IO流
什么是IO流
流可以看成一堆的数据的运动。输入流可以看成是你从数据源文件读取数据,输出流是将你的数据写到另一个数据文件中。
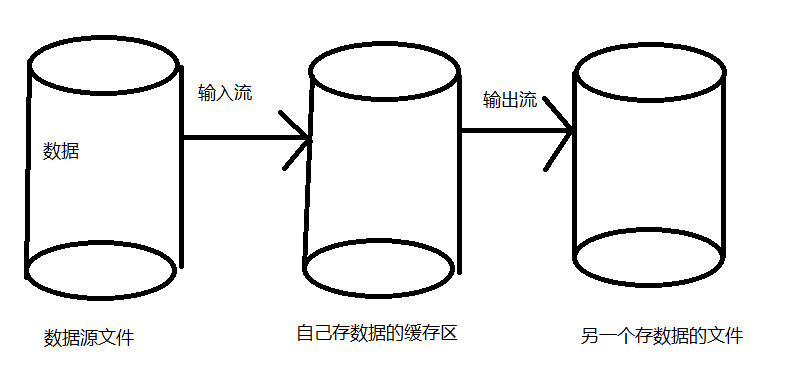
所以,判断要用输入流还是输出流,可以根据你是要把数据读取过来还是写出去来判断。
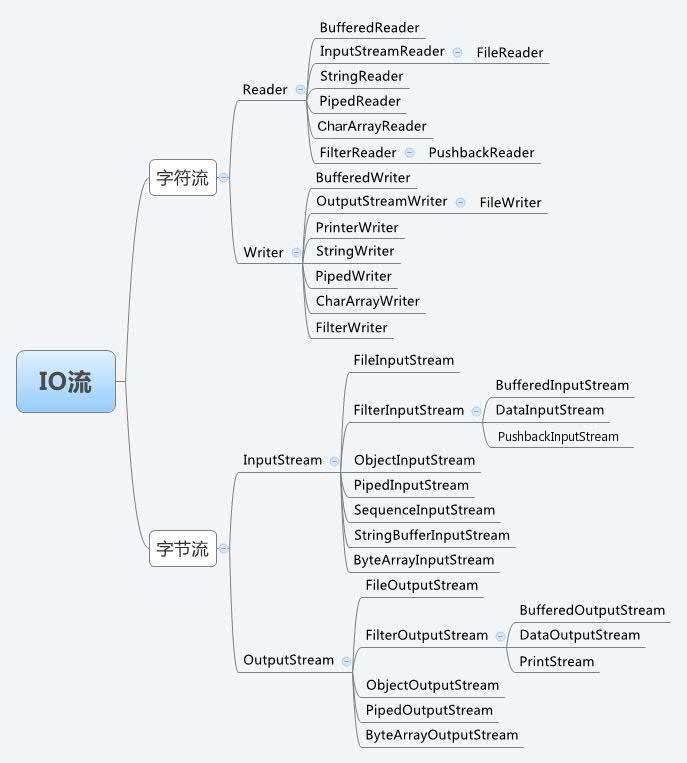
流图继承图:
流的编写格式
由于流对象用完是要关闭的,不然会占资源,有因为流经常要捕获异常,所以,流的关闭放在finally里
public class TestIO1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("f:/a.txt");
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int temp = 0;
//当temp=-1时,表示已经到了文件结尾
while ((temp = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
stringBuilder.append(((char) temp));
}
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
//写在finally里,保证了即使是遇到异常流也会关闭
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
四大IO抽象类
1. InputStream
InputStream是抽象类,是字节输入流的所有类的父类。数据的读取要依靠它的子类来实现,数据的单位为字节。
常用方法:
- int read();读取一个字节的数据,并把字节的值作为int类型的返回值,如未读出字节则返回-1。
- void close():关闭输入流对象,释放资源。
2. OutputStream
OutputStream是抽象类,是字节输出流的所有类的父类。数据的输入要依靠它的子类来实现,数据的单位为字节。
常用方法:
- void write(int n):向目的地写入一个字节。
- void close():关闭输出流对象,释放资源。
3. Reader
Reader用来读取的字符流抽象类,数据单元为字符。
常用方法:
- int read():读取一个字符的数据,并把字符的值作为int类型的返回值,如未读出字符则返回-1。
- void close():关闭输入流对象,释放资源。
4. Writer
Writer用来写出的字符流抽象类,数据单元为字符。
常用方法:
- void writer(int n):向输出流中写入一个字符。
- void close():关闭输出流对象,释放资源。
基流类
1. 字节流类
字节流是以字节为单位获取数据,命名以Stream结尾的流一般是字节流。
FileInputStream、FileOutputStream
//FileInputStream
public class TestIO1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("f:/a.txt");
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int temp = 0;
//当temp=-1时,表示已经到了文件结尾
while ((temp = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
stringBuilder.append(((char) temp));
}
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
//写在finally里,保证了即使是遇到异常流也会关闭
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream
public class TestIO3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将字符串转变成字节数组
byte[] b = "asdfghjkl".getBytes();
fun(b);
}
public static void fun(byte[] b) {
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = null;
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int temp = 0;
//用来白痴读取到的字节数
int num = 0;
try {
byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(b);
while ((temp = byteArrayInputStream.read()) != -1) {
stringBuilder.append((char) temp);
num++;
}
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
System.out.println("读取到的字节数:" + num);
} finally {
try {
byteArrayInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2. 字符流类
字符流是以字符为单位获取数据,命名上以Reader/writer结尾的流一般是字符流。
FileReader、FileWriter
public class TestIO04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fileReader = null;
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
int len = 0;
//缓冲用的字符数组
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
//边读边写
try {
fileReader = new FileReader("f:/a.txt");
fileWriter = new FileWriter("f:/b.txt");
while ((len = fileReader.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fileWriter.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fileWriter != null) {
fileWriter.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fileReader != null) {
fileReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
包装流类
包装流又称为处理流,创建对象时只要传入对应的基流对象就好。
1. 字节包装流类
BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream(缓冲流)
这个流作用是增加缓冲,大大提高读写文本文件的效率
public class TestIO1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("f:/a.txt");
bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);//直接在实例化时将字节基流作为参数放进去就好
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int temp = 0;
//当temp=-1时,表示已经到了文件结尾
while ((temp = bufferedInputStream.read()) != -1) {//后面就直接用缓冲流对象就行了
stringBuilder.append(((char) temp));
}
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (bufferedInputStream != null) {
bufferedInputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
//写在finally里,保证了即使是遇到异常流也会关闭
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
DataInputStream、DataOutputStream(数据流)
数据流是以“基本数据类型与字符串类型”作为数据源。
数据流提供了可以存取与机器无关的所有Java基础类型数据(如:int、double、String等)方法。
public class TestIO06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
DataInputStream dataInputStream = null;
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("f:/a.txt");
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("f:/a.txt");
//用数据流来对基流进行包装
dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(fileInputStream);
//用数据流特有的基础类型数据方法将数据写入文件
dataOutputStream.writeChar('a');
dataOutputStream.writeInt(1);
dataOutputStream.writeDouble(1.1);
