Java暑期学习第二十八天日报
一、今日学习的内容:
今日学习了12.2.7打印流的内容和12.2.8Random AccessFile随机访问文件的内容。。
二、遇到的问题:
无。
三、明日计划:
明天计划学习12.3的综合实例的内容。
今日学习的具体内容:
1.打印流
Java的PrintStream是打印流,输出数据很方便,如果遇到打印文件,首先考虑使用PrintStream。
实例——使用PrintStream写入数据
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.PrintStream; public class PrintStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args)throws FileNotFoundException{ PrintStream out=new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\people.txt")); out.println(true); out.println('A'); out.println(12); out.println("hello"); out.println(20.0); out.close(); } }
测试截图:

2.RandomAccessFile随机访问文件
.(1)RandomAccessFile可以随机读写文件,可以任意访问文件的位置,这是其他流不能操纵的,.RandomAccessFile类包括一个记录指针,用于标识当前流的读写位置,这个位置可以向前移动,也可以向后移动。.RandomAccessFile包含两个方法来操作文件记录指针。
| long getFilePoint() | 记录文件的当前位置 |
| void seek(long pos) | 将文件指针定位到pos位置 |
(2)RandomAccessFile类的构造函数如下;
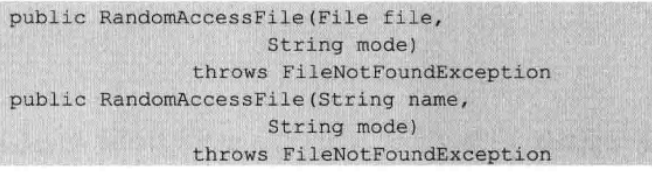
(3)RandomAccessFile读写文件有四种模式:

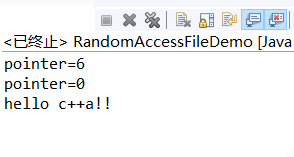
(4)实例——使用RandomAccessFile随机读写文件
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; public class RandomAccessFileDemo { public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{ RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("D:\\hello","rw"); byte[] b="hello java!!".getBytes(); raf.write(b); raf.seek(6); System.out.println("pointer="+raf.getFilePointer()); byte[] b2="c++".getBytes(); raf.write(b2); int len=-1; byte[] buf=new byte[1024]; raf.seek(0); System.out.println("pointer="+raf.getFilePointer()); while((len=raf.read(buf))!=-1) { String s=new String(buf,0,len); System.out.println(s); } } }
测试截图:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号