612.1.002 ALGS4 | Analysis of Algorithms
我们生活在大数的时代
培养数量级的敏感!
Tip:见招拆招
- 作为工程师,你先要能实现出来。
- 充实基础,没有什么不好意思
- 哪怕不完美。但是有时候完成比完美更重要。
- 之后再去想优化
P.S.作者Robert Sedgewick的导师是Knuth(高德纳!)
Conclusion First
1.Running Time

- Operation table

2.Memory
1 SOP - Analysis
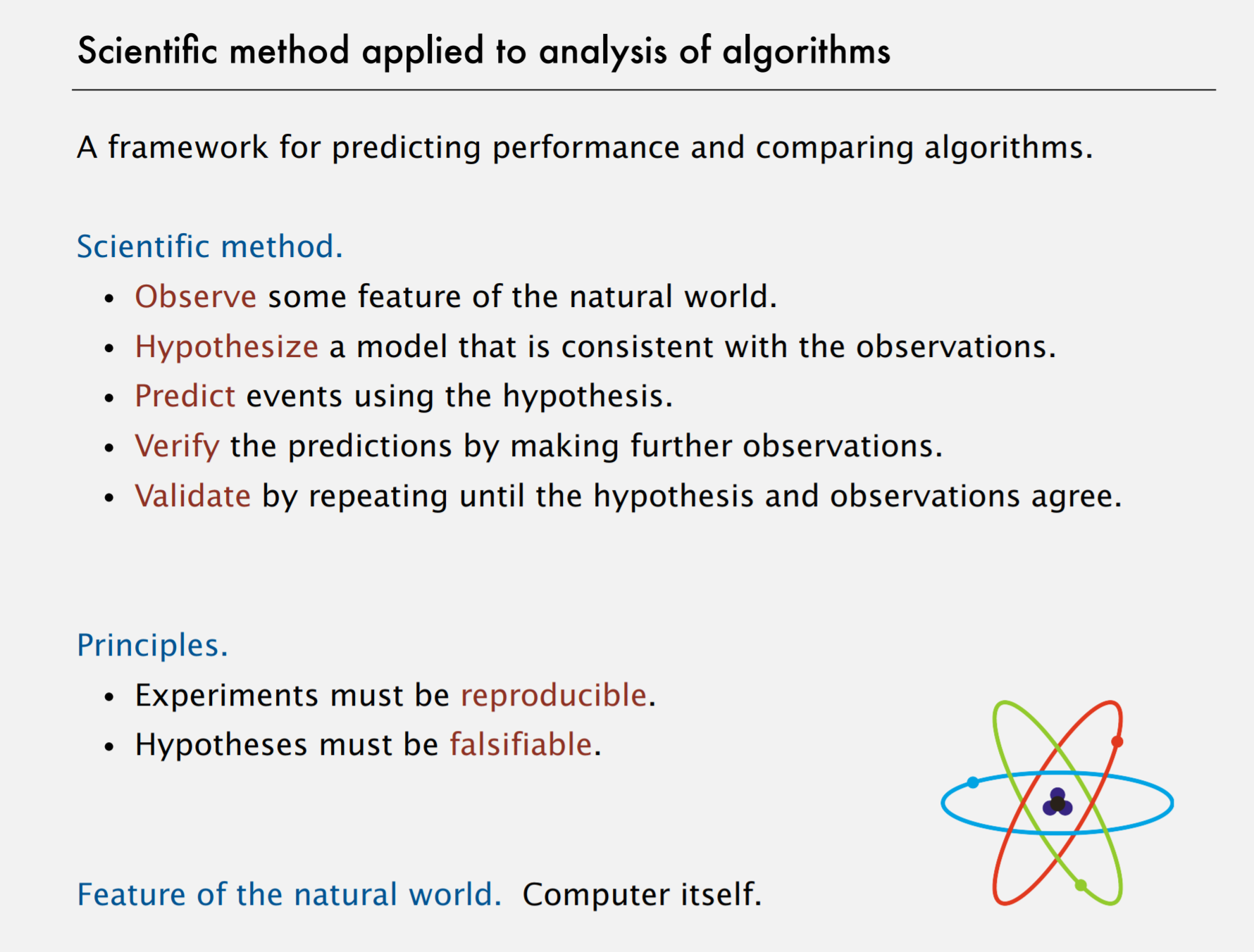
2 Observations
- Measuring the running time - automatic
public class Stopwatch(part of stdlib.jar/algs4.course)
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
int[] a = in.readAllInts();
Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
int count = count(a);
StdOut.println("elapsed time = " + timer.elapsedTime());//time since creation (in seconds)
StdOut.println(count);
