Linq与UniRx 操作符
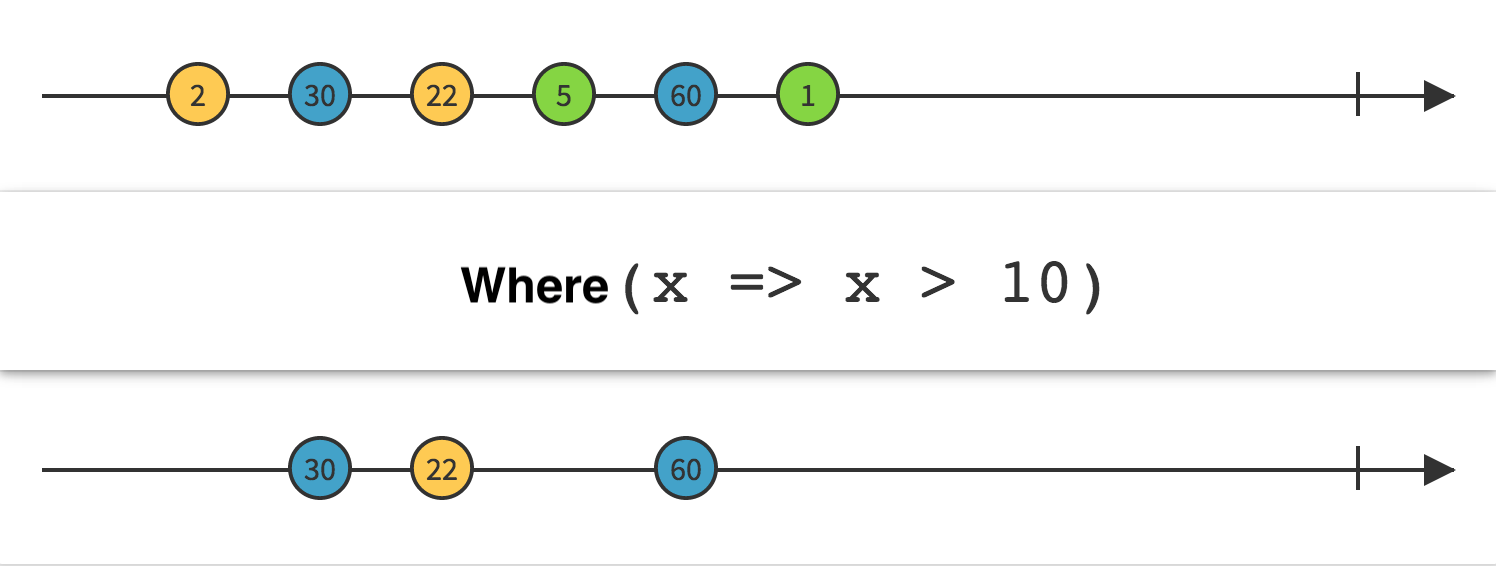
1.Where
Linq Where
LINQ 中的 Where 操作符与 SQL 命令中的 Where 作用相似,都是起到范围限定也就是过滤作用的,而
条判断条件就是它后面所接的子句。

class WhereSample { static void Main() { // Simple data source. Arrays support IEnumerable<T>. int[] numbers = { 5, 4, 1, 3, 9, 8, 6, 7, 2, 0 }; var queryLowNums = from num in numbers where num < 5 select num; //var queryLowNums = numbers.Where(num=>num<5) foreach (var s in queryLowNums) { Console.Write(s.ToString() + " "); } } } //Output: 4 1 3 2 0
UniRx Where
public class UniRxWhereExamle : MonoBehaviour { private void Start() { Observable.EveryUpdate() .Where(_ => Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0)) .Subscribe(_ => { Debug.Log("mouse down"); }) .AddTo(this);
} }
UniRx Where 查询式

using UnityEngine; using UniRx; public class UnIRxWhereQueryExample : MonoBehaviour { void Start() { var mouseClickEventStreams = from updateEvent in Observable.EveryUpdate() where Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0) select updateEvent; mouseClickEventStreams.Subscribe(_ => { Debug.Log("鼠标按下"); }) .AddTo(this); } }
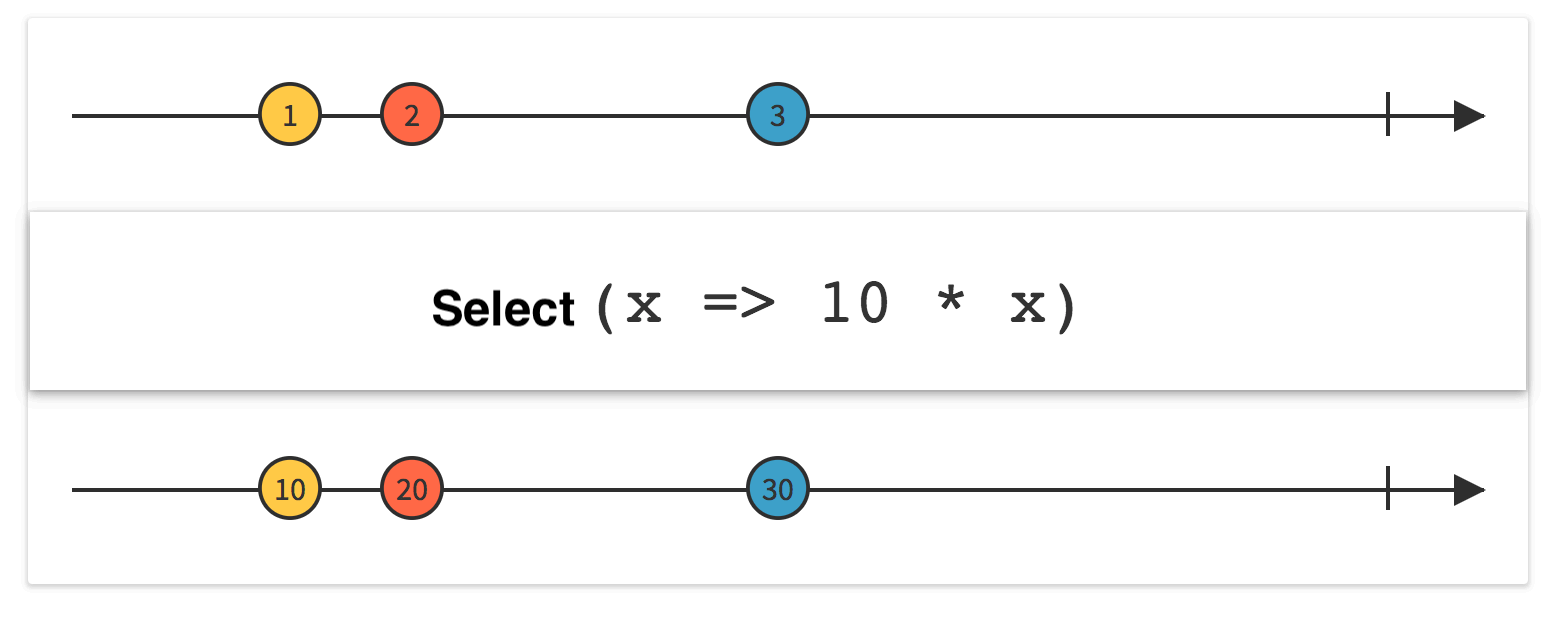
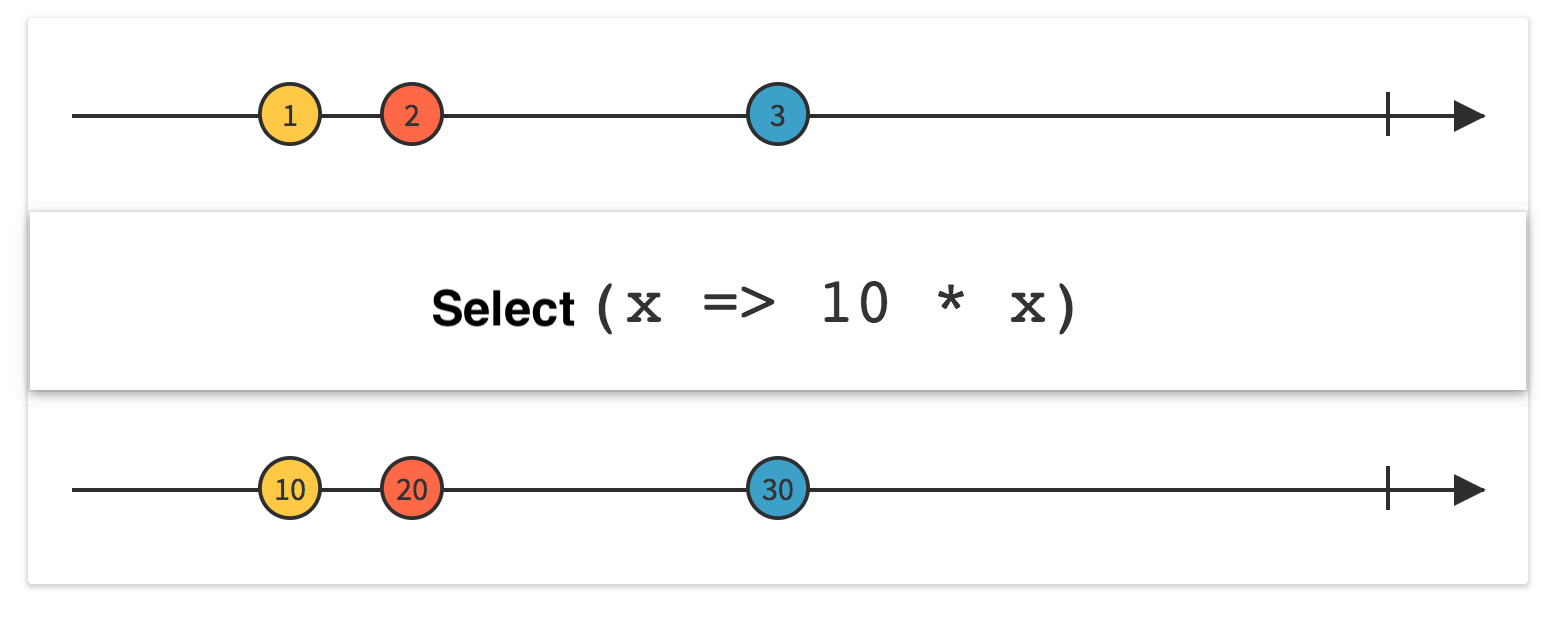
2.Select
Linq Select
LINQ 中的 Select 操作符 与 SQL 命令中的 Select 作用相似,但是位置不同,查询表达式中的 select 及所接子句是放在最后并把子句中的变量也就是结果返回来。
|
Select<TSource,TResult(IEnumerable<TSource>,Func<TSource,TResult>) |
将序列中的每个元素投影到新表单。 |
| Select<TSource,TResult(IEnumerable<TSource>,Func<TSource,Int32,TResult>) | 通过合并元素的索引,将序列的每个元素投影到新窗体中。 |
class SelectSample1 { static void Main() { //Create the data source List<int> Scores = new List<int>() { 97, 92, 81, 60 }; // 查询式 IEnumerable<int> queryHighScores = from score in Scores where score > 80 select score; //表达式 *10 var queryHighScores1 = Scores .Where(s=>s.score>80).Select(score=>score*10);// Execute the query. foreach (int i in queryHighScores) { Console.Write(i + " "); }
}
}
Select<TSource,TResult(IEnumerable<TSource>,Func<TSource,Int32,TResult>)投影值序列并使用每个元素的索引。
public static void Main(string[] args) { var list = new List<int>() { 10, 20, 30,40,50, 60,70,80,90,100,110,120, }; var rateList = list.Select((item, index) => { return index == 0 ? 0 : Math.Round(((decimal)list[index] - list[index - 1]) / list[index - 1], 2); }).ToList(); rateList.ForEach(Console.WriteLine); } ------------------- output ------------------- 0 1 0.5 0.33 0.25 0.2 0.17 0.14 0.12 0.11 0.1 0.09
string[] fruits = { "apple", "banana", "mango", "orange", "passionfruit", "grape" }; var query =fruits.Select((fruit, index) =>new { index, str = fruit.Substring(0, index) }); foreach (var obj in query) { Console.WriteLine("{0}", obj); } /* This code produces the following output: {index=0, str=} {index=1, str=b} {index=2, str=ma} {index=3, str=ora} {index=4, str=pass} {index=5, str=grape} */
UniRX Select
using UniRx; using UnityEngine; namespace UniRxLesson { public class UniRxSelectExample : MonoBehaviour { void Start() { Observable.EveryUpdate() .Where(_ => Input.GetMouseButtonUp(0)) .Select(_ => "mouse up") .Subscribe(Debug.Log) .AddTo(this);
//查询式
var mouseUpEventSteam = from updateEvent in Observable.EveryUpdate()
where Input.GetMouseButtonUp(0)
select "mouse up";
mouseUpEventSteam
.Subscribe(Debug.Log)
.AddTo(this);
}
}
}
3.First
Linq First
取序列中的第一个元素。First 有两种形式,一种是直接获取第一个元素,第二种则是取序列中满足条件的第一个元素
| First<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Boolean>) | 返回序列中满足指定条件的第一个元素。 |
| First<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>) | 返回序列中的第一个元素。 |
如果在 中source找不到匹配元素,该方法First<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Boolean>)将引发异常。 若要在找不到匹配元素时返回默认值,请使用 FirstOrDefault 该方法。
UniRx First
public class UniRxFirstExample : MonoBehaviour { private void Start() { Observable.EveryUpdate() .First(_ => Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0)) .Subscribe(_ => { Debug.Log("mouse down"); }) .AddTo(this); } }
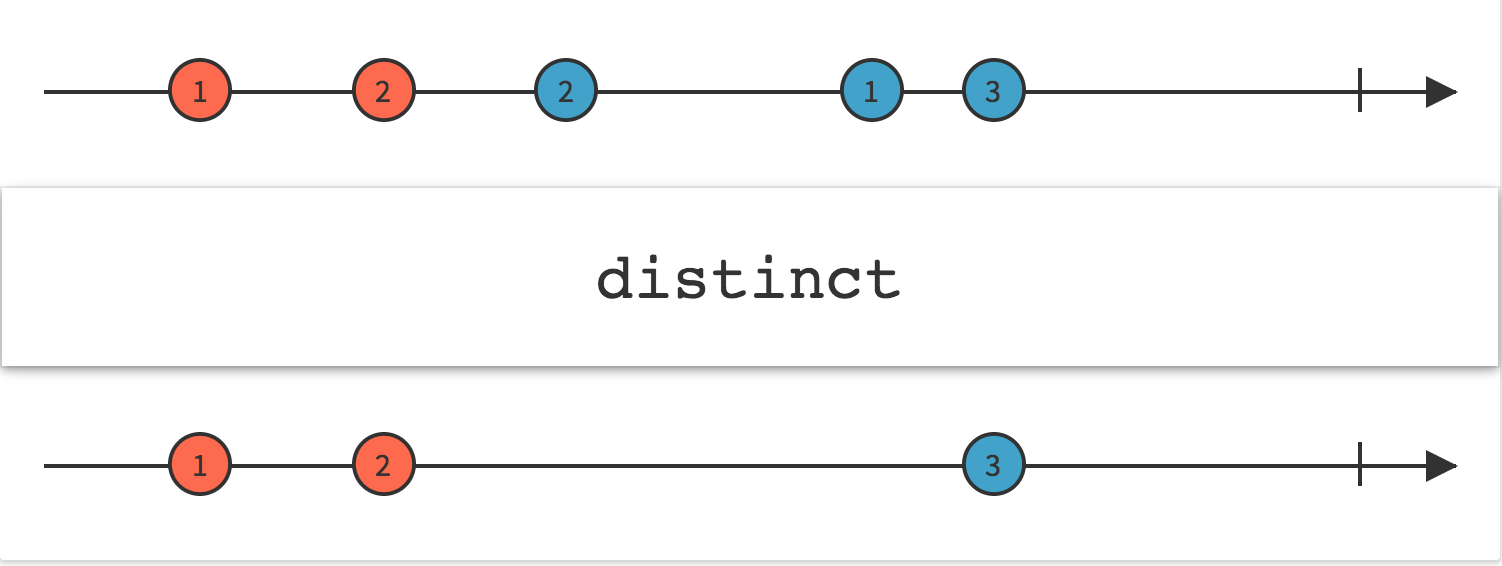
4.Distinct
Linq Distinct
返回序列中的非重复元素
| Distinct<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>) | 通过使用默认的相等比较器对值进行比较,返回序列中的非重复元素 |
| Distinct<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, IEqualityComparer<TSource>) | 通过使用指定的 IEqualityComparer<T> 对值进行比较,返回序列中的非重复元素。 |
