树状数组(不能有0,否则加lowbit一直为0死循环)
lowbit:lowbit(x) = x & -x
我们知道反码 = 全1 - x(当前数) + 1 => 补码,即 (反码 + 1)(补码) - x
111111 - x + 1 <=> 1000000 - x
e.g.此时有前面x & -x有前面消去
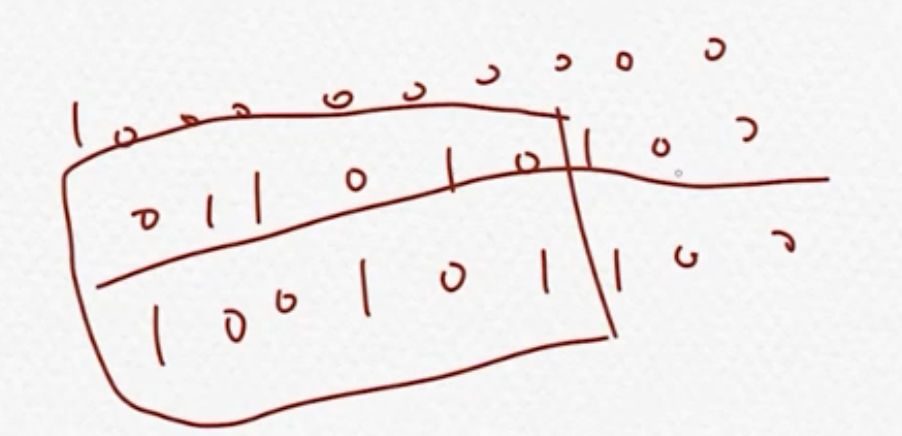
树状数组
维护序列a1,a2··an,有O(logn)完成单点加值以及查询前缀和操作
原理:树状数组c[i] = a[i] - lowbit(i) + 1 ~ i的和
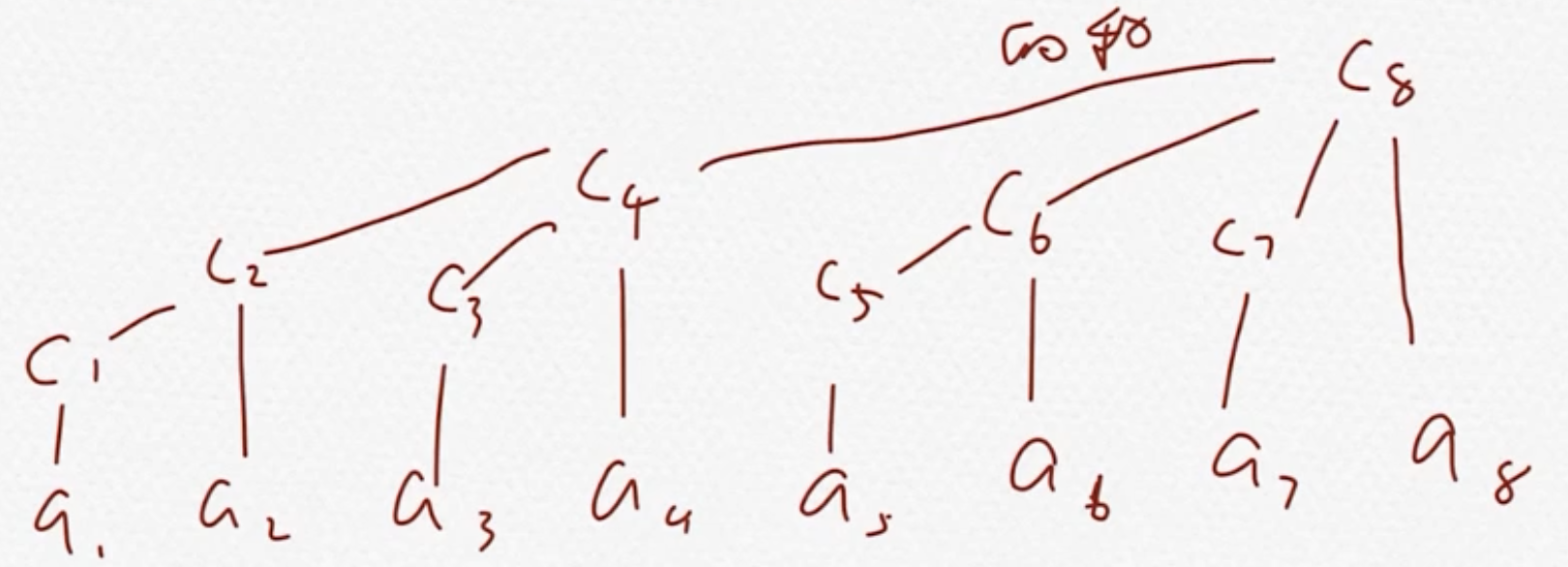
对于c[i] = a[i] - lowbit[i] + 1 ~ i, 有定义:
1 = 1 ~ 1,2 = 1 ~ 2,3 = 3 ~ 3,4 = 1 ~ 4,5 = 5 ~ 5,6 = 5 ~ 6,7 = 7 ~ 7,8 = 1 ~ 8
即有ci=???1000,实际记录的为???0001~???1000之和
???代表相同数
查询: 若查询1~x的和,当x!=0时(不断重复进行s+=c[x],x-=lowbit(x)操作)
每次减掉lowbit相当于去掉二进制最后一个1,即求一段和(存在和对应区间相接为整个区间,相加为1~x的和)
e.g.对于110110101每次减掉lowbit()存在:
110110001 ~ 110110100
110100001 ~ 110110000
110000001 ~ 110100000
100000001 ~ 110100000
依次求得区间[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] ,最终得到有连续区间
LL query(int x) {//1....x
LL s = 0;
for(; x; x -= x & (-x)) {
s += c[x];
}
return s;
}
修改:
方向相反,查询时不断减去,这里修改不断加
原理:看哪些c包含修改的数(受到影响),对应修改
void modify(int x, LL s) {//a[x] += s;
for(; x <= n; x += x & (-x)) {
c[x] += s;
}
}
树状数组1:单点更新,区间查询 树状数组1
对于修改操作,可近似等价于modify中加操作:对于5->10的操作,即+5
即求出原本的值,再知道差值,即可对应修改 <=> 加操作
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 501000;
int a[N], n, q;
LL c[N];
LL query(int x) {
LL s = 0;
for(; x; x -= x & (-x)) {
s += c[x];
}
return s;
}
void modify(int x, LL s) {//a[x] += s;
for(; x <= n; x += x & (-x)) {
c[x] += s;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
modify(i, a[i]);//对树状数组一开始为0,现给a[i]位置上加上值
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++ i) {
int ty;
scanf("%d", &ty);
if(ty == 1) {//modify
int x, d;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &d);
modify(x, d);
}
else {//query
int x, y;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
printf("%lld\n", query(y) - query(x - 1));
}
}
}
修改值版本:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 201000;
int a[N], n, q;
LL c[N];
LL query(int x) {
LL s = 0;
for(; x; x -= x & (-x)) {
s += c[x];
}
return s;
}
void modify(int x, LL s) {//a[x] += s;
