作业4:词频统计——基本功能
一、基本信息
1.本次作业的地址: https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/ntu/Embedded_Application/homework/2088
2.项目Git的地址:https://gitee.com/ntucs/PairProg/tree/SE016_017
3.开发环境:Pycharm2018、Python3.6
4.结对成员:1613072013 刘赛、1613072011蒋兆丰
二、项目分析
2.1 程序运行模块(方法、函数)介绍
①任务一:读取文件、统计行数写入result.txt方法
import re
import jieba
from string import punctuation
def process_file(dst): # 读文件到缓冲区
try: # 打开文件
f=open(dst,'r')
except IOError as s:
print (s)
return None
try: # 读文件到缓冲区
x=f.read()
except:
print ("Read File Error!")
return None
bvffer=x
return bvffer
②任务一:使用正则表达式统计词频,存放如字典模块
def line_count(dst):
count=0
for index,line in enumerate(open(dst,'r')):
count+=1
print("text line :",count)
def process_buffer(bvffer):
c=bvffer.lower()
result=re.sub("[0-9]+[a-z]+"," ",c)
re1=re.findall('[a-z]+\w+',result)
d=open("stopwords.txt",'r').read()
if re1:
word_freq = {}
# 下面添加处理缓冲区 bvffer代码,统计每个单词的频率,存放在字典word_freq
for word in re1:
if word not in d:
if word not in word_freq:
word_freq[word]=0
word_freq[word]+=1
return word_freq
③任务一:保存排名前十结果至result.txt模块
def output_result(word_freq):
doc=open('result.txt','w')
if word_freq:
sorted_word_freq = sorted(word_freq.items(), key=lambda v: v[1], reverse=True)
print(len(word_freq))
for item in sorted_word_freq[:10]: # 输出 Top 10 的单词
print(item[0],":",item[1])
print(item[0],":",item[1],file=doc)
doc.close()
④任务一:主函数调用各个模块逻辑
