实验3 类与数组、指针
实验任务1

#pragma once #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; class Point { public: Point(int x0 = 0, int y0 = 0); ~Point() = default; int get_x() const; int get_y() const; void show() const; void move(int new_x, int new_y); private: int x, y; }; Point::Point(int x0, int y0): x{x0}, y{y0} { } int Point::get_x() const { return x; } int Point::get_y() const { return y; } void Point::show() const { cout << "(" << x << ", " << y << ")" << endl; } void Point::move(int new_x, int new_y) { x = new_x; y = new_y; }

#include <iostream> #include "point.hpp" #include <vector> using std::vector; using std::cin; void output(const vector<Point> &v) { for(auto &t: v) t.show(); } void test() { int n; cout << "输入动态Point数组类对象中元素个数: "; cin >> n; vector<Point> x(n); cout << "x对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); vector<Point> y(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(y); cout << "\n更新x对象......" << endl; x.at(0).move(30, 50); x.push_back(Point(2, 2)); cout << "\nx对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(y); } int main() { test(); }
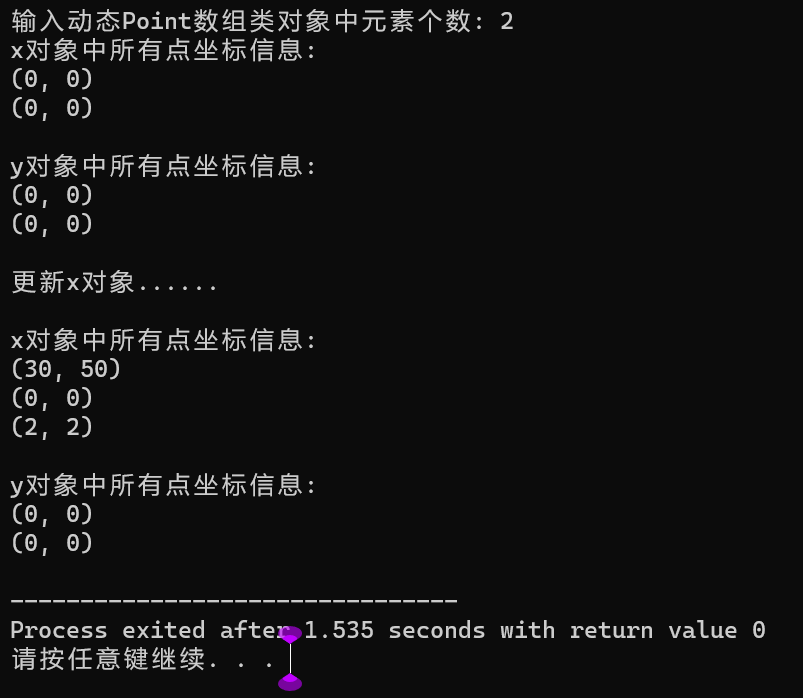
问题1:对x对象进行更新时,基于 vector <Point>对象x创建的对象y不发生变化
问题2:标准库模板类vector在复制一个动态数组对象时,实现的是深复制
实验任务2

#pragma once #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; class Point { public: Point(int x0 = 0, int y0 = 0); ~Point() = default; int get_x() const; int get_y() const; void show() const; void move(int new_x, int new_y); private: int x, y; }; Point::Point(int x0, int y0): x{x0}, y{y0} { } int Point::get_x() const { return x; } int Point::get_y() const { return y; } void Point::show() const { cout << "(" << x << ", " << y << ")" << endl; } void Point::move(int new_x, int new_y) { x = new_x; y = new_y; }

