java多态
在java中有两种方式实现多态:继承和接口。
继承都是单继承,接口可以多继承多实现。
实例分析
public class A {
public String show(D obj) {
return ("A and D");
}
public String show(A obj) {
return ("A and A");
}
}
public class B extends A{
public String show(B obj){
return ("B and B");
}
public String show(A obj){
return ("B and A");
}
}
public class C extends B {
}
public class D extends B {
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a1 = new A();
A a2 = new B();
B b = new B();
C c = new C();
D d = new D();
System.out.println("1--" + a1.show(b));
System.out.println("2--" + a1.show(c));
System.out.println("3--" + a1.show(d));
System.out.println("4--" + a2.show(b));
System.out.println("5--" + a2.show(c));
System.out.println("6--" + a2.show(d));
System.out.println("7--" + b.show(b));
System.out.println("8--" + b.show(c));
System.out.println("9--" + b.show(d));
}
}
结果:
1--A and A
2--A and A
3--A and D
4--B and A
5--B and A
6--A and D
7--B and B
8--B and B
9--A and D
上面的程序A B C D 存在如下关系:
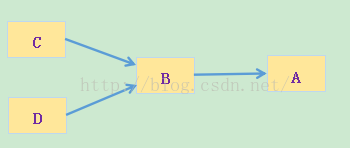
当超类对象引用变量引用子类对象时,被引用对象的类型而不是引用变量的类型决定了调用谁的成员方法,但是这个被调用的方法必须是在超类中定义过的,也就是说被子类覆盖的方法。(但是如果强制把超类转换成子类的话,就可以调用子类中新添加而超类没有的方法了。) 在继承链中对象方法的调用存在一个优先级:this.show(O)、super.show(O)、this.show((super)O)、super.show((super)O)。
分析4:
a2.show(b), a2是一个引用变量,类型为A,则this为a2,b是B的实例,于是到A里面找show(B obj),没找到;于是到A的super找,而A没有super;
因此转到this.show((super)O),this仍然是a2,这里O为B,(super)O即(super)B,即为A,因此到A里面找show(A obj)方法,类A有这个方法,但是由于a2引用的是类B的对象,B覆盖了A的show(A obj),因此锁定类B的show(A obj),输出"B and A".



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号