面对对象程序设计————PTA大作业六到七三次作业总结
PTA大作业六——题目集1
整体总结:
此次题目初步接触了接口与抽象类的混合使用,同时也初步接触了通过创建各种类来进行用户注册与功能的实现。
题目集1 7-1 电信计费系列1-座机计费
整体思路分析 :
1.根据所给类图,能初步判定User类为储存创建用户账号的类,UserRecords类为储存用户打电话与接电话信息的类,ChargeMode及其子类用于实现计费,其中所含有的ChargeRule及其子类用于计算规则。
2.本题主要要求座机用户的创建以及根据其打电话区域的不同来进行对应的计费规则,可通过判断打向电话的区域来将改信息存储在不同的Records里面。
3.需要判断创建用户与打电话信息之间的分割点,需要解决错误输入自动忽略在其中造成的混乱问题;
度量分析
圈复杂度分析使用 SourceMonitor 软件
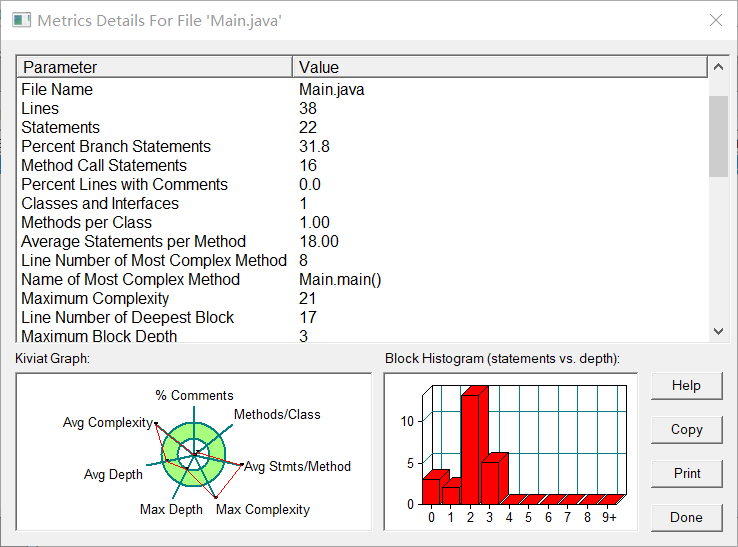
核心代码分析:
1.判断座机注册,座机打座机,座机打电话,电话打电话各种正确格式的正则表达式
public static boolean Correct(int m,String a) throws Exception
{
if(m==1)//注册
{
String pattern = "u-[0-9]{11,12} [0-1]{1}$";
boolean is1;
return is1 = Pattern.matches(pattern, a);
}
else if(m==2)//座机打座机
{
String pattern ="t-[0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$";
boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a);
return is;
}
else if(m==3)//座机打电话
{
String pattern ="t-[0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$";
boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a);
return is;
}
else//电话打电话
{
String pattern ="t-[1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$";
boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a);
return is;
}
}
2.实现计费的规则类
class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode
{
private double monthlyRent = 20;
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords)
{
double sum=0;
ArrayList<CallRecord> a =userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords();
CallChargeRule b1 =new LandPhoneInCityRule();
sum = sum+b1.calCost(a);
a =userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords();
CallChargeRule b2 =new LandPhoneInlandRule();
sum = sum+b2.calCost(a);
a =userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords();
CallChargeRule b3 =new LandPhoneInProvinceRule();
sum = sum+b3.calCost(a);
return sum;
}
public double getMonthlyRent()
{
return monthlyRent;
}
}
3.计费规则:市内打市内,市内打省内,市内打国内
class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule
{
public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)
{
double sum=0;
for (CallRecord a :callRecords)
{
long time = a.getEndTime().getTime()-a.getStartTime().getTime();
if(time%60000>0)
time=time/60000+1;
else
time = time/60000;
sum=sum+time*0.1;
}
return sum;
}
}
class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule
{
public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)
{
double sum=0;
for (CallRecord a :callRecords)
{
long time = a.getEndTime().getTime()-a.getStartTime().getTime();
if(time%60000>0)
time=time/60000+1;
else
time = time/60000;
sum=sum+time*0.6;
}
return sum;
}
}
class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule
{
public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)
{
double sum=0;
for (CallRecord a :callRecords)
{
long time = a.getEndTime().getTime()-a.getStartTime().getTime();
if(time%60000>0)
time=time/60000+1;
else
time = time/60000;
sum=sum+time*0.3;
}
return sum;
}
}
踩坑心得:
1.仅适用于座机系列,对于电话和短信系列的计费尚未完善;
2.main函数复杂度还是较高,也有部分重复部分;
3.由于接电话不计费,所以忽略了接电话信息储存;
改进建议:
1.寻找更好的逻辑避免重复代码;
PTA大作业七 题目集二
整体总结
此次题目集逻辑难度大幅加强,更需要去理解题目意思,进一步接触了接口与抽象类的混合使用,同时也更深入了通过创建各种类来进行用户注册与功能的实现。
题目集二 7-1 电信计费系列2-手机+座机计费
整体思路分析:
1.根据所给类图,能初步判定User类为储存创建用户账号的类,UserRecords类为储存用户打电话与接电话信息的类,ChargeMode及其子类用于实现计费,其中所含有的ChargeRule及其子类用于计算规则。
2.本题主要要求座机和电话用户的创建以及根据其打电话区域的不同来进行对应的计费规则,可通过判断打向电话的区域来将改信息存储在不同的Records里面,不同的是此次接电话也计算在内
3.需要判断创建用户与打电话信息之间的分割点,需要解决错误输入自动忽略在其中造成的混乱问题;
度量分析
圈复杂度分析使用 SourceMonitor 软件
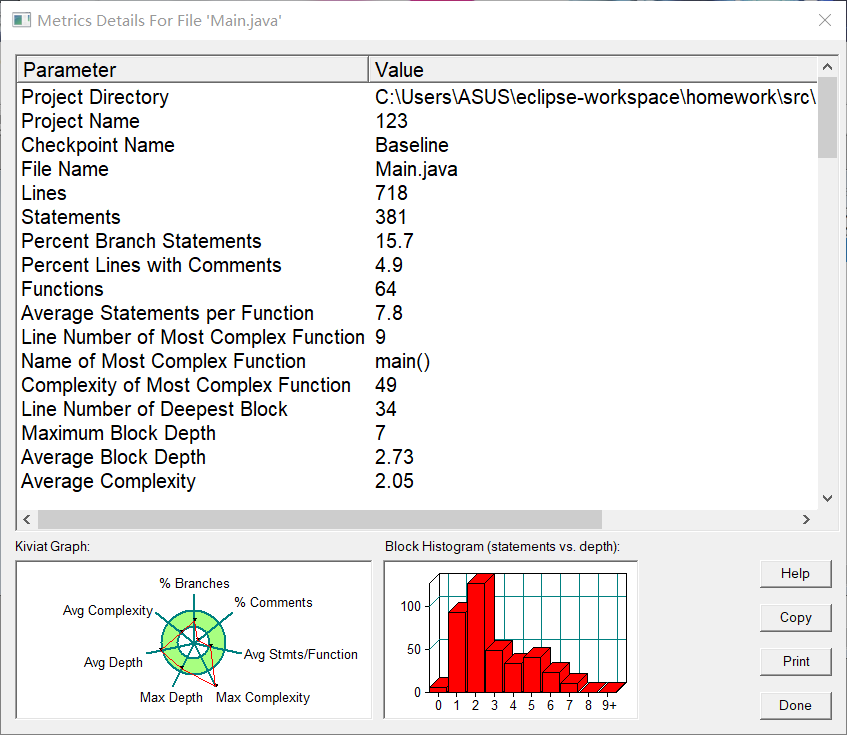
核心代码分析
1.判断座机注册,电话注册,座机打座机,座机打电话,电话打电话,电话打座机各种正确格式的正则表达式
public static boolean Correct(int m,String a) throws Exception { if(m==1)//注册 { String pattern = "u-[0-9]{11,12} [0-1]{1}$"; boolean is1; return is1 = Pattern.matches(pattern, a); } else if(m==2)//座机打座机 { String pattern ="t-[0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } else if(m==3)//座机打电话 { String pattern ="t-[0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } else if(m==4)//电话打电话 { String pattern ="t-[1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } else if(m==5)//电话打座机 { String pattern ="t-[1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } else { String pattern ="079[0-9]{1}|0791$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } } }
2.实现计费的规则类
class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { private double monthlyRent = 20; public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sum=0; ArrayList<CallRecord> a =userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords(); CallChargeRule b1 =new LandPhoneInCityRule(); sum = sum+b1.calCost(a); a =userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords(); CallChargeRule b2 =new LandPhoneInlandRule(); sum = sum+b2.calCost(a); a =userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords(); CallChargeRule b3 =new LandPhoneInProvinceRule(); sum = sum+b3.calCost(a); return sum; } public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } } class PhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { private double monthlyRent = 15; public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sum=0; ArrayList<CallRecord> a =userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords(); CallChargeRule b1 =new PhoneInCityRule(); sum = sum+b1.calCost(a); a =userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords(); CallChargeRule