上海理工大学第二届“联想杯”全国程序设计邀请赛题解
上海理工大学第二届“联想杯”全国程序设计邀请赛
比赛链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/17574
A. A-SOUL!
题意:给出n个数,与公差d。问将n个数重新排列后最长的等差数列的长度是多少。
思路:从小到大排序后用map记录并维护当前数结尾的等差数列长度。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
typedef long long LL ;
const int maxn = 1e5+10;
LL arr[maxn];
int main()
{
memset(arr, 0 ,sizeof arr);
LL n ,k;
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
cin >> arr[i];
}
sort(arr, arr+n);
map<LL , LL> rec;
LL ans = 1;
rec[arr[0]] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<n;++i)
{
LL tem = arr[i];
rec[tem] = max(1LL, rec[tem]);
if(rec.count(tem-k))
{
rec[tem] = max(rec[tem] ,rec[tem-k]+1 );
}
ans = max(ans, rec[tem]);
}
cout << ans;
}
B. Bheith i ngra le
题意:一个n*m的网格,颜色为白或者黑。我们定义当前网格为好。
1.所有黑色的方格为一个联通块
2.对于每一列所有黑色方格的最下端的方格必须是黑色,且该列所有黑色方格必须相连。
我们定义在列i的最高的黑色方格为\(h_i\)。我们定义一个好的网格图为一个山峰,当该网格至少存在一个整数对(l,r)满足
- 1 \(\leq\)l\(\leq\)r\(\leq\)n
- 所有的\(h_i\)(1 \(\leq\) i \(\leq\) l) 是非严格单调递增
- 所有的\(h_i\)(r \(\leq\) i \(\leq\) n)非严格单调递减
- 所有的\(h_i\) (l \(\leq\) i \(\leq\) r)相同
输出n*m的网格中总共可以画几座山,结果mod \(10^9+7\)
思路:
DP[i][j]= \(\sum_{x=1}^n\)DP[i-1][x] * (n+1-x) // O(\(n^2\)*m)
= DP[i][j-1] + \(\sum_{x=1}^j\) ( DP[i-1][x] * (n+1-x) ) //用前缀和后 O(n*m)
ans = \(\sum_{i=1}^n\)\(\sum_{j=1}^m\) ( DP[i][j] * (n+1-j) ) ;
DP[i][j]为底座宽度为j,高度为i的山的种类。
比如DP[3][2] = 5;有5种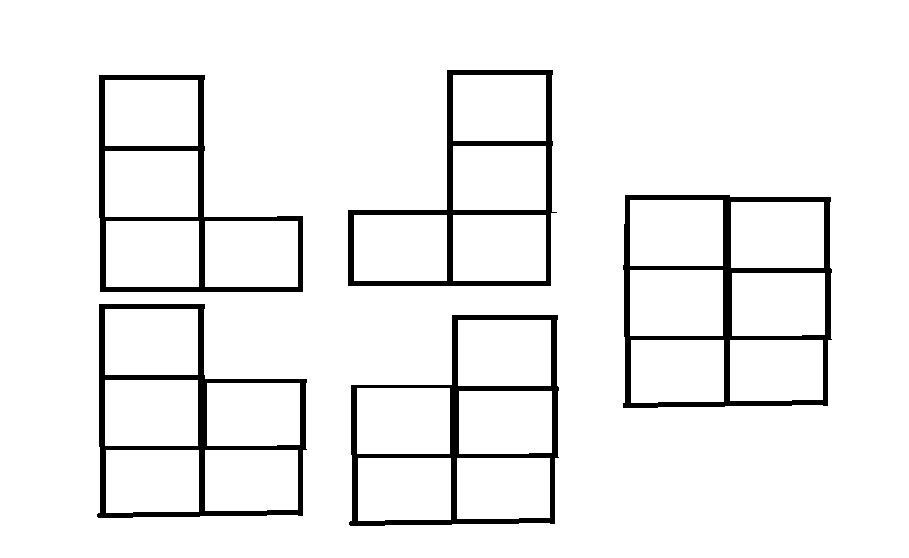
底座长度为3高度为3的山的形状种类DP[3][3] =DP[2][1] * 3 + DP[2][2] * 2 + DP[2][1] * 1,即在长度3的底座长度首先上摆放高度为2底座长度为1的山。同时因为该山底座长度为1,在长度为3的底座上有左、中、右三种摆法。同理高度为2底座长度为2的山有两种摆法,高度为2长度为3的山只有一种摆法。
因此 DP[i][j] = \(\sum_{x=1}^j\)DP[i-1][x] * (j+1-x); 此时时间复杂度为 O(\(n^2*m\)),DP方程可以优化为DP[i][j] = DP[i][j-1] + \(\sum_{x=1}^j\) DP[i-1][x] 用前缀和优化表示
\(\sum_{x=1}^j\) DP[i-1][x],时间复杂度变为了 O(n*m);
当跑到DP[n][m]后,我们以及得到了在画布内可以画出的所有山的形状的数量。将画布视为长度为n的底座, 每种底座长度为j的山,在画布上从最左侧摆到最右侧都有(n+1-j)种摆法方法。
ans = \(\sum_{i=1}^n\)\(\sum_{j=1}^m\) ( DP[i][j] * (n+1-j) ) ;
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
typedef long long LL ;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
const int maxn = 2e3+10;
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
const int INF = 1e9+7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double eps = 1e-7;
LL DP[maxn][maxn];
LL pre[maxn];
void solve()
{
int n, m;cin >>n >> m;
memset(pre, 0, sizeof pre);
LL ans = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j)
{
if(j==1)
{
DP[i][j] = 1;
pre[j] = 1;
}
else
{
DP[i][j] = (DP[i][j-1]+pre[j]) % MOD;
pre[j] = (DP[i][j]+ pre[j-1])%MOD;
}
ans = (ans%MOD + (DP[i][j] * (n+1-j)) % MOD) % MOD;
}
printf("%lld" , (ans+1)%MOD);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
}