}
3 Mathematical Model - Knuth(高德纳!)
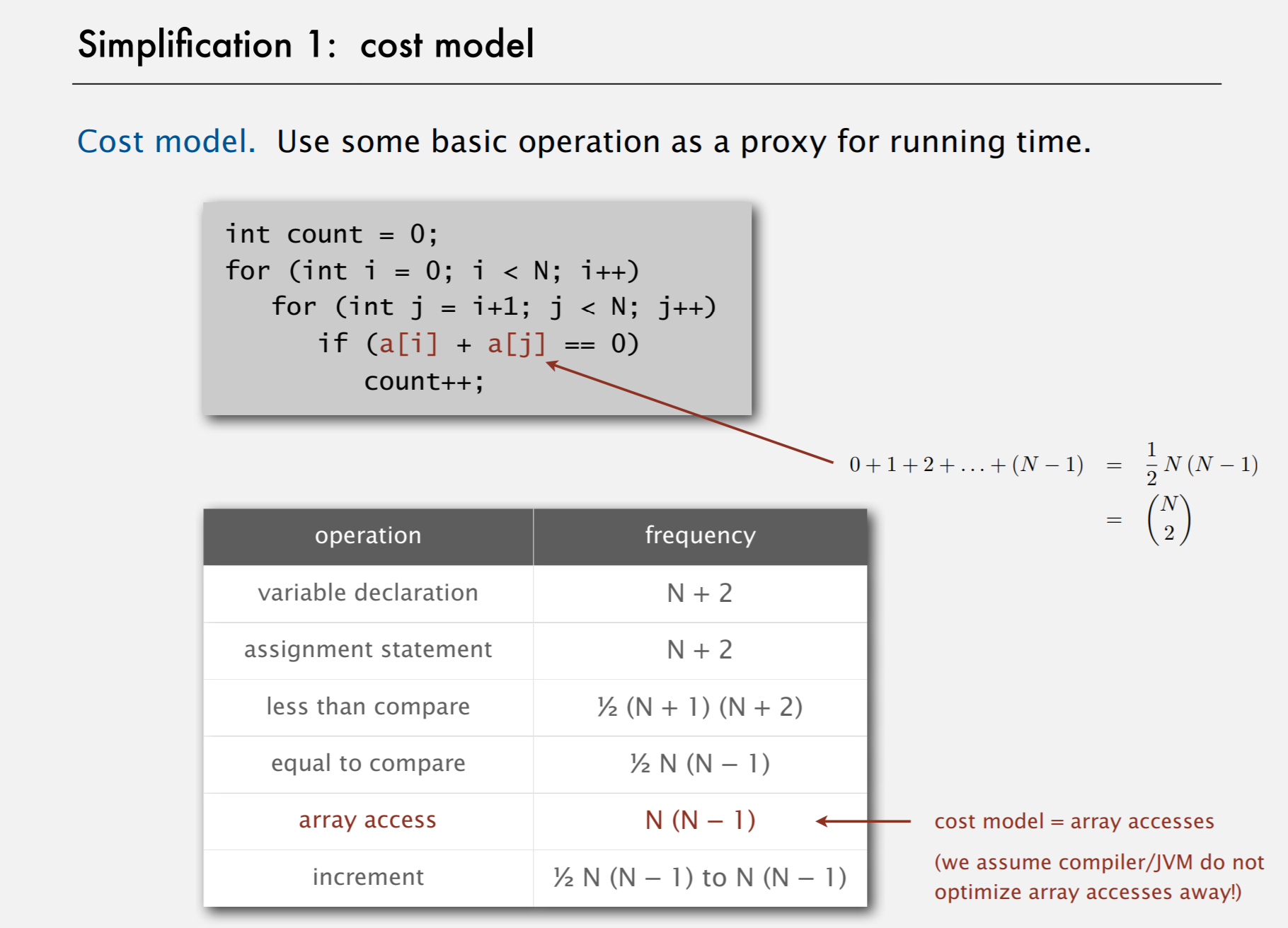
Simplification 1: cost model
