Java 多线程
核心概念

通过继承Thread类实现
步骤
1.定义类继承Thread类
2.重写run方法
3.创建线程对象,调用start()方法
public class ThreadDemo1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
System.out.println("正在第"+i+"次做该事情");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadDemo1 threadDemo1=new ThreadDemo1();
threadDemo1.start();//调用start方法才能实现多线程
for(int i=0;i<=20;i++){
System.out.println("主线程正在第"+i+"次做该事情");
}
}
}
运行出来会发现并不是线性顺序,会交替执行。
通过Runnable接口实现(推荐做法)
public class ThreadDemo2 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
System.out.println("正在第"+i+"次做该事情");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadDemo2 threadDemo2=new ThreadDemo2();
//需要创建一个线程对象
//Thread thread=new Thread(threadDemo2);
//thread.start();
new Thread(threadDemo2).start();
for(int i=0;i<=20;i++){
System.out.println("主线程正在第"+i+"次做该事情");
}
}
}
简单例子:模拟龟兔赛跑
public class Race implements Runnable{
private static String winner=null;
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<=100;i++){
if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("兔子") && i%10==0){
//模拟兔子睡觉
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(gameOver(i)) break;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"跑了"+i+"米");
}
}
private boolean gameOver(int step){
if(winner!=null) return true;
if(step>=100){
winner=Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("winner"+"is"+winner);
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Race race=new Race();
new Thread(race,"兔子").start();
new Thread(race,"乌龟").start();
}
}
线程的安全性
//多个线程操作同一个对象
public class ThreadDemo3 implements Runnable{
private int tickNums=10;
public int sum=0;
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);//模拟延时
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
while(true){
if(tickNums<=0) break;
//Thread.currentThread().getName() 获取当前线程的名字
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拿到了第"+tickNums--+"票");
sum++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadDemo3 threadDemo3=new ThreadDemo3();
new Thread(threadDemo3,"小明").start();
new Thread(threadDemo3,"小红").start();
new Thread(threadDemo3,"小蓝").start();
}
}
该程序有可能会出现问题。需要加🔒
Lambda表达式
概念:对于只包含唯一一个抽象方法的接口,那么就被定义为函数式接口
对函数式接口,我们可以通过lambda表达式来创建接口的对象
代码例子
传统写法:
interface InterfaceDemo{
void fun();
}
public class LambdaDemo implements InterfaceDemo{
public void fun() {
System.out.println("实现接口--");
}
}
class Run{
public static void main(String[] args) {
LambdaDemo lambdaDemo=new LambdaDemo();
lambdaDemo.fun();
}
}
使用匿名内部类
interface InterfaceDemo{
void fun();
}
class Run{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//匿名内部类 必须借助接口或者父类
InterfaceDemo demo = new InterfaceDemo() {
public void fun() {
System.out.println("实现接口--");
}
};
demo.fun();
}
}
Lambda
interface InterfaceDemo{
void fun();
}
class Run{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Lambda
InterfaceDemo demo = ()->{
System.out.println("Lambda的实现");
};
demo.fun();
}
}
线程的状态
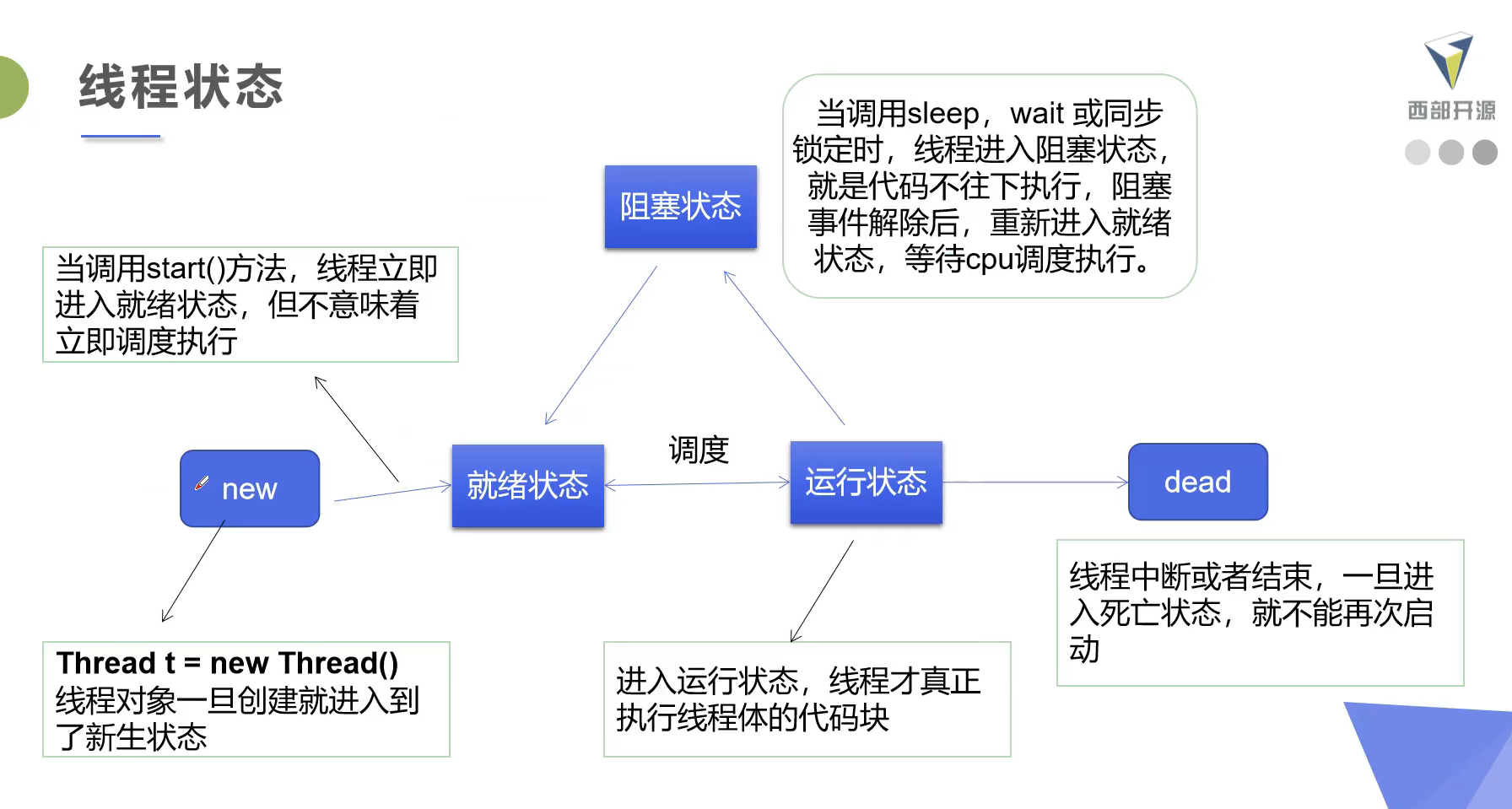
在java里线程状态的表示