#pragma once #include "point.hpp" #include <cassert> #include <iostream> class vectorPoint{ public: vectorPoint(int n); ~vectorPoint(); int get_size() const; Point& at(int index); Point& at(int index) const; vectorPoint(const vectorPoint &vp); private: int size; Point *ptr; }; vectorPoint::vectorPoint(int n) : size{n} { ptr = new Point[n]; } vectorPoint::~vectorPoint() { delete[] ptr; } int vectorPoint::get_size() const { return size; } Point& vectorPoint::at(int index) { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); return ptr[index]; } Point& vectorPoint::at(int index) const { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); return ptr[index]; } vectorPoint::vectorPoint(const vectorPoint &vp): size{vp.size}, ptr{vp.ptr} { }

#include "vectorPoint.hpp" #include <iostream> void output(const vectorPoint &v) { for(auto i = 0; i < v.get_size(); ++i) v.at(i).show(); } void test() { using namespace std; int n; cout << "输入vectorPoint对象中元素个数: "; cin >> n; vectorPoint x(n); cout << "x对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); vectorPoint y(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(y); cout << "\n更新x对象中点坐标信息......" << endl; x.at(0).move(30, 50); x.at(1).move(-1, -1); cout << "x对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(y); } int main() { test(); }

问题1:观察更新对象x后,基于 vectorPoint 对象x创建的对象y发生变化。
问题2:编译器为vectorPoint类创建的默认复制构造函数,在复制一个动态数组对象时,实现的是浅复制。
问题3:在类vectorPoint内部,手动增加的以下复制构造函数声明和定义,实现的是浅复制。
声明:vectorPoint(const vectorPoint &vp);
实现:vectorPoint::vectorPoint(const vectorPoint &vp): size{vp.size}, ptr{vp.ptr} { }
实验任务3

#pragma once #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; class Point { public: Point(int x0 = 0, int y0 = 0); ~Point() = default; int get_x() const; int get_y() const; void show() const; void move(int new_x, int new_y); private: int x, y; }; Point::Point(int x0, int y0): x{x0}, y{y0} { } int Point::get_x() const { return x; } int Point::get_y() const { return y; } void Point::show() const { cout << "(" << x << ", " << y << ")" << endl; } void Point::move(int new_x, int new_y) { x = new_x; y = new_y; }

#pragma once #include "point.hpp" #include <cassert> #include <iostream> class vectorPoint{ public: vectorPoint(int n); vectorPoint(const vectorPoint &vp); ~vectorPoint(); int get_size() const; Point& at(int index); Point& at(int index) const; private: int size; Point *ptr; }; vectorPoint::vectorPoint(int n) : size{n} { ptr = new Point[n]; } vectorPoint::vectorPoint(const vectorPoint &vp): size{vp.size}, ptr{new Point[size]} { for(auto i = 0; i < size; ++i) ptr[i] = vp.ptr[i]; } vectorPoint::~vectorPoint() { delete[] ptr; } int vectorPoint::get_size() const { return size; } Point& vectorPoint::at(int index) { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); return ptr[index]; } Point& vectorPoint::at(int index) const { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); return ptr[index]; }