C.Counting Cats!
题意:给出一系列字符串,"c" "a" "t" "ca" "at" "cat"有用,问最多这些字符串可以拼接出几个"cat"字符串。
思路:直接匹配
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
typedef long long LL ;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
const int maxn = 1e5+10;
const int MOD = 998244353;
const int INF = 1e9+7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double eps = 1e-7;
int rec[10];
void solve()
{
int n ;cin >> n;
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
string x;cin >> x;
if(x=="c") rec[0]++;
if(x=="a") rec[1]++;
if(x=="t") rec[2]++;
if(x=="ca") rec[3]++;
if(x=="at") rec[4] ++;
if(x=="cat") ans++;
}
int tem= INF;
ans+=min(rec[0] , rec[4]);
tem = min(rec[0] , rec[4]);
rec[0]-=tem;
rec[4]-=tem;
tem = INF;
tem = min(rec[2], rec[3]);
ans+=tem;
rec[2]-=tem;
rec[3]-=tem;
ans+=min(rec[0], min(rec[1], rec[2]));
printf("%d", ans);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
}
D.Dahno Dahno
题意: 给出N个物品,你要将物品分成两A类,B类。每类都不能为空。当物品i,j在同一类中时会产生\(v_{i,j}\) + \(v_{j, i}\) 的能量,求最大的能量值.
思路:先假设可以得到所有能量,所有能量减去无向图最小割即可。无向图最小割Stoer_Wagner算法模板题。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<sstream>
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
#define REP(i,a,b) for(LL i=a;i<b;i++)
typedef long long LL ;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef pair<LL, LL> P;
const LL maxn = 5e2+5;
const LL MOD = 1e9+7;
const LL INF = 1e9+7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double eps = 1e-7;
LL G[maxn][maxn]; //临接矩阵表示边,时间复杂度为O(n^3),因此空间一定放的下
LL f[maxn]; // v[i]代表节点i合并到的顶点
LL w[maxn]; // 定义w(A,x) = ∑w(v[i],x),v[i]∈A
bool vis[maxn]; // 标记该点是否加入A集合。
LL squ[maxn]; //记录移除的节点次序,用于输出两个割的内容
LL Index ; //标记最后一次更新最小割的位置,作为两个割的分界线
LL Stoer_Wagner(LL n)
{
LL min_cnt = INF, r = 0;
for(LL i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
f[i] = i;// 初始还未合并,都代表节点本身
}
while(n > 1 )
{
// printf("TEST1\n");
LL pre = 0 ;// pre用来表示之前加入A集合的点(在t之前一个加进去的点)
memset(vis, 0 , sizeof vis);
memset(w, 0 , sizeof w);
for(LL i = 0 ; i < n -1 ;++i)
{
//printf("TEST2\n");
LL k = -1;
for(LL j = 1 ; j < n; ++j)
{
if(!vis[f[j]])
{
w[ f[j] ] += G[ f[pre] ][f[j]];
if(k == -1 || w[f[k]] < w[f[j]])
{
k =j;
LL x = x;
}
}
}
vis[f[k]] = true; //标记该点x已经加入A集合
if(i==n-2) //若|A|=|V|(所有点都加入了A),结束
{
// printf("pre = %lld k =%lld \n", pre, k);
const LL u = f[pre] , v = f[k]; // 令倒数第二个加入A的点(v[pre])为s,最后一个加入A的点(v[k])为t
//printf("%lld ----> %lld \n" , v ,u); //v 向 u 合并
squ[r++] = v;
if(w[v] < min_cnt)// 则s-t最小割为w(A,v),用其更新min_cut
{
min_cnt = w[v];
Index = r;
}
for(LL j = 0; j < n ; ++j)// merge(u, v)
{
G[u][f[j]] += G[f[j]][v];
G[f[j]][u] += G[f[j]][v];
}
f[k] = f[--n];
}
pre = k;
}
}