Distinct<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>)
List<int> ages = new List<int> { 21, 46, 46, 55, 17, 21, 55, 55 };
IEnumerable<int> distinctAges = ages.Distinct();
foreach (int age in distinctAges)
{
Console.WriteLine(age);
}
/*
21 46 55 17
*/如果要从某些自定义数据类型的对象序列中返回不同的元素,则必须在类中实现 IEquatable<T> 泛型接口。 下面的代码示例演示如何在自定义数据类型中实现此接口并提供 GetHashCode 和 Equals 方法。
public class MyProduct : IEquatable<MyProduct>
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Code { get; set; }
public bool Equals(MyProduct other)
{
//Check whether the compared object is null.
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(other, null)) return false;
//Check whether the compared object references the same data.
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(this, other)) return true;
//Check whether the products' properties are equal.
return Code.Equals(other.Code) && Name.Equals(other.Name);
}
// If Equals() returns true for a pair of objects
// then GetHashCode() must return the same value for these objects.
public override int GetHashCode()
{
//Get hash code for the Name field if it is not null.
int hashProductName = Name == null ? 0 : Name.GetHashCode();
//Get hash code for the Code field.
int hashProductCode = Code.GetHashCode();
//Calculate the hash code for the product.
return hashProductName ^ hashProductCode;
}
}注意事项:Distinct方法不会改变原链表,会返回一个新对象,通过该对象可以枚举原链表中的非重复元素,但是并没有把非重复元素复制一份到新的对象中(连浅拷贝也没有)。此方法通过使用延迟执行来实现。 即时返回值是一个对象,用于存储执行操作所需的所有信息。 只有在通过直接调用其方法或在For Each调用该GetEnumerator对象,否则不会执行此方法表示的查询。
Distinct<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, IEqualityComparer<TSource>)
public class User
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
var list = new List<User>()
{
new User() { Id = 1, Name = "张三" } ,
new User() { Id = 1, Name = "张三" } ,
new User() { Id = 3, Name = "李四" } ,
};
var newList1 = list.Distinct().ToList();运行上述代码会发现,并不是预期想要的结果,newList1还是有3个元素。之所以会产生这样的结果,是因为Distinct()是通过使用默认的相等比较器对值进行比较返回序列中的非重复元素。对于值类型,默认的相等比较器是比较值是否相等,对于引用类型,默认的相等比较器是比较对象的引用地址,所以上述例子中即使属性值都相同,也不能去重。
IEqualityComparer<TSource> comparer,是一个泛型接口,我们只需要对这个接口进行实现,即可满足我们的去重需求:
public class UserComparer : IEqualityComparer<User>
{
public bool Equals(User x, User y)
{
return x.Id == y.Id && x.Name == y.Name;
}
public int GetHashCode(User obj)
{
return obj.ToString().GetHashCode();
}
}IEqualityComparer<TSource> 定义了两个方法,一个是Equals,一个是GetHashCode。进行比较时,默认先通过GetHashCode对两个元素进行比较,如果HashCode不同,则认为两个元素不同,如果相同则再通过Equals方法比较。
UniRX Distinct
UniRx 的 Distinct 在操作 List 时候,除了支持 LINQ 所支持的两种方式外,还⽀持传⼊⼀个特定条件函数
Distinct<TSource, TKey>(this IObservable<TSource> source,Func<TSource, TKey> keySelector)
public class UniRxDistinctExample : MonoBehaviour
{
class Student
{
public string Name;
public int Age;
}
void Start()
{
var students = new List<Student>()
{
new Student(){ Name="张三",Age=50},
new Student(){ Name="张三",Age=50},
new Student(){ Name="李四",Age=40},
};
students.ToObservable()
.Distinct(student => student.Name)
.Subscribe(student =>
{
Debug.Log(student.Name);
});
}
}需求:不管点击多少次鼠标左键,还是鼠标右键,输出只输出一次 “left clicked” 和“right clicked”。
public class UniRxDistinctExample2 : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var leftClickStream = Observable.EveryUpdate()
.Where(_ => Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0))
.Select(_ => "left clicked");
var rightClickStream = Observable.EveryUpdate()
.Where(_ => Input.GetMouseButtonDown(1))
.Select(_ => "right clicked");
Observable.Merge(leftClickStream, rightClickStream)
.Distinct()
.Subscribe(Debug.Log)
.AddTo(this);
}
}
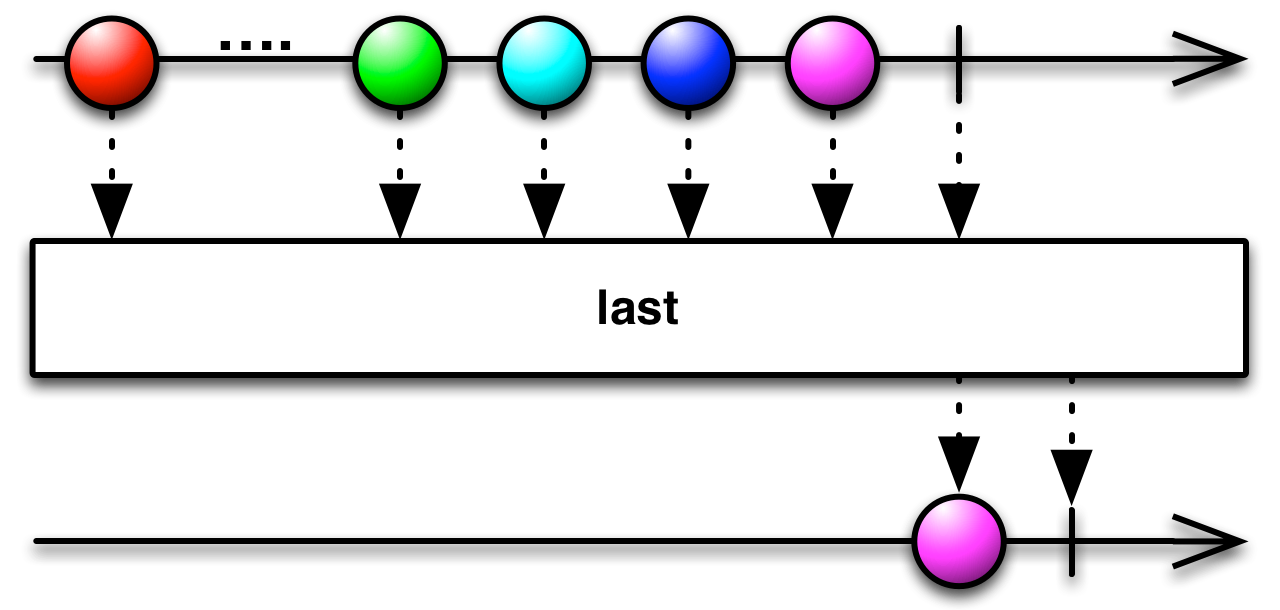
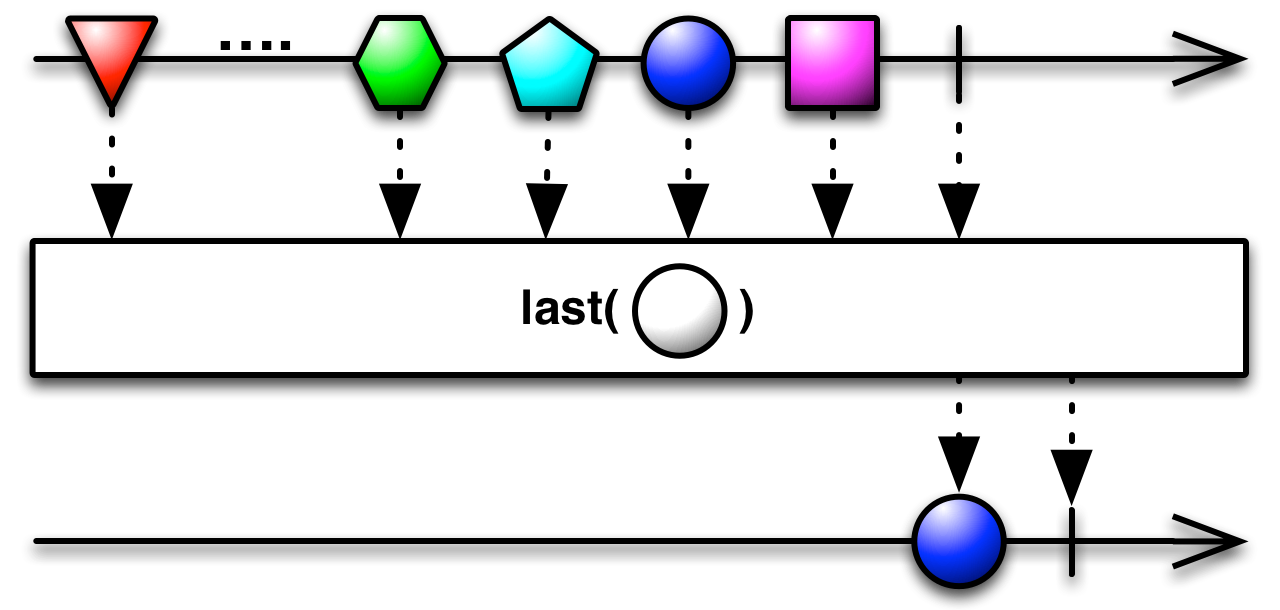
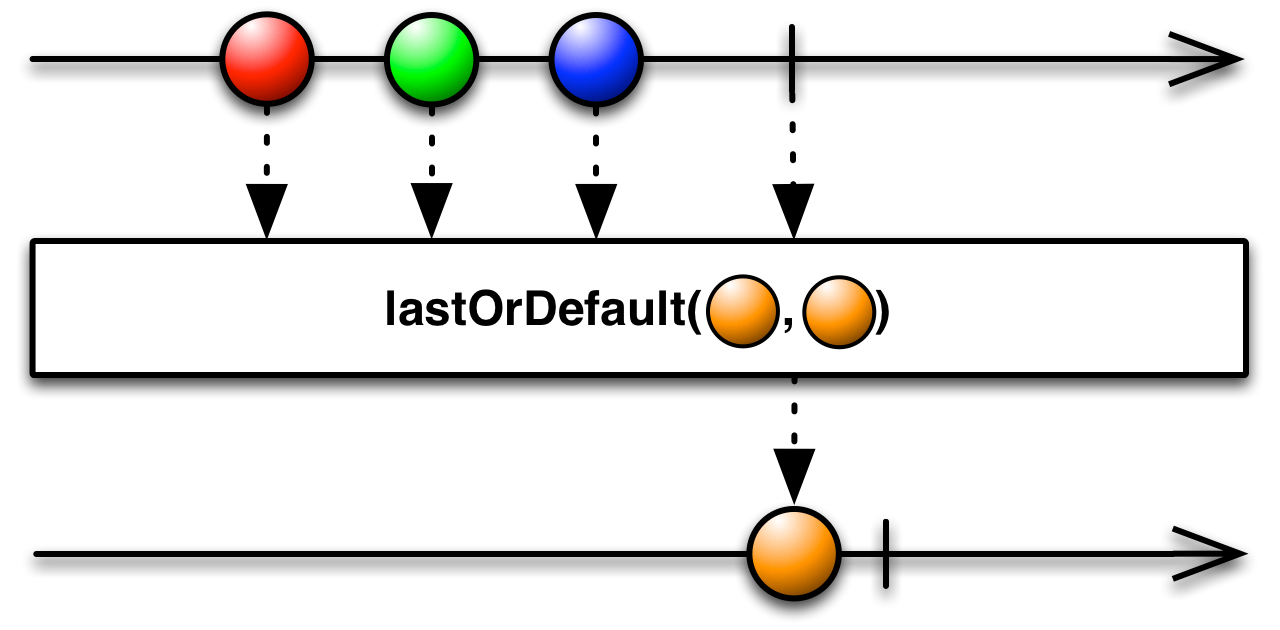
5.Last
返回序列的最后一个元素。
| Last<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>) | 返回序列的最后一个元素。 |
| Last<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Boolean>) | 返回序列中满足指定条件的最后一个元素。 |
如果您只对 Observable 发出的最后一项或满足某些条件的最后一项感兴趣,则可以使用Last运算符过滤 Observable
6.SelectMany
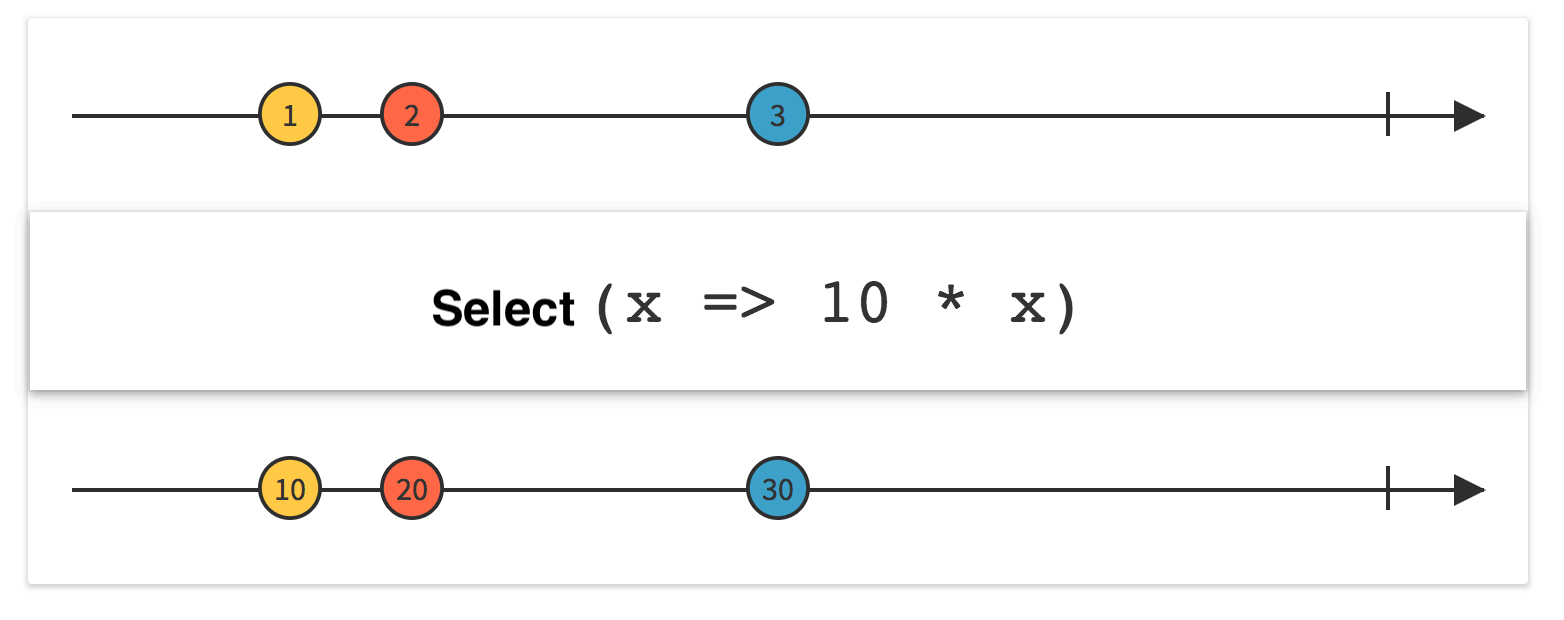
Linq SelectMany
将序列的每个元素投影到 IEnumerable<T> 并将结果序列合并为一个序列。
SelectMany用来对多重嵌套的序列操作很方便,能扁平化序列。