#include "vectorPoint.hpp" #include <iostream> void output(const vectorPoint &v) { for(auto i = 0; i < v.get_size(); ++i) v.at(i).show(); } void test() { using namespace std; int n; cout << "输入vectorPoint对象中元素个数: "; cin >> n; vectorPoint x(n); cout << "x对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); vectorPoint y(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(y); cout << "\n更新x对象中点坐标信息......" << endl; x.at(0).move(30, 50); x.at(1).move(-1, -1); cout << "x对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(y); } int main() { test(); }
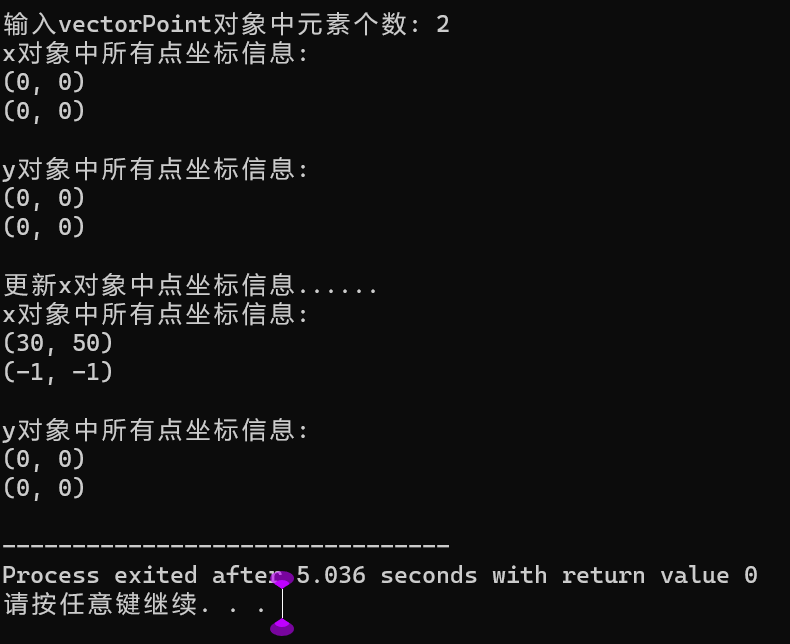
问题1:观察更新对象x后,基于 vectorPoint 对象x创建的对象y不发生变化。
问题2:这个vectorPoint 类的实现中,复制构造函数实现的是深复制。
问题3:基于实验任务2和3,总结当类的成员中包含指针域成员时深复制与浅复制的区别。
浅复制只是复制指针本身,而不会复制指针所指向的内存区域,这样会导致多个指针指向同一块内存区域,当其中一个指针释放内存时,其他指针也会受到影 响。而深复制则会复制指针所指向的内存区域,这样每个指针都有自己独立的内存空间,互不干扰。深复制需要在类中定义复制构造函数。
实验任务4

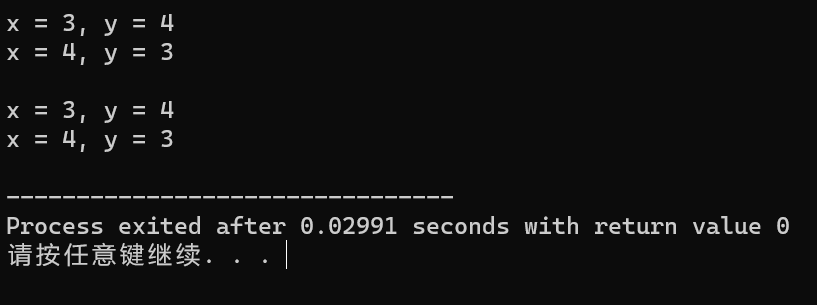
#include <iostream> using namespace std; void swap1(int &rx, int &ry); void swap2(int *px, int *py); void print(int x, int y); void test() { int x = 3, y = 4; print(x, y); swap1(x, y); print(x, y); cout << endl; x = 3, y = 4; print(x, y); swap2(&x, &y); print(x, y); } int main() { test(); } void swap1(int &rx, int &ry) { int t; t = rx; rx = ry; ry = t; } void swap2(int *px, int *py) { int t; t = *px; *px = *py; *py = t; } void print(int x, int y) { std::cout << "x = " << x << ", y = " << y << "\n"; }

