一个数组管理两个栈
一个数组管理两个栈
栈实现的一个基础方案是数组,一般来说一个栈对应一个数组,当然这个数组也可以是动态分配。栈是一种先进后出的数据结构,这使得栈这种结构所能传递的信息有限,有时我们需要两个栈。如果按照通常的设计,两个栈对应两个数组,要是数组比较大就会造成空间浪费,所以就有了一个数组管理两个栈。在一个数组中区别两个栈的思路是准备两个迭代器(C++术语,数组中直接用标签定位就好了)。因为数组是线性结构,所以两个迭代器相向而行,一个从低位到高位,另一个从高位到低位。模型图如下:
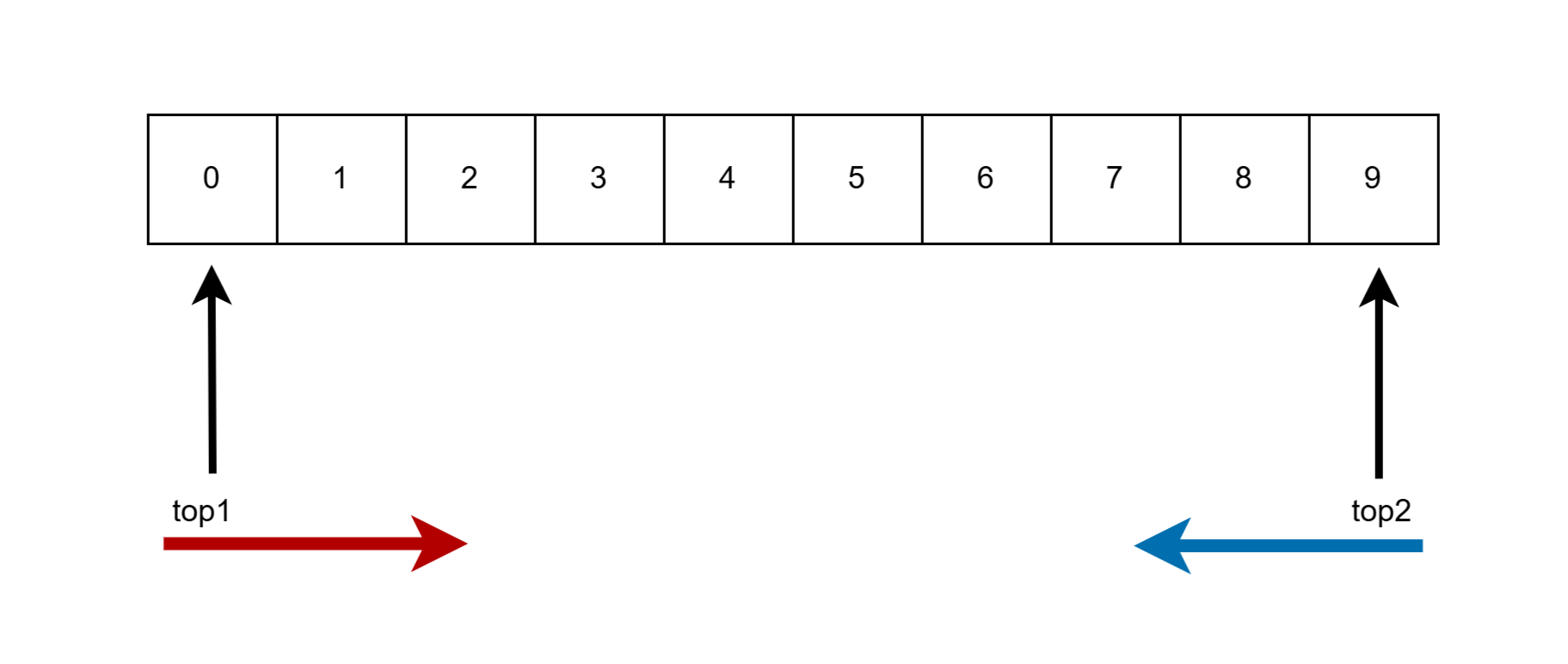
代码大致如下:
template <typename Object>
class Double_Stack
{
private:
static const int CAPCITY = 20;
Object arr[ CAPCITY ];
int top1, top2;
public:
/*
基本函数
*/
// 第一个栈
bool emptyLow( ) const
{
if( top1 > -1 )
return false;
return true;
}
const Object & topLow( ) const
{
if( !emptyLow( ) )
return arr[ top1 ];
}
void popLow( )
{
if( !emptyLow( ) )
--top1;
}
void pushLow( const Object & obj )
{
if( top1 + 1 < top2 )
arr[ ++top1 ] = obj;
}
// 第二个栈
bool emptyHigh( ) const
{
if( top2 < CAPCITY )
return false;
return true;
}
const Object & topHigh( ) const
{
if( !emptyHigh( ) )
return arr[ top2 ];
}
void popHigh( )
{
if( !emptyHigh( ) )
++top2;
}
void pushHigh( const Object & obj )
{
if( top2 - 1 > top1 )
arr[ --top2 ] = obj;
}
...