| SelectMany<TSource,TCollection,TResult>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Int32,IEnumerable<TCollection>>, Func<TSource,TCollection,TResult>) | 将序列的每个元素投影到 IEnumerable<T>,并将结果序列合并为一个序列,并对其中每个元素调用结果选择器函数。 每个源元素的索引用于该元素的中间投影表。 |
| SelectMany<TSource,TCollection,TResult>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,IEnumerable<TCollection>>, Func<TSource,TCollection,TResult>) | 将序列的每个元素投影到 IEnumerable<T>,并将结果序列合并为一个序列,并对其中每个元素调用结果选择器函数。 |
| SelectMany<TSource,TResult>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,IEnumerable<TResult>>) | 将序列的每个元素投影到 IEnumerable<T> 并将结果序列合并为一个序列。 |
| SelectMany<TSource,TResult>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Int32,IEnumerable<TResult>>) | 将序列的每个元素投影到 IEnumerable<T> 并将结果序列合并为一个序列。 每个源元素的索引用于该元素的投影表。 |
下面的代码示例演示如何用于 SelectMany<TSource,TCollection,TResult>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,IEnumerable<TCollection>>, Func<TSource,TCollection,TResult>) 对数组执行一对多投影,并使用结果选择器函数将每个相应元素从源序列中保留到最终调用 Select的范围。
class PetOwner
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public List<string> Pets { get; set; }
}
public static void SelectManyEx3()
{
PetOwner[] petOwners =
{ new PetOwner { Name="Higa",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Scruffy", "Sam" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Ashkenazi",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Walker", "Sugar" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Price",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Scratches", "Diesel" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Hines",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Dusty" } } };
// Project the pet owner's name and the pet's name.
var query =
petOwners
.SelectMany(petOwner => petOwner.Pets, (petOwner, petName) => new { petOwner, petName })
.Where(ownerAndPet => ownerAndPet.petName.StartsWith("S"))
.Select(ownerAndPet =>
new
{
Owner = ownerAndPet.petOwner.Name,
Pet = ownerAndPet.petName
}
);
// Print the results.
foreach (var obj in query)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
}
// This code produces the following output:
// {Owner=Higa, Pet=Scruffy}
// {Owner=Higa, Pet=Sam}
// {Owner=Ashkenazi, Pet=Sugar}
// {Owner=Price, Pet=Scratches}下面的代码示例演示如何用于 SelectMany<TSource,TResult>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Int32,IEnumerable<TResult>>) 对数组执行一对多投影,并使用每个外部元素的索引。
class PetOwner
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public List<string> Pets { get; set; }
}
public static void SelectManyEx2()
{
PetOwner[] petOwners =
{ new PetOwner { Name="Higa, Sidney",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Scruffy", "Sam" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Ashkenazi, Ronen",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Walker", "Sugar" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Price, Vernette",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Scratches", "Diesel" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Hines, Patrick",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Dusty" } } };
// Project the items in the array by appending the index
// of each PetOwner to each pet's name in that petOwner's
// array of pets.
IEnumerable<string> query =
petOwners.SelectMany((petOwner, index) =>
petOwner.Pets.Select(pet => index + pet));
foreach (string pet in query)
{
Console.WriteLine(pet);
}
}
//0Scruffy 0Sam 1Walker 1Sugar 2Scratches 2Diesel 3DustyUniRx SelectMany
public class SelectMany : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var a = Observable.FromCoroutine(A);
var b = Observable.FromCoroutine(B);
var c = Observable.FromCoroutine(C);
//对协程执行顺序进行任意组合
//原理是协程(可观察的)默认只会在结束后被观察到一次,A结束后被转成了B,B结束后又转成了C ,全部观察完后 输出end
a.SelectMany(b.SelectMany(c)).Subscribe(_ => print("end"));
//a.SelectMany(sa=> {
// print("a convered to b");
// return b;
//}).Subscribe(_=>print("end"));
//todo怎么组合带参数的协程?
}
IEnumerator A()
{
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1.0f);
print("A");
}
IEnumerator B()
{
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1.0f);
print("B");
}
IEnumerator C()
{
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1.0f);
print("C");
}
}协程被UniRx转换成Observable以后,默认只会在结束后返回一次,所以在A结束后,把B返回出去继续观察,B观察完了,C继续。 就实现了协程顺序的任意组合!!