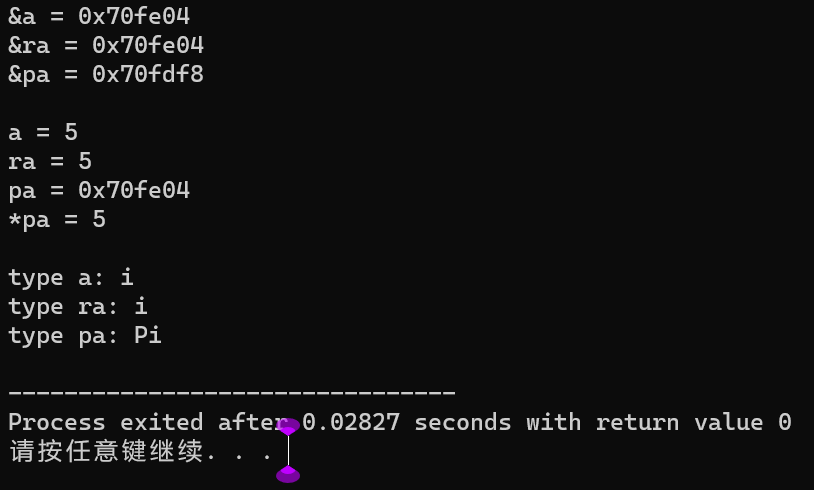
#include <iostream> #include <typeinfo> using namespace std; int main() { int a; int &ra = a; ra = 4; int *pa = &a; *pa = 5; cout << "&a = " << hex << &a << endl; cout << "&ra = " << hex << &ra << endl; cout << "&pa = " << hex << &pa << "\n\n"; cout << "a = " << a << endl; cout << "ra = " << a << endl; cout << "pa = " << hex << pa << endl; cout << "*pa = " << *pa << "\n\n"; cout << "type a: " << typeid(a).name() << endl; cout << "type ra: " << typeid(ra).name() << endl; cout << "type pa: " << typeid(pa).name() << endl; }

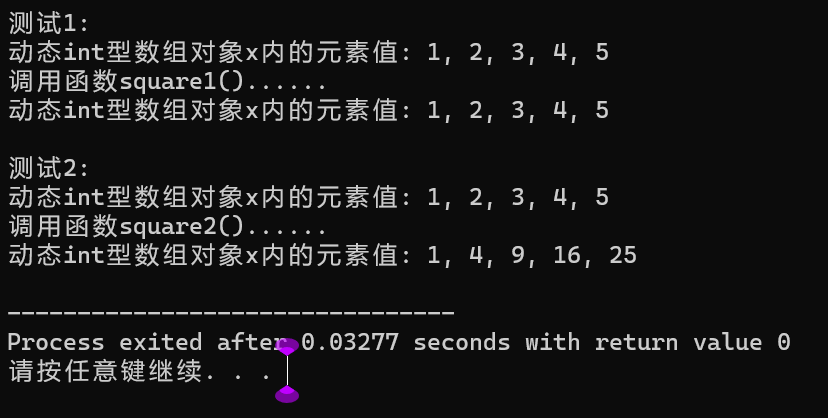
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; template<typename T> void output(const T &x) { for(auto i: x) std::cout << i << ", "; std::cout << "\b\b \n"; } template<typename T> void square1(T &x) { for(auto i: x) i *= i; } template<typename T> void square2(T &x) { for(auto &i: x) i *= i; } void test1() { vector<int> x {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; cout << "动态int型数组对象x内的元素值: "; output(x); cout << "调用函数square1()......" << endl; square1(x); cout << "动态int型数组对象x内的元素值: "; output(x); } void test2() { vector<int> x {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; cout << "动态int型数组对象x内的元素值: "; output(x); cout << "调用函数square2()......" << endl; square2(x); cout << "动态int型数组对象x内的元素值: "; output(x); } int main() { cout << "测试1: " << endl; test1(); cout << "\n测试2: " << endl; test2(); }
总结引用类型、指针类型的区别:引用没有自己的地址。引用变量的类型和值,与它所绑定的普通变量是相同的。
指针变量有自己的地址。指针变量的类型决定了它所指向的变量的类型,而指针变量的值则存储了它所指向的普通变量的地址。
实验任务5

