Hibernate初试
hibernate框架是什么
hibernate是一款orm框架,它对JDBC进行了非常轻量级的对象封装,它将POJO与数据库表建立映射关系,是一个全自动的orm框架,hibernate可以自动生成SQL语句,自动执行,使得Java程序员可以随心所欲的使用对象编程思维来操纵数据库。 Hibernate可以应用在任何使用JDBC的场合,既可以在Java的客户端程序使用,也可以在Servlet/JSP的Web应用中使用。
hibernate的好处:
操作数据库的时候,可以以面向对象的方式来完成,不需要书写SQL语句
orm: object relation mapping对象关系映射
orm分3级:
hibernate属于3级:完全面向对象操作数据库
mybatis属于2级
dbutils属于1级
hibernate框架的搭建
1、导包
使用hibernate框架需要先导入一系列的jar包,包括 hibernate的核心包跟 JDBC驱动包
在lib目录下导入下列包:
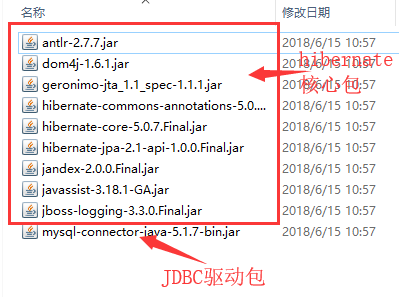
2、创建数据库,创建表
虽然hibernate可以自动建表,但是仍然建议自己手动建表
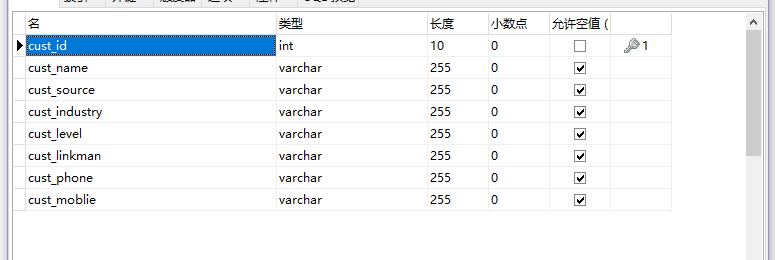
3、创建实体类
创建与数据库表列名相对应的javabean类
package com.jinxin.hibernate;
public class Customer {
private Long cust_id;
private String cust_name;
private String cust_source;
private String cust_industry;
private String cust_level;
private String cust_linkman;
private String cust_phone;
private String cust_moblie;
public Long getCust_id() {
return cust_id;
}
public void setCust_id(Long cust_id) {
this.cust_id = cust_id;
}
public String getCust_name() {
return cust_name;
}
public void setCust_name(String cust_name) {
this.cust_name = cust_name;
}
public String getCust_source() {
return cust_source;
}
public void setCust_source(String cust_source) {
this.cust_source = cust_source;
}
public String getCust_industry() {
return cust_industry;
}
public void setCust_industry(String cust_industry) {
this.cust_industry = cust_industry;
}
public String getCust_level() {
return cust_level;
}
public void setCust_level(String cust_level) {
this.cust_level = cust_level;
}
public String getCust_linkman() {
return cust_linkman;
}
public void setCust_linkman(String cust_linkman) {
this.cust_linkman = cust_linkman;
}
public String getCust_phone() {
return cust_phone;
}
public void setCust_phone(String cust_phone) {
this.cust_phone = cust_phone;
}
public String getCust_moblie() {
return cust_moblie;
}
public void setCust_moblie(String cust_moblie) {
this.cust_moblie = cust_moblie;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [cust_id=" + cust_id + ", cust_name=" + cust_name + "]";
}
}
3、书写orm元数据
在与javabean类同一目录下建立 Customer.hbm.xml 文件,在文件中书写orm元数据
导入约束
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
配置表与实体类的关系
<id name="cust_id">
<!-- generate:主键生成的策略 -->
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="cust_name" column="</property>
<property name="cust_source" column="cust_source"></property>
<property name="cust_industry" column="cust_industry"></property>
<property name="cust_level" column="cust_level"></property>
<property name="cust_linkman" column="cust_linkman"></property>
<property name="cust_phone" column="cust_phone"></property>
<property name="cust_moblie" column="cust_moblie"></property>
完整的内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!-- 配置表与实体对象(javabean类)的关系 -->
<!--
当配置包名后,后面凡是需要书写完整类名的地方只需要直接书写类名即可,
不必要在书写完整的包名和类名
-->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.jinxin.hibernate">
<!--
class标签:配置实体(即javabean类)与表的对应关系
name: 与表对应的javabean类名
table: 数据库表名
-->
<class name="Customer" table="cst_customer">
<!--
id标签:配置主键映射的属性
name: 填写主键对应的属性名(即javabean类中的字段名)
column(非必填): 填写表中的主键列名 默认值:列名会使用属性名
type(非必填): 填写列(属性)的类型,hibernate会自动检测实体的属性类型。
每个类型有三种填法:java类型 | hibernate类型 | 数据库类型 (注意:最好是让hibernate自动检测,不必要自己设置类型)
not-null(非必填): 配置该属性(列)是否不能为空,默认值:false
length(非必填): 配置数据库列的长度,默认值:使用数据库该类型的最大值
-->
<id name="cust_id">
<!-- generate:主键生成的策略 -->
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<!--
property标签:除了主键列之外的普通属性的映射
name: 填写主键对应的属性名(即javabean类中的字段名)
column(非必填): 填写表中的主键列名 默认值:列名会使用属性名
type(非必填): 填写列(属性)的类型,hibernate会自动检测实体的属性类型。
