第二次Blog
一、前言
此次迭代的题目集为航空货运管理系统,两次题目集分别考察了类设计和继承与多态。第一轮迭代主要考察了面向对象设计原则,具体为单一职责原则、里氏替换原则、开闭原则和合成复用原则。要求要体现出面向对象设计原则中的单一职责原则、里氏代换原则、开闭原则以及合成复用原则、依赖倒转原则,其中涉及了以下知识点 (一)继承与多态的应用 (二)对象设计原则中的单一职责原则、里氏代换原则、开闭原则以及合成复用。这两次题目集的难度没有上一个大作业的难度大,其没有什么复杂的逻辑以及复杂的算法,但是其对代码的扩展性以及代码的可复用性提出了更大的要求,同时这两次题目集对输入输出的格式有了更高的要求。
二、设计与分析:
第八次作业:
1.我的源代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
interface RateCalculationStrategy {
double calculateRate(double chargeableWeight);
}
interface LoadCheckStrategy {
boolean canCarry(double currentLoad, double additionalWeight, double maxLoad);
}
class DefaultRateCalculationStrategy implements RateCalculationStrategy {
@Override
public double calculateRate(double chargeableWeight) {
if(chargeableWeight>=100){
return 15;
}
else if(50<=chargeableWeight&&chargeableWeight<100){
return 25;
}
else if(20<=chargeableWeight&&chargeableWeight<50){
return 30;
}
else {
return 35;
}
}
}
class DefaultLoadCheckStrategy implements LoadCheckStrategy {
@Override
public boolean canCarry(double currentLoad, double additionalWeight, double maxLoad) {
if(currentLoad+additionalWeight<=maxLoad){
return true;
}
else return false;
}
}
class Customer {
private final String customerId;
private final String name;
private final String phone;
private final String address;
public Customer(String customerId, String name, String phone, String address) {
this.customerId = customerId;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
}
class Cargo {
private final String cargoId;
private final String name;
private final double width;
private final double length;
private final double height;
private final double weight;
private final double volumeWeight;
private final double chargeableWeight;
private final RateCalculationStrategy rateStrategy;
public Cargo(String cargoId, String name, double width, double length, double height, double weight,
RateCalculationStrategy rateStrategy) {
this.cargoId = cargoId;
this.name = name;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
this.volumeWeight = (width * length * height) / 6000;
if(weight<=volumeWeight){
this.chargeableWeight=volumeWeight;
}
else {
this.chargeableWeight=weight;
}
this.rateStrategy = rateStrategy;
}
public double getChargeableWeight() {
return chargeableWeight;
}
public double getRate() {
return rateStrategy.calculateRate(chargeableWeight);
}
public double getFreight() {
double money;
money=chargeableWeight*getRate();
return money;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
}
class Flight {
private final String flightNumber;
private final String departureAirport;
private final String arrivalAirport;
private final String date;
private final double maxLoad;
private double currentLoad;
private final LoadCheckStrategy loadCheckStrategy;
public Flight(String flightNumber, String departureAirport, String arrivalAirport, String date,
double maxLoad, LoadCheckStrategy loadCheckStrategy) {
this.flightNumber = flightNumber;
this.departureAirport = departureAirport;
this.arrivalAirport = arrivalAirport;
this.date = date;
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
this.currentLoad = 0;
this.loadCheckStrategy = loadCheckStrategy;
