Qt迷宫实现简单的创建和寻路
一,问题描述
1,问题描述
迷宫实验是取自心理学的一个古典实验。在该实验中,把一只老鼠从一个无顶大盒子的门放入,在盒中设置了许多墙,对行进方向形成了多处阻挡。盒子仅有一个出口,在出口处放置一块奶酪,吸引老鼠在迷宫中寻找道路以到达出口。对同一只老鼠重复进行上述实验,一直到老鼠从入口到出口,而不走错一步。老鼠经多次试验终于得到它学习走迷宫的路线。
2,设计功能要求
迷宫由 m 行 n 列的二维数组设置,0 表示无障碍,1 表示有障碍。设入口为(1,1),出口为(m,n),每次只能从一个无障碍单元移到周围四个方向上任一无障碍单元。编程实现对任意设定的迷宫,求出一条从入口到出口的通路,或得出没有通路的结论。
- 算法输入:代表迷宫入口的坐标
- 算法输出:穿过迷宫的结果。
- 算法要点:创建迷宫,试探法查找路。
二,设计思路
1,迷宫的创建
- 如何保存?
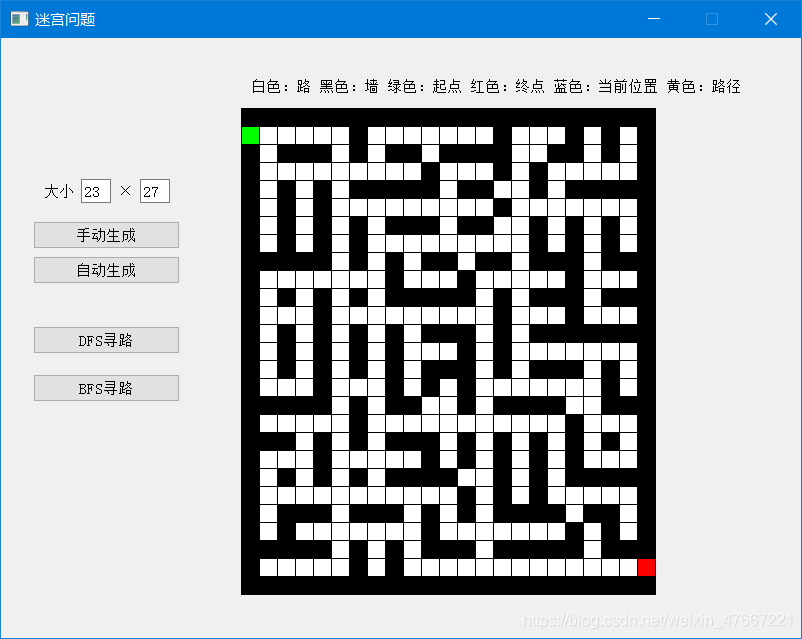
使用二维数组进行保存,0 代表路,1 代表墙,2 代表起点,3 代表终点 - 如何创建?
1,手动创建:手动输入二维数组进行创建
2,自动创建:通过使用自然分岔型[1]进行创建
2,如何寻路
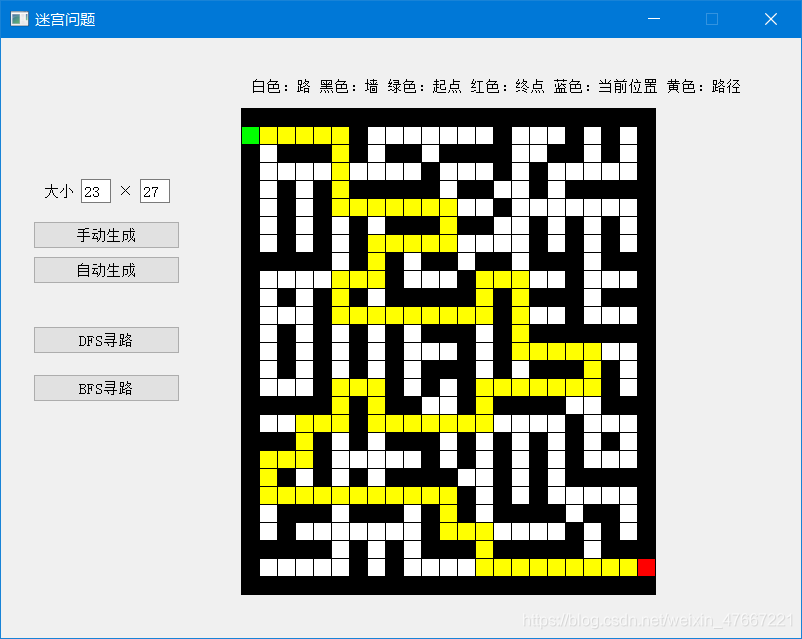
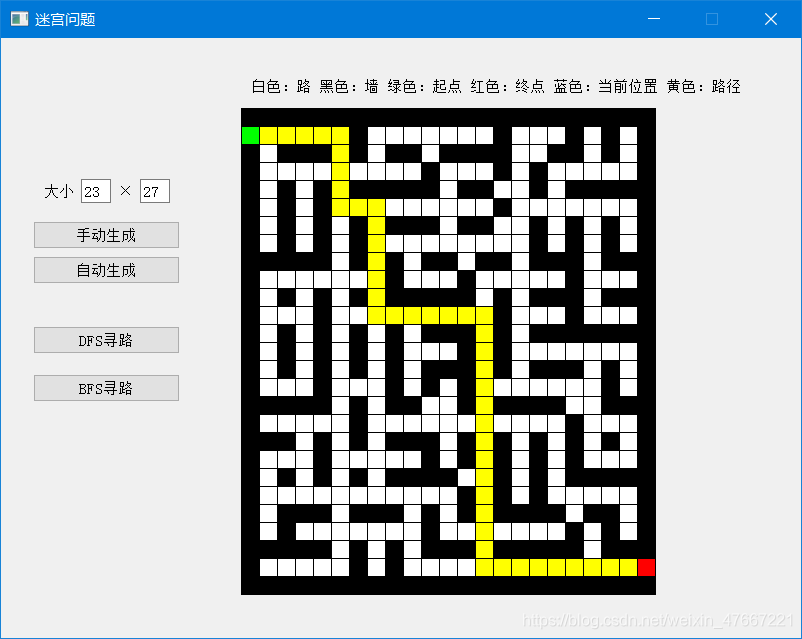
- BFS 广度优先搜索
通过创建栈进行寻路 - DFS 深度优先搜索
通过创建队列进行寻路
3,如何展示及想要实现的效果
- 使用Qt创建可视化的迷宫界面
- 可直接在迷宫界面对迷宫进行修改
- 将迷宫的通路可视化显示在迷宫界面上,并且有动画效果
三,效果展示
四,部分代码细节
1,如何在界面上绘制迷宫
我使用 maze_record 保存迷宫原始数据,使用 maze_data 来保存迷宫的其他细节,如果某位置 P(x,y) 已经被访问,则将 maze_data[x][y] 设为 -1,最后绘图时使用 maze_data 的数据
void MyWidget::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event) {
// 迷宫的最大长度或宽度为500个像素
Q_UNUSED(event);
paint = new QPainter;
paint->begin(this);
paint->setPen(QPen(Qt::black, 1, Qt::SolidLine));//设置画笔形式
// 得到迷宫中每个方块的大小
int max_size = (this->row > this->col) ? this->row : this->col;
int each_box_size = 500 / max_size;
for (int i = 0; i < this->row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < this->col; j++) {
// 重复对每个方块进行绘制
if (this->maze_data[i][j] == 0) {
// 如果是路则将画笔设为白色
paint->setBrush(QBrush(Qt::white, Qt::SolidPattern));//设置画刷形式
}else if(this->maze_data[i][j] == -1) {
// 如果是墙路径则将画笔设为黄色
paint->setBrush(QBrush(Qt::yellow, Qt::SolidPattern));
}else if (this->maze_data[i][j] == 1) {
// 如果是墙则将画笔设为黑色
paint->setBrush(QBrush(Qt::black, Qt::SolidPattern));
} else if (this->maze_data[i][j] == 2) {
// 如果是起点则将画笔设为绿色
paint->setBrush(QBrush(Qt::green, Qt::SolidPattern));
} else if (this->maze_data[i][j] == 3) {
// 如果是终点则将画笔设为红色
paint->setBrush(QBrush(Qt::red, Qt::SolidPattern));
}
paint->drawRect(240 + each_box_size * i, 70 + each_box_size * j, each_box_size, each_box_size);
}
}
paint->end();
}
在其他地方只需调用 repaint() 函数即可重新绘制迷宫
2,如何手动创建迷宫
获取鼠标每次点击时的位置并判断点击到第几个迷宫的方块,然后改变该方块的状态并保存到 maze_record 中
void MyWidget::mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event) {