if __name__ == "__main__":
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('dst')
args = parser.parse_args()
dst = args.dst
line_count(dst)
bvffer = process_file(dst)
word_freq = process_buffer(bvffer)
output_result(word_freq)
word_frequency(bvffer)
⑤任务二:停词表模块
功能实现方法:使用 nltk(Natural Language Toolkit,自然语言处理工具包,在NLP领域中,最常使用的一个Python库。)下载英文停词表,存放到list_stopWords集合中,接着对将要处理的英文单词进行判断是否与list_stopWords中的词汇相等,如果相等则跳过,即停词功能。
代码模块如下:
d=open("stopwords.txt",'r').read() #停词
if re1:
word_freq = {}
# 下面添加处理缓冲区 bvffer代码,统计每个单词的频率,存放在字典word_freq
for word in re1:
if word not in d:
if word not in word_freq:
word_freq[word]=0
word_freq[word]+=1
return word_freq
任务二:列出高频短语模块
def Phrase_statistics(bvffer): #统计高频词组
text=nltk.text.Text(bvffer.split())
print(text.collocations())
2.2 程序算法时间、空间复杂度分析
def process_buffer(bvffer):
c=bvffer.lower()
result=re.sub("[0-9]+[a-z]+"," ",c)
re1=re.findall('[a-z]+\w+',result)
d=open("stopwords.txt",'r').read()
if re1:
word_freq = {}
# 下面添加处理缓冲区 bvffer代码,统计每个单词的频率,存放在字典word_freq
for word in re1:
if word not in d:
if word not in word_freq:
word_freq[word]=0
word_freq[word]+=1
return word_freq
假设字典中有n个元素,执行一次就循环一次,共n次,所以时间复杂度为O(n),每次创建一个空间存放将要使用词,所以空间复杂度为O(1)
2.3 程序运行案例截图
result运行截图:


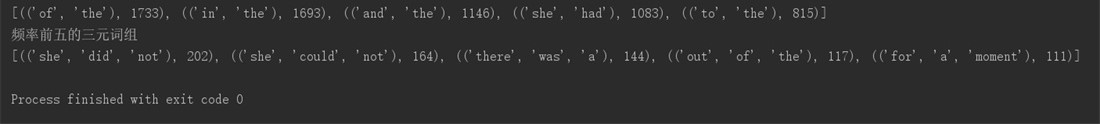
高频词组截图:
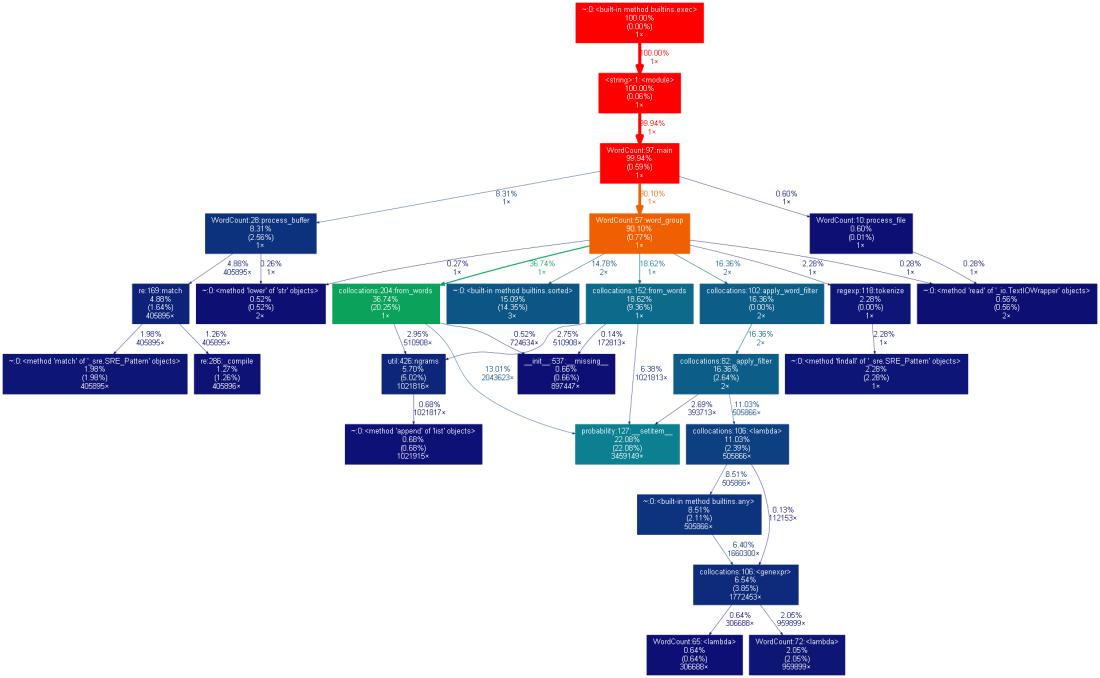
三、性能分析
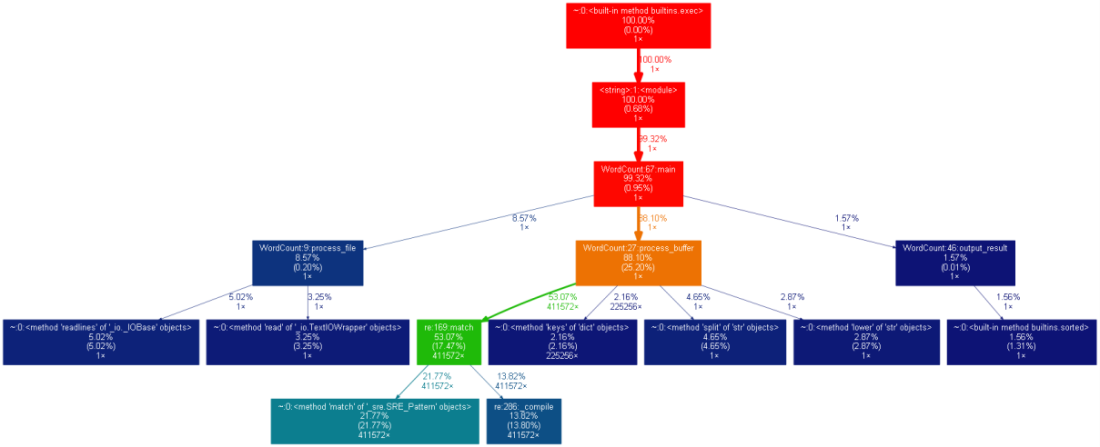
1.