return min_cnt;
}
void solve()
{
LL n ;cin >> n;
memset( G, 0, sizeof G);
LL ans = 0;
for(LL i=0;i<n;++i)
{
for(LL j=0 ; j < n; ++j)
{
LL x; cin >> x;
ans += x;
G[i][j] +=x;
G[j][i] +=x;
}
}
//printf("归并的步骤为:\n");
LL res = Stoer_Wagner(n);
// printf("最小割为%lld \n 图划分部分为A:" , res);
// for(LL i=0; i < n;++i)
// {
// if(i==Index)
// printf("部分B:");
// printf("%lld ", squ[i]);
// }
// printf("\n");
printf("%lld", ans - res);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
return 0 ;
}
E.Experiment Class
题意:给出点A , B, C, D 和原点O(0, 0)都在第一象限且A , B 不和原点重合.问从C出发经过射线OA, OB后到达点D的最短距离.
思路:首先找出OA, OB中斜率大(小)的射线记为:UP(down),和OC,OD中斜率较大(小)的点记为:P_up,(p_down)。现在有四种情况。
1.两点都在OA,OB所成夹角之外,直接连接CD即为最短距离。
2.P_up在夹角内,P_downD在夹角外。此时做P_up关于射线UP的对称点,连接对称点和P_down即为最小距离。
3.P_down在角内,P_up在角外。同理做P_dow关于射线DOWN的对称点,连接对称点和P_up。即为最小距离。
4.二者都在角内,此时做P_up关于射线UP的对称点,做P_dow关于射线DOWN的对称点,连接二个对称点即为最小距离。
最后我要吐槽官方题解点在角内,角外写反了
大佬们的优美代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
using namespace std;
void get(double a, double b, double& x, double& y)//求点关于直线的对称点。
{
// a b c为直线的一般式参数
//公式 x'=((b*b-a*a)*x-2*a*b*y-2*a*c)/(a*a+b*b);
// y'=((b*b-a*a)*y-2*a*b*x-2*b*c)/(a*a+b*b);
double x1 = ((b * b - a * a) * x - 2 * a * b * y ) / (a * a + b * b);
double y1 = ((a * a - b * b) * y - 2 * a * b * x ) / (a * a + b * b);
x = x1, y = y1;
}
int main()
{
double a, b, c, d, x0, y0, x1, y1;
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &a, &b, &c, &d, &x0, &y0, &x1, &y1);
if (b * c < a * d)swap(a, c), swap(b, d);//两条河边按照斜率排序
if (y0 * x1 < y1 * x0)swap(x0, x1), swap(y0, y1);//两个点按照斜率排序
if (b * x0 > y0 * a)get(-b, a, x0, y0);//把上面那个点翻到角外面
if (c * y1 > x1 * d)get(-d, c, x1, y1);//把下面那个点翻到角外面
printf("%.3lf\n", sqrt((x1 - x0) * (x1 - x0) + (y1 - y0) * (y1 - y0)));//两点之间直线最短
return 0;
}
我补题时丑陋的模板代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<sstream>
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
typedef long long LL ;
typedef unsigned long long Uint;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
const int maxn = 5e2+5;
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
const int INF = 1e9+7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double eps = 1e-7;
struct Point
{
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0 , double y = 0) : x(x) , y(y) {}
};
typedef Point Vector;
Vector operator + (Vector A, Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x + B.x , A.y + B.y);
}
Vector operator - (Vector A, Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x - B.x , A.y - B.y);
}
Vector operator * (Vector A, double p)
{
return Vector(A.x * p , A.y * p);
}
struct Line
{
Point v, p;