for(; x <= n; x += x & (-x)) {
c[x] += s;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
modify(i, a[i]);//对树状数组一开始为0,现给a[i]位置上加上值
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++ i) {
int ty;
scanf("%d", &ty);
if(ty == 1) {//x=1为修改操作
int x, d;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &d);
modify(x, d - a[x]);//a[x]为原来值,改为d那么增量为d-x
a[x] = d;
}
else {
int x;
scanf("%d%d", &x);
printf("%lld\n", query(x));
}
}
}
单点修改值: 由于树状数组支持单点更新,此时有old = a[x],现想将值更改有new = d,那么有new = old + (new + old) 即 a[x] += (d - a[x])
e.g.5 -> 8
+3(8 - 5)
即modify(x, d - a[x]),在x位置上增量d - a[x],然后将a[x] = d(新值),否则a[x]里面还存着之前的old值
逆序对2:逆序对2
树状数组2:区间更新,单点查询 树状数组2:差分 + 推式子
考虑区间加,单点查询,有:
-
对于区间加:考虑其差分数组,另d[i] = a[i] - a[i - 1],a[i] = d1 + d2 + ··· + di,此时将[l,r] + 1即操作\(d_l\) + 1 和 \(d_{r+ 1}\) - 1两值即构造出区间更新
-
对于单点查询:构造出差分后,单点查询即d的前缀和
扩展:前缀查询
对于a1 = d1,a2 = d2,a3 = d3,实际上即x * d1 + (x-1) * d2 + d3 ->
\(\sum_{i = 1}^{x} (x + 1 - i)d_i = (x + 1)\sum_{i = 1}^{x}d_i - \sum_{i = 1}^{x}i * d_i\) 即维护\(d_i\)前缀和 和 i * \(d_i\)的前缀和
i * \(d_i\)的前缀和可以看做一个新的数组d'[i] = i * \(d_i\),维护d'[i]的前缀和即可
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 501000;
int a[N], n, q;
LL c[N];
LL query(int x) {
LL s = 0;
for(; x; x -= x & (-x)) {
s += c[x];
}
return s;
}
void modify(int x, LL s) {
for(; x <= n; x += x & (-x)) {
c[x] += s;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
//差分
modify(1, a[1]);
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++ i) {
modify(i, a[i] - a[i - 1]);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++ i) {
int ty;
scanf("%d", &ty);
if(ty == 1) {
int l, r, d;
scanf("%d%d%d", &l, &r, &d);
modify(l, d);
modify(r + 1, -d);
}
else {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("%lld\n", query(x));//对差分求前缀和
}
}
}
扩展版:
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long u64;//对2^64取模,用无符号整型自然溢出即可
const int N = 201000;
int n, q;
template<class T>//C++模版,可以自行搜索,T为自定义类型
//封装是因为有两个树状数组
struct BIT {
T c[N];
int size;
void resize(int s) {
size = s;
}