}
以上的方法均为简写,但是思路差不多。
应用——保留最小元素的栈
因为栈是按照数据添加顺序安排的,所以寻找特定元素比较困难,另一方面,栈数据进出公用一个通路且不是随机访问,即便按序排序也很难找到特定的元素。因此,想要寻找特定元素可以安排两个栈,第一个栈正常使用,第二个栈只有当条件满足的时候才能添加新元素。比如保留最小元素的栈,第一个栈执行栈的常规容器方法,第二个栈根据第一个栈所添加的元素在栈顶添加新元素。
不妨令第一个栈是S,第二个栈是M。这只为叙述方便,在程序设计时变量命名时可自由裁定。
当第一个栈执行
S.push( x )时,如果第二个栈为空或者x小于等于第二个栈的栈顶,则第二个栈执行M.push( x )。当第一个栈执行
S.pop( )时,如果第一个栈在执行S.pop( )前,S的栈顶与M的栈顶相等,则第二个栈也执行M.pop( )。结束后,第二个栈的栈顶即为最小元素。
整体思路如上,细节方面扩充如下述代码所示。
// top1为-1时,第一个栈为空
// top2为CAPCITY时,第二个栈为空
template <typename Object>
class FindMin_Stack
{
private:
static const int CAPCITY = 20;
Object arr[ CAPCITY ];
int top1, top2;
bool emptyMin( ) const
{ return !( top2 < CAPCITY ); }
const Object & topMin( ) const
{
if( !emptyMin( ) )
return arr[ top2 ];
std::cerr << "The stack which stores minimum element is empty!\n";
exit( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
void popMin( )
{
if( !emptyMin( ) && top( ) == topMin( ) )
++top2;
}
void pushMin( const Object & obj )
{
if( top2 - 1 > top1 && ( emptyMin( ) || obj <= topMin( ) ) )
arr[ --top2 ] = obj;
else
std::cerr << "The stack which stores minimum element is full!\n";
}
void pushMin( Object && obj )
{
if( top2 - 1 > top1 && ( emptyMin( ) || obj <= topMin( ) ) )
arr[ --top2 ] = std::move( obj );
else
std::cerr << "The stack which stores minimum element is full!\n";
}
public:
/*
基本函数
*/
bool empty( ) const
{ return !( top1 > -1 ); }
const Object & top( ) const
{
if( !empty( ) )
return arr[ top1 ];
std::cerr << "The stack is empty!";
exit( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
void pop( )
{
if( !empty( ) )
{
popMin( );
--top1;
}
}
void push( const Object & obj )
{
if( top1 + 1 < top2 )
{
arr[ ++top1 ] = obj;
pushMin( obj );
return;
}
std::cerr << "The stack is full!\n";
}
void push( Object && obj )
{
if( top1 + 1 < top2 )
{
arr[ ++top1 ] = std::move( obj );
pushMin( obj );
return;
}
std::cerr << "The stack is full!\n";
}
const Object & findMin( ) const
{ return topMin( ); }
}
第二个栈的多数方法被封装到private部分,这是因为第二个栈是用于存储最小元素的,我们希望它的方法不在客户端中被使用,这样能提高数据隐藏以避免干扰。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号