Line(Point v, Point p) : v(v) , p(p) {}
Point Point(double t)
{
return v + (p-v)*t;
}
};
double Dot(Vector A, Vector B)
{
return A.x * B.x + A.y *B.y;
}
Point GetLineProjection(Point P, Point A, Point B)
{
Vector v = B - A;
return A + v * ( Dot(v, P - A) / Dot(v, v));
}
Point GetLineSymmetry(Point a, Line b)
{
Point c = GetLineProjection(a, b.p, b.v);
return a + ((c - a)*2);
}
void solve()
{
Point b , c ,d ,e;
Point start;
cin >> b.x >>b.y >>c.x >> c.y >>d.x >>d.y >>e.x >>e.y;
Line up = Line(start , b) , down = Line(start ,c);
if(up.p.y*down.p.x <= up.p.x*down.p.y) swap(up, down);
if(d.y*e.x <= d.x*e.y) swap(d, e);
if(up.p.y*d.x > up.p.x*d.y)
{
d = GetLineSymmetry(d , up);
}
if(down.p.y*e.x < down.p.x * e.y)
{
e =GetLineSymmetry(e, down);
}
Vector ans = d-e;
printf("%.3lf", sqrt(Dot(ans , ans)));
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
return 0 ;
}
I. Identical Day
题意:给出一串01串和k,当存在一段连续的1长度为n.这段1的UNHAPPY值为n *(n+1)/2.给出01串的UNHAPPY值为所有连续的1的UNHAPPY值之和记为 ALL。现在你可以用一次操作将01串中的1变为0.求使用最少的操作次数使得给出01串的ALL值\(\leq\) k。
最开始我想到的是每次找到最长的1,然后将中间的1变为0.但是11111按照我的思路两次操作后变为10011,显然正确的操作是变为10101。
正确的方法我们先定义(L, X)是将长度为L的1串进行X-1次操作,平均分为X段1之后获得的UNHAPPY值。首先我们要证明有 (L, X) - (L,X+1) \(\geq\) (L,Y)-(L,Y+1) 当(X< Y).(但是这个我整不出来).对于01串中每一段连续1,将一次操作后ALL的减少值(L, X+1) - (L, X) (1 \(\leq\) X \(\leq\) L)存入优先队列。然后我们每次取队列中最大的数就是当前的最优的ALL减少值,此时一次操作所能获得的最大的差值,同时ans+1.当ALL <= k时 ans即为结果。
最开始时我可以理解每次取的值就是最优,但是无法理解为什么这个最优的值可以取得到?因为我的想法是如果有最开始时如果有(L, 4) - (L , 3)就是最优,但是在最开始不存在(L, 3)这个状态。后面手推了几次之后感觉有上面那个不等式。在优先队列中的最大值必定是那些(L,X) 中 X更小的情况,因此不可能直接跳过当前可行分割的状态,而从队列中取出之后的分割状态。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<sstream>
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
typedef long long LL ;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
const int maxn = 2e7+10;
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
const int INF = 1e9+7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double eps = 1e-7;
LL calc(LL len, LL x)
{
len -= (x-1);
LL a = len / x;
LL b = len %x;
LL res= (x - b) * (a) * (a+1) / 2 + (b) * (a+1) * (a+2) /2;
//printf("len = %lld, x= %lld, res = %lld \n", len, x, res);
return res;
}
void solve()
{
LL n , k;cin >> n >> k;
LL ans = 0;
LL sum = 0;
LL len = 0;
string arr;cin >>arr;
vector<LL> rec;
priority_queue<LL> full;
for(int i=0;i<arr.size();++i)
{
if(arr[i]=='0')
{
if(len>0)
{
sum += len*(len+1)/2;
rec.push_back(len);
len = 0 ;
}
}
else
{
len++;
}
}
if(len)
{
rec.push_back(len);
sum += len *(len+1) /2;
}
for(int i=0;i<rec.size();++i)
for(int k=1;k<=rec[i];++k)
{
full.push(calc(rec[i], k) - calc(rec[i], k+1));
}
while(sum>k)
{
ans ++;
//printf("%lld\n", full.top());
