day 18
nohup命令
nohup 默认情况下会输出到当前目录并在当前目录创建文件 nohup.txt
nohup command & 放到后台去运行
nohup command 不加 & 还是在前台运行
直接用 nohup command : 就在前台运行,只不过把运行记录到了 nohup.txt
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# nohup ping baidu.com
nohup: ignoring input and appending output to ‘nohup.out’
用 ctrl + z 暂停后台任务 可以看到在终端可以进行其他操作了,但是后台运行的任务被停止了
^Z
[2]+ Stopped nohup ping baidu.com
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
用 jobs 可以查看后台任务的情况
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# jobs
[2]+ Stopped nohup ping baidu.com #可以看到这个任务目前是停止的
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
用 bg + 任务号 可以继续在后台运行
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# bg 2
[2]+ nohup ping baidu.com &
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# jobs
[2]+ Running nohup ping baidu.com & #此时是运行起来了,并且可以在终端进行其他操作
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
用 fg + 任务号 把任务拿到前台运行
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# fg 2
nohup ping baidu.com
这个 nohup 命令来管理前台,后台任务。这样做的好处就是把一个任务放到后台进行,还不影响我们其他操作。
如果知识在前台运行,遇到故障,这个任务就会丢失。而放到后台运行,是不会丢失的。
如下
#此时这个任务在后台运行。把这个终端关掉再开一个终端来查看进程
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# jobs
[2]+ Running nohup ping baidu.com &
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ps -ef | grep ping #查看 ping 进程还是活着的
root 3278 1 0 16:12 ? 00:00:00 ping baidu.com
root 3380 3347 0 16:24 pts/3 00:00:00 grep --color=auto ping
监测一下这个 nohup.txt 文件看它是否还在写入数据
可以从下图看到,这个程序还是在进行的。
理解linux的数据流
执行linux命令时,linux默认为用户进程提供了3种数据流
- stdin
- 标准输入、0
- 一般是键盘输入数据
- 比如cat命令等待用户输入
- stdout
- 标准输出、1
- 程序执行结果,输出到终端
- stderr
- 标准错误输出,2
- 程序执行结果,输出到终端
标准输入重定向
[root@167 opt]# cat < /etc/passwd # 输入重定向,原本是来自于终端的键盘输入,改为了,可以是来自于文件的输入
# 比如用在数据库的,数据导入
mysql < /opt/back.sql
理解重定向符号和数据流代号
练习数据流
练习数据流
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat #交互式的输出,你输入什么它就输出什么
你好
你好
我是Linux
我是Linux
# ctrl + d 没有提示退出
我似乎
我是Linux
我是Linux
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