另一个操作符concat也能随意组合流的顺序他们的区别是 concat后的订阅是基于每个流的,不是针对整体的结束
7.Take
Linq Take
从序列的开头返回指定数量的相邻元素
| Take<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Int32) | 从序列的开头返回指定数量的相邻元素。 |
| Take<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Range) | 返回序列中连续元素的指定范围。 |
int[] grades = { 59, 82, 70, 56, 92, 98, 85 };
IEnumerable<int> topThreeGrades =
grades.OrderByDescending(grade => grade).Take(3);
// 98 92 85UniRx Take
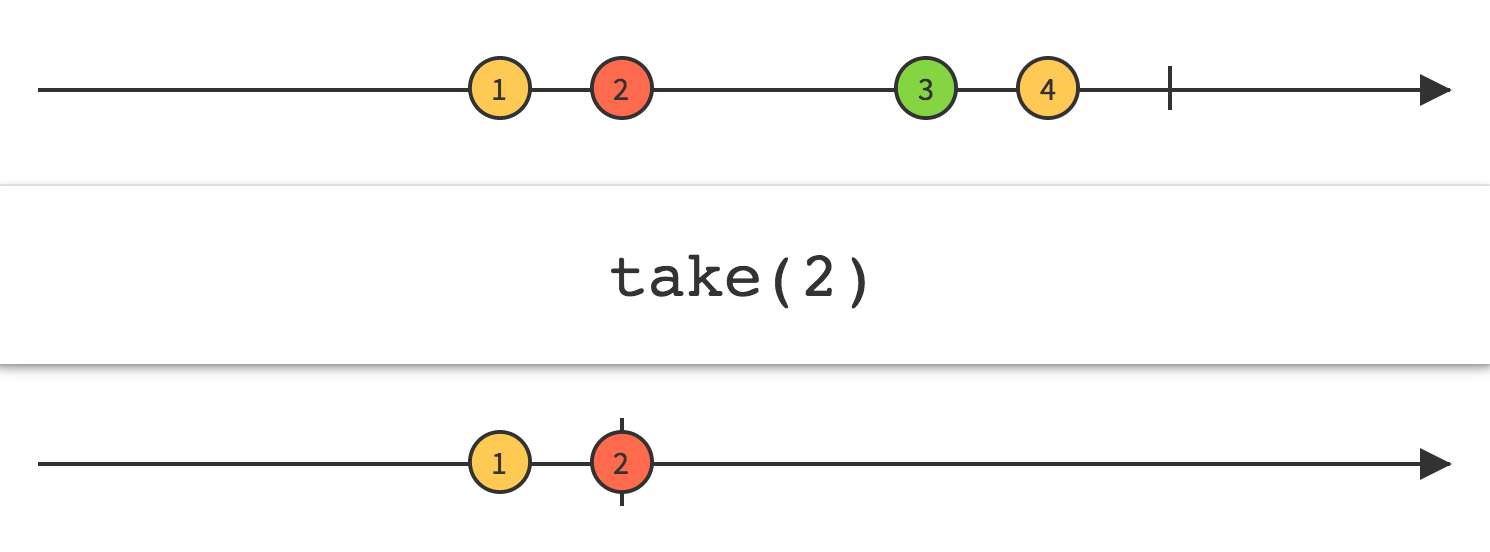
使用Take操作符让你可以修改Observable的行为,只返回前面的N项数据,然后发射完成通知,忽略剩余的数据。
public class UniRxTakeExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
this.UpdateAsObservable()
.Where(_ => Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0))
.Take(5)
.Subscribe(_ => Debug.Log(1));
}
}
8.Concat
Linq Concat
连接两个序列
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class LINQConcatExample : MonoBehaviour
{
private class Pet
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
void Start()
{
Pet[] cats =
{
new Pet {Name = "Barley", Age = 8},
new Pet {Name = "Boots", Age = 4},
new Pet {Name = "Whiskers", Age = 1}
};
Pet[] dogs =
{
new Pet {Name = "Bounder", Age = 3},
new Pet {Name = "Snoopy", Age = 14},
new Pet {Name = "Fido", Age = 9}
};
var petNames = cats.Select(cat => cat.Name)
.Concat(dogs.Select(dog => dog.Name));
foreach (var petName in petNames)
{
Debug.Log(petName);
}
}
}
/*
Barley
Boots
Whiskers
Bounder
Snoopy
Fido
*/UniRx Concat
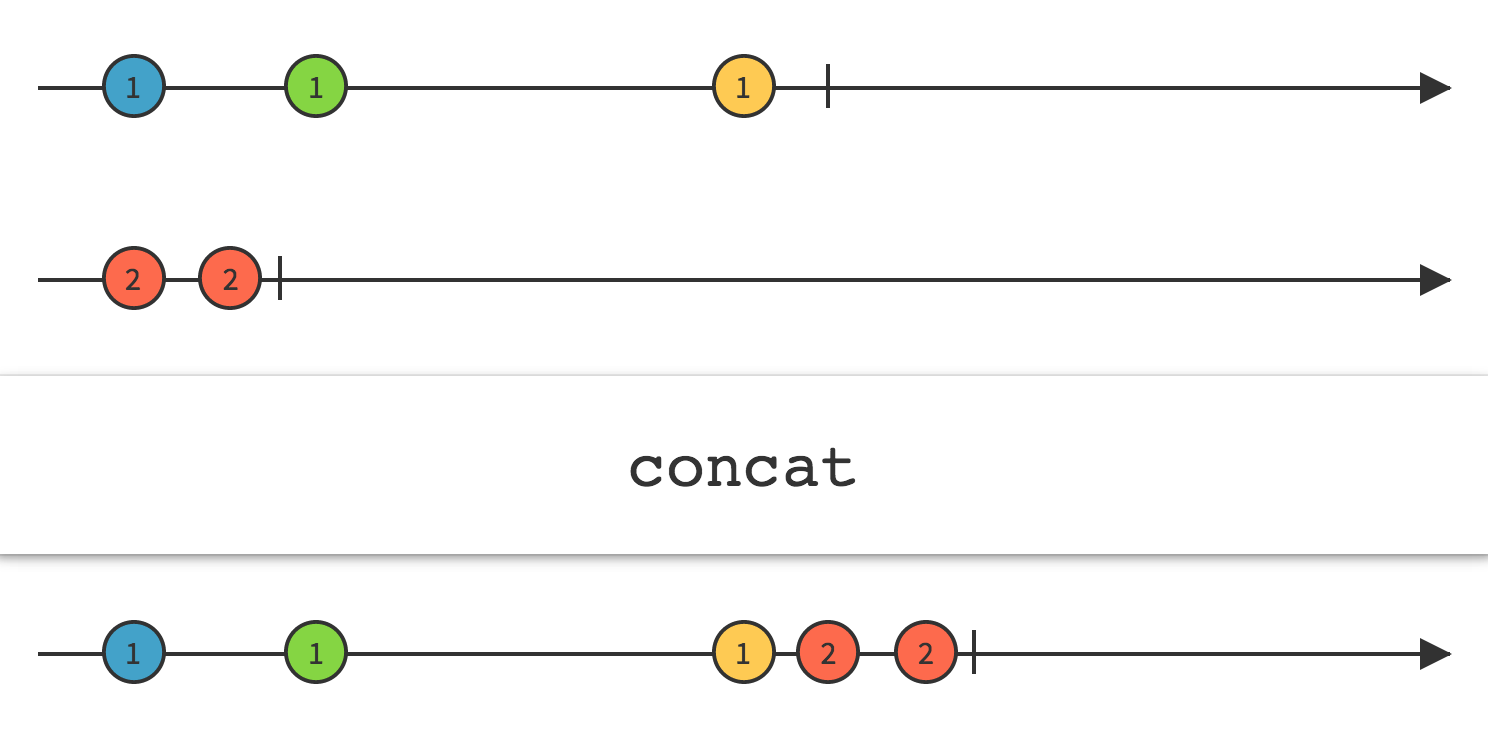
Concat 操作符连接多个 Observable 的输出,就好像它们是一个 Observable,第一个 Observable发射的所有数据在第二个 Observable 发射的任何数据前面,以此类推。
直到前面一个Observable终止,Concat 才会订阅额外的一个 Observable。注意:因此,如果你尝试连接一个"热" Observable(这种 Observable 在创建后立即开始发射数据,即使没有订阅者),Concat 将不会看到也不会发射它之前发射的任何数据。
public class UniRxConcatExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var a = this.UpdateAsObservable().Take(3).Select(_ => "A");
var b = this.UpdateAsObservable().Take(2).Select(_ => "B");
var c = a.Concat(b);
c.Subscribe(Debug.Log);
}
}
9.WhenAll
Linq All
确定序列中的所有元素是否都满⾜条件
此方法不返回集合的所有元素。 而是确定集合的所有元素是否满足条件。
class Pet
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
public static void AllEx()
{
// Create an array of Pets.
Pet[] pets = { new Pet { Name="Barley", Age=10 },
new Pet { Name="Boots", Age=4 },
new Pet { Name="Whiskers", Age=6 } };
// Determine whether all pet names
// in the array start with 'B'.
bool allStartWithB = pets.All(pet =>
pet.Name.StartsWith("B"));
Console.WriteLine(
"{0} pet names start with 'B'.",
allStartWithB ? "All" : "Not all");
}
// This code produces the following output:
// Not all pet names start with 'B'.UniRx WhenAll
判定是否Observable发射的所有数据都满⾜某个条件
传递一个判定函数给 WhenAll 操作符,这个函数接受原始 Observable 发射的数据,根据计算返回一个布尔值。WhenAll 返回一个只发射一个单个布尔值的 Observable,如果原始 Observable 正常终止并且每一项数据都满足条件,就返回 true;如果原始 Observable 的任意一项数据不满⾜足条件就返回False。
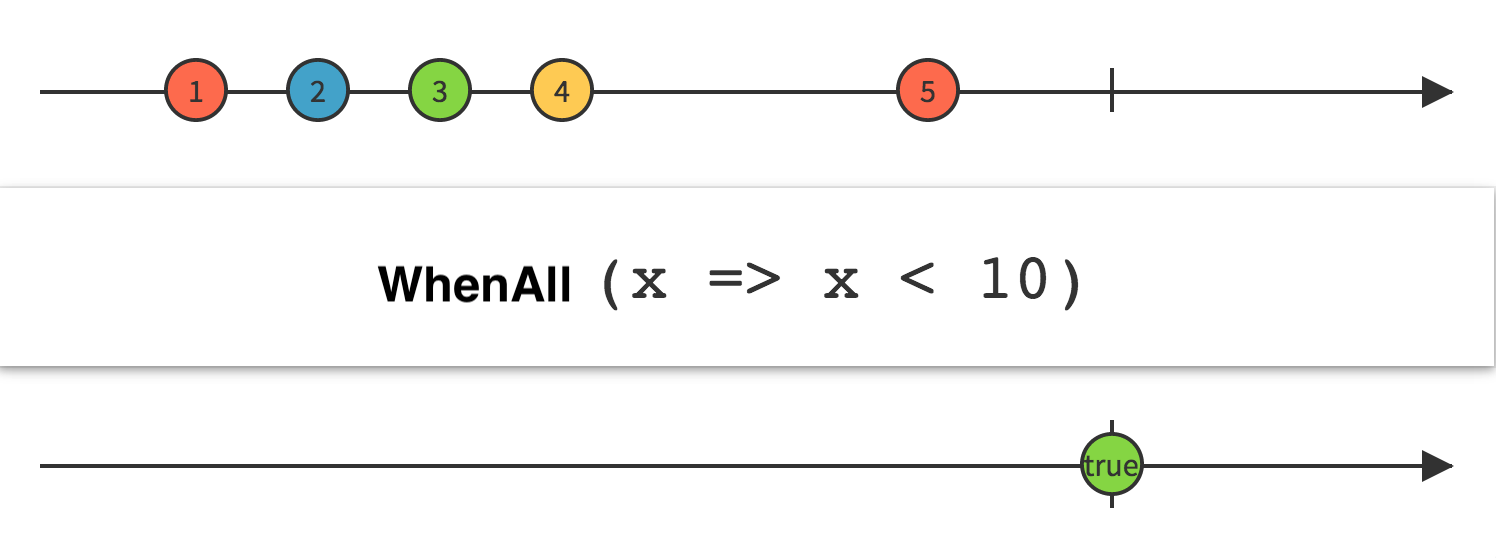
using System.Collections;
using UniRx;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxWhenAllExample : MonoBehaviour
{
IEnumerator A()
{
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1.0f);
Debug.Log("A");
}
IEnumerator B()
{
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1.0f);
Debug.Log("B");
}
IEnumerator C()
{
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1.0f);
Debug.Log("C");
}
private void Start()
{
var streamA = Observable.FromCoroutine(A);
var streamB = Observable.FromCoroutine(B);
var streamC = Observable.FromCoroutine(C);
Observable.WhenAll(streamA, streamB, streamC)