#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <cassert> using namespace std; class vectorInt { public: vectorInt(int n); vectorInt(int n, int value); vectorInt(const vectorInt &vi); ~vectorInt(); int get_size() const; int& at(int index); int& at(int index) const; private: int size; int *ptr; }; vectorInt::vectorInt(int n) : size{n} { ptr = new int[size]; cout << "constructor vectorInt(int n) called." << endl; } vectorInt::vectorInt(int n, int value) : size{n} { ptr = new int[size]; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { ptr[i] = value; } cout << "constructor vectorInt(int n, int value) called." << endl; } vectorInt::vectorInt(const vectorInt &vi): size{vi.size}, ptr{new int[size]} { for(auto i = 0; i < size; ++i) ptr[i] = vi.ptr[i]; cout << "copy constructor called." << endl; } vectorInt::~vectorInt() { delete[] ptr; cout << "destructor called." << endl; } int vectorInt::get_size() const { return size; } int& vectorInt::at(int index) { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); return ptr[index]; } int& vectorInt::at(int index) const { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); return ptr[index]; }

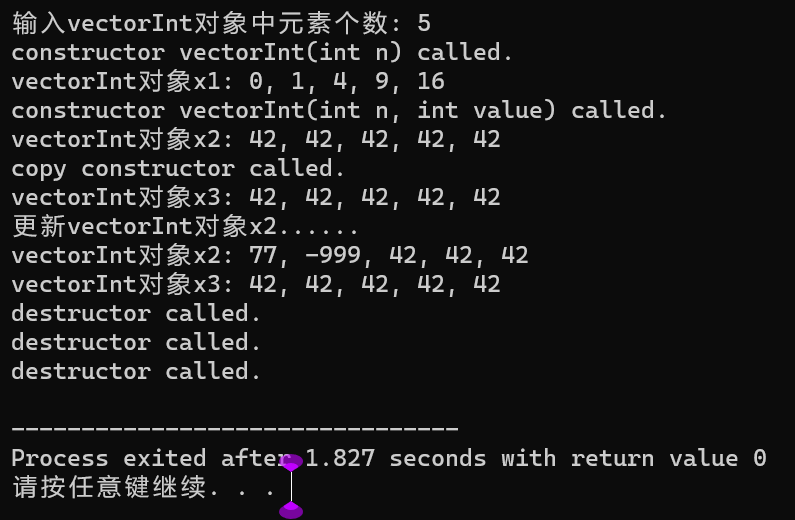
#include "vectorInt.hpp" #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::endl; void output(const vectorInt &vi) { for(auto i = 0; i < vi.get_size(); i++) cout << vi.at(i) << ", "; cout << "\b\b \n"; } void test() { int n; cout << "输入vectorInt对象中元素个数: "; cin >> n; vectorInt x1(n); for(auto i = 0; i < n; ++i) x1.at(i) = i*i; cout << "vectorInt对象x1: " ; output(x1); vectorInt x2(n, 42); cout << "vectorInt对象x2: " ; output(x2); vectorInt x3(x2); cout << "vectorInt对象x3: " ; output(x3); cout << "更新vectorInt对象x2......\n" ; x2.at(0) = 77; x2.at(1) = -999; cout << "vectorInt对象x2: "; output(x2); cout << "vectorInt对象x3: "; output(x3); } int main() { test(); }
实验任务6