ctrl + c 会出先 ^C 这样的一个中断 符号
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat
nihao
nihao
linux
linux
^C
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# llll /opt #输入错误的命令 会有一个报错
-bash: llll: command not found
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ls /oppp #输入错误的文件目录,也会报错
ls: cannot access /oppp: No such file or directory
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
如何把这报错的信息不让他显示在终端呢?就需要借用重定向符号了。
> 覆盖写入内容到文件
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ls /opt > /tmp/opt.log #当我们用了重定向符号后,就不会在终端显示出信息,把信息输入到了指定的文件内
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ls /opt > /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat /tmp/opt.log
jumpserver
log
messages
opt
tengine233
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
>> 追加内容写入到文件
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ls /opt >> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ls /opt >> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat /tmp/opt.log
jumpserver
log
messages
opt
tengine233
jumpserver
log
messages
opt
tengine233
jumpserver
log
messages
opt
tengine233
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
2> 2是stderr的代号,也就是报错信息,覆盖内容到指定文件
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# lllll /opt 2> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# lllll /opt 2> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# lllll /opt 2> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat /tmp/opt.log
-bash: lllll: command not found
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
2>> 追加报错内容到指定文件
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# lllll /opt 2>> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# lllll /opt 2>> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat /tmp/opt.log
-bash: lllll: command not found
-bash: lllll: command not found
-bash: lllll: command not found
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