.Subscribe(_ => { Debug.Log("Completed"); });
}
}
10.OfType
Linq OfType
根据指定类型筛选 IEnumerable 的元素。
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class LINQOfTypeExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var list = new ArrayList { 30, 30.0f, "test" };
var filterList = list.OfType<float>();
foreach (var obj in filterList)
{
Debug.Log(obj);
}
}
}
//30.0fUniRx OfType
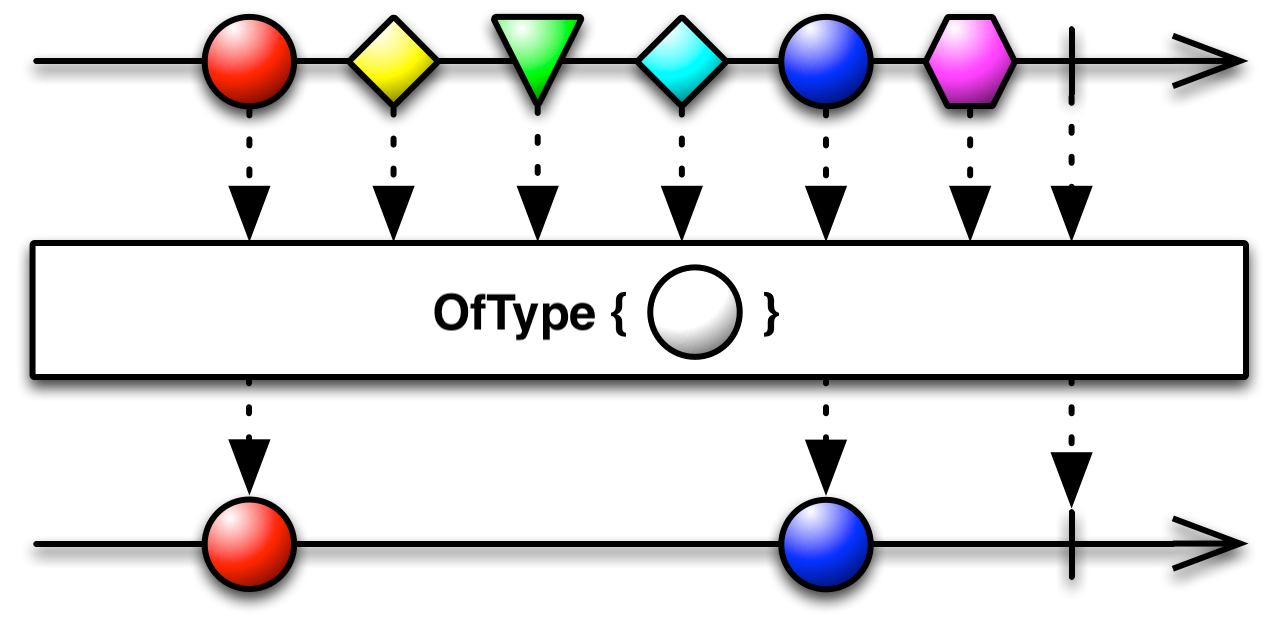
using UniRx;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxOfTypeExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
// 创建一个 Subject(Observable)
var objects = new Subject<object>();
// 订阅该 Observable,进行类型过滤
objects.OfType<object, string>().Subscribe(Debug.Log);
//手动发送数据
objects.OnNext(1);
objects.OnNext(2);
objects.OnNext("3");
objects.OnNext(4);
//手动结束
objects.OnCompleted();
}
}
//3
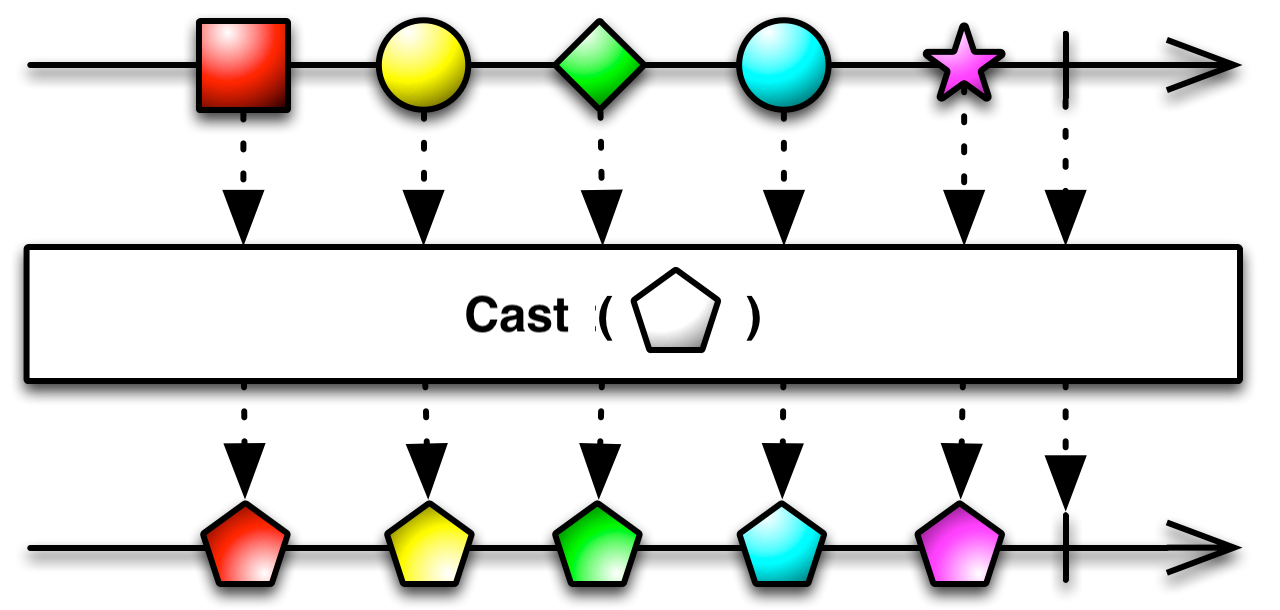
11.Cast
Linq Cast
将 IEnumerable 的元素强制转换为指定的类型。
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class LINQCastExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var fruits = new ArrayList { "mango", "apple", "lemon" };
var fruitNames =fruits.Cast<string>();
// 等同于
// var fruitNames = fruits.Select(fruit => fruit.ToString);
foreach (var fruit in fruitNames)
{
Debug.Log(fruit);
}
}
}UniRx Cast
using UniRx;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxCastExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
// 创建一个 Subject(Observable)
var objects = new Subject<object>();
// 订阅该 Observable,进行类型转换
objects.Cast<object, int>().Subscribe(i => Debug.Log(i));
// 手动发送数据
objects.OnNext(1);
objects.OnNext(2);
objects.OnNext(3);
// 手动结束
objects.OnCompleted();
}
}
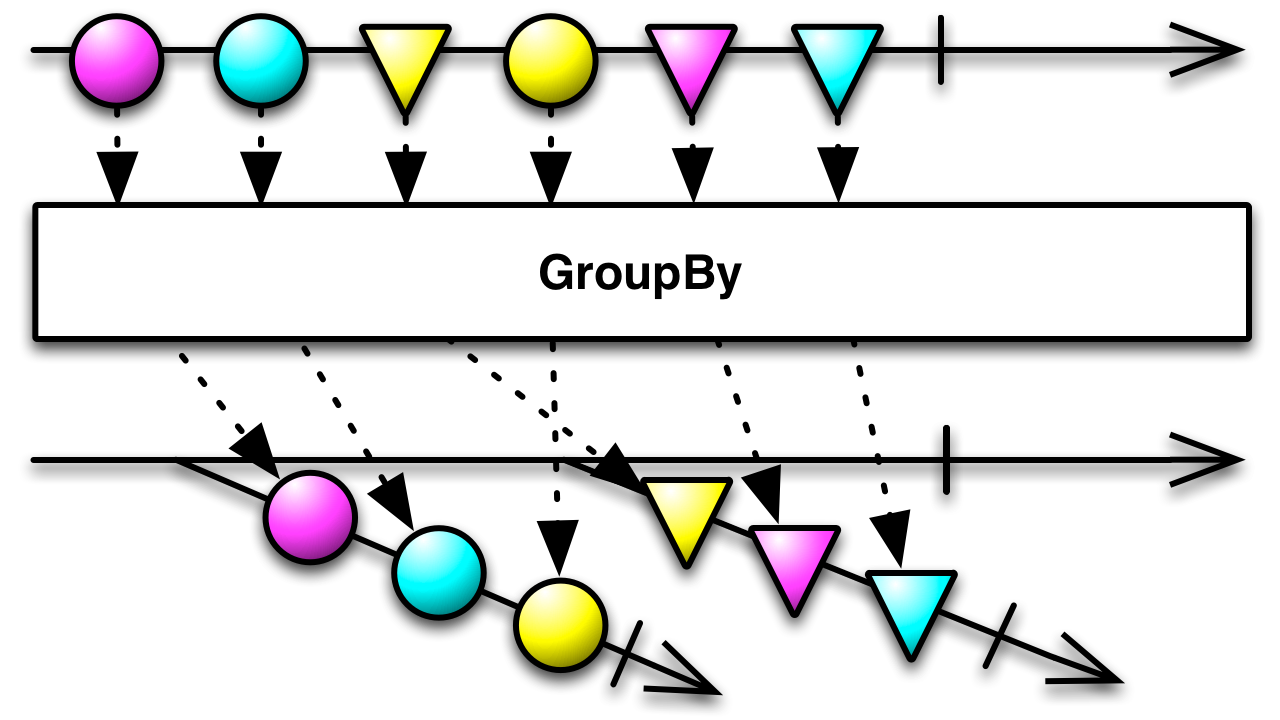
12.GroupBy
Linq GroupBy
对序列中的元素进行分组。
UniRx GroupBy
GroupBy操作符将一个发出项目 的Observable 划分为一个发出 Observable 的 Observable,每个 Observable 发出来自原始源 Observable 的项目的一些子集。哪些项目最终会出现在哪个 Observable 上,通常由一个判别函数决定,该函数评估每个项目并为其分配一个键。具有相同键的所有项目都由相同的 Observable 发出。
using System;
using UniRx;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxGroupByExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
Observable.Interval(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.1))
.Take(10)
.GroupBy(i => i % 3)
.Subscribe(group =>
{
group.Subscribe(number =>
{
Debug.LogFormat("Key:{0},Number:{1}", group.Key, number);
});
});
}
}
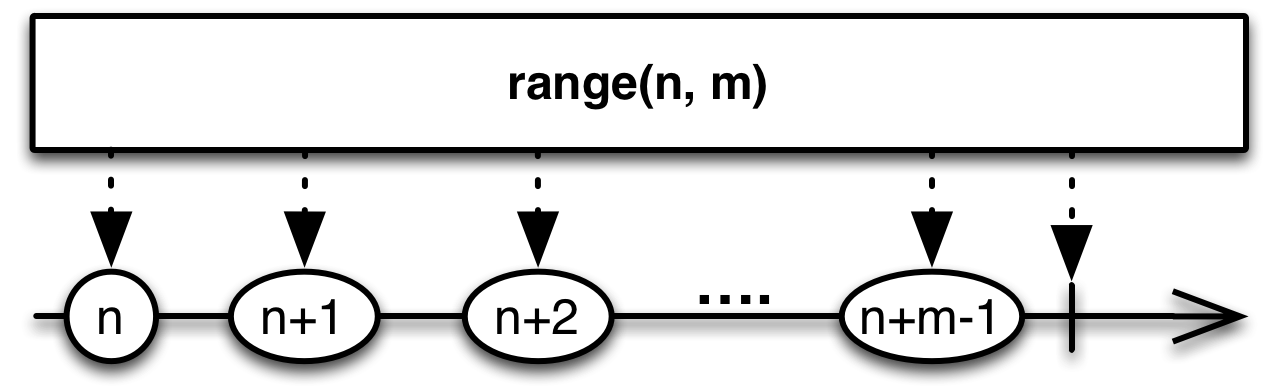
13.Range
Linq Range
生成指定范围内的整数的序列
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class LINQRangeExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var squares = Enumerable.Range(5, 3).Select(x => x * x);
foreach (var square in squares)
{
Debug.Log(square);
}
}
}
//25 36 49UniRx Range
using UniRx;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxRangeExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var squares = Observable.Range(5, 3).Select(x => x * x);
squares.Subscribe(square => { Debug.Log(square); });
}
}
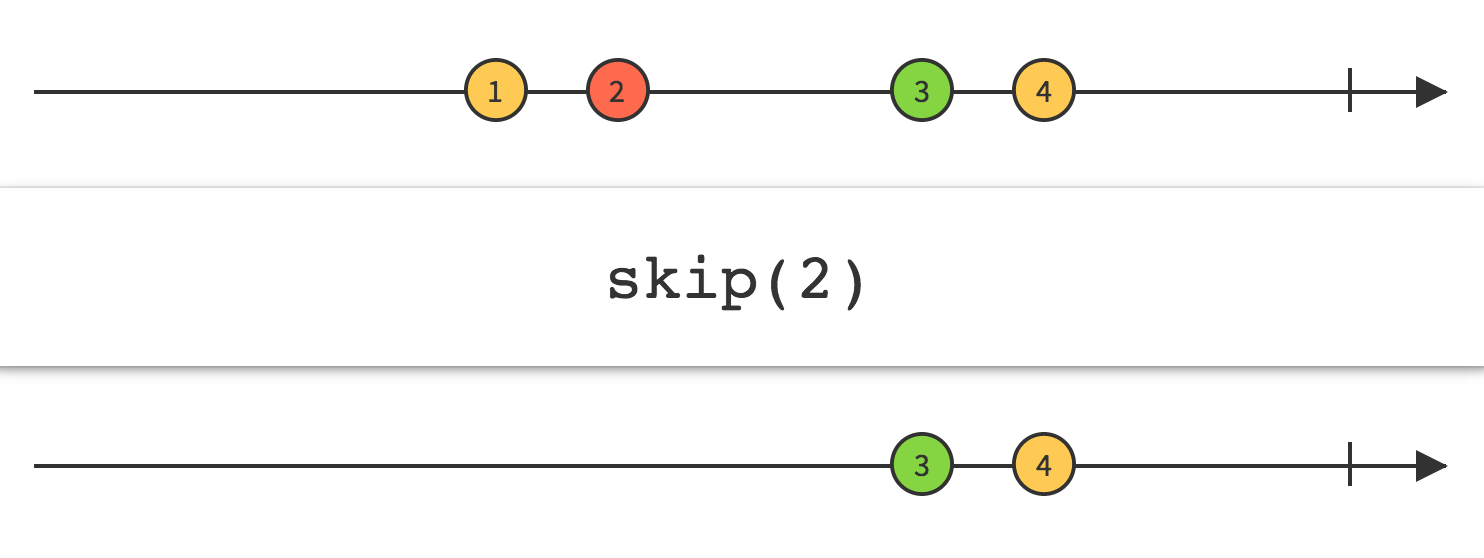
14.Skip
Linq Skip
跳过序列中指定数量的元素,然后返回剩余的元素。
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class LINQSkipExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
int[] grades = { 59, 82, 70, 56, 92, 98, 85 };
var lowerGrades =
grades.OrderByDescending(g => g).Skip(3);
foreach (var grade in lowerGrades)
{
Debug.Log(grade);
}
}
}
//82 70 59 56UniRx Skip
抑制Observable发出的前n项
通过使用Skip操作符修改Observable,你可以忽略Observable发出的前n项,只关注后面的那些项。
using UniRx;
using UniRx.Triggers;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxSkipExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