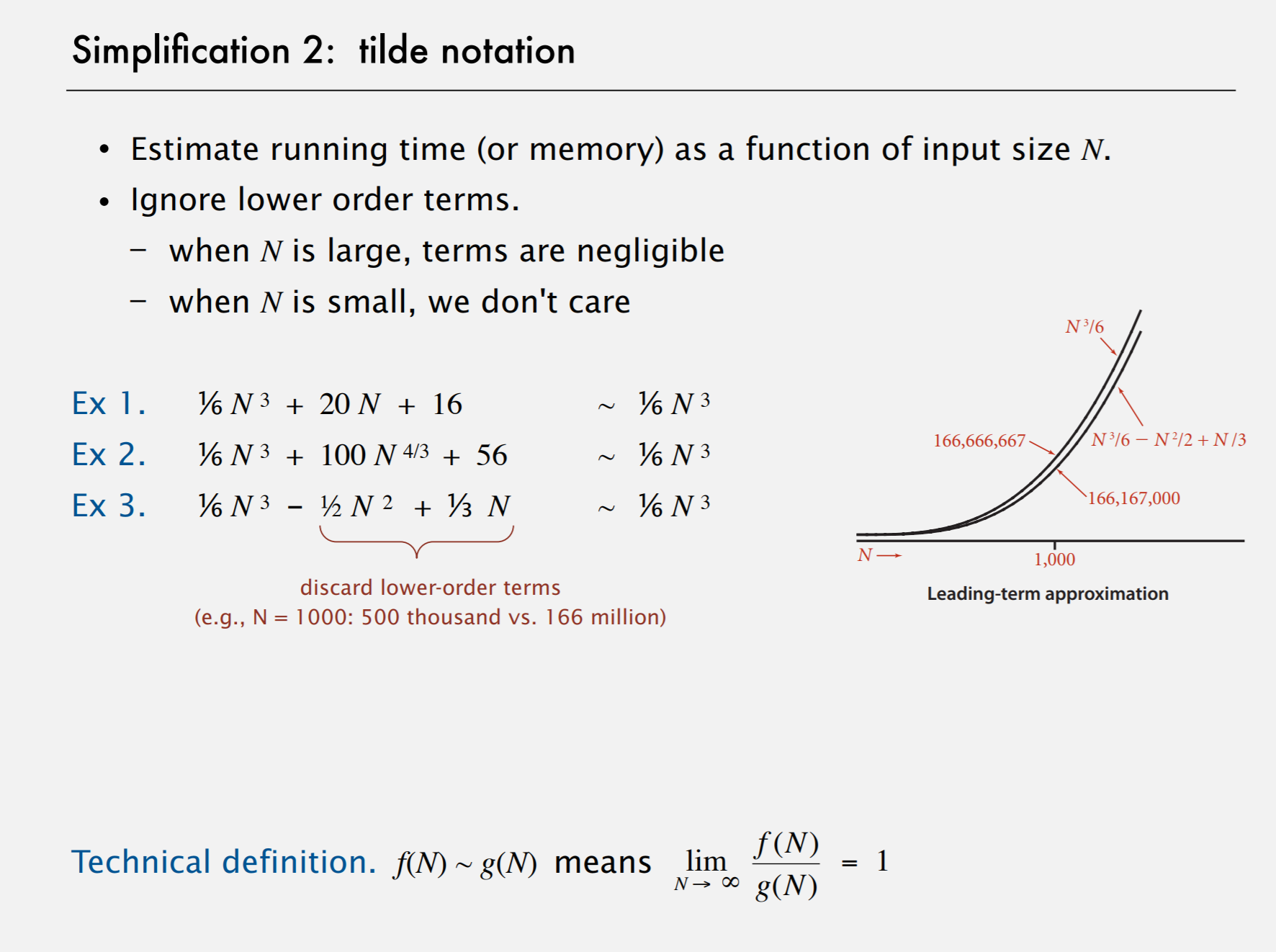
Simplification 2: tilde notation
approximate
工程近似