b2 =new PhoneInlandRule(); sum = sum+b2.calCost(a); a =userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords(); CallChargeRule b3 =new PhoneInProvinceRule(); sum = sum+b3.calCost(a); a =userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords(); CallChargeRule b4 =new PhoneInlandAnswerRule(); sum = sum+b4.calCost(a); return sum; } public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } }
3.计费规则:座机:市内打市内,市内打省内,市内打国内,电话:市内电话打各个区域,省内漫游接听,国内漫游接听;
class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule//座机 { public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for (CallRecord a :callRecords) { long time = a.getEndTime().getTime()-a.getStartTime().getTime(); if(time%60000>0) time=time/60000+1; else time = time/60000; sum=sum+time*0.1; } return sum; } } class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule//座机 { public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for (CallRecord a :callRecords) { long time = a.getEndTime().getTime()-a.getStartTime().getTime(); if(time%60000>0) time=time/60000+1; else time = time/60000; sum=sum+time*0.6; } return sum; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule//座机 { public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for (CallRecord a :callRecords) { long time = a.getEndTime().getTime()-a.getStartTime().getTime(); if(time%60000>0) time=time/60000+1; else time = time/60000; sum=sum+time*0.3; } return sum; } } class PhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule { public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for (CallRecord a :callRecords) { double b=Math.ceil(Double.valueOf(a.getEndTime(). getTime()-a.getStartTime().getTime())/1000/60); if(a.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().equals("0791")) sum=sum+b*0.1; else if(a.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().equals("0701")||(a.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().subSequence(0, 3).equals("079")&&a.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().charAt(3)>='0'&&a.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().charAt(3)<='9')) sum=sum+b*0.2; else sum=sum+b*0.3; } return sum; } } class PhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule { public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for (CallRecord a :callRecords) { double b=Math.ceil(Double.valueOf(a.getEndTime(). getTime()-a.getStartTime().getTime())/1000/60); sum=sum+b*0.6; } return sum; } } class PhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule { public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for (CallRecord a :callRecords) { double b=Math.ceil(Double.valueOf(a.getEndTime(). getTime()-a.getStartTime().getTime())/1000/60); sum=sum+b*0.3; } return sum; } } class PhoneInlandAnswerRule extends CallChargeRule { public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for (CallRecord a :callRecords) { double b=Math.ceil(Double.valueOf(a.getEndTime(). getTime()-a.getStartTime().getTime())/1000/60); sum=sum+b*0.3; } return sum; } }
踩坑心得:
1.double的精度问题,题目要求与保留2位小数,但最后结果全是1位小数;
2.没有处理好账号与打电话直接的分割点,对于创建用户正确-错误形式-创建用户正确-打电话的形式,错误的将第二个用户当成了已经开始储存打电话,从而导致因格式错误还略过;
3.忽略了0701也属于省内区域而导致部分测试点始终过不了;
改进建议:
通过双重循环进一步判断分割点;
题目集二 7-3 阅读程序,按照题目需求修改程序
1.此题逻辑清晰,且主要代码已经给出,较为简单;
2.此题主要考察了迭代器的使用——用于访问列表成员;
度量分析
圈复杂度分析使用 SourceMonitor 软件
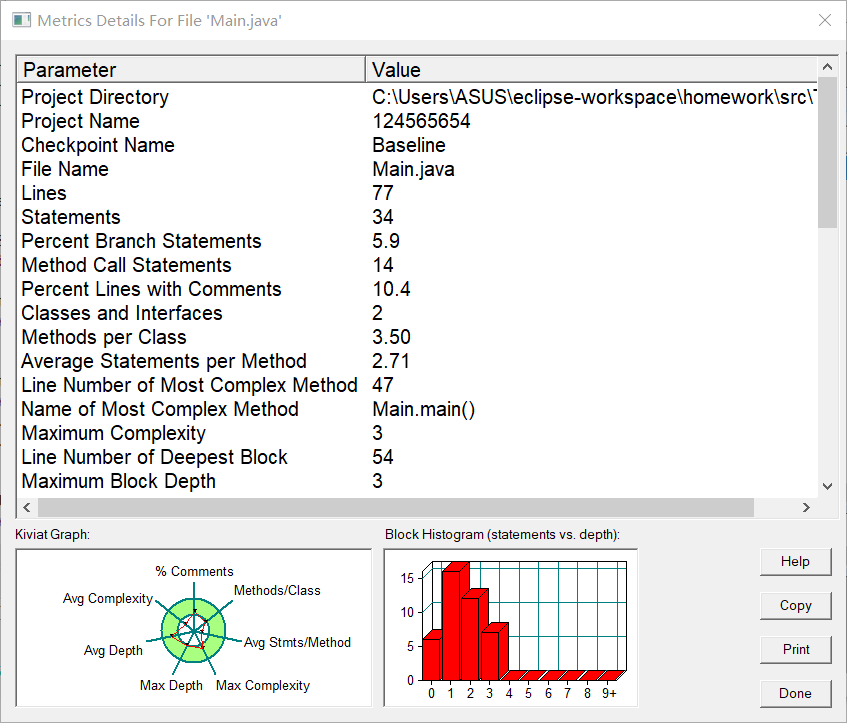
核心代码分析:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Scanner; //1、导入相关包 //定义员工类 class Employee { private String name; private int age; public Employee() { super(); } public Employee(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } } //主函数 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建有序集合对象 ArrayList<Employee> c=new ArrayList<>(); // 创建3个员工元素对象 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String employeeName = sc.nextLine(); int employeeAge = sc.nextInt(); Employee employee = new Employee(employeeName, employeeAge); c.add(employee); } // 2、创建迭代器遍历集合 Iterator<Employee> it= c.iterator(); //3、遍历 while (it.hasNext()) { //4、集合中对象未知,向下转型 Employee e = it.next(); System.out.println(e.getName() + "---" + e.getAge()); } } }
踩坑心得:
一遍过,无踩坑;
改进建议:
无;
PTA大作业八 题目集三
整体总结
此次题目集逻辑难度大幅加强,更需要去理解题目意思,进一步接触了接口与抽象类的混合使用,同时也更深入了通过创建各种类来进行用户注册与功能的实现。
题目集三 7-1 电信计费系列3-短信计费
整体分析
1.根据所给类图,能初步判定User类为储存创建用户账号的类,UserRecords类为储存用户打电话与接电话信息的类,ChargeMode及其子类用于实现计费,其中所含有的ChargeRule及其子类用于计算规则。
2.本题主要要求座机和电话用户的创建以及根据其发短信区域的不同来进行对应的计费规则,可通过判断发短信的区域来将改信息存储在不同的Records里面,不同的是此次接电话也计算在内
3.需要判断创建用户与发短信信息之间的分割点,需要解决错误输入自动忽略在其中造成的混乱问题;
4.需要新增短信各种格式的判断以及计费方法
度量分析
圈复杂度分析使用 SourceMonitor 软件
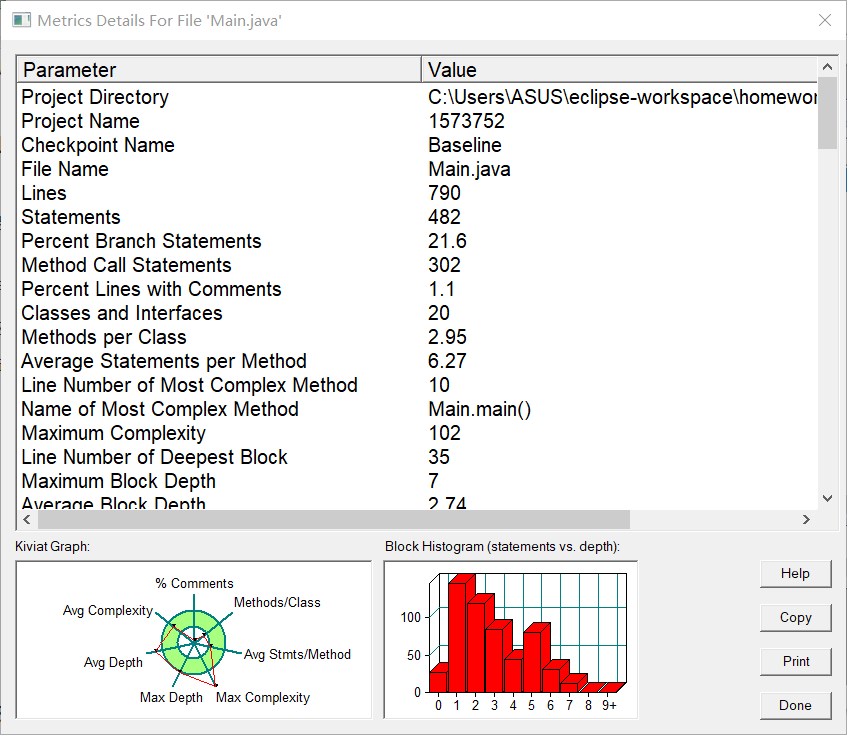
核心代码分析:
1.判断座机注册,电话注册,座机打座机,座机打电话,电话打电话,电话打座机各种正确格式的正则表达式
public static boolean Correct(int m,String a) throws Exception { if(m==1)//注册 { String pattern = "u-[0-9]{11,12} [0-3]{1}$"; boolean is1; return is1 = Pattern.matches(pattern, a); } else if(m==2)//座机打座机 { String pattern ="t-[0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } else if(m==3)//座机打电话 { String pattern ="t-[0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } else if(m==4)//电话打电话 { String pattern ="t-[1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } else if(m==5)//电话打座机 { String pattern ="t-[1]{1}[0-9]{10} [0-9]{3,4} [0]{1}[0-9]{9,11} [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|(3[0-1])) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9]) [0-9]{4}[.](([1-9]{1})|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))[.]