this.UpdateAsObservable()
.Where(_ => Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0))
.Skip(5).Subscribe(_ => { Debug.Log("mouse clicked"); });
}
}输出结果为,鼠标点击第六次时,才开始输出”mouse clicked”
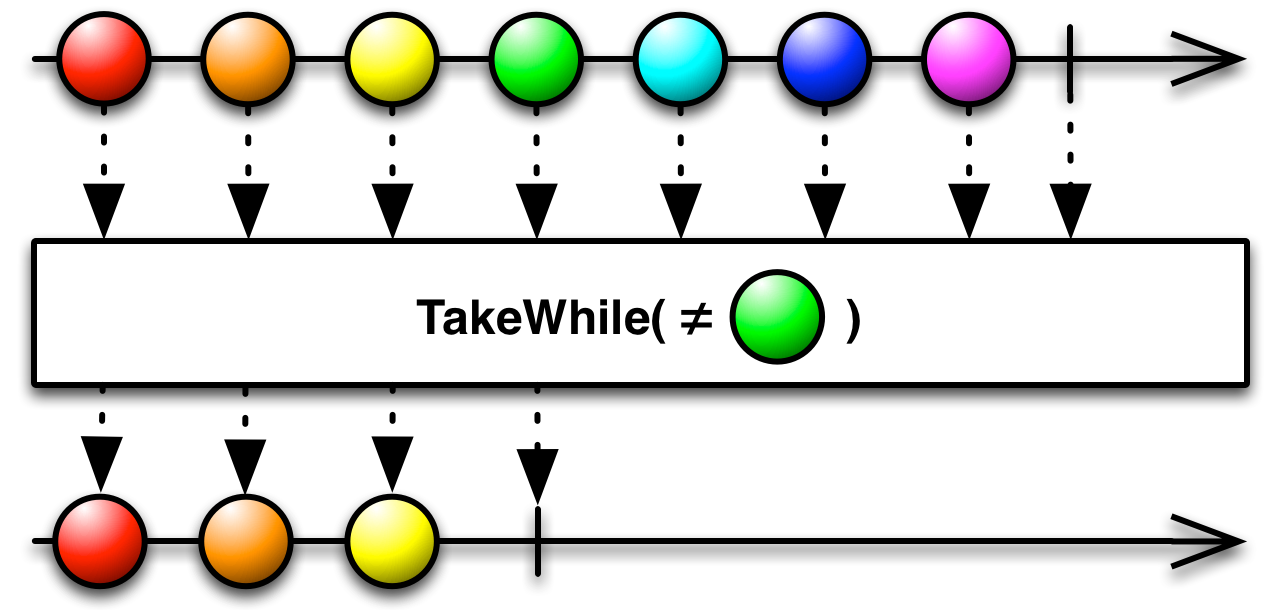
15.TakeWhile
Linq TakeWhile
如果指定的条件为 true,则返回序列中的元素,然后跳过剩余的元素
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class LINQTakeWhileExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var fruits = new[]
{
"apple", "banana", "mango", "orange","passionfruit", "grape"
};
var fruitsAfterOrange = fruits.TakeWhile(fruit => fruit != "orange");
foreach (var fruit in fruitsAfterOrange)
{
Debug.Log(fruit);
}
}
}UniRx TakeWhile
using UniRx;
using UniRx.Triggers;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxTakeWhileExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
this.UpdateAsObservable()
.TakeWhile(l => !Input.GetMouseButton(0))
.Subscribe(_ => Debug.Log("before mouse clicked"));
}
}持续输出”before mouse clicked”,当鼠标点击之后不再输出 “before mouse clicked”
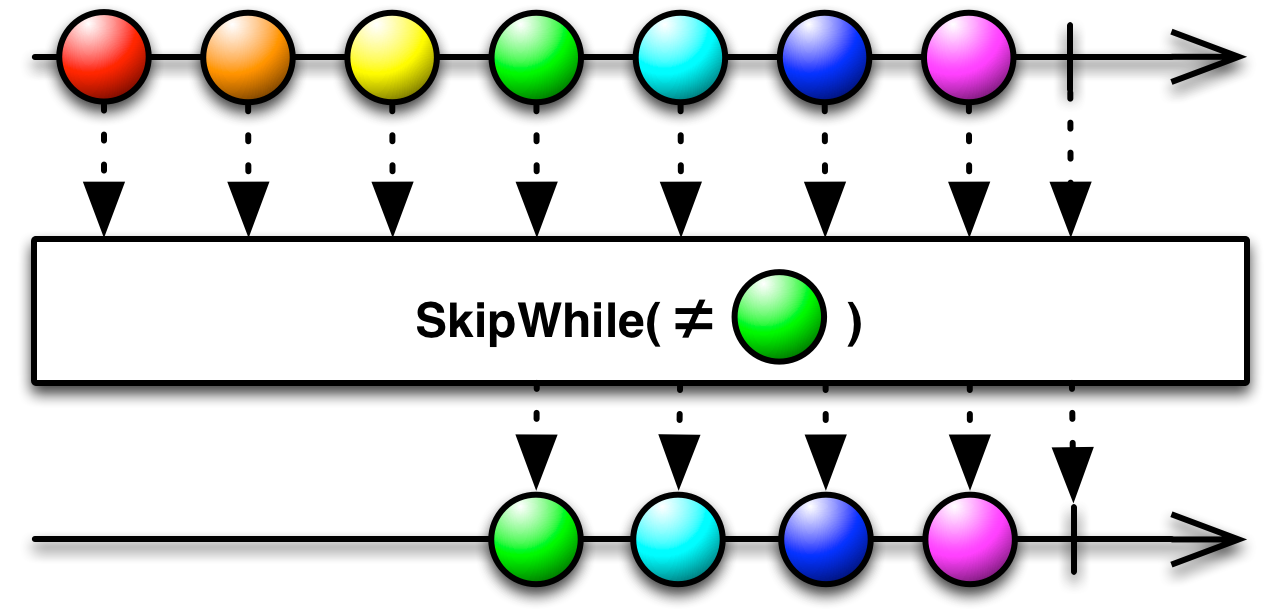
16.SkipWhile
Linq SkipWhile
如果指定的条件为 true,则跳过序列中的元素,然后返回剩余的元素。
| SkipWhile<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Int32,Boolean>) | 如果指定的条件为 true,则跳过序列中的元素,然后返回剩余的元素。 将在谓词函数的逻辑中使用元素的索引。 |
| SkipWhile<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Boolean>) | 如果指定的条件为 true,则跳过序列中的元素,然后返回剩余的元素。 |
下面的代码示例演示如何在 SkipWhile<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Int32,Boolean>) 依赖于元素索引的条件为 true 的情况下跳过数组的元素。
int[] amounts = { 5000, 2500, 9000, 8000,
6500, 4000, 1500, 5500 };
IEnumerable<int> query =
amounts.SkipWhile((amount, index) => amount > index * 1000);
foreach (int amount in query)
{
Console.WriteLine(amount);
}
/*
4000 1500 5500
*/下面的代码示例演示如何在 SkipWhile<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Boolean>) 条件为 true 的情况下跳过数组的元素。
int[] grades = { 59, 82, 70, 56, 92, 98, 85 };
IEnumerable<int> lowerGrades =
grades
.OrderByDescending(grade => grade)
.SkipWhile(grade => grade >= 80);
Console.WriteLine("All grades below 80:");
foreach (int grade in lowerGrades)
{
Console.WriteLine(grade);
}
/* 70 59 56 */UniRx SkipWhile
SkipWhile订阅源 Observable,但忽略 其发射,直到您指定的某些条件变为 false,此时 SkipWhile开始镜像源 Observable。
using UniRx;
using UniRx.Triggers;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxSkipWhileExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
this.UpdateAsObservable()
.SkipWhile(_ => !Input.GetMouseButton(0))
.Subscribe(_ => { Debug.Log("mouse button down"); });
}
}当点击鼠标后,持续输出 mouse button down
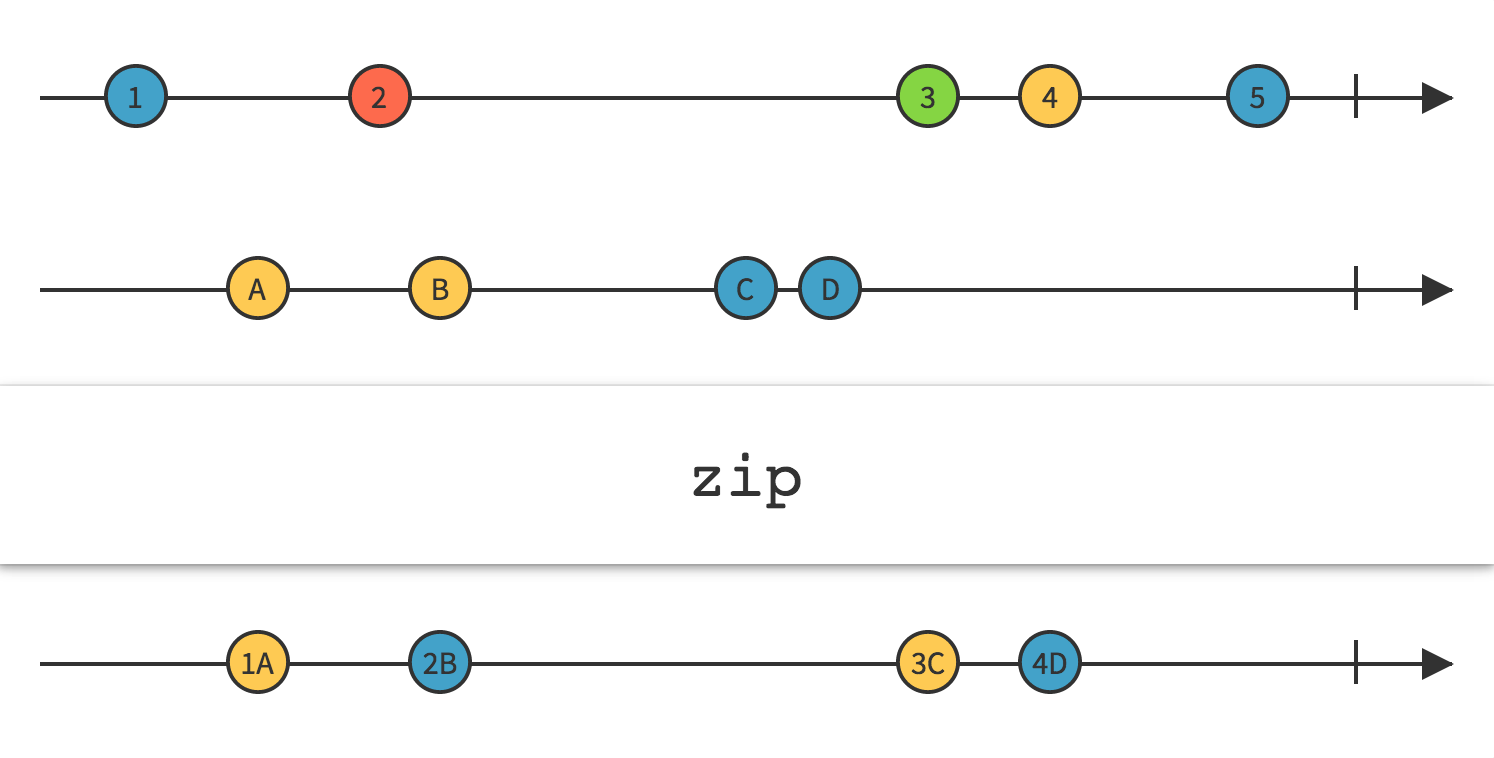
17.Zip
Linq Zip
将指定函数应⽤于两个序列的对应元素,以⽣成结果序列。
| Zip<TFirst,TSecond,TResult>(IEnumerable<TFirst>, IEnumerable<TSecond>, Func<TFirst,TSecond,TResult>) | 将指定函数应用于两个序列的对应元素,以生成结果序列。 |
| Zip<TFirst,TSecond,TThird>(IEnumerable<TFirst>, IEnumerable<TSecond>, IEnumerable<TThird>) | 生成包含三个指定序列中的元素的元组序列。 |
| Zip<TFirst,TSecond>(IEnumerable<TFirst>, IEnumerable<TSecond>) | 使用两个指定序列中的元素生成元组序列。 |
下面的代码示例演示如何使用 Zip 该方法合并两个序列
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class LINQZipExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
string[] words = { "one", "two", "three" };
var numbersAndWords = numbers.Zip(words, (first, second) => first + " " + second);
foreach (var item in numbersAndWords)
{
Debug.Log(item);
}
}
}
/*1 one
2 two
3 three*/UniRx Zip
