Java基础:运算符
Java基础:运算符
算术运算符
package operator;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//二元运算符
//Ctrl + D :复制当前行到下一行
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 25;
int d = 30;
System.out.println(a+b);
System.out.println(a-b);
System.out.println(a*b);
System.out.println(a/(double)b);
}
}

package operator;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long a = 13246422435L;
int b = 123;
short c = 10;
byte d = 8;
System.out.println(a+b+c+d); //Long
System.out.println(b+c+d); //Int
System.out.println(b+d); //Int
}
}

package operator;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//关系运算符返回的结果: 正确,错误 布尔值
//if
int a = 10;
int b = 15;
int c = 25;
//取余 模运算
System.out.println(c%a);
System.out.println(a<b);
System.out.println(a>b);
System.out.println(a==b);
System.out.println(a!=b);
}
}

package operator;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//++ -- 自增,自减 一元运算符
int a = 3;
int b = a++; //执行完这行代码后,先给b赋值,再自增
//a=a+1;
System.out.println(a);
//a=a+1;
int c = ++a; //执行完这段代码前,先自增,再给b赋值
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
//幂运算 2^3 2*2*2=8 很多运算,我们会使用一些工具类来操作!
double pow = Math.pow(2,3);
System.out.println(pow);
}
}

逻辑运算符
package operator;
//逻辑运算符
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//与(and) 或(or) 非(取反)
boolean a = true;
boolean b = false;
System.out.println("a&&b:"+(b&&a)); //逻辑与运算:两个变量都为真,结果才为ture
System.out.println("a||b:"+(b||a)); //逻辑与运算:两个变量有一个为真,则结果才为ture
System.out.println("!(a&&b):"+!(b&&a)); //如果为真,则变为假,如果是假则变为真
//短路运算
int c = 5;
boolean d = (c<4)&&(c++<4);
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(c);
}
}

位运算符
package operator;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
A = 0011 1100
B = 0101 0110
A&B = 0001 0100
A|B = 0111 1110
A^B = 0110 1010
~B = 1010 1001
2*8 = 16 2*2*2*2
效率极高
<< *2
>> /2
0000 0000 0
0000 0001 1
0000 0010 2
0000 0011 3
0000 0100 4
0000 1000 8
0001 0000 16
*/
System.out.println(2<<3);
}
}

条件运算符 ?:
package operator;
//三元运算符
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// x ? y : z
// 如果x=ture,则结果为y,否则结果为z
int score = 50;
String type = score <60 ?"不及格":"及格"; //必须掌握
//if
System.out.println(type);
}
}

扩展赋值运算符
package operator;
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
a+=b; //a=a+b
a-=b; //a=a-b
System.out.println(a);
//字符串连接符 + , String
System.out.println(""+a+b);
System.out.println(a+b+"");
}
}

Java运算符优先级
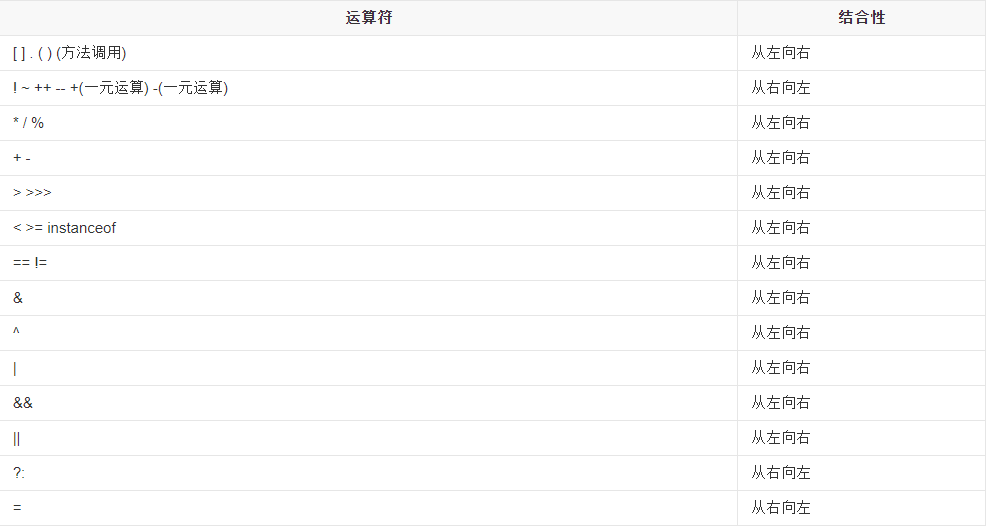
一个特殊的例子:
public class stlye{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a=10,b=6;
System.out.println("改变之前的数:a="+a+",b="+b);
a-=b++;
System.out.println("改变之后的数:a="+a+",b="+b);
}
}
运算结果为:
改变之前的数:a=10,b=6
改变之后的数:a=4,b=7
因为b++运算中先执行++,再返回后置++运算表达式(b++)的返回值(6)给-=运算符。
在这个程序中a-=b++等于a=a-b++=10-6,所以a=4。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号