异常
try{
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" run");
});
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
小扩展 通过代码获得CPU核心做为线程池最大值
通常我们吧线程池最大值设置为CPU核心数 达到最高性能
通过这句代码获取当前允许环境的最大核心数
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
I/O密集 时如何调优



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号