这Zip方法返回一个 Observable,它将您选择的函数应用到由两个(或更多)其他 Observable 按顺序发出的项目组合,此函数的结果成为返回的 Observable 发出的项目。它以严格的顺序应用此函数,因此新 Observable 发出的第一项将是应用于 Observable1 发出的第一项和 Observable2 发出的第一项的函数的结果;新 zip-Observable 发出的第二个项目将是应用于 Observable 1 发出的第二个项目和 Observable 2 发出的第二个项目的函数的结果;等等。它只会发射与发射最少项目的源 Observable 发射的项目数量一样多的项目。
using UniRx;
using UniRx.Triggers;
using UnityEngine;
public class ZipExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var rightStream = this.UpdateAsObservable()
.Where(_ =>Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0));
var leftStream = this.UpdateAsObservable()
.Where(_ =>Input.GetMouseButtonDown(1));
leftStream.Zip(rightStream, (l, r) => Unit.Default)
.Subscribe(_ => { Debug.Log("ok"); });
}
}
运行之后,点击鼠标的顺序为, 左->右->左->右->左->左->左->右->右->右
输出的结果为:
// 左
ok // 右
// 左
ok // 右
// 左
// 左
// 左
ok // 右
ok // 右
ok // 右
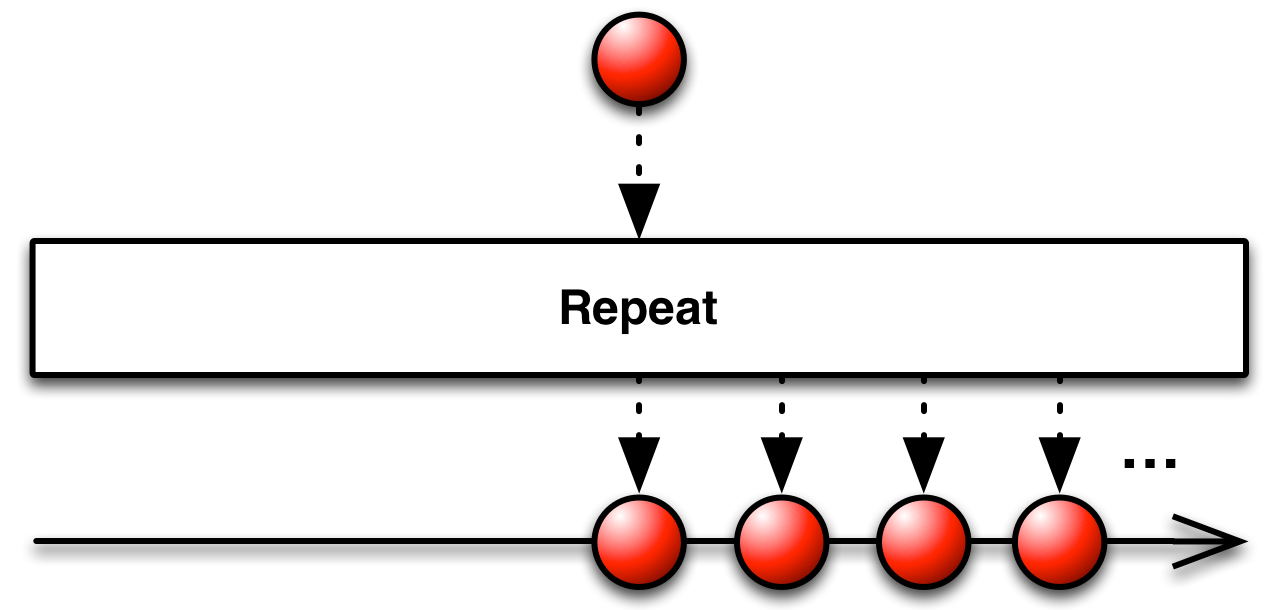
18.Repeat
Linq Repeat
生成包含一个重复值的序列
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class LINQRepeatExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var strings = Enumerable.Repeat("I like programming.", 5);
foreach (var str in strings)
{
Debug.Log(str);
}
}
}UniRx Repeat
Repeat运算符重复发出一个项目 。此运算符的某些实现允许您重复一系列项目,而某些实现允许您限制重复次数。
当你处理事件时,Repeat是一种重要但危险的方法,它可能会造成程序的无线循环,因此,请谨慎使用它:
using UniRx;
using UniRx.Triggers;
public class DangerousDragAndDrop:MonoBehaviour{
void Start(){
this.gameObject.OnMouseDownAsObservable()
.SelectMany(_=>this.gameObject.UpdateAsObservable())
.TakeUtil(this.gameObject.OnMouseUpAsObservable())
.Select(_=>Input.mousePosition)
.Repeat()
.Subscribe(x=>Debug.Log(x));
}
}UniRx另外提供了一种安全使用Repeat的方法。RepeatSafe:
如果重复调用OnComplete,Repeat将会停止。RepeatUntilDestroy(gameObject/component), RepeatUntilDisable(gameObject/component)允许在目标对象被销毁时停止。
this.gameObject.OnMouseDownAsObservable()
.SelectMany(_ => this.gameObject.UpdateAsObservable())
.TakeUntil(this.gameObject.OnMouseUpAsObservable())
.Select(_ => Input.mousePosition)
.RepeatUntilDestroy(this) // safety way
.Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x));
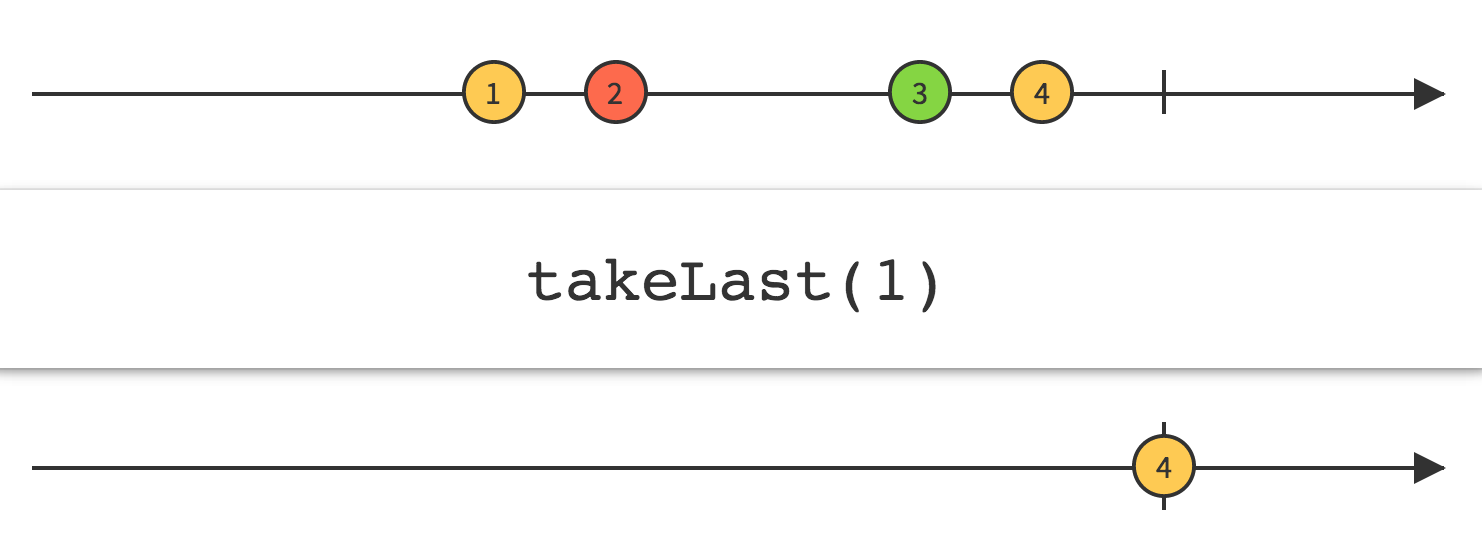
19.TakeLast
Linq TakeLast
获取序列的最后⼏项
UniRx TakeLast
通过使用TakeLast操作符修改Observable,你可以只发出由Observable发出的最后n项,并忽略在它们之前的那些项。
using System.Linq;
using UniRx;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxTakeLastExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
int[] grades = { 59, 82, 70, 56, 92, 98, 85 };
var bottomThreeGrades = grades.OrderByDescending(grade => grade)
.ToObservable().TakeLast(3);
bottomThreeGrades.Subscribe(buttomThreeGrade => Debug.Log(buttomThreeGrade));
}
}
20.Single
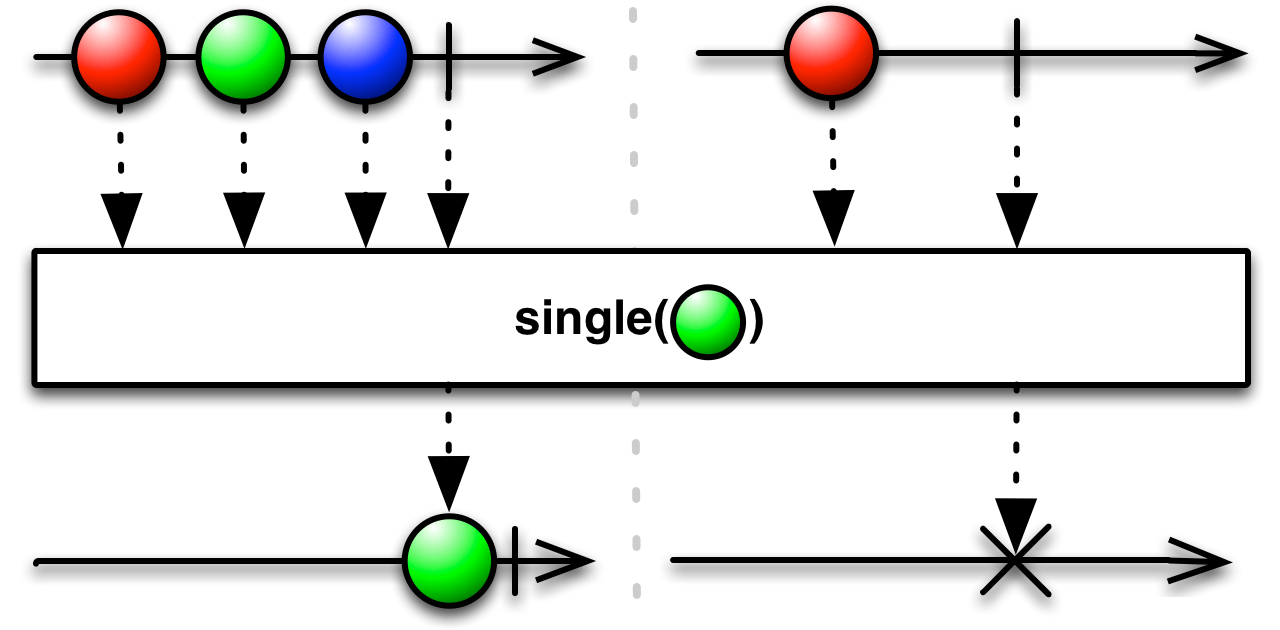
Linq Single
返回序列中的单个特定元素,与 First ⾮常类似,但是 Single 要确保其满⾜条件的元素在序列中只有⼀个
| Single<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>) | 返回序列的唯一元素;如果该序列并非恰好包含一个元素,则会引发异常。 |
| Single<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Boolean>) | 返回序列中满足指定条件的唯一元素;如果有多个这样的元素存在,则会引发异常。 |
下面的代码示例演示如何用于 Single<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>) 选择数组的唯一元素。
string[] fruits1 = { "orange" };
string fruit1 = fruits1.Single();
Console.WriteLine(fruit1);
/* orange */下面的代码示例演示如何在 Single<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>) 序列并非包含一个元素时引发异常。
string[] fruits2 = { "orange", "apple" };
string fruit2 = null;
try
{
fruit2 = fruits2.Single();
}
catch (System.InvalidOperationException)
{
Console.WriteLine("The collection does not contain exactly one element.");
}
Console.WriteLine(fruit2);
/*
The collection does not contain exactly one element.
