特殊问题:
1.有时候编译器会提一些无理取闹的错误,很有可能是基本的地方出了问题,比如int main()后面的()可能没带,最好的方法是,新建一个代码,对比看有哪些基本的地方没做好。这种基本都是因为在本身的代码改了很久或者用的别的软件过来的代码
2.还可以用网上的在线编译查看,说的会比codeblocks里的编译器清楚一些
知识拓展:
1.模板 template
用法:不对变量类型进行限制,有点类似C11的auto
举例:比较两个值的大小,值可能是int,float,double不确定,所以需要在编写比较函数时,用模板的定义代替变量类型
template<typename T> 这个是定义模板的固定格式,规定了的..模板应该可以理解到它的意思吧.. 比如你想求2个int float 或double型变量的值,只需要定义这么一个函数就可以了,假如不用模板的话,你就必须针对每种类型都定义一个sum函数..int sum(int, int);float sum(float, float);double sum(double, double);
1.因为T是一个模版实例化时才知道的类型,所以编译器更对T不知所云,为了通知编译器T是一个合法的类型,使用typename语句可以避免编译器报错。 2.template < typename var_name > class class_name; 表示var_name是一个类型, 在模版实例化时可以替换任意类型,不仅包括内置类型(int等),也包括自定义类型class。 换句话说,在template<typename Y>和template<class Y>中, typename和class的意义完全一样。
代码:
<pre name="code" class="cpp">// TemplateTest.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 ///<summary> ///测试C++中的template(模板)的使用方法 最新整理时间2016.5.21 ///</summary> ///<remarks>1:template的使用是为了简化不同类型的函数和类的重复定义. ///<remarks>2:char类型变量c,d输入的都是字母,不是数字,如输入32则c=3,d=2. #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; template <typename T> T mmax(T a,T b) { return a>b?a:b; } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { cout<<"Please enter the value of a and b:"<<endl; int a,b; cin>>a>>b; cout<<mmax(a,b)<<endl; cout<<"Please enter the value of c and d:"<<endl; char c,d; cin>>c>>d; cout<<mmax(c,d)<<endl; cout<<"Please enter the value of f and g:"<<endl; double f,g; cin>>f>>g; cout<<mmax(f,g)<<endl; while(1); return 0; }
唯一注意是,这个是在studio中跑的,在codeblocks中要更改
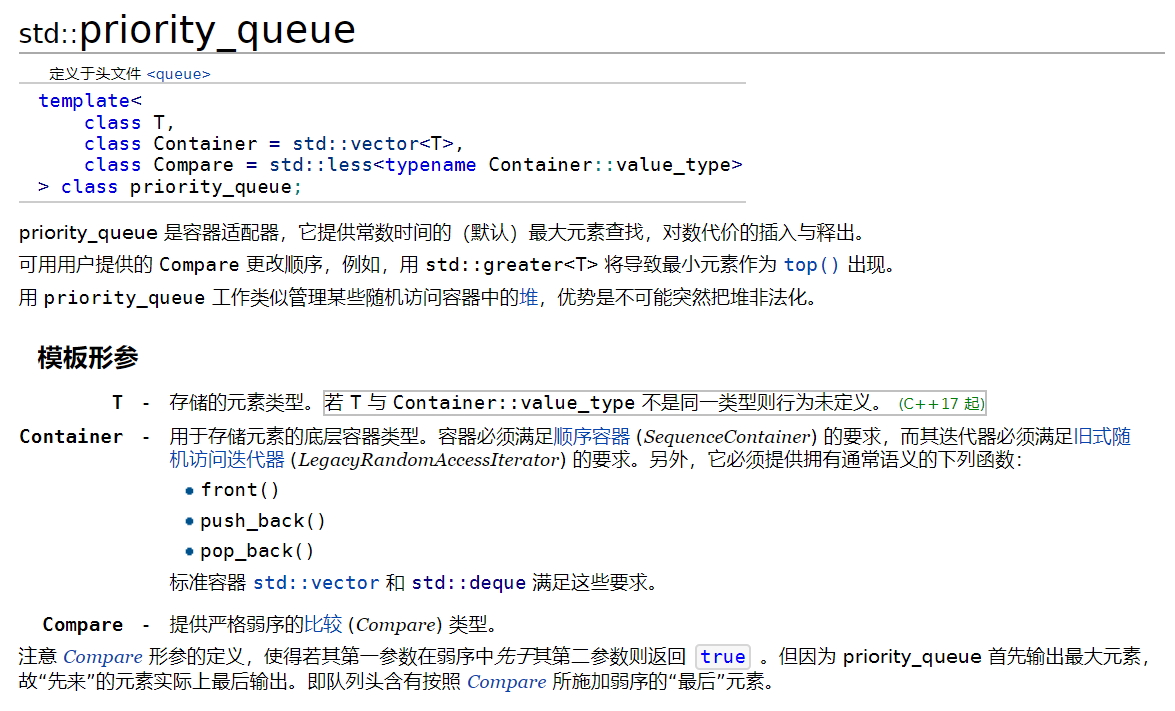
2.堆heap 《=》priority_queue
heap is a special tool in STL can help you make queue(or other containers in order automatically)
usage:
Code Sample:
#include <functional> #include <queue> #include <vector> #include <iostream>
//this code show the usage of template and priority_queue in different situation
template<typename T> void print_queue(T& q) { while(!q.empty()) { std::cout << q.top() << " "; q.pop(); } std::cout << '\n'; } int main() {
//normal definition std::priority_queue<int> q; for(int n : {1,8,5,6,3,4,0,9,7,2}) q.push(n); print_queue(q);
//specify parameter std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int> > q2; for(int n : {1,8,5,6,3,4,0,9,7,2}) q2.push(n); print_queue(q2);
//use lambda specify compare function // 用 lambda 比较元素。 auto cmp = [](int left, int right) { return (left ^ 1) < (right ^ 1);}; std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, decltype(cmp)> q3(cmp); for(int n : {1,8,5,6,3,4,0,9,7,2}) q3.push(n); print_queue(q3); }
特殊问题:
1.有时候编译器会提一些无理取闹的错误,很有可能是基本的地方出了问题,比如int main()后面的()可能没带,最好的方法是,新建一个代码,对比看有哪些基本的地方没做好。这种基本都是因为在本身的代码改了很久或者用的别的软件过来的代码
2.还可以用网上的在线编译查看,说的会比codeblocks里的编译器清楚一些
知识拓展:
1.模板 template
用法:不对变量类型进行限制,有点类似C11的auto
举例:比较两个值的大小,值可能是int,float,double不确定,所以需要在编写比较函数时,用模板的定义代替变量类型
template<typename T> 这个是定义模板的固定格式,规定了的..模板应该可以理解到它的意思吧.. 比如你想求2个int float 或double型变量的值,只需要定义这么一个函数就可以了,假如不用模板的话,你就必须针对每种类型都定义一个sum函数..int sum(int, int);float sum(float, float);double sum(double, double);
1.因为T是一个模版实例化时才知道的类型,所以编译器更对T不知所云,为了通知编译器T是一个合法的类型,使用typename语句可以避免编译器报错。 2.template < typename var_name > class class_name; 表示var_name是一个类型, 在模版实例化时可以替换任意类型,不仅包括内置类型(int等),也包括自定义类型class。 换句话说,在template<typename Y>和template<class Y>中, typename和class的意义完全一样。
代码:
<pre name="code" class="cpp">// TemplateTest.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 ///<summary> ///测试C++中的template(模板)的使用方法 最新整理时间2016.5.21 ///</summary> ///<remarks>1:template的使用是为了简化不同类型的函数和类的重复定义. ///<remarks>2:char类型变量c,d输入的都是字母,不是数字,如输入32则c=3,d=2. #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; template <typename T> T mmax(T a,T b) { return a>b?a:b; } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { cout<<"Please enter the value of a and b:"<<endl; int a,b; cin>>a>>b; cout<<mmax(a,b)<<endl; cout<<"Please enter the value of c and d:"<<endl; char c,d; cin>>c>>d; cout<<mmax(c,d)<<endl; cout<<"Please enter the value of f and g:"<<endl; double f,g; cin>>f>>g; cout<<mmax(f,g)<<endl; while(1); return 0; }
唯一注意是,这个是在studio中跑的,在codeblocks中要更改
2.堆heap 《=》priority_queue
heap is a special tool in STL can help you make queue(or other containers in order automatically)
usage:

Code Sample:
#include <functional> #include <queue> #include <vector> #include <iostream>
//this code show the usage of template and priority_queue in different situation
template<typename T> void print_queue(T& q) { while(!q.empty()) { std::cout << q.top() << " "; q.pop(); } std::cout << '\n'; } int main() {
//normal definition std::priority_queue<int> q; for(int n : {1,8,5,6,3,4,0,9,7,2}) q.push(n); print_queue(q);
//specify parameter std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int> > q2; for(int n : {1,8,5,6,3,4,0,9,7,2}) q2.push(n); print_queue(q2);
//use lambda specify compare function // 用 lambda 比较元素。 auto cmp = [](int left, int right) { return (left ^ 1) < (right ^ 1);}; std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, decltype(cmp)> q3(cmp); for(int n : {1,8,5,6,3,4,0,9,7,2}) q3.push(n); print_queue(q3); }
当前函数有问题,main函数next构建值的方法有问题,导致无法按顺序输出
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include<iomanip> #include<vector> #include<list> #include<queue> #include<algorithm> #include<stack> #include<map> using namespace std; struct ListNode { int val; ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} }; class Solution { public: ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) { ListNode res(0); ListNode *cur=&res; //this is a compare function but it's also a sentence so it's need ; to end it; auto comp = [](ListNode* a,ListNode* b){ return a->val>b->val; }; priority_queue<ListNode*,vector<ListNode*>,decltype(comp)> q(comp); for(ListNode* list:lists) { if(list) q.push(list); } //cout<<q.size()<<endl; while(!q.empty()) { cur->next=q.top();q.pop(); cur=cur->next; if(cur->next) { q.push(cur->next); } } while (res.next!=NULL) { cout << res.val << " "; res=res.next; } return res.next; } }; void printList(ListNode* node) { while (node != NULL) { printf("%d ", node->val); node = node->next; } } // Utility function to create a new node. //ListNode *newNode(int data) //{ // struct ListNode *temp = new ListNode(0); // temp->val = data; // temp->next = NULL; // return temp; //} // Driver program to test above functions int main() { Solution s; vector<ListNode*> lists; ListNode q1(37); ListNode *res=&q1; res->next=new ListNode(44); res=res->next; res->next=new ListNode(5); res=res->next; res->next=new ListNode(6); lists.push_back(&q1); ListNode* q2=new ListNode(31); q2->next=new ListNode(41); q2->next->next=new ListNode(4); q2->next->next->next=new ListNode(21); lists.push_back(q2); // Merge all lists ListNode* head = s.mergeKLists(lists); //printList(q2); return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号