([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1]) (([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))[:]([0-5][0-9])[:]([0-5][0-9])$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } else if(m==6) { String pattern ="079[0-9]{1}|0791$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } else /*if(m==7)*/ { String pattern ="m-[1]{1}[0-9]{10} [1]{1}[0-9]{10}$"; boolean is=Pattern.matches(pattern, a); return is; } }
2.实现计费的规则类(仅短信计费)
class PhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { private double monthlyRent = 0; public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sum=0; ArrayList<CallRecord> a =userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords(); CallChargeRule b1 =new PhoneInCityRule(); sum = sum+b1.calCost(a); a =userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords(); CallChargeRule b2 =new PhoneInlandRule(); sum = sum+b2.calCost(a); a =userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords(); CallChargeRule b3 =new PhoneInProvinceRule(); sum = sum+b3.calCost(a); a =userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords(); CallChargeRule b4 =new PhoneInlandAnswerRule(); sum = sum+b4.calCost(a); ArrayList<MessageRecord> b=userRecords.getSendMessageRecords(); MessageRule b5 =new SendMessageRule(); sum = sum+b5.calCost(b); return sum; } public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } }
3.计费规则:短信大小计费
class SendMessageRule extends MessageRule { public double calCost(ArrayList<MessageRecord> messageRecords) { double sum=0,count=0; for (MessageRecord a :messageRecords) { int t; if(a.getMessage().length()%10!=0) t=a.getMessage().length()/10+1; else t=a.getMessage().length()/10; count=count+t; } for(int i=1;i<=count;i++) { if(i<=3) sum=sum+0.1; else if(i>3&&i<=5) sum=sum+0.2; else sum=sum+0.3; } return sum; } }
踩坑心得:
1.判断短信格式出现错误,忽略了“(空格) ”也属于正确字符而导致全体出现错误;
改进建议:
此次题目内容较简短,只是逻辑不够完美,需要更好的拍理减少代码量;
总结
1.对于这三次大作业的编写,由于第一次接触多数量类的结合使用而无法静下心来减少代码的复杂度,只完全执着于过测试点,而忽略了代码的复杂度问题,最终造成了700行代码的“惨烈壮举”,希望以后能引以为戒,追求结果的同时也不能网络质量的好坏,将其养成习惯,持之以恒;
2.这三次作业让我知晓了能被真正使用的代码形式——不是一个main方法包含所有代码,而是通过分块,将各个功能分部与各个类中,通过类与类之间的关系构造最后的系统,尽管过程有点艰辛,但收获也十分丰厚;
3.这三次作业唯一的缺陷就是尽管类创建的足够完美,但main方法依旧十分冗杂,需要学习他人的代码,摸清他人良好的逻辑,我的实力才能进一步提升;
4.第三次大作业让我意识到,难度较高的代码如果出现错误,很难凭借眼力找出,这时,debug的重要性就显现了,通过debug,大幅度减少了我找bug的时间,所以,掌握每门语言、每种软件的debug技巧十分重要;
5.通过这几次作业,让我认识到正则所带来的便利之大,但我目前只是浅浅的了解了一些正则的使用,还需要更深层次的学习;



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号