sum -= full.top();full.pop();
}
printf("%lld", ans);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
return 0 ;
}
J. JXC&Jesus
题意:懒得写了
只要我们迅速得到x的最小的质数因子,就可以迅速计算出f(x,m)。因此问题就在于如何快速得到最小的质数因子。线性筛法正是通过枚举合数的最小质因子来筛取素数。先预处理\(10^7\)个数得到它们的最小质因子即可。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
typedef long long LL ;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
const int maxn = 2e7+10;
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
const int INF = 1e9+7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double eps = 1e-7;
LL pre[maxn];
void init()
{
for(int i=2;i<=maxn-5;++i)
{
if(pre[i]) continue;
for(int k=i;k<=maxn-5;k+=i)
{
if(pre[k]) continue;
pre[k] = i;
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
LL n , m , L;
cin >> n >>m >> L;
init();
LL ans = 0;
if(m==1)
{
printf("0");
return 0;
}
for(int i=L+1;i<=L+n;++i)
{
LL di = pre[i];
LL tem = i;
LL cnt = 0;
while(tem%di==0)
{
cnt++;tem/=di;
}
tem = i;
cnt = cnt - cnt/m;
while(cnt--) tem/=di;
ans += i-tem;
}
cout << ans;
}
K. Kazusa’s Party
题意:有男女生各n个人,每个男生有一个整数a,女生有一个整数b。当一对男女gcd(a , b)> 1,男女可以配对。问最多有几个配对。
n <= 8直接暴力枚举。
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
typedef long long LL ;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
const int maxn = 1e5+10;
const int MOD = 998244353;
const int INF = 1e9+7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double eps = 1e-7;
LL arr[maxn];
int boy[19];
int girl[10];
int p[19];
int n;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
while(a^=b^=a^=b%=a);
return b;
}
int calc()
{
int rec= 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
if(gcd(boy[i], girl[p[i]])>1) rec++;
}
return rec;
}
void solve()
{
memset(boy, 0 , sizeof boy);
memset(girl , 0 ,sizeof girl);
for(int i=1;i<=8;++i)
p[i] = i;
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
cin >> boy[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
cin >> girl[i];
}
int ans = 0;
do
{
ans = max(ans, calc());
}while(next_permutation(p+1, p+1+n));
cout << ans;
}
int main()
{
solve();
}
L. Little Witch Academia
题意:你有宽度为a高度为1和宽度为b高度为1的砖很多个。两种砖块宽度不等现在要砌一个高度为h宽度为w的墙。同时你的砖不能旋转,只能横着摆。同时为了墙的安全,上下两层不能存在位置相同的竖缝。比如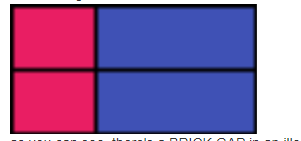
。但是最左侧与最右侧的边缘不算,因此可以由一块砖构成一层。
墙最宽为20,而砖块最短为2和3.此时一层有114种摆放方法。因此最多有每层有114种情况。将每种情况用整数表示,二进制的1即为缝的位置。当两种情况A&B==0,这两种可以摆放在相邻层。
dfs搜索一层中所有的摆放情况,用无向图中的点表示一层的所有摆放情况,两个点之间有边表示这两种情况可以摆放在相邻层。问题便转化为了在一个无向图中从任意点出发走h-1步,共有多少种路径。
用矩阵\(A_k\)[i][j],走了k步之后,从i出发在j结束有几种不同的路径。T[i][j]=1表点i, j 之间有边。有\(A_{k+1}\)= \(A_k\)* T.
\(A_0\)为单位矩阵, \(A_k\) = T * \({A_0}^k\). ans = \(\sum\)\(A_{h-1}\) .运用矩阵快速幂时间复杂度为O(\(114^3*log^{10^9}\)).
