VueX的使用
一、Vuex是什么?
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
什么情况下我应该使用 Vuex?
Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,并附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要对短期和长期效益进行权衡。
如果您不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。确实是如此——如果您的应用够简单,您最好不要使用 Vuex。一个简单的 store 模式就足够您所需了。但是,如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,您很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择。
二、使用步骤
1.引入库
先在脚手架中下载 Vuex
npm install vuex --save
在项目的src目录下新增一个utils文件夹,里面建一个store.js
初始化store.js中的内容
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' //挂载Vuex Vue.use(Vuex) //创建VueX对象 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state:{ //存放的键值对就是所要管理的状态 name:'helloVueX' } }) export default store
2.将store挂载到当前项目的Vue实例当中去
打开main.js
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import router from './router' import store from './store' Vue.config.productionTip = false /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', router, store, //store:store 和router一样,将我们创建的Vuex实例挂载到这个vue实例中 render: h => h(App) })
3.在组件中使用Vuex
例如在App.vue中,我们要将state中定义的name拿来在h1标签中显示
<template>
<div id='app'>
name:
<h1>{{ $store.state.name }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
或者要在组件方法中使用
methods:{ add(){ console.log(this.$store.state.name) } },
二、VueX中的属性
state:存放变量
mutations:修改state 中的数据
actions: 只能调用mutations中的方法
getters:类似与计算属性 可以对state中的数据做一些逻辑性操作
modules: 将仓库分模块存储
Vuex工作流程
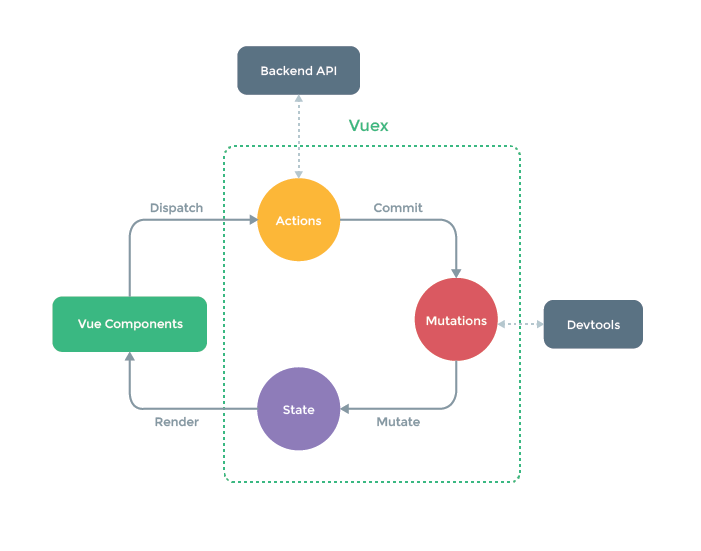
Mutation传值
在实际生产过程中,会遇到需要在提交某个mutation时需要携带一些参数给方法使用。
单个值提交时: this.$store.commit('edit',15) 1 当需要多参提交时,推荐把他们放在一个对象中来提交: this.$store.commit('edit',{age:15,sex:'男'}) 1 接收挂载的参数: edit(state,payload){ state.name = 'jack' console.log(payload) // 15或{age:15,sex:'男'} }
Actions
由于直接在mutation方法中进行异步操作,将会引起数据失效。所以提供了Actions来专门进行异步操作,最终提交mutation方法。
Actions中的方法有两个默认参数
context 上下文(相当于箭头函数中的this)对象
payload 挂载参数
例如,我们在两秒中后执行2.2.2节中的edit方法
由于setTimeout是异步操作,所以需要使用actions
actions:{ aEdit(context,payload){ setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('edit',payload) },2000) } }
在组件中调用: this.$store.dispatch('aEdit',{age:15}) 1 改进: 由于是异步操作,所以我们可以为我们的异步操作封装为一个Promise对象 aEdit(context,payload){ return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{ setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('edit',payload) resolve() },2000) }) }
Getters
可以对state中的成员加工后传递给外界
Getters中的方法有两个默认参数
state 当前VueX对象中的状态对象
getters 当前getters对象,用于将getters下的其他getter拿来用
getters:{ nameInfo(state){ return "姓名:"+state.name }, fullInfo(state,getters){ return getters.nameInfo+'年龄:'+state.age } }
组件中调用
this.$store.getters.fullInfo
Models
当项目庞大,状态非常多时,可以采用模块化管理模式。Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割。
我们在store里面创建一个文件夹moudules.
在moudles中,存放不通模块的处理逻辑。举个例子:
moudules里面放home.js、list.js、login.js
这三个文件呢,里面的结构我们可以这样写:
const state = {}; const getters = {}; const mutations = {}; const actions = {}; export default { // namespaced: true, 这个属性大家自己百度吧,防止命名冲突 state, actions, mutations };
那index.js就很简单了:
import Vue from "vue"; import Vuex from "vuex"; import login from "./modules/login"; import list from "./modules/common"; import home from "./modules/common"; Vue.use(Vuex); export default new Vuex.Store({ modules: { login, list, home} });
这样维护起来是不是就很方便了呢?

models:{
a:{
state:{},
getters:{},
....
}
}
组件内调用模块a的状态:
this.$store.state.a
1
而提交或者dispatch某个方法和以前一样,会自动执行所有模块内的对应type的方法:
this.$store.commit('editKey')
this.$store.dispatch('aEditKey')
映射
在需要使用Vuex的组件中导入
import {mapState} from 'vuex';
映射关系
mapState > computed
mapGetters > computed
mapMutations > methods
mapActions > methods
methods:{ //将store.mutations映射到methods ...mapMutations() //将store.actions映射到methods ...mapMutations() } computed:{ //将store.state中的属性映射到computed ...mapState() //将store.getters映射到computed ...mapGetters() }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号