每个类型有三种填法:java类型 | hibernate类型 | 数据库类型 (注意:最好是让hibernate自动检测,不必要自己设置类型)
not-null(非必填): 配置该属性(列)是否不能为空,默认值:false
length(非必填): 配置数据库列的长度,默认值:使用数据库该类型的最大值
-->
<property name="cust_name" column="cust_name">
<!-- 设置列的类型(用数据库的类型设置),一般不推荐设置 -->
<!-- <column name="cust_name" sql-type="varchar"></column>-->
</property>
<property name="cust_source" column="cust_source"></property>
<property name="cust_industry" column="cust_industry"></property>
<property name="cust_level" column="cust_level"></property>
<property name="cust_linkman" column="cust_linkman"></property>
<property name="cust_phone" column="cust_phone"></property>
<property name="cust_moblie" column="cust_moblie"></property>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
4、书写主配置文件
在src目录新建 hibernate.cfg.xml 文件,在文件中书写主配置,包括JDBC加载驱动类,数据库连接的URL,连接数据库的用户名,连接数据库的用户名密码,数据库方言,映射orm元数据
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- # hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect # hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect # hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLMyISAMDialect # hibernate.connection.driver_class com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # hibernate.connection.url jdbc:mysql:///test # hibernate.connection.username gavin # hibernate.connection.password --> <!-- 数据驱动 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <!-- 数据库URL --> <!-- ///表示: //localhost:3306/ --> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///1806</property> <!-- 连接数据库的用户名 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <!-- 数据库连接密码 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">123</property> <!-- 数据方言: 不同的数据中,sql语句略有区别,指定方言可以让hiberante框架在生成sql语句时,针对数据库的方言生成. sql99标准:DDL:定义语言 库表的增删该查 DCL:控制语言 事务 权限 DML:操作语言 增删该查 注意事项: mysql在选择方言时,选择最短的方言.hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect --> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> <!-- # hibernate.show_sql true # hibernate.format_sql true --> <!-- 将hibernate生成的sql语句打印到控制台 --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <!-- 格式化生成的sql语句,不格式化会生成一列答打印--> <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property> <!-- ## auto schema export 自动导出表结构.自动建表 # hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create-drop 自动建表,每次框架运行结束都会将所有表删除.(开发环境中测试使用) # hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create 自动建表,每次框架运行都会创建新的表。以前的表将会被覆盖。表数据会丢失.(开发环境中测试使用) # hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto update (推荐使用) 自动生成表.如果已经存在不会在生成。如果表有变动,自动更新表.(自动更新表不会删除任何数据) # hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto validate 校验。不自动生成表.每次启动校验数据库中表是否正确 --> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <!-- 引入orm元数据,填写src下的路径 --> <mapping resource="com/jinxin/hibernate/Customer.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
5、测试
新建一个测试类 Demo.java,往数据库插入一条数据
package com.jinxin.test.a_hello;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.jinxin.hibernate.Customer;
// 测试Hibernate框架
public class Demo {
@Test
public void fun1(){
Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = conf.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
//----------------------------------------------------------
// 两条横线里面的是对数据库进行操作的内容,譬如这里是想数据库添加一条数据
Customer c = new Customer();
c.setCust_name("scarlett");
session.save(c);//执行保存
//----------------------------------------------------------
tx.commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
当程序运行后会在控制台打印对应放入SQL语句,比如这里是
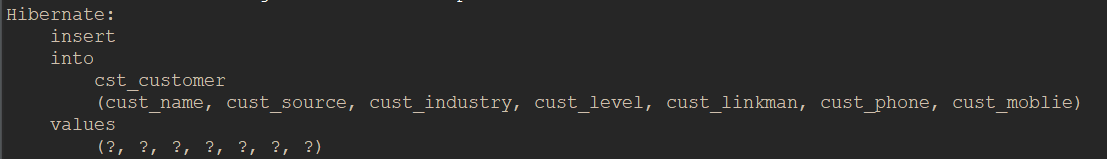
这是数据库中对应的表中也插入了相应的数据




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号