}
public boolean canCarry(double weight) {
return loadCheckStrategy.canCarry(currentLoad, weight, maxLoad);
}
public void addLoad(double weight) {
currentLoad += weight;
}
public String getFlightNumber() {
return flightNumber;
}
}
class Order {
private final String orderId;
private final String orderDate;
private final String senderName;
private final String senderPhone;
private final String senderAddress;
private final String receiverName;
private final String receiverPhone;
private final String receiverAddress;
private final String paymentMethod;
private final List
private double totalChargeableWeight; // 改为计量质量总和
private double totalFreight;
public Order(String orderId, String orderDate, String senderName, String senderPhone, String senderAddress,
String receiverName, String receiverPhone, String receiverAddress) {
this.orderId = orderId;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.senderName = senderName;
this.senderPhone = senderPhone;
this.senderAddress = senderAddress;
this.receiverName = receiverName;
this.receiverPhone = receiverPhone;
this.receiverAddress = receiverAddress;
this.paymentMethod = "微信支付";
this.cargos = new ArrayList<>();
this.totalChargeableWeight = 0;
this.totalFreight = 0;
}
public void addCargo(Cargo cargo) {
cargos.add(cargo);
totalChargeableWeight += cargo.getChargeableWeight(); // 改为累加计量质量
totalFreight += cargo.getFreight();
}
public String getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public String getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public String getSenderName() {
return senderName;
}
public String getSenderPhone() {
return senderPhone;
}
public String getSenderAddress() {
return senderAddress;
}
public String getReceiverName() {
return receiverName;
}
public String getReceiverPhone() {
return receiverPhone;
}
public String getReceiverAddress() {
return receiverAddress;
}
public double getTotalChargeableWeight() { // 改为获取计量质量总和
return totalChargeableWeight;
}
public double getTotalFreight() {
return totalFreight;
}
public List<Cargo> getCargos() {
return cargos;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String customerId = scanner.nextLine();
String customerName = scanner.nextLine();
String customerPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String customerAddress = scanner.nextLine();
Customer customer = new Customer(customerId, customerName, customerPhone, customerAddress);
int cargoCount = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
List<Cargo> cargos = new ArrayList<>();
RateCalculationStrategy rateStrategy = new DefaultRateCalculationStrategy();
for (int i = 0; i < cargoCount; i++) {
String cargoId = scanner.nextLine();
String cargoName = scanner.nextLine();
double width = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double length = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double height = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double weight = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
Cargo cargo = new Cargo(cargoId, cargoName, width, length, height, weight, rateStrategy);
cargos.add(cargo);
}