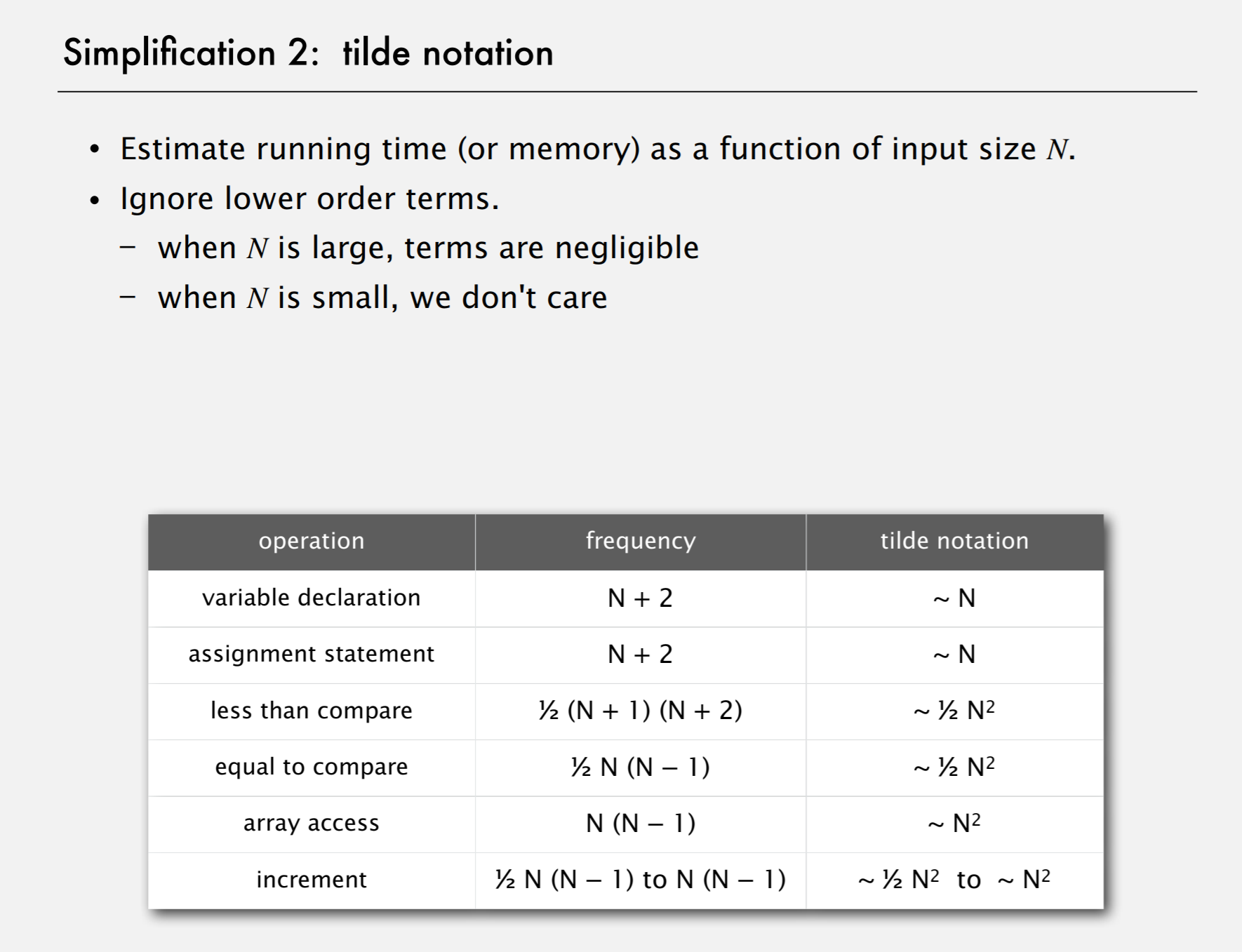
- Bottom line. Use cost model and tilde notation to simplify counts.
