跟着迪哥学Python数据分析和机器学习(一)
Numpy
1、ndarray中所有元素必须是同一类型,否则会自动向下转换,int→float→str
2、得到索引位置
df['amount'].argmin()
out:最小值的index
3、用元素的索引位置替代排序后的实际结果
np.argsort(df['amount'])
4、按照大小顺序把它们插入刚创建的数组中,返回位置
values=np.array([2,5,10,6,7,4,5]) add_np=np.array([1,9]) np.searchsorted(values,add_np) out:array([0, 7], dtype=int64)
5、文件读写
%%writefile tang.txt # %%writefile myFirstBook.py # Notebook的魔法指令,相当于写一个文件 1 2 3 4
罗列Notebook所有魔法
%lsmagic
tips:使用魔法方法前不能有任何内容
pandas
1、iloc():用位置找数据
df.iloc[0]
df.iloc[0:5]
df.iloc[1:5,1:4] # 1-5行,1-4列
2、loc():用标签找数据
ddd=ddd.assign(name=['A','B','C','D']) ddd.set_index(['name'],inplace=True) ddd.loc['A']
ddd.loc[['A','B']]
3、设置显示 set_option、获取当前设置参数get_option
pd.set_option('display.max_rows',6) # 设置显示6条数据 pd.set_option('display.max_columns',6) # 设置显示6行数据
4、读取数据时,如果想以时间特征为索引,可以将parse_dates参数设置为True
data=pd.read_csv('....',index_col=0,parse_dates=True)
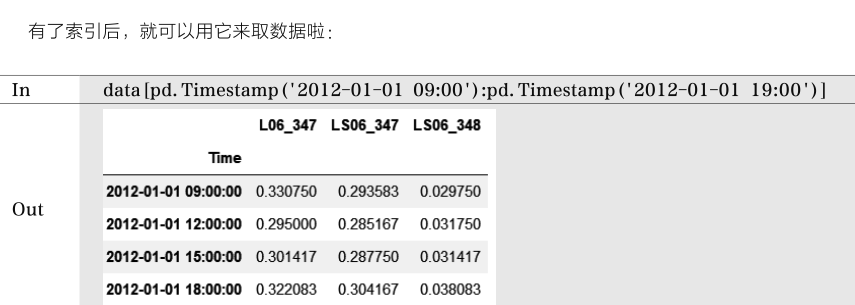
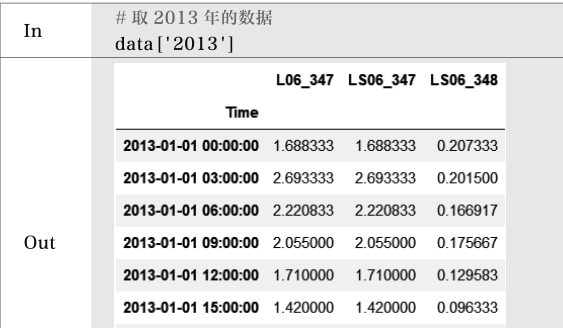
也用data['2012-01':'2012-03']指定具体月份,或者更细致一些,在小时上继续进行判断,如data[(data.index.hour>8)&(data.index.hur<12)]
5、resample 重采样
Pandas中的resample,重新采样,是对原样本重新处理的一个方法,是一个对常规时间序列数据重新采样和频率转换的便捷的方法。
方法的格式是:
DataFrame.resample(rule, how=None, axis=0, fill_method=None, closed=None, label=None, convention='start',kind=None, loffset=None, limit=None, base=0)
# 按天统计 data.resample('D').mean().head() # 按3天统计 data.resample('3D').mean().head() # 按月统计 data.resample('M').mean().head()
6、DataFrame.select_dtypes(include=None, exclude=None)
Notes
- 要选择所有数字类型,请使用
np.number或'number' - 要选择字符串,您必须使用
objectdtype,但是请注意,这将返回所有对象dtype列 - 请参见numpy dtype层次结构
- 要选择日期时间,使用
np.datetime64,'datetime'或'datetime64' - 要选择
timedeltas,使用np.timedelta64,'timedelta'或'timedelta64' - 要选择
Pandas类别dtype,请使用'category' - 要选择
Pandas datetimetz dtypes,请使用'datetimetz'(0.20.0中的新增功能)或'datetime64[ns, tz]'
xrp_out_detail.select_dtypes(include=['O']) xrp_out_detail.select_dtypes(include=['int'])


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号