// 获取鼠标相对迷宫左上角的坐标
int x = event->x() - 240;
int y = event->y() - 70;
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || this->maze_data == nullptr) {
// 如果x,y小于0则直接跳出
return;
}
// 得到迷宫中每个方块的大小
int max_size = (this->row > this->col) ? this->row : this->col;
int each_box_size = 500 / max_size;
// 计算出鼠标点击的方块位置
int click_row = x / each_box_size;
int click_col = y / each_box_size;
// 改变方块当前状态
if (this->maze_record[click_row][click_col] == 0) {
// 如果是路则变为墙
this->maze_record[click_row][click_col] = 1;
}else if (this->maze_record[click_row][click_col] == 1) {
// 如果是墙则变为起点
this->maze_record[click_row][click_col] = 2;
if (this->start != nullptr) {
// 如果已经有起点
this->maze_record[this->start->x][this->start->y] = 0;
this->start->x = click_row;
this->start->y = click_col;
}else {
// 如果未设置起点则设为起点
this->start = nullptr;
this->start = new Point(click_row, click_col, 2);
}
}else if (this->maze_record[click_row][click_col] == 2) {
// 如果是起点,则设置为终点
delete this->start;
this->start = nullptr;
this->maze_record[click_row][click_col] = 3;
if (this->end != nullptr) {
// 如果终点已经存在
this->maze_record[this->end->x][this->end->y] = 0;
this->end->x = click_row;
this->end->y = click_col;
}else {
this->end = new Point(click_row, click_col, 3);
}
}else if (this->maze_record[click_row][click_col] == 3) {
// 如果是终点,则设置为路
delete this->end;
this->end = nullptr;
this->maze_record[click_row][click_col] = 0;
}
this->resetMazeData(); // 就是把maze_record拷贝给maze_data
this->repaint();
如果鼠标点击的位置在迷宫外面就直接退出该函数了,对其他操作没有影响
3,如何自动创建迷宫
参考自然分岔型[1:1],思路说的很清楚,我感觉自己代码写的好乱。。。不建议参考
int **MyWidget::autoSetMaze(int row, int col) {
QList<Point*> path_list;
int ** res = new int * [row];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
res[i] = new int[col];
}
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
int flag = i % 2;
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (flag == 0) {
// 单数行全为墙
res[i][j] = 1;
}else {
// 偶数行墙和路依次分布
if (j % 2 == 0) {
res[i][j] = 1;
}else {
res[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
// 随机选取地图边缘的路
int flag_xy = randomNumber(0, 10);
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
if (flag_xy % 2 == 0) {
x = 1;
y = 2 * randomNumber(0, (col - 1) / 2) + 1;