*/Single<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Boolean>),返回序列中满足指定条件的唯一元素;如果有多个这样的元素存在,则会引发异常。
string[] fruits = { "apple", "banana", "mango",
"orange", "passionfruit", "grape" };
string fruit1 = fruits.Single(fruit => fruit.Length > 10);
Console.WriteLine(fruit1);
/*
passionfruit
*/
string fruit2 = null;
try
{
fruit2 = fruits.Single(fruit => fruit.Length > 15);
}
catch (System.InvalidOperationException)
{
Console.WriteLine(@"The collection does not contain exactly
one element whose length is greater than 15.");
}
Console.WriteLine(fruit2);
// The collection does not contain exactly
// one element whose length is greater than 15.如果输入序列不包含匹配元素,该方法 Single<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,Boolean>) 将引发异常。 若要在找不到匹配元素时返回 null ,请使用 SingleOrDefault。
UniRx Single
Single 操作符也与 First 类似,但是如果原始 Observable 在完成之前不是正好发射⼀次数据,它会抛出⼀个 NoSuchElementException。
using UniRx;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxSingleExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
string[] fruits = { "apple", "banana", "mango","orange", "passionfruit", "grape" };
fruits.ToObservable().Single(fruit => fruit.Length > 10)
.Subscribe(Debug.Log);
}
}
21.ToArray
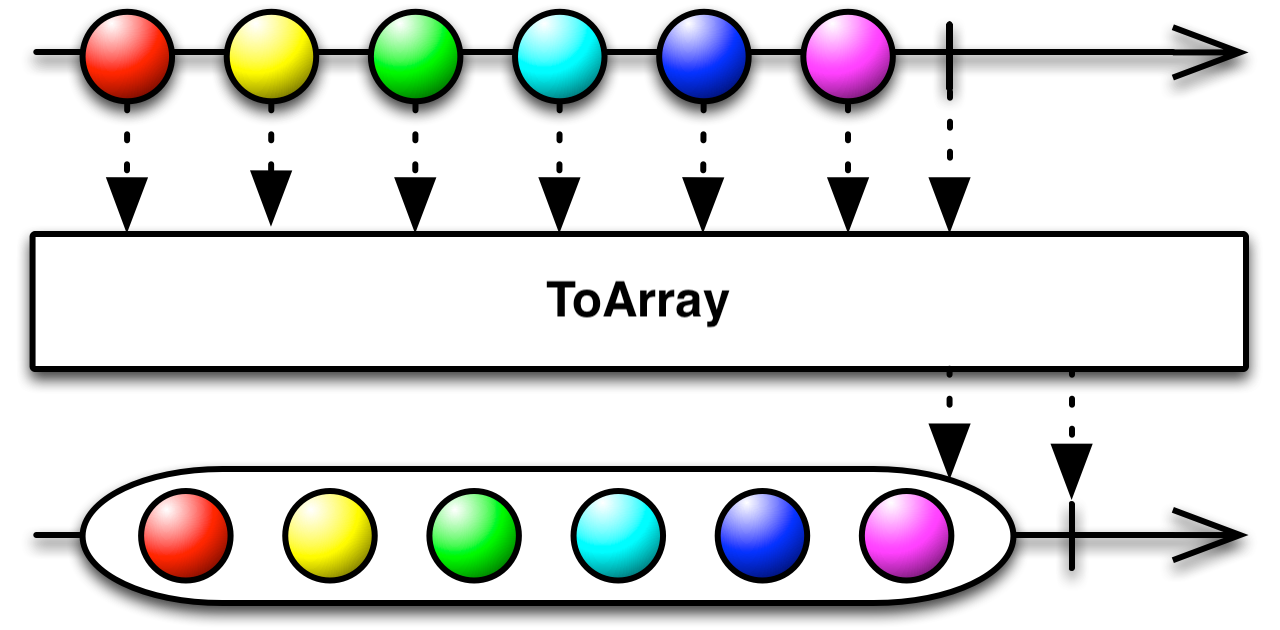
Linq ToArray
从 IEnumerable<T> 中创建数组
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class LINQToArrayExample : MonoBehaviour
{
private class Package
{
public string Company { get; set; }
public double Weight { get; set; }
}
void Start()
{
var packages =
new List<Package>
{
new Package {Company = "Coho Vineyard", Weight = 25.2},
new Package {Company = "Lucerne Publishing", Weight = 18.7},
new Package {Company = "Wingtip Toys", Weight = 6.0},
new Package {Company = "Adventure Works", Weight = 33.8}
};
var companies = packages.Select(pkg => pkg.Company).ToArray();
foreach (var company in companies)
{
Debug.Log(company);
}
}
}该方法 ToArray<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>) 强制立即进行查询计算,并返回包含查询结果的数组。 可以将此方法追加到查询中,以获取查询结果的缓存副本。
ToList 具有类似的行为,但返回的 List<T> 不是数组。
UniRx ToArray
using UniRx;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxToArrayExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var subject = new Subject<int>();
subject.ToArray().Subscribe(intArray =>
{
Debug.Log(intArray.GetType().ToString());
foreach (var i in intArray)
{
Debug.Log(i);
}
});
subject.OnNext(1);
subject.OnNext(2);
subject.OnNext(3);
subject.OnCompleted();
}
}
22.ToList
Linq ToList
从 IEnumerable<T> 创建一个 List<T>。
详情参考ToArray
UniRx ToList
详情参考ToArray
23.Aggregate
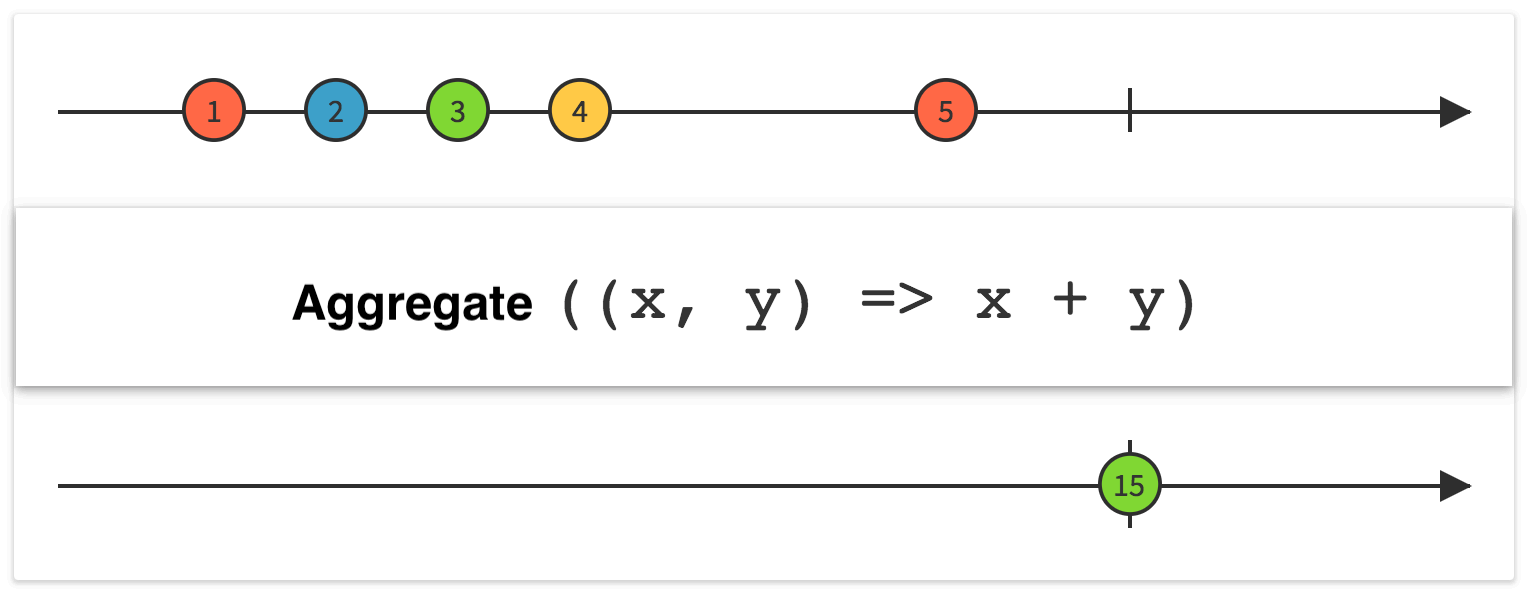
Linq Aggregate
对序列应用累加器函数。 将指定的种子值用作累加器的初始值,并使用指定的函数选择结果值。
| Aggregate<TSource,TAccumulate,TResult>(IEnumerable<TSource>, TAccumulate, Func<TAccumulate,TSource,TAccumulate>, Func<TAccumulate,TResult>) | 对序列应用累加器函数。 将指定的种子值用作累加器的初始值,并使用指定的函数选择结果值。 |
| Aggregate<TSource,TAccumulate>(IEnumerable<TSource>, TAccumulate, Func<TAccumulate,TSource,TAccumulate>) | 对序列应用累加器函数。 将指定的种子值用作累加器初始值。 |
| Aggregate<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,TSource,TSource>) | 对序列应用累加器函数。 |
下面的代码示例演示如何用于 Aggregate 应用累加器函数和结果选择器。
string[] fruits = { "apple", "mango", "orange", "passionfruit", "grape" };
// 确定数组中的任何字符串是否比"banana"长。
string longestName =
fruits.Aggregate("banana",
(longest, next) =>
next.Length > longest.Length ? next : longest,
// 以大写字符串的形式返回最终结果。
fruit => fruit.ToUpper());
Console.WriteLine(
"The fruit with the longest name is {0}.",
longestName);
// This code produces the following output:
//
// The fruit with the longest name is PASSIONFRUIT.UniRx Aggregate
Aggregate是内聚,是聚合操作的一种;功能是将一个数据列表挨个按照遍历的顺序去轮询,
内聚操作每次都会有返回值,必须要有返回;返回的值将作为下一次内聚操作的x值,
继续进行内聚,直到原始的数据列表结束。
using UniRx;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxAggregateExample : MonoBehaviour
{
private void Start()
{
Observable.Range(0, 8)
.Aggregate(0, (acc, currentValue) => acc + 5)
.Subscribe(xx =>{Debug.Log(xx);});
}
}
24.Empty
Linq Empty
返回具有指定类型参数的空 IEnumerable<T>
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class LINQEmptyExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
string[] names1 = { "Hartono, Tommy" };
string[] names2 = { "Adams, Terry", "Andersen, Henriette Thaulow","Hedlund, Magnus", "Ito, Shu" };
string[] names3 = { "Solanki, Ajay", "Hoeing, Helge","Andersen, Henriette Thaulow","Potra, Cristina", "Iallo, Lucio" };
var namesList = new List<string[]> { names1, names2, names3 };
var allNames = namesList.Aggregate(Enumerable.Empty<string>(),(current, next) => next.Length > 3 ? current.Union(next) :current);
foreach (var name in allNames)
{
Debug.Log(name);
}
}
}UniRx Empty

using UniRx;
using UnityEngine;
public class UniRxEmptyExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
var s = Observable.Empty<Unit>();
s.Subscribe(e => Debug.Log("e: " + e), () => Debug.Log("OnCompleted"));
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号