线程的方法
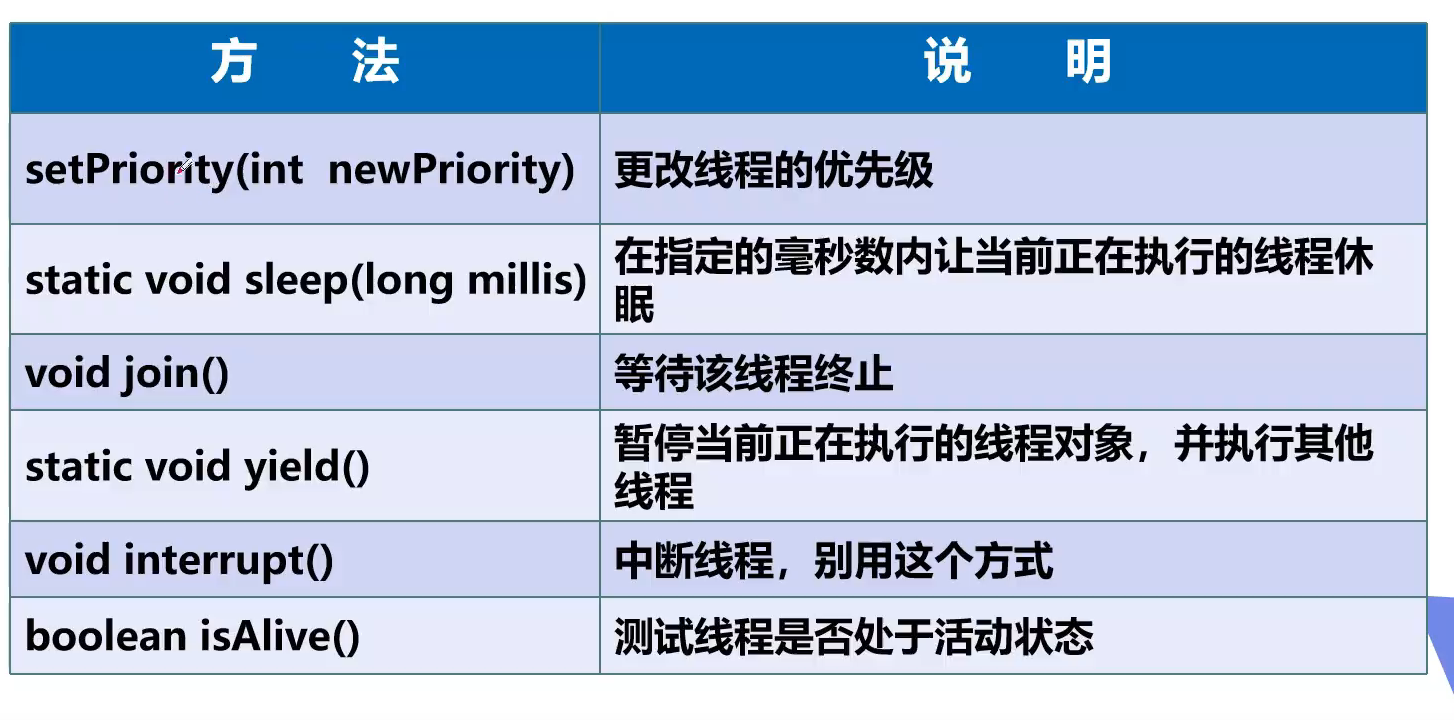

sleep

yield

意思就是假设A在运行状态,调用yield函数后变成就绪状态。 有可能仍然被CPU调度
join
即强行插队
线程的优先级
通过setPriority设置,越高优先级越高。但是要注意优先级越高只是表明CPU选择该线程的概率加大。
守护线程



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号