JDBC 尚硅谷 数据库链接+操作(上篇)
days01
1. JDBC(Java Database Connectivitu):是一个独立于特定数据库管理系统、通用的SQL数据库存储和操作的公共接口;
2. JDBC接口包括两个层次
面向应用的API:Java API,抽象接口,开发使用(连接数据库,执行语句,获得结构);
面向数据库的API:供开发商使用;
3. JDBC使用流程以及连接方式(主要记方式五,其他几种为过渡)
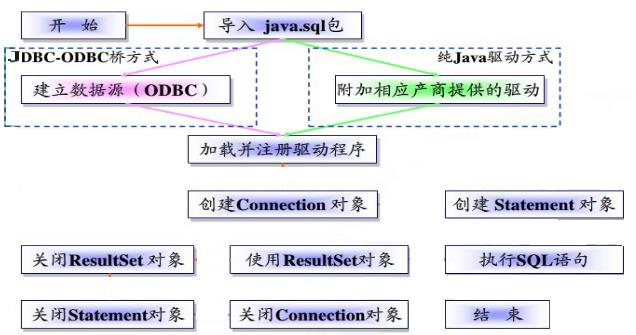
方式五:实现了数据代码的分离,实现解耦;修改时可以直接修改,不必修改程序再打包;
// 方式五(最终版,由1-4推进而来),将数据库连接需要的4个基本信息申明在配置文件中,通过读取配置文件的方式,获取连接 public static void testConnection5() throws Exception { // 1.读取配置文件中的4个基本信息,配置文件中等号两边不加空格 InputStream is = test.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"); // 2.加载配置文件中的数据 Properties pros = new Properties(); pros.load(is); // 获取 String user = pros.getProperty("user"); String password = pros.getProperty("password"); String url = pros.getProperty("url"); String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass"); Class.forName(driverClass); // 3.获取连接 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); }
// 连接方式一:使用第三方插件的方式连接 public static void testConnection1() throws SQLException { Driver dirver = new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver(); // jdbc:mysql:协议 // localhost:ip地址 // 3306:默认mysql的端口号 // jdbc_learn:数据库 String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/abc?serverTimezone=UTC"; // 将用户名和密码封装在Properties中 Properties info = new Properties(); info.setProperty("user", "root"); info.setProperty("password", "root"); Connection connection = dirver.connect(url, info); } // 连接方式二:使用反射方式连接 public static void testConnection2() throws Exception { // 1.获取Driver实现类对象,使用反射 // 替换方式一中使用第三方插件获取driver对象 Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance(); ... } // 方式三:使用DriverManager代替Driver public static void testConnection3() throws Exception { ... // 1.获取Driver实现类对象 Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance(); // 注册驱动 DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); // 获取连接 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); } // 方式四:省略注册驱动 public static void testConnection4() throws Exception { ... Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance(); // 注册驱动 // DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); // mysql的Driver中存在静态代码块,自动注册 // 3.获取连接 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); }
days02
使用PreparedStatement实现CRUD操作
1. 操作和访问数据库,Java.sql有3个接口定义数据库调用的不同方式:
Statement:用于执行静态SQL语句并返回他所成结果的对象;(需要拼字符串,存在SQL注入)
PreparedStatement:SQL语句被预编译并存储在此对象中,可以使用次对象多次高效的执行该语句;
CallableStatement:用于执行SQL存储过程;
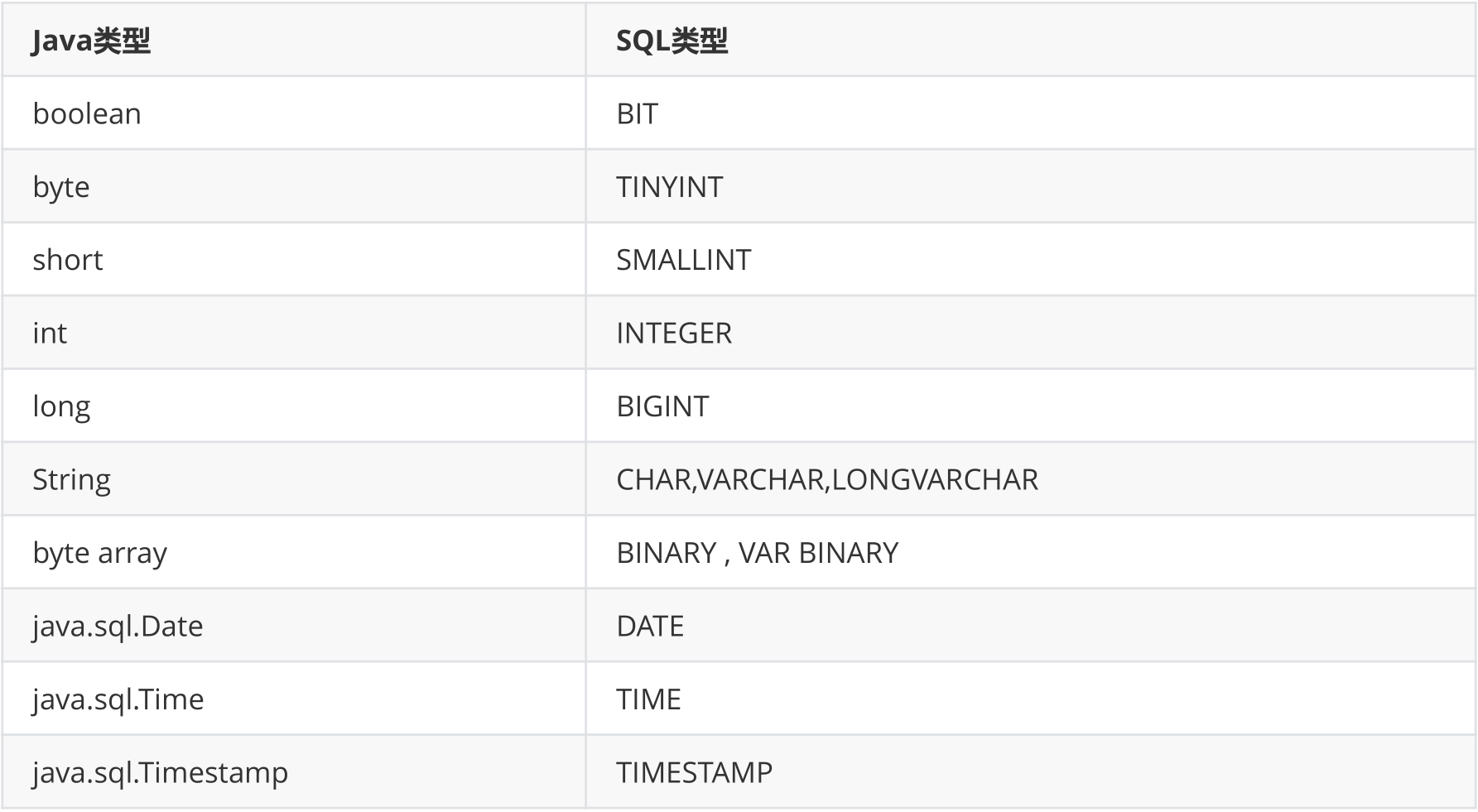
2. Java与SQL对应数据类型转换表
3. PreparedStatement 解决SQL注入问题
原理:PreparedStatement 采用预编译SQL语句,通过填充占位符的方式,表示谁且谁的关系,不管填什么,且的关系不会改变;
优势:PreparedStatement 操作Blob的数据,而 Statement 做不到;
可以实现更高效的批量操作;
4. 操作 Blob 数据:
插入:PreparedStatement.setBlob(位置,输入流);//把文件读入 FileInputStream
如果在指定了相关的Blob类型以后,报错:xxx too large;
那么在mysql的安装目录下,找my.ini文件加上如下的配置参数: max_allowed_packet=16M。
同时注意:修改了my.ini文件之后,需要重新启动mysql服务。
5. 更高效的批量操作
方式一:使用 Statement,拼接一条新的sql语句,再执行一条,循环执行插入的条数;
方式二:使用 PreparedStatement,内存中只有一条sql语句模板,只是占位符不同,使用预编译方式;
方式三 -----> 方式二:提升约 150倍
方式三:(批处理)使用 addBatch()、executeBatch()、clearBatch() 组合,累积一定量的 sql 语句,批量执行;
方式四 -----> 方式三:提升约 3 倍
方式四(终极版):设置不允许自动提交数据,批处理全都提交结束之后,再 commit() 提交处理;(需要把自动提交关闭)
预编译:
DBServer会对预编译语句提供性能优化。因为预编译语句有可能被重复调用;
所以语句在被DBServer的编译器编译后的执行代码被缓存下来,那么下次调用时只要是相同的预编译语句就不需要编译;
只要将参数直接传入编译过的语句执行代码中就会得到执行。
批处理:
mysql服务器默认是关闭批处理的,需要添加一个参数,开启mysql批处理:?rewriteBatchedStatements=true 写在配置文件的url后面;
使用更新的 mysql 驱动:mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar,自动支持;
6. PreparedStatement 和 Statement 的区别
① 都是Sun公司接口里的规范,因此不是第三方的;
② PreparedStatement 属于 Statement 的一个子接口,因此实现的功能一样(都是传送 sql 语句到数据库中执行操作);
③ 一般都是用 PreparedStatement 替换 Statement 进行操作;
Statement 存在两个弊端:存在拼串操作比较繁琐、存在SQL注入问题;
PreparedStatement 可以对 Blob 进行操作;
PreparedStatement 可以实现更高效的批量操作;



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号