2>&1 把stderr当作stdout去处理
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# lllll /opt > /tmp/opt.log 2>&1
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# lllll /opt > /tmp/opt.log 2>&1
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat /tmp/opt.log
-bash: lllll: command not found
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
&> 跟2>&1一个原理
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ls /oppppp &> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ls /oppppp &> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat /tmp/opt.log
ls: cannot access /oppppp: No such file or directory
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ls /oppppp &>> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# ls /oppppp &>> /tmp/opt.log
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat /tmp/opt.log
ls: cannot access /oppppp: No such file or directory
ls: cannot access /oppppp: No such file or directory
ls: cannot access /oppppp: No such file or directory
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
Linux资源管理篇
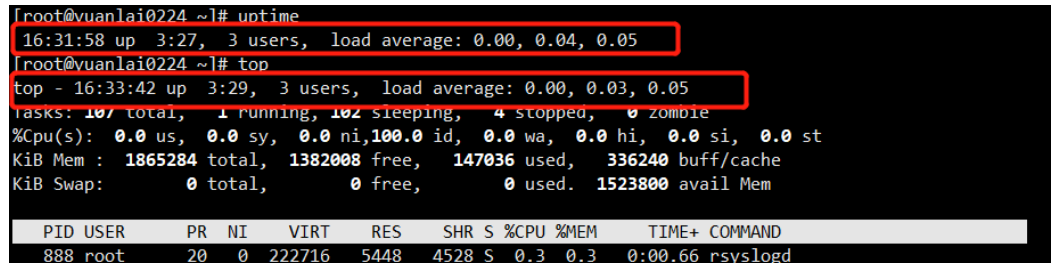
uptime
uptime 查看机器负载。系统在单位时间内的压力
等同于 top 查看资源管理的 第一行内容
只不过 top 查看到的是动态的,uptime 查看的是在某一时间的负载。
查看当前机器是几核的 cpu
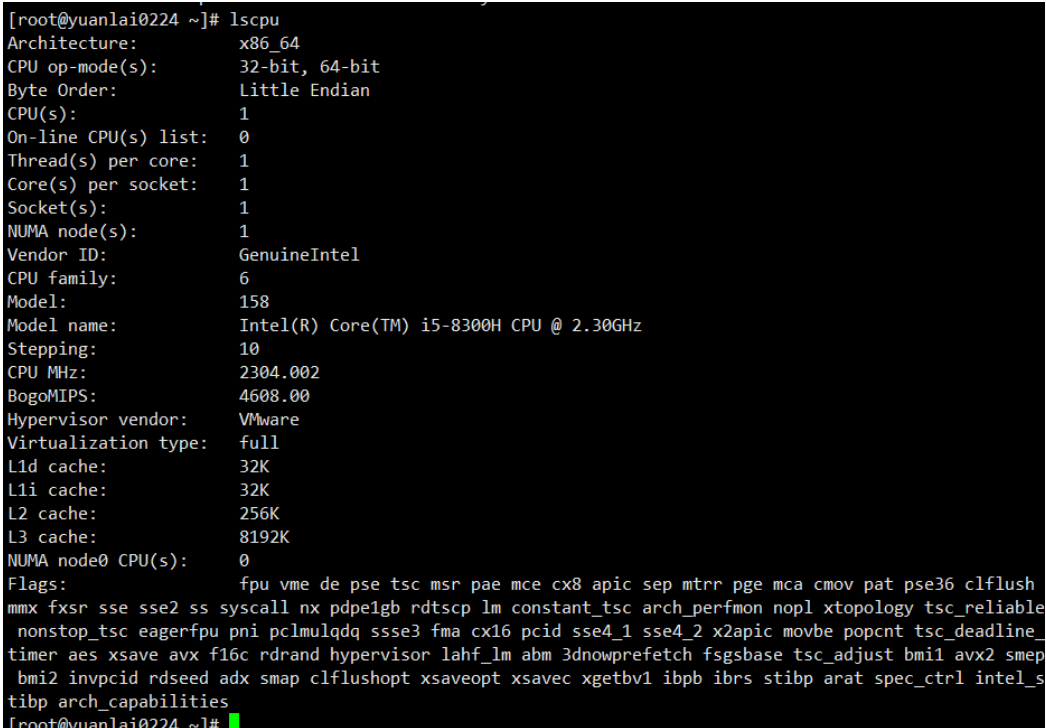
lscpu
查看机器的cpu详细信息
仅查看 cpu 有几核
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# lscpu |grep -i 'cpu(s)'
CPU(s): 1 # cpu 个数
On-line CPU(s) list: 0
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
查看 cpu 有几个
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep 'core id'
core id : 0 #这里的 0 是 cpu 的 id
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep 'process'
processor : 0
stress压力测试命令
如何让机器上的每一核利用到最大化
CPU 压力测试
#安装 stress 命令
yum install stress -y
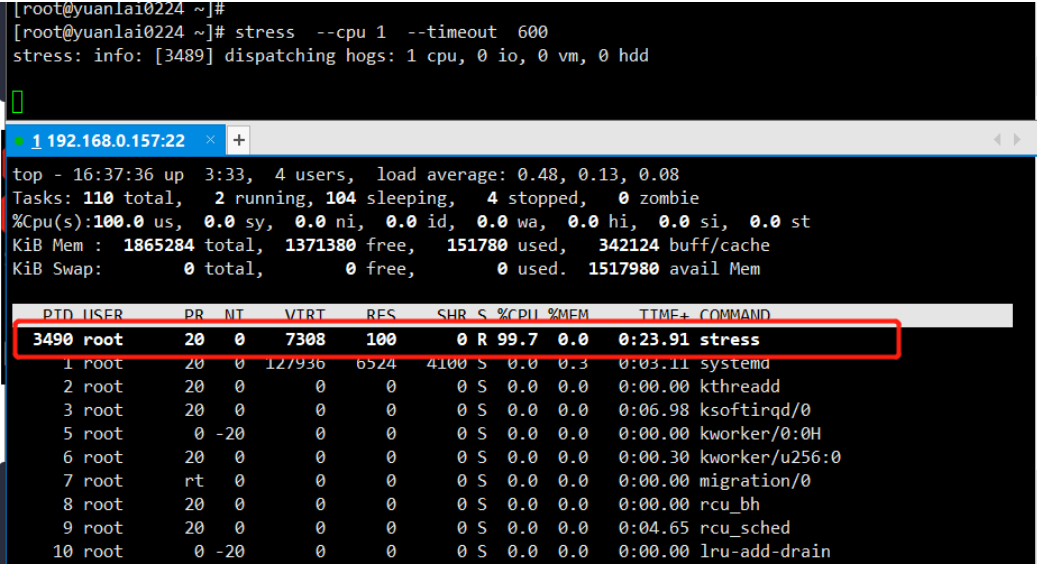
1. stress --cpu 1 --timeout 600 #让一个 cpu 完全跑起来
2.死循环打印nihao
while true ; do echo 'nihao' ; done
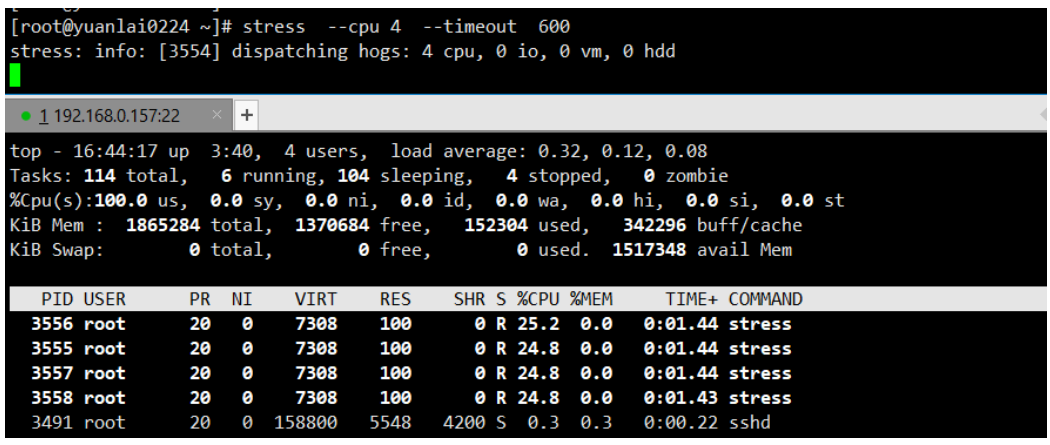
从下图可以看到, stress 的 CPU 使用率接近 100%。
为什么没有达到100%呢?