#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <cassert> using std::cout; using std::endl; class Matrix { public: Matrix(int n, int m); Matrix(int n); Matrix(const Matrix &x); ~Matrix(); void set(const double *pvalue); void set(int i, int j, double value); double& at(int i, int j) const; double& at(int i, int j); int get_lines() const; int get_cols() const; void print() const; private: int lines; int cols; double *ptr; }; Matrix::Matrix(int n, int m): lines{n}, cols{m} { assert(n > 0 && m > 0); ptr = new double[n * m]; } Matrix::Matrix(int n) : Matrix(n, n) {} Matrix::Matrix(const Matrix& x) : lines{x.lines}, cols{x.cols} { ptr = new double[lines * cols]; for (int i = 0; i < lines * cols; ++i) { ptr[i] = x.ptr[i]; } } Matrix::~Matrix() { delete[] ptr; } void Matrix::set(const double* pvalue) { for (int i = 0; i < lines * cols; ++i) { ptr[i] = pvalue[i]; } } void Matrix::set(int i, int j, double value) { assert(i >= 0 && i < lines && j >= 0 && j < cols); ptr[i * cols + j] = value; } double& Matrix::at(int i, int j) const { assert(i >= 0 && i < lines && j >= 0 && j < cols); return ptr[i * cols + j]; } double& Matrix::at(int i, int j) { assert(i >= 0 && i < lines && j >= 0 && j < cols); return ptr[i * cols + j]; } int Matrix::get_lines() const { return lines; } int Matrix::get_cols() const { return cols; } void Matrix::print() const { for (int i = 0; i < lines; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) { cout << ptr[i * cols + j] << " "; } cout << endl; } }

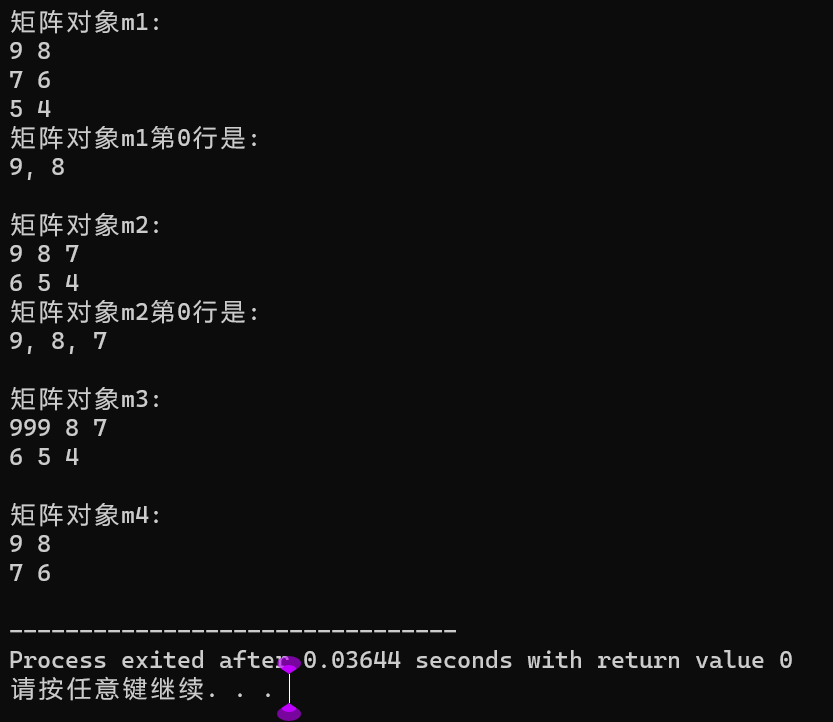
#include <iostream> #include "matrix.hpp" using namespace std; const int N1 = 3; const int N2 = 2; void output(const Matrix &m, int index) { for(auto j = 0; j < m.get_cols(); ++j) cout << m.at(index, j) << ", "; cout << "\b\b \n"; } void test() { double x[N1*N2] = {9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4}; Matrix m1(N1, N2); m1.set(x); cout << "矩阵对象m1: " << endl; m1.print(); cout << "矩阵对象m1第0行是: " << endl; output(m1, 0); cout << endl; Matrix m2(N2, N1); m2.set(x); cout << "矩阵对象m2: " << endl; m2.print(); cout << "矩阵对象m2第0行是: " << endl; output(m2, 0); cout << endl; Matrix m3(m2); m3.set(0, 0, 999); cout << "矩阵对象m3:" << endl; m3.print(); cout << endl; Matrix m4(2); m4.set(x); cout << "矩阵对象m4:" << endl; m4.print(); } int main() { test(); }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号