String flightNumber = scanner.nextLine();
String departureAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String arrivalAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String flightDate = scanner.nextLine();
double maxLoad = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
LoadCheckStrategy loadCheckStrategy = new DefaultLoadCheckStrategy();
Flight flight = new Flight(flightNumber, departureAirport, arrivalAirport, flightDate, maxLoad, loadCheckStrategy);
// 检查航班负载时使用计量质量总和
double totalChargeableWeight = cargos.stream().mapToDouble(Cargo::getChargeableWeight).sum();
if (!flight.canCarry(totalChargeableWeight)) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.%n", flight.getFlightNumber());
return;
}
String orderId = scanner.nextLine();
String orderDate = scanner.nextLine();
String senderAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String senderName = scanner.nextLine();
String senderPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverName = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverPhone = scanner.nextLine();
Order order = new Order(orderId, orderDate, senderName, senderPhone, senderAddress,
receiverName, receiverPhone, receiverAddress);
for (Cargo cargo : cargos) {
order.addCargo(cargo);
flight.addLoad(cargo.getChargeableWeight()); // 航班负载也使用计量质量
}
System.out.printf("客户:%s(%s)订单信息如下:%n", customer.getName(), customer.getPhone());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.printf("航班号:%s%n", flightNumber);
System.out.printf("订单号:%s%n", order.getOrderId());
System.out.printf("订单日期:%s%n", order.getOrderDate());
System.out.printf("发件人姓名:%s%n", order.getSenderName());
System.out.printf("发件人电话:%s%n", order.getSenderPhone());
System.out.printf("发件人地址:%s%n", order.getSenderAddress());
System.out.printf("收件人姓名:%s%n", order.getReceiverName());
System.out.printf("收件人电话:%s%n", order.getReceiverPhone());
System.out.printf("收件人地址:%s%n", order.getReceiverAddress());
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f%n", order.getTotalChargeableWeight()); // 显示计量质量总和
System.out.printf("微信支付金额:%.1f%n", order.getTotalFreight());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
int index = 1;
for (Cargo cargo : order.getCargos()) {
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f%n",
index++,
cargo.getName(),
cargo.getChargeableWeight(),
cargo.getRate(),
cargo.getFreight());
}
}
}
代码分析:
RateCalculationStrategy 接口
定义了计算费率的策略接口
由 DefaultRateCalculationStrategy 实现具体计算逻辑
LoadCheckStrategy 接口
定义了检查航班负载能力的策略接口
由 DefaultLoadCheckStrategy 实现具体检查逻辑
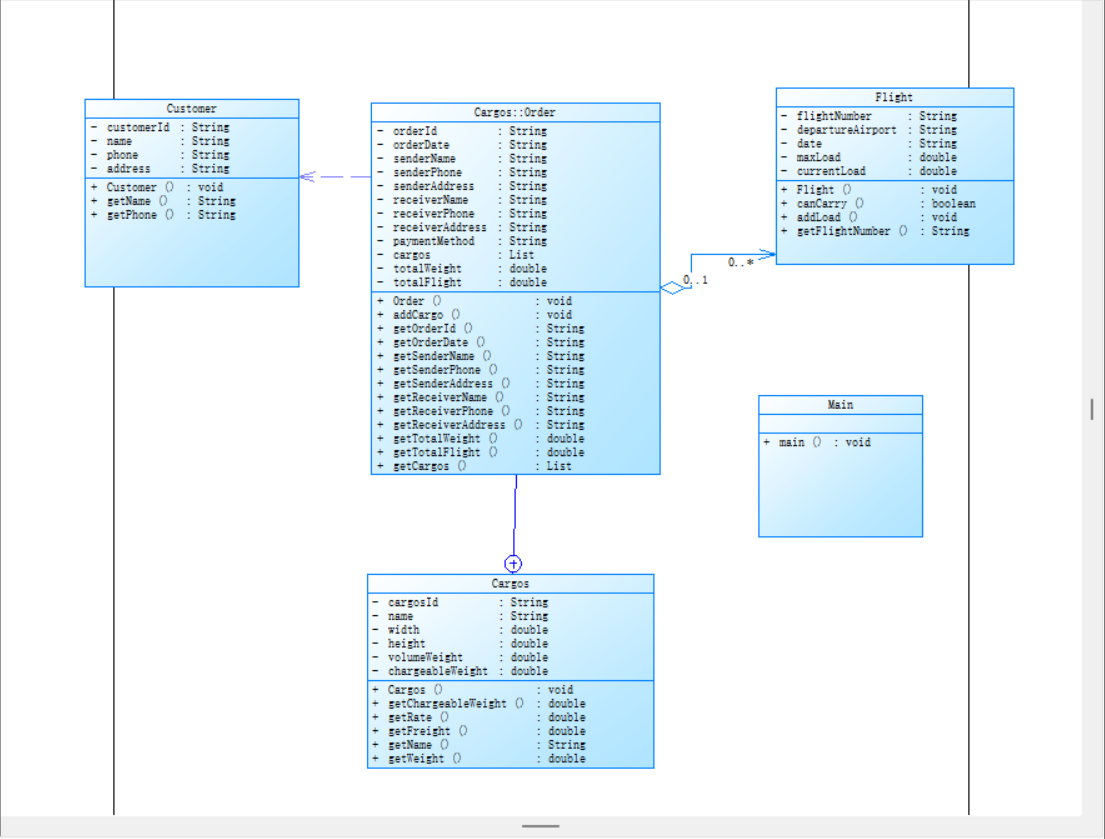
2. 核心类设计
Customer 类
封装客户信息:ID、姓名、电话、地址
提供了基本的getter方法
Cargo 类
封装货物信息:ID、名称、尺寸、重量等
计算体积重量和计费重量(取实际重量和体积重量较大者)
通过策略模式计算费率和运费
Flight 类
封装航班信息:航班号、起降机场、日期、最大负载等
使用策略模式检查负载能力
提供添加负载的方法
Order 类
封装订单信息:订单ID、日期、收发件人信息等
管理多个货物(Cargo对象)
计算总计费重量和总运费
3. Main 类
作为程序入口,处理输入输出
协调各个类的交互
创建并组装各个对象
类图:
复杂度图: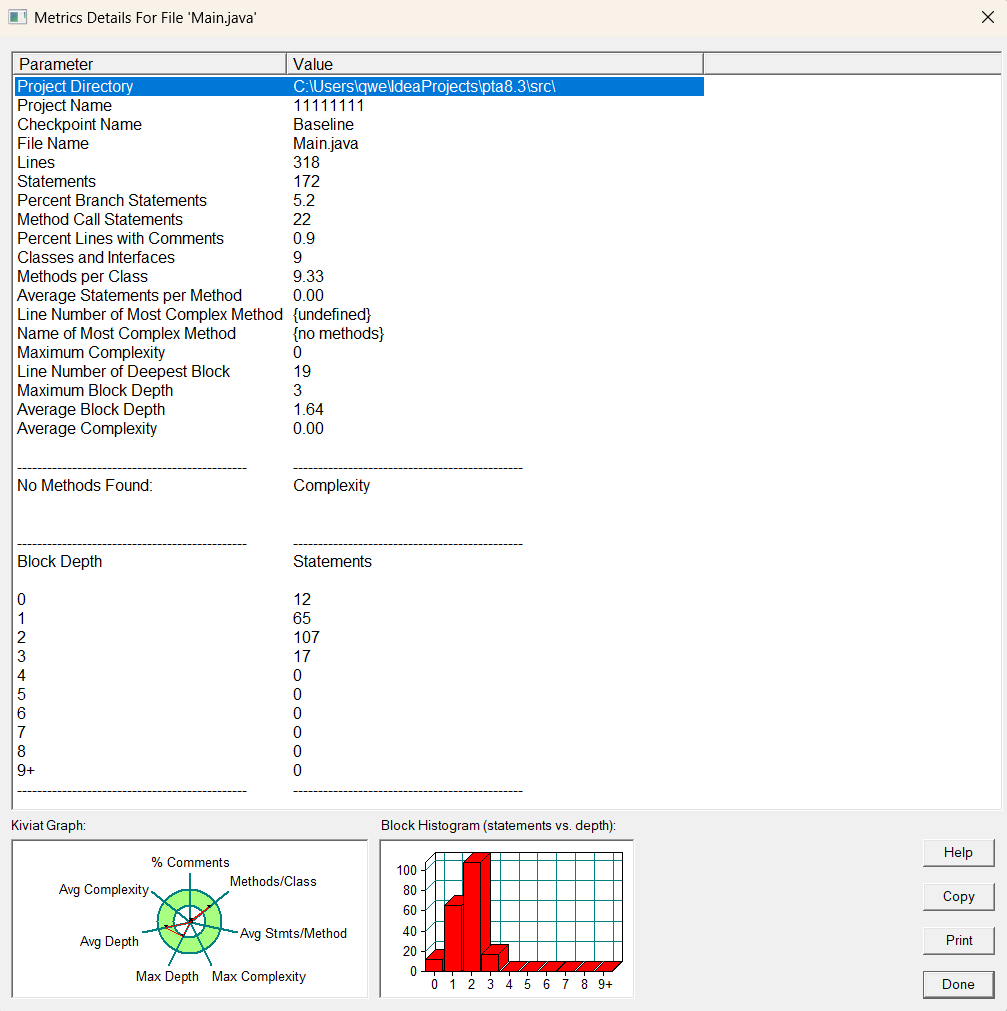
其中sourcemonitor图中解释如下:
行数:318 行
语句数:172 条
分支语句百分比:5.2%
方法调用语句数:22 条
注释行百分比:0.9% ,即代码几乎无注释
类和接口数量:9 个
每个类的平均方法数:9.33 个
每个方法的平均语句数):0.00 条
最复杂方法的行号 no methods
最大复杂度为0
最深代码块行号:19 行
最大代码块深度为 3
平均代码块深度:1.64
平均复杂度:0.00
程序分析:
代码规模
