循环链表实现的队列
循环链表实现队列
队列的实现并不复杂,可以使用数组,也可以使用链表。不管使用哪种方式,队列的数据在逻辑上是线性的,并且遵循先进先出的原则。队列的数据结构中通常要保留两个指向位置,一个头一个尾,头表示先进去的数据,尾表示后进去的数据。我们有时也会使用循环结构来实现队列,比如循环数组、循环链表。使用循环的一个好处是我们通常只需保留一个指向位置。因为队列主要操作是两个,入队与出队,所以只保留一个指向位置要考虑选择哪个位置。队列的第一个元素位置还是队列最后一个元素位置?我们一般选择最后一个位置,当然这并非绝对的。如果使用循环的双向链表,选择哪个位置通常没有影响,但是双向链表会涉及到哨兵节点,这会降低代码简洁性;而对于单向链表,选择最后一个位置可以很自然的过渡到第一个位置。
入队操作比较简单,只需要将最后位置往后添加一个新元素即可,因为它们是循环的。循环链表实现队列的模式图如下:
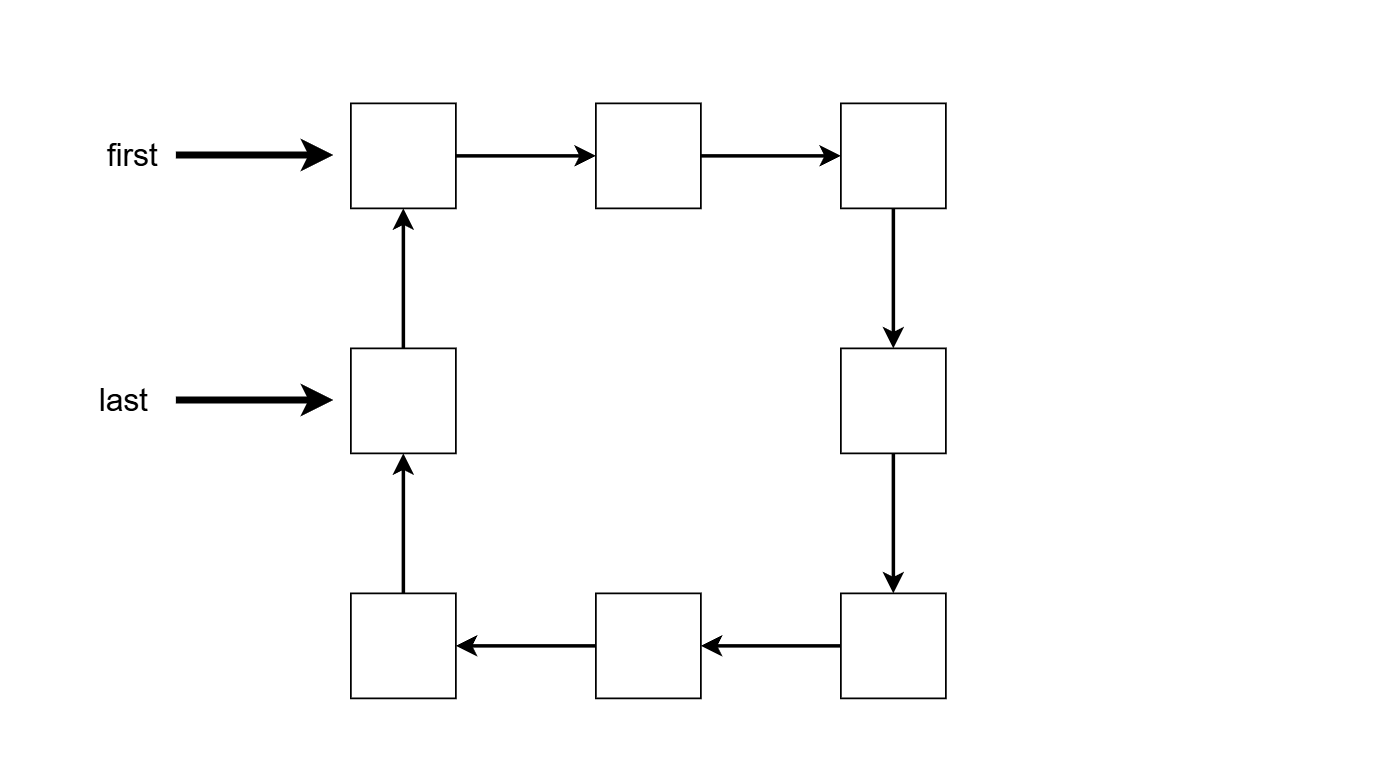
入队操作的代码:
void enqueue( const Object & x )
{ insert( end( ), x ); }
iterator insert( iterator itr, const Object & x )
{
Node * p = itr.current;
if( empty( ) )
{
++theSize;
p->data = x;
return { p };
}
else if( size( ) == 1 )
p->next = new Node{ x, p };
else
p->next = new Node{ x, p->next };
if( itr == end( ) )
last = p->next;
++theSize;
return { p->next };
}
iterator是内置的迭代器。以上作为方法整合在类中。因为是循环的,特别要注意当前队列的大小。在设计时我们需要标记最后位置,所以初始化时有last节点,这个节点并没有数据,并且记录当前队列大小为0。当队列大小为0时,入队操作仅对已被初始化但没有实际数据的last节点补充数据即可;而当队列大小1时,入队要注意形成二元环。入队结束以后要重新设置last位置。
出队操作与入队操作注意点也是队列大小。代码如下:
void dequeue( )
{ erase( end( ) ); }
iterator erase( iterator itr )
{
Node * p = itr.current;
Node * d;
iterator retVal;
if( size( ) > 1 )
{
d = p->next;
p->next = d->next;
retVal = d->next;
}
else
{
d = p;
retVal = nullptr;
}
delete d;
--theSize;
return retVal;
}
在方法dequeue( )中,传入的参数是end( )而非begin( ),这是因为如果队列大小为1时,begin( )与end( )相一致,传入end( )能够处理这一特殊情况。因为传入节点实际是last,而要删除的是第一个元素,基于循环实现,只需last->next即可,这在代码中也体现出来。
完整代码
template <typename Object>
class queueCircular
{
private:
struct Node
{
Object data;
Node * next;
Node( const Object & d = Object{ }, Node * n = nullptr ):
data{ d }, next{ n } { }
Node( Object && d, Node * n = nullptr ):
data{ std::move( d ) }, next{ n } { }
};
int theSize;
Node * last;
void init( )
{
theSize = 0;
last = new Node;
}
public:
class const_iterator
{
protected:
Node * current;
Object & retrieve( )
{ return current->data; }
const_iterator( Node * p ): current{ p } { }
public:
const_iterator( ): current{ nullptr } { }
const Object & operator*( ) const
{ return retrieve( ); }
const_iterator & operator++( )
{
current = current->next;
return *this;
}
const_iterator operator++( int )
{
const_iterator old = *this;
++( *this );
return old;
}
const_iterator operator+( int step )
{
const_iterator new_ = *this;
for( int i = 0; i < step; ++i )
++new_;
return new_;
}
bool operator==( const const_iterator & rhs ) const
{ return current == rhs.current; }
bool operator!=( const const_iterator & rhs ) const
{ return !( *this == rhs ); }
friend class queueCircular<Object>;
};
class iterator: public const_iterator
{
protected:
iterator( Node * p ): const_iterator{ p } { }
public:
iterator( ) { }
Object & operator*( )