} else {
y = 1;
x = 2 * randomNumber(0, (row - 1) / 2) + 1;
}
// 将该点做标记
res[x][y] = 10;
// 将该点周围的墙加入数组中
if (x != 1 && res[x - 1][y] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(x - 1, y, 0));
}
if (x != row - 2 && res[x + 1][y] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(x + 1, y, 0));
}
if (y != 1 && res[x][y - 1] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(x, y - 1, 0));
}
if (y != col - 2 && res[x][y + 1] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(x, y + 1, 0));
}
while (path_list.empty() == false) {
// 数组中随机选取一个点
int index = randomNumber(0, path_list.size());
Point * ptr = path_list[index];
int ptr_x = ptr->x;
int ptr_y = ptr->y;
// 从左到右
if (res[ptr_x - 1][ptr_y] == 10 && res[ptr_x + 1][ptr_y] == 0) {
res[ptr_x][ptr_y] = 10;
res[ptr_x + 1][ptr_y] = 10;
// 将周围的墙加入数组中
if (ptr_x + 1 != row - 2 && res[ptr_x + 3][ptr_y] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x + 2, ptr_y, 0));
}
if (ptr_y != 1 && res[ptr_x + 1][ptr_y - 2] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x + 1, ptr_y - 1, 0));
}
if (ptr_y != col - 2 && res[ptr_x + 1][ptr_y + 2] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x + 1, ptr_y + 1, 0));
}
}
// 从右到左
if (res[ptr_x + 1][ptr_y] == 10 && res[ptr_x - 1][ptr_y] == 0) {
res[ptr_x][ptr_y] = 10;
res[ptr_x - 1][ptr_y] = 10;
// 将周围的墙加入数组中
if (ptr_x - 1 != 1 && res[ptr_x - 3][ptr_y] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x - 2, ptr_y, 0));
}
if (ptr_y != 1 && res[ptr_x - 1][ptr_y - 2] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x - 1, ptr_y - 1, 0));
}
if (ptr_y != col - 2 && res[ptr_x - 1][ptr_y + 2] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x - 1, ptr_y + 1, 0));
}
}
// 从上到下
if (res[ptr_x][ptr_y - 1] == 10 && res[ptr_x][ptr_y + 1] == 0) {
res[ptr_x][ptr_y] = 10;
res[ptr_x][ptr_y + 1] = 10;
// 将周围的墙加入数组中
if (ptr_x != row - 2 && res[ptr_x + 2][ptr_y + 1] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x + 1, ptr_y + 1, 0));
}
if (ptr_x != 1 && res[ptr_x - 2][ptr_y + 1] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x - 1, ptr_y + 1, 0));
}
if (ptr_y + 1!= col - 2 && res[ptr_x][ptr_y + 3] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x, ptr_y + 2, 0));