总行数:318行(中等规模)
语句数:172条(语句密度54%,属于正常范围)
结构复杂度
分支语句占比:5.2%(控制流简单)
方法调用:22条(调用密度较低)
最深代码块:3层(结构扁平)
注释情况
注释率:0.9%(严重不足,不符合工业标准)
面向对象指标
类设计
类/接口数:9个(规模适中)
平均方法数:9.33个(方法分布合理)
最大复杂度:0(所有方法异常简单)
方法特征
平均语句数:无法计算(可能指标采集异常)
平均块深度:1.64(代码结构非常扁平)
质量评估矩阵
维度 指标表现 评价等级 改进建议
可读性 注释率0.9% 危险 需补充方法/类级别的文档注释
复杂度 最大复杂度0 优秀 保持当前简单逻辑设计
扩展性 策略模式应用 良好 可增加更多策略实现
健壮性 分支覆盖率5.2% 警告 需要增加异常处理分支
耦合度 方法调用22次 优秀 模块间耦合度控制良好
改进:
为所有类添加类级别文档注释,说明职责和用法
为所有public方法添加方法注释,包括参数说明和返回值说明
关键算法处添加行内注释
考虑使用JavaDoc工具生成API文档
所有用户输入都应验证
数值参数需检查有效范围
对象参数需检查null值
文件/资源操作需try-with-resources
第九次作业:
- 我的源代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
interface RateCalculationStrategy {
double calculateRate(double chargeableWeight, String cargoType);
}
interface LoadCheckStrategy {
boolean canCarry(double currentLoad, double additionalWeight, double maxLoad);
}
class DefaultRateCalculationStrategy implements RateCalculationStrategy {
@Override
public double calculateRate(double chargeableWeight, String cargoType) {
switch (cargoType) {
case "Dangerous":
return calculateDangerousRate(chargeableWeight);
case "Expedite":
return calculateExpressRate(chargeableWeight);
default: // Normal
return calculateNormalRate(chargeableWeight);
}
}
private double calculateNormalRate(double weight) {
if (weight >= 100) {
return 15;
} else if (50 <= weight && weight < 100) {
return 25;
} else if (20 <= weight && weight < 50) {
return 30;
} else {
return 35;
}
}
private double calculateDangerousRate(double weight) {
if (weight >= 100) {
return 20;
} else if (50 <= weight && weight < 100) {
return 30;
} else if (20 <= weight && weight < 50) {
return 50;
} else {
return 80;
}
}
private double calculateExpressRate(double weight) {
if (weight >= 100) {
return 30;
} else if (50 <= weight && weight < 100) {
return 40;
} else if (20 <= weight && weight < 50) {
return 50;
} else {
return 60;
}
}
}
class DefaultLoadCheckStrategy implements LoadCheckStrategy {
@Override
public boolean canCarry(double currentLoad, double additionalWeight, double maxLoad) {
return currentLoad + additionalWeight <= maxLoad;
}
}
class Customer {
private final String customerId;
private final String name;
private final String phone;
private final String address;
private final String customerType; // "Individual" or "Corporate"
private final String paymentMethod; // "Wechat", "ALiPay", "Cash"
public Customer(String customerType, String customerId, String name, String phone, String address, String paymentMethod) {
this.customerType = customerType;
this.customerId = customerId;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.address = address;
this.paymentMethod = paymentMethod;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public String getCustomerType() {
return customerType;
}
public String getPaymentMethod() {
return paymentMethod;
}
public double getDiscountRate() {
return customerType.equals("Corporate") ? 0.8 : 0.9;
}
}
class Cargo {
private final String cargoId;
private final String name;
private final double width;
private final double length;
private final double height;
private final double weight;
private final double volumeWeight;