dataOutputStream.writeBoolean(true);
dataOutputStream.writeUTF("你好世界");
dataOutputStream.flush();//刷新缓冲区,将流中的数据写入到文件中
//读取数据,要与写入的顺序一样
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readChar());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readInt());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readDouble());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readUTF());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (dataInputStream != null) {
dataInputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (dataOutputStream != null) {
dataOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream(对象流)和序列化、反序列化
对象流是以”对象“为数据源,对”对象“进行序列化和反序列化操作
序列化、反序列化实现:
1.要序列化对象,那个对象所属的类要继承Serializable接口
public class TestIO07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fileInputStream=null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=null;
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream=null;
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream=null;
try {
//实例化一个对象
Studnet studnet=new Studnet("法外狂徒张三",99);
//序列化
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("f:/a.txt");
objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(studnet);
objectOutputStream.flush();
//反序列化
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("f:/a.txt");
objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
Studnet studnet1=(Studnet) objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println(studnet1);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (objectInputStream!=null){
objectInputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fileInputStream!=null){
fileInputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(objectOutputStream!=null){
objectOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(fileOutputStream!=null){
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class Studnet implements Serializable {
//添加序列化ID,它决定着是否能够成功反序列化
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
String name;
int age;
public Studnet(String name,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Studnet{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter(字节->字符)
转流是用来将字节流转化为字符流的。
System.in是字节流对象,是键盘输入的,正常要按行接收用户的输入,就需要用到BufferedReader特有的readLine()。但,BufferedReader要传入的是Reader对象,这时就需要用转换流来解决了。
public class TestIO08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null;
try {
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
//使用字符输入和输出流
String str = bufferedReader.readLine();
//一直读取,直到用户输入end为止
while (!"end".equals(str)) {
//输出到控制台
bufferedWriter.write(str);
bufferedWriter.newLine();//换行
//再继续读取
str = bufferedReader.readLine();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (bufferedWriter != null) {
bufferedWriter.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (bufferedReader != null) {
bufferedReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2. 字符包装流类
BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
public class TestIO05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File src = new File("f:/a.txt");
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src));//将输入字符基流传入
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (null != reader) {
reader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
扩展
1. 简化关闭流的编写
在try后面加一个括号(),IO对象实例化时可以写在括号里,如果有多个用分号“;”隔开,这样就不用在finally里关闭流了。
示例:
public class TestIO07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("f:/a.txt");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("f:/a.txt");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream)) {
//实例化一个对象
Studnet studnet=new Studnet("法外狂徒张三",99);
//序列化
objectOutputStream.writeObject(studnet);
objectOutputStream.flush();
//反序列化
Studnet studnet1=(Studnet) objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println(studnet1);
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Studnet implements Serializable {
//添加序列化ID,它决定着是否能够成功反序列化
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
String name;
int age;
public Studnet(String name,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Studnet{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
2. FileUtils工具类
FileUtils工具类是别人已经将常用的文件操作方法写好了,封装在一起的工具类。我们只需要调用里面的方法,传入方法所需的参数就可以很简单的进行文件的操作了,不用自己编写。
我们想要使用这个工具类要先下载相应的Jar包
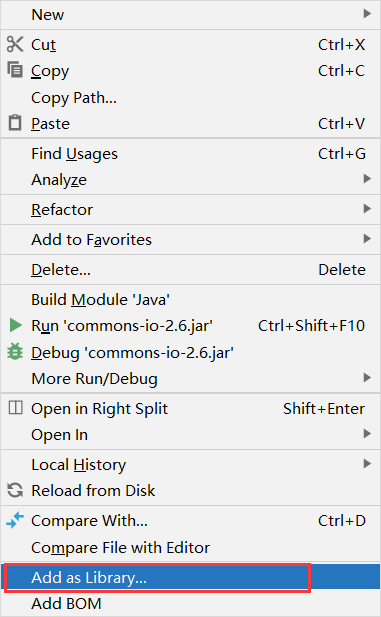
下载后导入jar包的方法
- 在java项目里创一个lib文件夹,将jar包复制粘贴进去
- 然后,点击它按右键在Add as Library那里点击即可使用。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号