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<sstream>
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
typedef long long LL ;
typedef unsigned long long Uint;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
const int maxn = 122;
const LL MOD = 1e9+7;
const int INF = 1e9+7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double eps = 1e-7;
struct Matrix
{
LL n , m;
LL a[maxn][maxn];
void clear()
{
n = m = 0;
memset(a, 0 , sizeof a);
}
Matrix operator * (const Matrix & b) const
{
Matrix tem;
tem.clear();
tem.n = n; tem.m = m;
for(int i = 0 ;i < n;++i)
for(int j = 0; j < b.m;++j)
for(int k=0;k<m;++k)
tem.a[i][j] = (tem.a[i][j] + (a[i][k] * b.a[k][j]) % MOD ) %MOD;
return tem;
}
};
Matrix qpow(Matrix T , LL n )
{
Matrix res;
res.clear();
// printf("T.n = %lld\n", T.n);
res.n = res.m = T.n;
for(int i=0 ; i<res.n;++i)
res.a[i][i] = 1;
while(n)
{
// printf("1\n");
if(n&1) res= res * T;
T = T * T;
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
vector<LL> rec;
void dfs(LL now ,LL gap , LL a, LL b , LL w)
{
// printf("now = %lld, a =%lld, b =%lld ,gap = %lld\n",now, a, b, gap);
if(now>w) return;
if(now==w) { rec.push_back(gap);return;}
if(now+a==w) dfs(now+a, gap, a, b, w);
else dfs(now+a, gap|(1<<(now+a)), a, b, w);
if(now+b==w) dfs(now+b, gap, a, b, w);
else dfs(now+b, gap|(1<<(now+b)), a, b, w);
return;
}
void solve()
{
rec.clear();
LL a , b ,w , h;cin >> a >> b >>w >> h;
dfs(0, 0, a, b, w);
int len = rec.size();
// printf("len = %lld\n" , len);
Matrix res ;
res.clear();
res. m = res.n = len;
for(int i=0 ; i< len ;++i)
for(int j = 0 ; j < len ; ++j)
{
LL a =rec[i] , b = rec[j];
if(a&b) continue;
res.a[i][j] = 1;
res.a[j][i] = 1;
// printf(" i = %d, j = %d\n", i , j);
}
LL ans = 0;
res = qpow(res , h-1);
for(int i=0;i<res.n;++i)
{
for(int j =0 ;j <res.m;++j)
{
ans = (ans + res.a[i][j]) % MOD;
}
}
printf("%lld\n" , ans);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int T;cin >> T;
while(T--)
solve();
}
M. Minecraft
题意:将长宽高为(n, m ,h)的立方体中的每一个位置用A-Z中的一个字母标记。每次你可以选择一个字母,然后空间中该字母位置的会放置一个沙子,一个沙子会掉落当该沙子下方没有沙子。为是否可以选择一系列字母顺序使得该立方体被填满。如果可以输出最大的字典序字母序列,不能输出-1.
思路:遍历第一层,对于每一个方格从下到上建立有向图后拓扑排序,并同时用优先队列维护最大字典序。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
typedef long long LL ;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
const int maxn = 2e3+10;
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
const int INF = 1e9+7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double eps = 1e-7;
string bloc[33][33];
int n, m , h;
int T;
int in[400];
int vis[400];
vector<int> vex[400];
void solve()
{
cin >> n >>m >>h;
//cout <<n <<m << h;
memset(in, 0, sizeof in);
memset(vis, 0 , sizeof vis);
for(int i='A';i<='Z';++i)
vex[i].clear();
for(int i=0;i<30;++i)
for(int k=0;k<30;++k)
bloc[i][k].clear();
for(int i=h-1;i>=0;--i)
{
for(int k=0;k<n;++k)
{
cin >>bloc[i][k];
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
for(int j =0 ; j<m;++j)
{
int now = bloc[0][i][j];
vis[now] = 1;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
for(int j =0 ; j<m;++j)
for(int k=0;k<h-1;k++)
{
int now = bloc[k][i][j];
int Next= bloc[k+1][i][j];
vis[now] = 1;
vis[Next] = 1;
if(now!=Next)
{
vex[now].push_back(Next);
in[Next]++;
}
}
priority_queue<int> rec;
for(int i='A';i<='Z';++i)
if(!in[i]) {rec.push(i);}
vector<int> ans;
int cnt = 0;
while(!rec.empty())
{
cnt++;
int u = rec.top();
rec.pop();
ans.push_back(u);
for(int i=0;i<vex[u].size();++i)
{
int v = vex[u][i];
in[v]--;
if(in[v]==0)
{
rec.push(v);
}
}
}
if(cnt< 26)
{
printf("-1");
}
else
{
for(auto c:ans)
if(vis[c])printf("%c", c);
}
printf("\n");
return;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> T;
while(T--)
solve();
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号