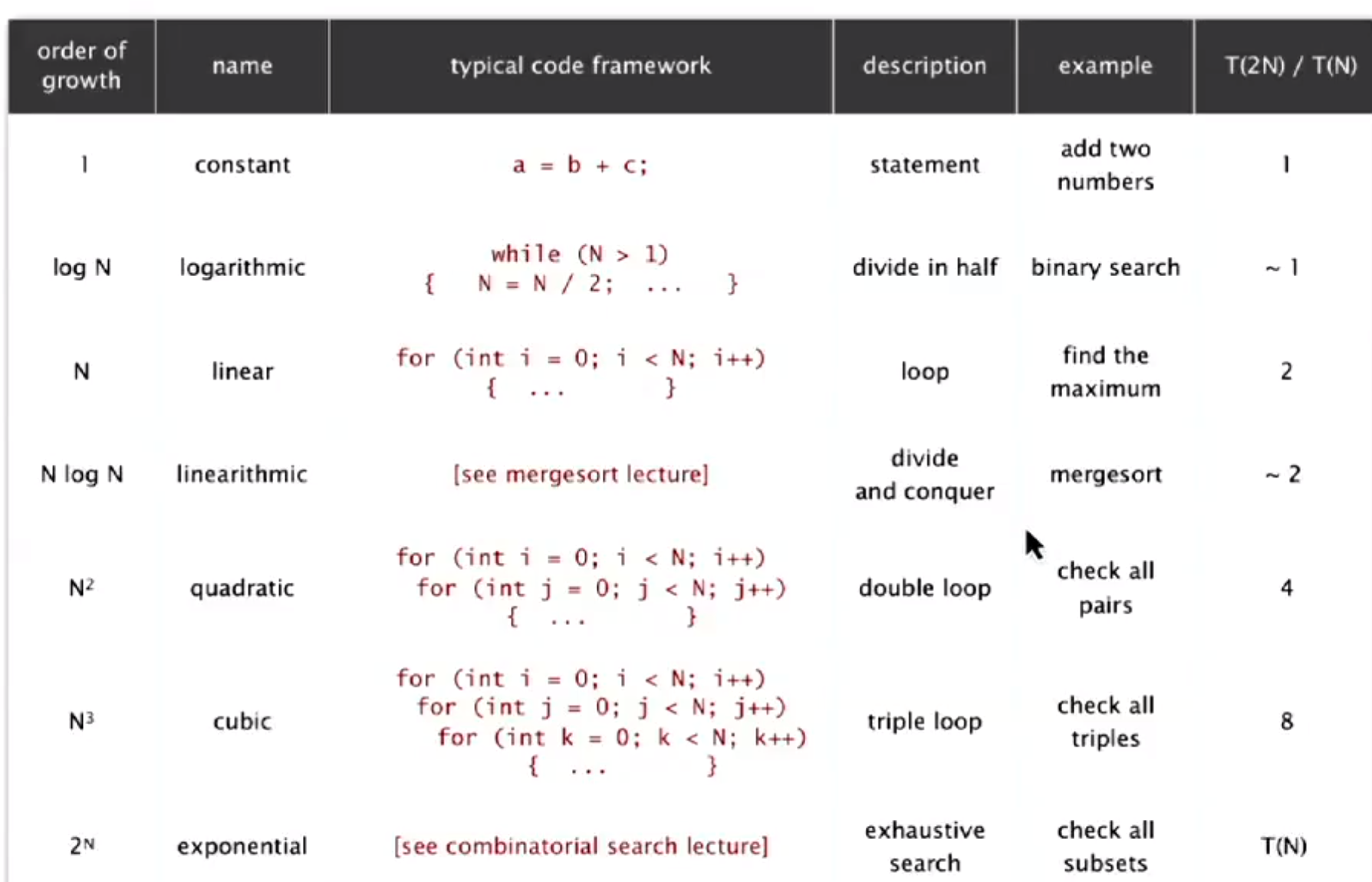
4 Order of growth
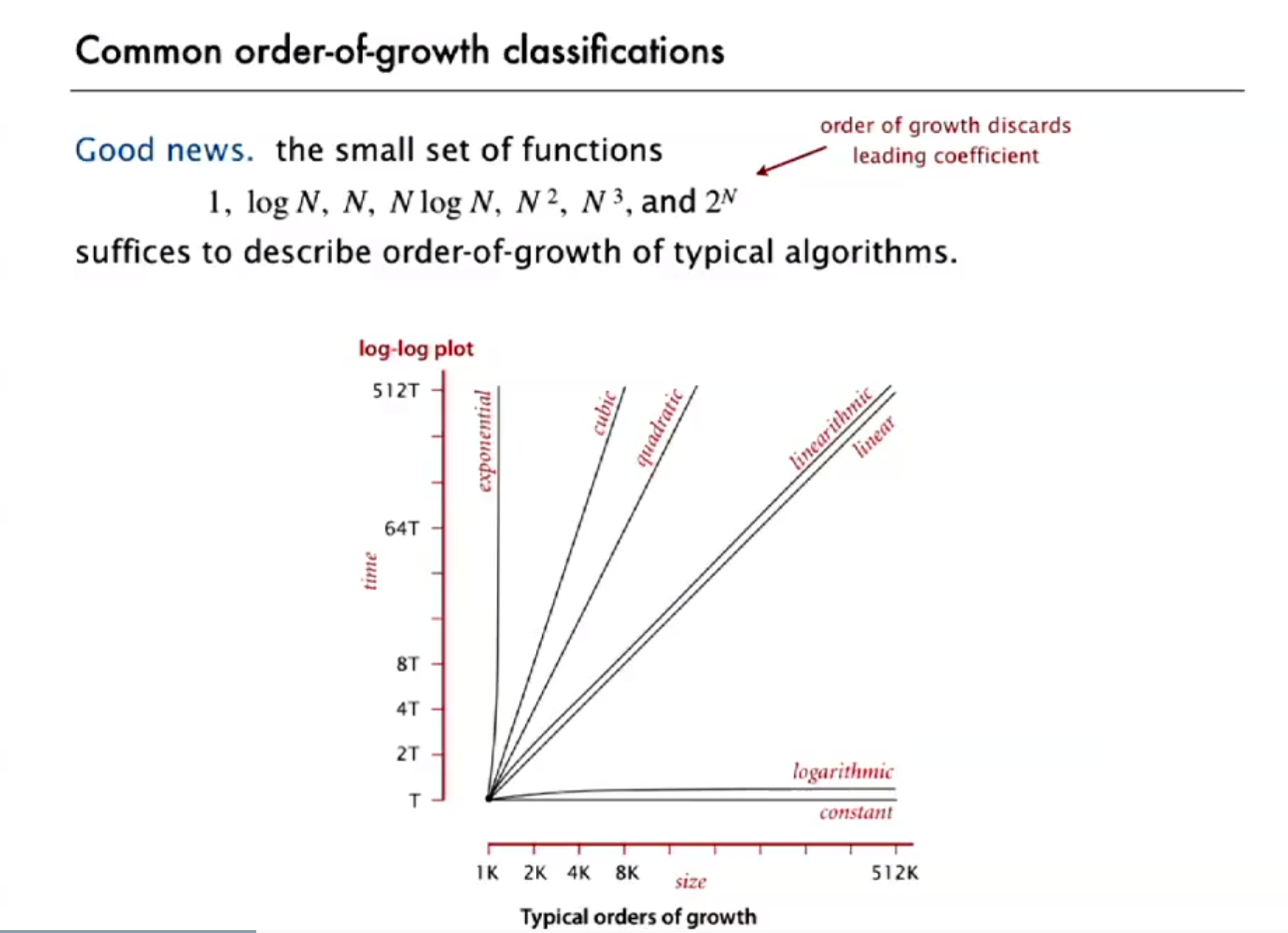
- Operation table
5 Binary Search - code 二分搜索