T query(int x) {
assert(x <= size);
T s = 0;
for(; x; x -= x & (-x)) {
s += c[x];
}
return s;
}
void modify(int x, T s) {
//一定不能有x = 0,x = 0会死循环
assert(x != 0);
for(; x <= size; x += x & (-x)) {//这里会判断,所以r+1范围>n也可
c[x] += s;
}
}
};
//封装之后比赛可以直接用,改一下类型即可
BIT<u64> c1, c2;//c1记前缀和,c2记i*di前缀和
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, & q);
c1.resize(n);
c2.resize(n);
for(int i = 0; i < q; ++ i) {
int ty;
scanf("%d", &ty);
if(ty == 1) {
int l, r;
u64 d;
scanf("%d%d%lld", &l, &r, &d);
c1.modify(l, d);
c1.modify(r + 1, -d);
c2.modify(l, l * d);
c2.modify(r + 1, (r + 1) * (-d));
}
else {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
u64 ans = (x + 1) * c1.query(x) - c2.query(x);
printf("%llu\n", ans);
}
}
}
树状数组二分:查询最大的T < s
int query(LL s) {
LL t = 0;//1~pos的和
int pos = 0;//pos记录当前走到什么位置
for(int j = 18; j >= 0; -- j) {//从高位往低位做,只要任意2整次幂>=n即可
if(pos + (1 << j) <= n && t + c[pos + (1 << j)] <= s) {
pos += (1 << j);
t += c[pos];
}
}
}
更常用写法:不记录t而是直接用s去减
s不断减去前缀,保证s >= 0即可(能减则减掉)
点击查看代码
int query(LL s) {
LL t = 0;
int pos = 0;
for(int j = 18; j >= 0; -- j) {
if(pos + (1 << j) <= n && c[pos + (1 << j)] <= s) {
pos += (1 << j);
s -= c[pos];
}
}
return pos;
}
有for j = $\left \lceil logn \right \rceil $ ~ 0,记录pos当前走到的位置,t记1~pos的和
有forj从高位->低位,令${pos}' $= pos + \(2^j\)
由于从高位->低位,做到j位时存在:
\((j~后j位都为0)_2\) = ???000000
c[ ${pos}' $ ]操作即将当前第j位变为1 -> 有???100000,即有c[${pos}' $]存的刚好是???000001 ~ ???100000的和
存的是pos+1 ~ ${pos}' $的和 (pos为???000000)
当t + c[${pos}' $] <= s,即将这位改为1,其和仍小于等于s(则可将其加上去),则将pos = \({pos}'\),令t += c[${pos}' $]
每次尝试将这位改为1,和仍小的话则改为1
从高位到低位枚举,最后pos即满足条件pos
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 501000;
int a[N], n, q;
LL c[N];
//查询变了, 不再是找前缀和, 变为最大前缀 <= s
int query(LL s) {
LL t = 0;//1~pos的和
int pos = 0;//pos记录当前走到什么位置
for(int j = 18; j >= 0; -- j) {//从高位往低位做,只要任意2整次幂>=n即可
if(pos + (1 << j) <= n && t + c[pos + (1 << j)] <= s) {
pos += (1 << j);
t += c[pos];
}
}
return pos;
}
void modify(int x, LL s) {
for(; x <= n; x += x & (-x)) {