{ return const_iterator::retrieve( ); }
const Object & operator*( ) const
{ return const_iterator::operator*( ); }
iterator & operator++( )
{
this->current = this->current->next;
return *this;
}
iterator operator++( int )
{
iterator old = *this;
++( *this );
return old;
}
iterator operator+( int step )
{
iterator new_ = *this;
for( int i = 0; i < step; ++i )
++new_;
return new_;
}
friend class queueCircular<Object>;
};
queueCircular( ) { init( ); }
queueCircular( std::initializer_list<Object> initial )
{
init( );
for( auto & x: initial )
enqueue( x );
}
~queueCircular( )
{ clear( ); }
bool empty( ) const
{ return theSize == 0; }
int size( ) const
{ return theSize; }
iterator begin( )
{
if( empty( ) )
{
std::cerr << "No any element.\n";
exit( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
else if( size( ) == 1 )
return { last };
else
return { last->next };
}
const_iterator begin( ) const
{
if( empty( ) )
{
std::cerr << "No any element.\n";
exit( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
else if( size( ) == 1 )
return { last };
else
return { last->next };
}
iterator end( )
{ return { last }; }
const_iterator end( ) const
{ return { last }; }
Object & front( )
{ return *begin( ); }
const Object & front( ) const
{ return *begin( ); }
Object & back( )
{ return *end( ); }
const Object & back( ) const
{ return *end( ); }
void enqueue( const Object & x )
{ insert( end( ), x ); }
void enqueue( Object && x )
{ insert( end( ), std::move( x ) ); }
void dequeue( )
{ erase( end( ) ); }
void clear( )
{
while( !empty( ) )
dequeue( );
}
void show( ) const
{
Node * p = begin( ).current;
if( !empty( ) )
for( int i = 0; i < size( ) + 1; ++i, p = p->next )
std::cout << p->data << ' ';
std::cout << std::endl;
}
protected:
iterator insert( iterator itr, const Object & x )
{
Node * p = itr.current;
if( empty( ) )
{
++theSize;
p->data = x;
return { p };
}
else if( size( ) == 1 )
p->next = new Node{ x, p };
else
p->next = new Node{ x, p->next };
if( itr == end( ) )
last = p->next;
++theSize;
return { p->next };
}
iterator insert( iterator itr, Object && x )
{
++theSize;
Node * p = itr.current;
if( empty( ) )
{
++theSize;
p->data = std::move( x );
return { p };
}
else if( size( ) == 1 )
p->next = new Node{ std::move( x ), p };
else
p->next = new Node{ std::move( x ), p->next };
if( itr == end( ) )
last = p->next;
++theSize;
return { p->next };
}
iterator erase( iterator itr )
{
Node * p = itr.current;
Node * d;
iterator retVal;
if( size( ) > 1 )
{
d = p->next;
p->next = d->next;
retVal = d->next;
}
else
{
d = p;
retVal = nullptr;
}
delete d;
--theSize;
return retVal;
}
};
protected部分不能被外部使用,这会破坏队列的规则与完整性。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号