Thymeleaf模板引擎
概念
前端交给我们的页面,是html页面。如果是我们以前开发,我们需要把他们转成jsp页面,jsp好处就是当我们查出一些数据转发到JSP页面以后,我们可以用jsp轻松实现数据的显示,及交互等。
jsp支持非常强大的功能,包括能写Java代码,但是呢,我们现在的这种情况,SpringBoot这个项目首先是以jar的方式,不是war,像第二,我们用的还是嵌入式的Tomcat,所以呢,他现在默认是不支持jsp的。
SpringBoot推荐你可以来使用模板引擎
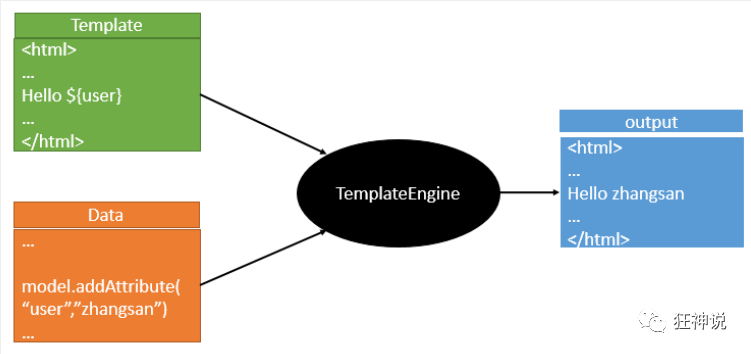
模板引擎的作用就是我们来写一个页面模板,比如有些值呢,是动态的,我们写一些表达式。而这些值,从哪来呢,就是我们在后台封装一些数据。然后把这个模板和这个数据交给我们模板引擎,模板引擎按照我们这个数据帮你把这表达式解析、填充到我们指定的位置,然后把这个数据最终生成一个我们想要的内容给我们写出去,这就是我们这个模板引擎,不管是jsp还是其他模板引擎,都是这个思想。只不过呢,就是说不同模板引擎之间,他们可能这个语法有点不一样。其他的我就不介绍了,我主要来介绍一下SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf模板引擎,这模板引擎呢,是一个高级语言的模板引擎,他的这个语法更简单。而且呢,功能更强大。
简单使用
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
找一下Thymeleaf的自动配置类:ThymeleafProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.thymeleaf"
)
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true;
private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/";
private String suffix = ".html";
private String mode = "HTML";
private Charset encoding;
}
我们可以在其中看到默认的前缀和后缀!
我们只需要把我们的html页面放在类路径下的templates下,thymeleaf就可以帮我们自动渲染了。
使用thymeleaf什么都不需要配置,只需要将他放在指定的文件夹下即可!
编写控制类
package com.jie.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return "index";
}
}
在templates文件夹下放index.html,模板引擎会自动找到
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
hello
</body>
</html>

语法
我们要使用thymeleaf,需要在html文件中导入命名空间的约束,方便提示。
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
控制类
package com.jie.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","hello springboot");
return "index";
}
}
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
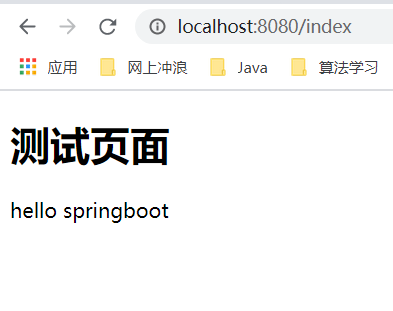
<h1>测试页面</h1>
<!--th:text就是将div中的内容设置为它指定的值,和之前学习的Vue一样-->
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
</body>
</html>
遍历数据
package com.jie.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("users", Arrays.asList("jie1","jie2"));
return "index";
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面</h1>
<!--th:text就是将div中的内容设置为它指定的值,和之前学习的Vue一样-->
<h3 th:each="user:${users}" th:text="${user}"></h3>
</body>
</html>

也可以用这种语法
<h3 th:each="user:${users}" >[[ ${user} ]]</h3>
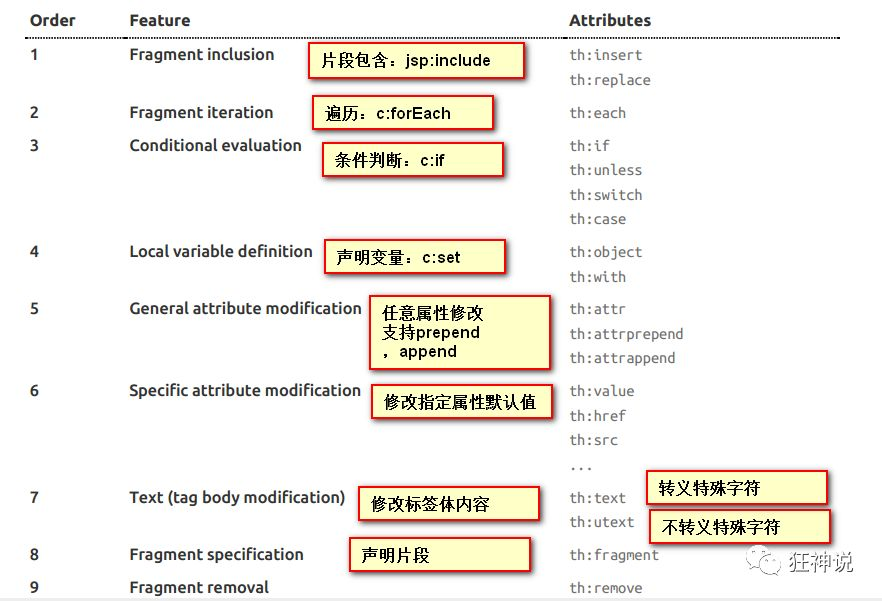
一些其他的语法参考文档


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号