c[x] += s;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
modify(i, a[i]);//对树状数组一开始为0,现给a[i]位置上加上值
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++ i) {
int ty;
scanf("%d", &ty);
if(ty == 1) {
int x, d;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &d);
modify(x, d - a[x]);
a[x] = d;
}
else {
LL s;
scanf("%lld", &s);
printf("%d\n", query(s));//对差分求前缀和
}
}
}
总结:对权值开树状数组可支持操作:(插入一个数,删除一个数,查询第k个),很像平衡树但也可通过树状数组做
插入一个数:即将对应的c[x] += 1(这里c[x]为x出现多少次的原数组)
删除一个数:c[x] -= 1
查询第k大:即查询从小->大的第k个,找到一最大前缀T有其和 <= k+1,即知道右边数字为小->大的第k个
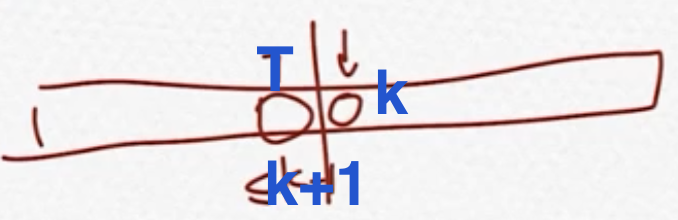
二进制位从小大的大,若T(大到小找到<=k+1)则剩余为k
查询第k个数可以通过树状数组二分来实现
高维树状数组(一般会和其他结合有神奇应用):单点修改值,区间查询
高维有类似的写法,即对于c[i][j]记录的是a[i - lowbit(i) + 1 ~ i][j - lowbit(j) + 1 ~ j]的前缀和
对于多维的错误写法:导致x执行1次时,y已经变为0
LL query(int x, int y) {
LL s = 0;
for(; x; x -= x & (-x)) for(; y; y -= y & (-y)){
s += c[x];
}
return s;
}
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 510;
int n, m, q;
int a[N][N];
LL c[N][N];
LL query(int x, int y) {
LL s = 0;
for(int p = x; p; p -= p & (-p)) {
for(int q = y; q; q -= q & (-q)) {//即保证x循环时存在y的写法
s += c[p][q];
}
}
return s;
}
void modify(int x, int y, LL s) {
for(int p = x; p <= n; p += p & (-p)) {
for(int q = y; q <= m; q += q & (-q)) {
c[p][q] += s;
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &q);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++ j) {
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
modify(i, j, a[i][j]);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++ i) {
int ty;
scanf("%d", &ty);
if(ty == 1) {
int x, y, d;
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &d);
modify(x, y, d - a[x][y]);
a[x][y] = d;
}
else {
int x, y;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y );
printf("%lld\n", query(x, y));
}
}
}
高维树状数组神奇应用:平面上插n个点,支持两维都小于(xi <= X并且 yi <= Y)的里面有多少点满足
即可想象有一n*n数组,给对应插点位置 + 1 ->即变为求前缀和
当n = 1e5时,用hash表 + 二维树状数组方法,将用到的位置存到hash表中,即O(n\(log^2\)n)做法




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号