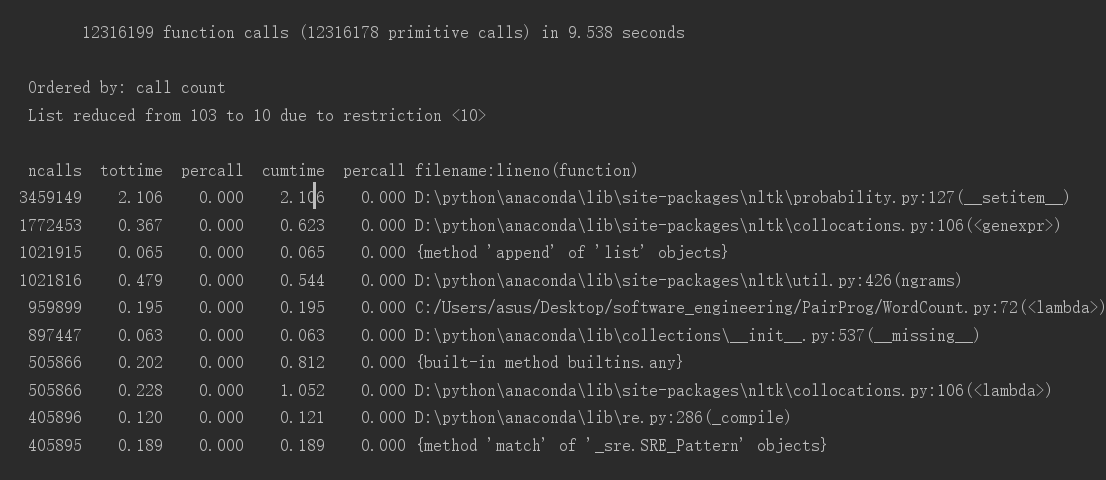
2.
四、其他
4.1 结队编程时间开销
由于之前没有接触过python,大部分的时间用于学习python的各种函数应用,,查阅资料,一边做,一边学。查阅技术文档、结队编程。大体分工为两位同学同时查阅技术文档,接着交流讨论。对各个技术方式实践结队编程最后选择最合适的方案。
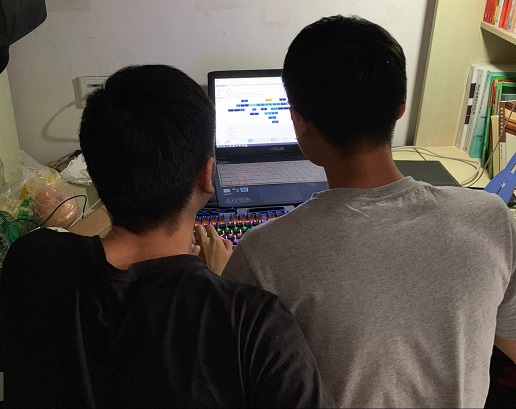
4.2 结队编程照片

五、事后分析与总结
五、事后分析与总结
5.1简述结对编程时,针对某个问题的讨论决策过程。
在实现查看高频短语的功能时,蒋兆丰的代码与我的代码一度产生冲突。蒋兆丰的想法是使用字符串组成想要提取的短语,我的想法是使用nltk中的collection方法。
5.2评价对方:请评价一下你的合作伙伴,又哪些具体的优点和需要改进的地方。 这个部分两人都要提供自己的看法。
(1)刘赛对蒋兆丰的评价:蒋兆丰同学积极主动,好学,在我们学习python的时候理解的很快也理解的很好。
(2)蒋兆丰对刘赛的评价:刘赛同学在编程的时候有遇到很多问题,讨论的时候提出了比较好的想法。
5.3评价整个过程
结对编程是一个相互学习、相互磨合的渐进过程,团队合作对于编程而言很重要。
5.5其他
在学习一门新的语言时要多查询资料多余同学讨论,并且要多敲代码,多进行实践。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号