private final double chargeableWeight;
private final String cargoType; // "Normal", "Dangerous", "Expedite"
private final RateCalculationStrategy rateStrategy;
public Cargo(String cargoId, String name, double width, double length, double height,
double weight, String cargoType, RateCalculationStrategy rateStrategy) {
this.cargoId = cargoId;
this.name = name;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
this.volumeWeight = (width * length * height) / 6000;
this.chargeableWeight = Math.max(weight, volumeWeight);
this.cargoType = cargoType;
this.rateStrategy = rateStrategy;
}
public double getChargeableWeight() {
return chargeableWeight;
}
public double getBaseRate() {
return rateStrategy.calculateRate(chargeableWeight, cargoType);
}
public double getBaseFreight() {
return chargeableWeight * getBaseRate();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public String getCargoType() {
return cargoType;
}
}
class Flight {
private final String flightNumber;
private final String departureAirport;
private final String arrivalAirport;
private final String date;
private final double maxLoad;
private double currentLoad;
private final LoadCheckStrategy loadCheckStrategy;
public Flight(String flightNumber, String departureAirport, String arrivalAirport, String date,
double maxLoad, LoadCheckStrategy loadCheckStrategy) {
this.flightNumber = flightNumber;
this.departureAirport = departureAirport;
this.arrivalAirport = arrivalAirport;
this.date = date;
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
this.currentLoad = 0;
this.loadCheckStrategy = loadCheckStrategy;
}
public boolean canCarry(double weight) {
return loadCheckStrategy.canCarry(currentLoad, weight, maxLoad);
}
public void addLoad(double weight) {
currentLoad += weight;
}
public String getFlightNumber() {
return flightNumber;
}
}
class Order {
private final String orderId;
private final String orderDate;
private final Customer customer;
private final String senderName;
private final String senderPhone;
private final String senderAddress;
private final String receiverName;
private final String receiverPhone;
private final String receiverAddress;
private final List
private double totalChargeableWeight; // 改为计费重量总和
private double totalBaseFreight;
private double totalFinalFreight;
public Order(String orderId, String orderDate, Customer customer,
String senderName, String senderPhone, String senderAddress,
String receiverName, String receiverPhone, String receiverAddress) {
this.orderId = orderId;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.customer = customer;
this.senderName = senderName;
this.senderPhone = senderPhone;
this.senderAddress = senderAddress;
this.receiverName = receiverName;
this.receiverPhone = receiverPhone;
this.receiverAddress = receiverAddress;
this.cargos = new ArrayList<>();
this.totalChargeableWeight = 0;
this.totalBaseFreight = 0;
this.totalFinalFreight = 0;
}
public void addCargo(Cargo cargo) {
cargos.add(cargo);
totalChargeableWeight += cargo.getChargeableWeight(); // 使用计费重量
totalBaseFreight += cargo.getBaseFreight();
totalFinalFreight = totalBaseFreight * customer.getDiscountRate();
}