因为在机器上还有其它进程在使用 cpu 所有是没有达到100%,但是它是无限接近100%的。
如果 stress --cpu 这里的参数比机器中的 cpu 要多会出现什么情况呢?
stress --cpu 4 --timeout 600
可以看到如果这个参数比机器中的 cpu 要多,他就会形成多个进程来平摊 cpu 使用率。
free命令
free 查看内存情况
参数
-m 显示内存单位为M
-h 以可读形式显示容量
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# free
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1865284 148760 1374224 9892 342300 1521080
Swap: 0 0 0
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1821 142 1344 9 334 1487
Swap: 0 0 0
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1.8G 142M 1.3G 9.6M 334M 1.5G
Swap: 0B 0B 0B
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
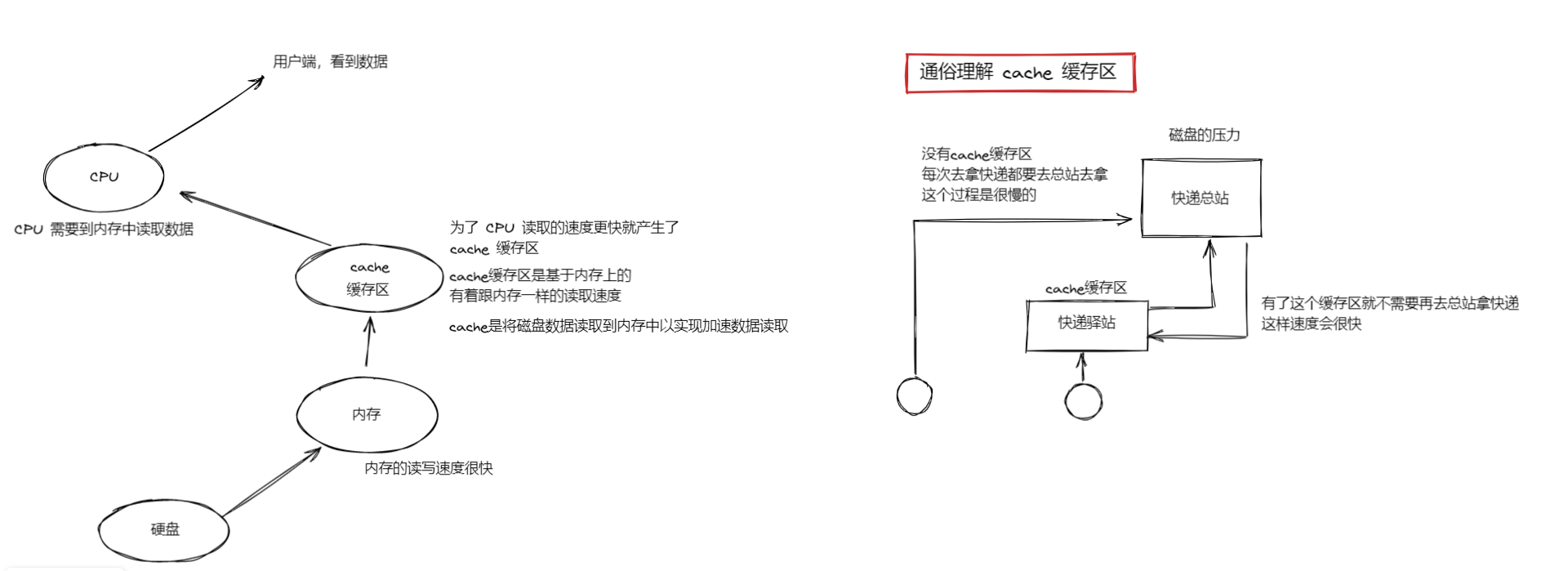
解释 cache 缓存的概念
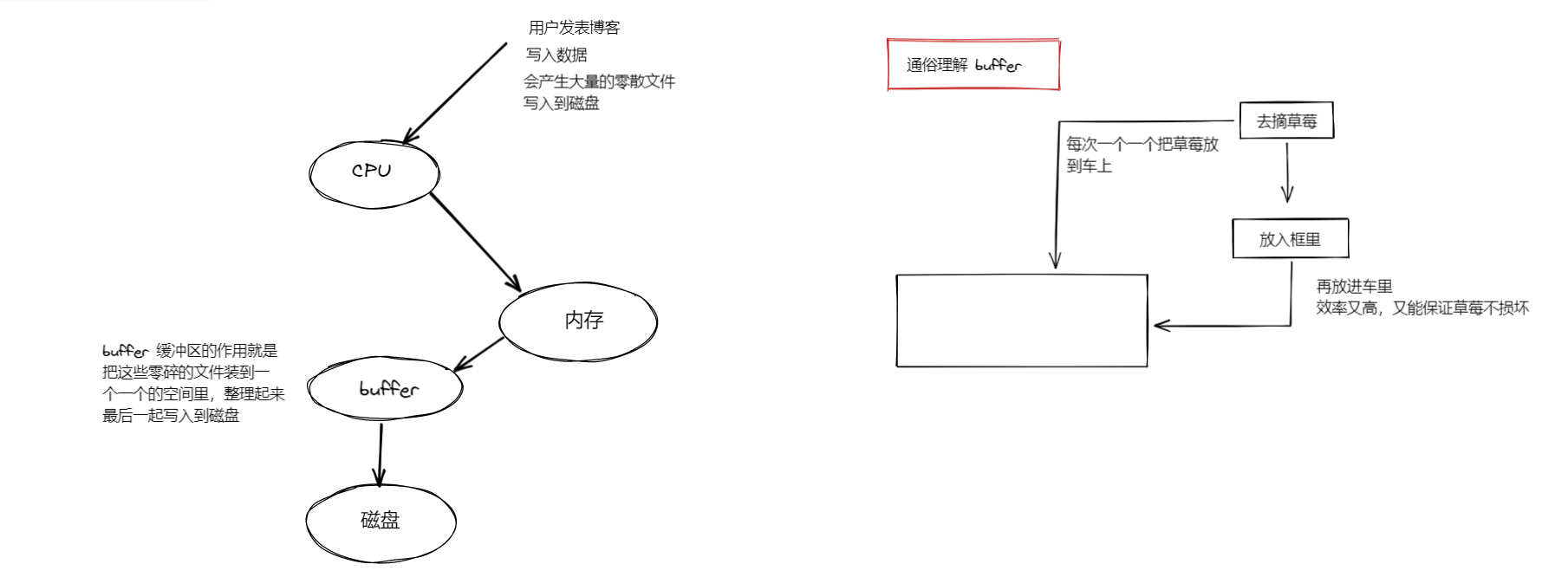