不看代码自己写
public static int binarySearch(int[]a,int key)
{
int lo=0;
int hi=a.length-1;
while(lo<=hi){
int mid=lo+(hi-lo)/2;
if(key>a[mid])lo=mid+1;
else if(key<a[mid])hi=mid-1;
else return mid;
}
return-1;
}
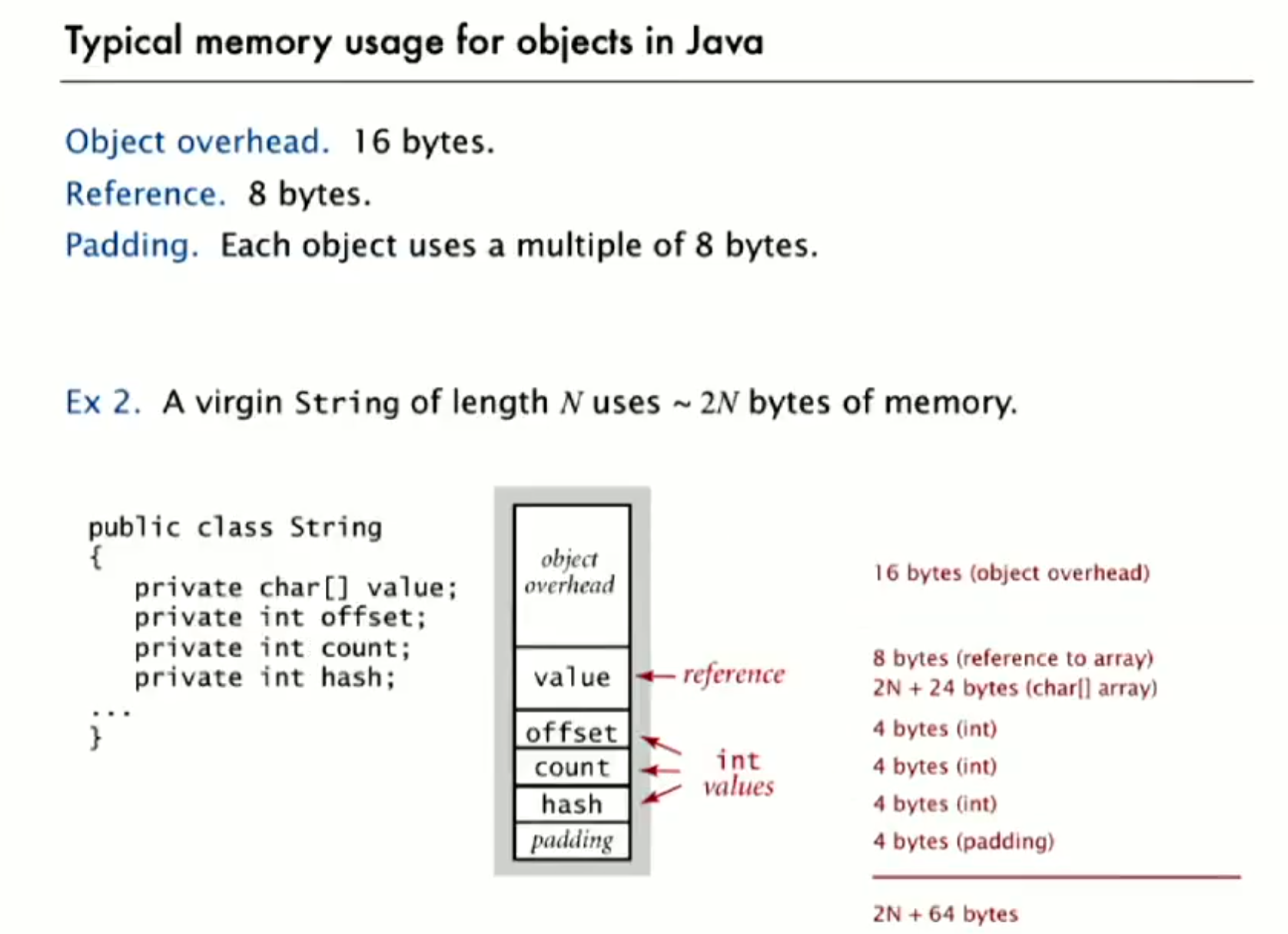
6 Memory
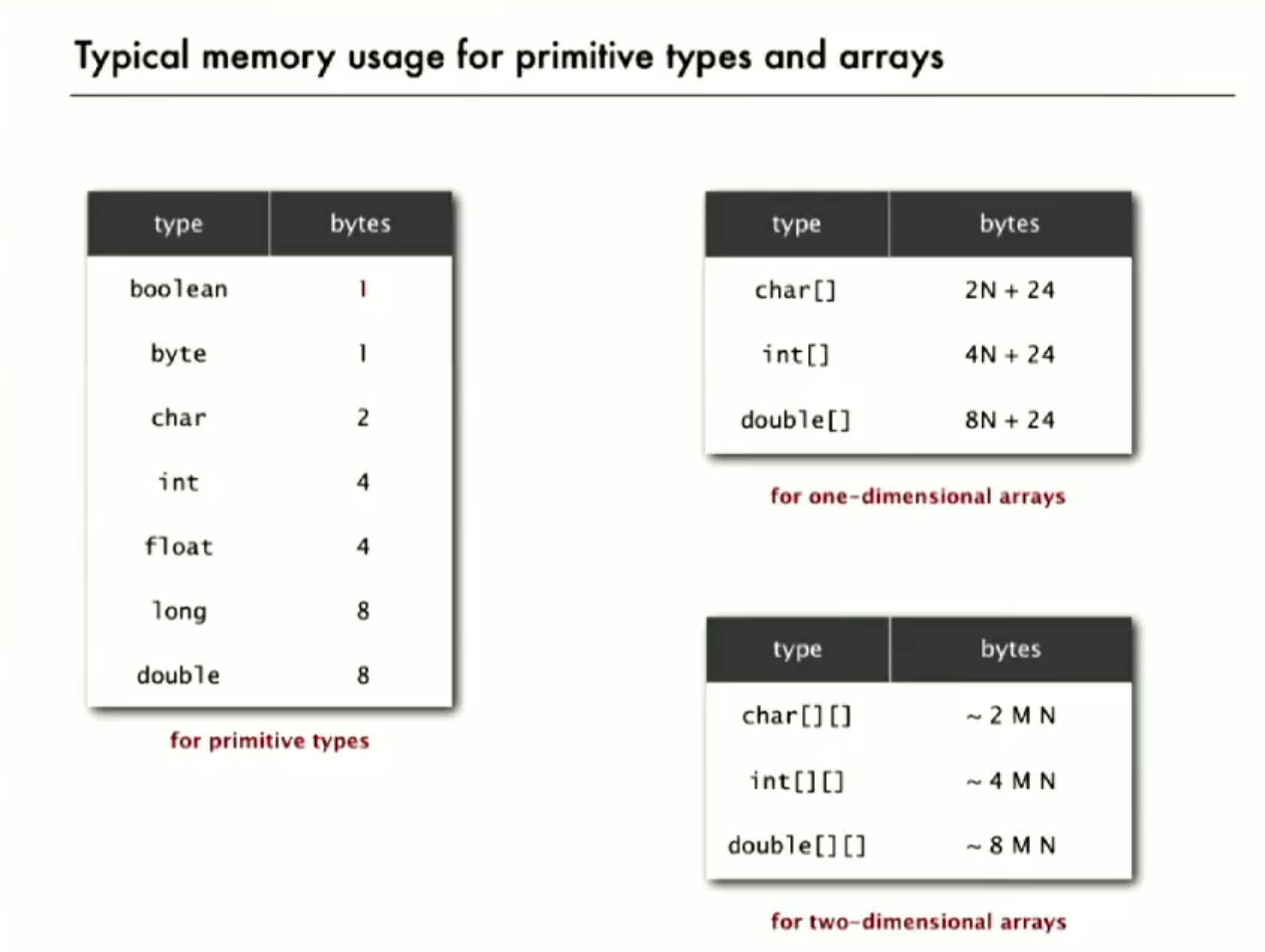
Typical memory usage of Java
Object overhead - 对象开销
QuickUnion




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号