}
}
// 从下到上
if (res[ptr_x][ptr_y + 1] == 10 && res[ptr_x][ptr_y - 1] == 0) {
res[ptr_x][ptr_y] = 10;
res[ptr_x][ptr_y - 1] = 10;
// 将周围的墙加入数组中
if (ptr_x != row - 2 && res[ptr_x + 2][ptr_y - 1] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x + 1, ptr_y - 1, 0));
}
if (ptr_x != 1 && res[ptr_x - 2][ptr_y - 1] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x - 1, ptr_y - 1, 0));
}
if (ptr_y - 1 != 1 && res[ptr_x][ptr_y - 3] != 10) {
path_list.push_back(new Point(ptr_x, ptr_y - 2, 0));
}
}
path_list.removeAt(index);
}
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (res[i][j] == 10) {
res[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// 随机选取一些墙将其变为路,方法随意,这里仅供参考
if (col > 20 || row > 20) {
for (int i = 0; i < row * 5; i++) {
int x = randomNumber(0, 100) % (row - 2) + 1;
int y = randomNumber(0, 100) % (col - 2) + 1;
if (res[x][y] == 1) {
// 这里是要判断这面墙的上下左右至少有2面都为墙
int flag = 0;
if (res[x - 1][y] == 1) {
flag++;
}
if (res[x + 1][y] == 1) {
flag++;
}
if (res[x][y - 1] == 1) {
flag++;
}
if (res[x][y + 1] == 1) {
flag++;
}
if (flag > 1) {
res[x][y] = 0;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
因为单纯使用自然分岔的方法产生的迷宫的通路很少,所以在行数或列数大于 20 的时候随机选取一些墙将其变为路,这样一个迷宫可以有好多条路可以走。
4,关于 BFS 寻路的细节
DFS 寻路的路径直接保存到栈中,所以路径可以直接得出;而 BFS 寻路使用的是队列,无法直接保存路径,所以我自定义了队列 MyQueue,使用线性结构,在 Point 类中添加 pioneer 属性,其值是该点在 MyQueue 中后继的点,最后寻路时直接通过不断访问 MyQueue[Point.pioneer] 就可以得到整个路径
class Point {
public:
Point();
Point(int x, int y, int stat);
bool operator!=(const Point & p);
public:
int x;
int y;
int status;
int pioneer;
};
class MyQueue {
public:
MyQueue();
bool isEmpty();
void push(Point * p);
void pop();
Point* frontPoint();
Point ** queue;
int front;
int end;
};
5,寻路动画的实现
不管使用 BFS 或 DFS 寻路时最后都会用到栈,将通路节点依次出栈的同时将 maze_data 相应位置变为 -1,然后进行 repaint() 并延时 0.1s
这里给出我使用的延时函数
void MyWidget::sleep(int sec) {
QElapsedTimer t;
t.start();
while(t.elapsed()<sec);
}
五,其他
这次的程序写了好久。。。主要是不知道怎么使用Qt。
还有一种思路其实更节省空间,每走一步将maze_data该处的值减去已走过的步数,如[2,0,0,0,0,0,3]走完就变成[2,-1,-2,-3,-4,-5,3],直到无路可走时直接原路返回,如果某处相邻点值为0,则走到该点处,并将该点数值设为已走过的步数,最后寻路时优先选择相邻位置差值最大的点。
自然分岔型:三套简单的迷宫地图生成方案 - 兔四的文章 - 知乎,这里介绍了几种自动生成迷宫的方法 ↩︎ ↩︎



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号