算法随想Day8【字符串】| LC28-实现 strStr() 、LC459-重复的子字符串
KMP算法
前缀是包含首字母,不包含尾字母的所有子串。
后缀是包含尾字母,不包含首字母的所有子串。
如有:
文本串 aabaabaaf
模式串 aabaaf
对模式串来说,其前后缀:
| 前缀有 | 后缀有 |
|---|---|
| a | f |
| aa | af |
| aab | aaf |
| aaba | baaf |
| aabaa | abaaf |
前缀表,通常被称为next数组
| a | 0 |
|---|---|
| aa | 1 |
| aab | 0 |
| aaba | 1 |
| aabaa | 2 |
| aabaaf | 0 |
这样就对模式串生成了一个序列:
a a b a a f
0 1 0 1 2 0
遇到第一个不匹配的字符时,如aabaaf匹配文本串,遇到第一个不匹配的为f字符,然后找f前面那个字符在序列中对应的数值(“2”),之后的匹配就不用从模式串的第一个a开始匹配了,可以从aabaa中的a开始,而b的索引下标刚好是最长相等前缀的长度 -- “2”。
next数组的实现
初始化:
-
前缀末尾:prefix_tail,同时也代表着suffix_tail,包括suffix_tail之前的子串的最长相等前后缀的长度
-
后缀末尾:suffix_tail,这里的后缀末尾指的是,如aabaa中的第三个"a"
需要比较前缀和后缀所对应的字符是否相等,因为后缀是不包含字符串的首字母的,所以suffix_tail应该初始化为1。
在建立next数组时,要考虑的情况有:
- 前后缀不相同的情况:不断地让prefix_tail往回退,直到重新与当前suffix匹配或回到字符串首字母
- 前后缀相同的情况:让prefix_tail向前走一步
void getNext(vector<int>& next, string s)
{
int prefix_tail = 0;
//vector<int> next(s.size(), 0)
next[0] = 0;
for (suffix_tail = 1; suffix_tail < s.size(); suffix_tail++)
{
while (prefix_tail > 0 && s[suffix_tail] != s[prefix_tail])
{
prefix_tail = next[prefix_tail - 1];
}
if (s[suffix_tail] == s[prefix_tail])
{
prefix_tail++;
}
next[suffix_tail] = prefix_tail;
}
}
模拟运行过程时,从头遍历的是文本串,如若遇到某个模式串的字符与当前文本串指向字符不同的时候,让模式串的当前指针根据next表( next[ptr_needle - 1] )进行回退。
int strStr(string haystack, string needle)
{
if (needle.size() == 0) //和库函数strstr()保持一致
{
return 0;
}
int needle_size = needle.size();
vector<int> next(needle_size, 0);
getNext(next, needle);
int ptr_needle = 0, ptr_haystack = 0;
for (ptr_haystack = 0; ptr_haystack < haystack.size(); ptr_haystack++)
{
while (ptr_needle > 0 && needle[ptr_needle] != haystack[ptr_haystack])
{
ptr_needle = next[ptr_needle - 1];
}
if (needle[ptr_needle] == haystack[ptr_haystack])