解释buffer 缓冲区的概念
查看磁盘使用情况
df -h 查看磁盘使用情况
磁盘io 监控
#安装 iostat命令 (input output stat) 静态
yum install sysstat -y
#安装 iotop命令 动态
yum install iotop -y
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]# df -h
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/centos-root 19G 3.6G 16G 19% /
devtmpfs 899M 0 899M 0% /dev
tmpfs 911M 0 911M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 911M 9.6M 902M 2% /run
tmpfs 911M 0 911M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 1014M 142M 873M 14% /boot
tmpfs 183M 0 183M 0% /run/user/0
[root@yuanlai0224 ~]#
网络资源监控
网络端口查看
理解网络是什么
IP地址,对那个了 tcp/ip 协议的IP地址号
端口号,对应了应用层的 如 80 端口(伴随着 http协议的服务,如nginx这样的网站服务)
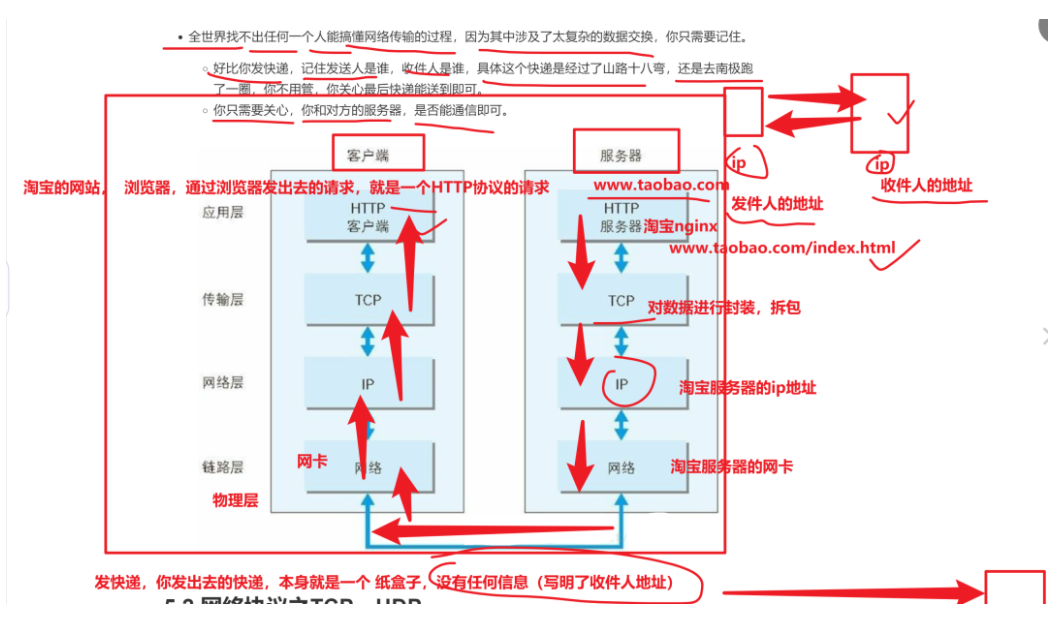
理解tcp和udp
tcp 用再网站的通信
是双方达成协议,速度慢,但是安全可靠
udp (不管对方需不需要某个信息,还是疯狂输入给对面。 例如 刷视频就是通过 udp 发送的)
双发没有达成协议,速度快,不安全
netstat命令
network status 网络状态命令
安装 yum install net-tools -y
命令 netstat
作用 查看网络连接状态
语法 netstat -tunlp
参数
-t:表示只列出tcp 协议的连接;(你可以看到你的nginx的运行)
-n:表示将地址从字母组合转化成ip 地址,将协议转化成端口号来显示;(netsta默认会看到机器的主机名 -n 直接显示ip)
-l :表示过滤出"state(状态)"列中其值为LISTEN(监听)的连接;(你的nginx是否监听了0.0.0.0:80)确认端口在运行中,等待客户来访问
-p:表示显示发起连接的进程pid 和进程名称; (显示使用该端口的进程的id号)
-u :查看udp连接 (ntpd服务)
ss命令
用法和netstat一模一样
ss -tunlp |grep nginx
在高并发场景, ss 比 netstat 性能要好
iftop
#安装 iftop命令
yum install iftop -y 动态
用起来和top命令很像,动态的掌握服务器的流量情况
能够看到你机器,有多少流量进来,有多少流量出去



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号