{
ptr_needle++;
}
if (ptr_needle == needle_size)
{
return (ptr_haystack - needle_size + 1);
}
}
}
思考总结:
创建next数组和模拟运行,这两个过程的编码思想十分的相似,但又有些细节的不同。
-
创建next数组中,是在模式串中运用双指针,固定一个指针(suffix)用于遍历,而另一个prefix是根据suffix的行为而动态移动的。
-
模拟运行中,在文本串和模式串中各自应用一个指针,其中文本串的指针用于从头遍历,而模式串中的指针则根据前者的行为而动态移动。
LC459. 重复的子字符串
暴力解法
bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string s)
{
int i, j;
bool flag = true;
int size = s.size();
if (size < 2)
{
return false;
}
for (i = 1; i < (size >> 1); i++) //这里要用<=,即对半分字符串的情况
{
if (size % i != 0)
{
continue;
}
flag = true;
for (j = i; j < size; j++)
{
if (s[j] != s[j - i])
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
移除匹配法:
bool repeatedSubstringPattern_erase(string s)
{
string str = s + s;
str.erase(str.begin()); //对新字符串进行掐头去尾
str.erase(str.end() - 1);
//新字符串中若能再出现s,说明满足题意
if ((str.find(s)) == std::string::npos)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
KMP妙解法:
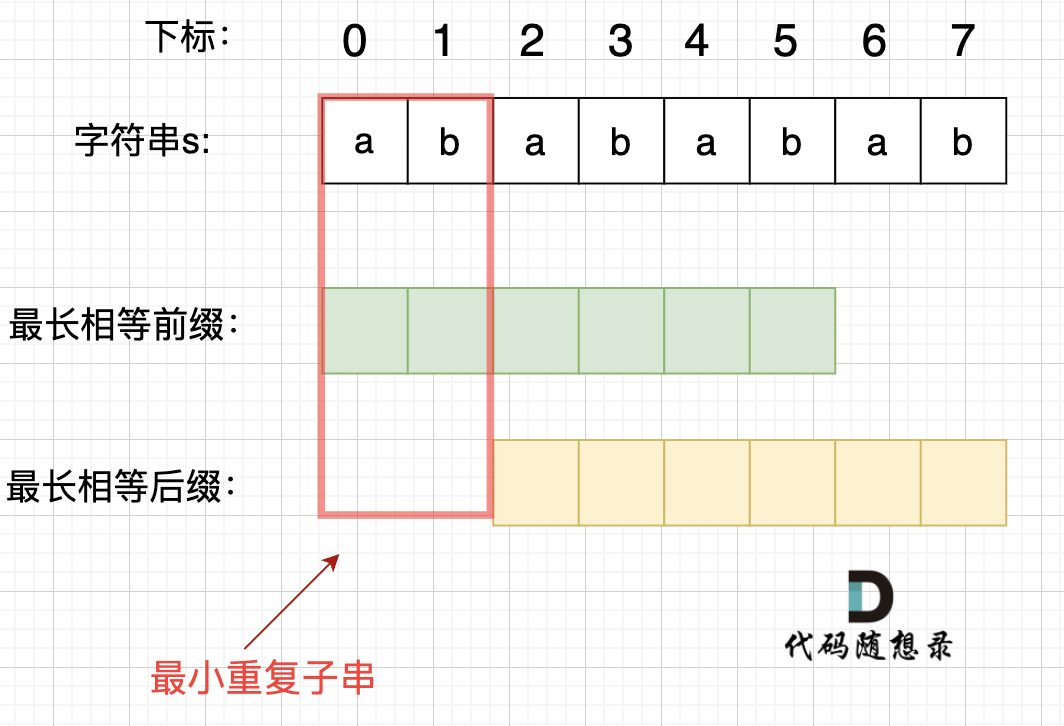
找到字符串的最长相等前后缀,如果该字符串是由重复的子字符串构成的,最长相等前缀和最长相等后缀是相同的,两者错开的长度,就是会重复的子字符串。
对abababab,next数组应该为00123456,通过数学公式,可推得:
next[len - 1] != 0 && len % (len - (next[len - 1] ) == 0
代码实现:
class Solution {
public:
void getNext (int* next, const string& s){
next[0] = 0;
int j = 0;
for(int i = 1;i < s.size(); i++){
while(j > 0 && s[i] != s[j]) {
j = next[j - 1];
}
if(s[i] == s[j]) {
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
}
bool repeatedSubstringPattern (string s) {
if (s.size() == 0) {
return false;
}
int next[s.size()];
getNext(next, s);
int len = s.size();
if (next[len - 1] != 0 && len % (len - (next[len - 1] )) == 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
};




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号