public String getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public String getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public String getSenderName() {
return senderName;
}
public String getSenderPhone() {
return senderPhone;
}
public String getSenderAddress() {
return senderAddress;
}
public String getReceiverName() {
return receiverName;
}
public String getReceiverPhone() {
return receiverPhone;
}
public String getReceiverAddress() {
return receiverAddress;
}
public double getTotalChargeableWeight() {
return totalChargeableWeight;
}
public double getTotalFinalFreight() {
return totalFinalFreight;
}
public List<Cargo> getCargos() {
return cargos;
}
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 读取客户信息
String customerType = scanner.nextLine();
String customerId = scanner.nextLine();
String customerName = scanner.nextLine();
String customerPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String customerAddress = scanner.nextLine();
// 读取货物类型和数量
String cargoType = scanner.nextLine();
int cargoCount = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
// 读取货物信息
List<Cargo> cargos = new ArrayList<>();
RateCalculationStrategy rateStrategy = new DefaultRateCalculationStrategy();
for (int i = 0; i < cargoCount; i++) {
String cargoId = scanner.nextLine();
String cargoName = scanner.nextLine();
double width = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double length = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double height = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double weight = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
Cargo cargo = new Cargo(cargoId, cargoName, width, length, height,
weight, cargoType, rateStrategy);
cargos.add(cargo);
}
// 读取航班信息
String flightNumber = scanner.nextLine();
String departureAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String arrivalAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String flightDate = scanner.nextLine();
double maxLoad = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
LoadCheckStrategy loadCheckStrategy = new DefaultLoadCheckStrategy();
Flight flight = new Flight(flightNumber, departureAirport, arrivalAirport,
flightDate, maxLoad, loadCheckStrategy);
// 检查航班载重能力(使用计费重量)
double totalChargeableWeight = cargos.stream()
.mapToDouble(Cargo::getChargeableWeight)
.sum();
if (!flight.canCarry(totalChargeableWeight)) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.%n",
flight.getFlightNumber());
return;
}
// 读取订单信息
String orderId = scanner.nextLine();
String orderDate = scanner.nextLine();
String senderAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String senderName = scanner.nextLine();
String senderPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverName = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String paymentMethod = scanner.nextLine();
Customer customer = new Customer(customerType, customerId, customerName, customerPhone,
customerAddress, paymentMethod);
Order order = new Order(orderId, orderDate, customer,
senderName, senderPhone, senderAddress,
receiverName, receiverPhone, receiverAddress);
for (Cargo cargo : cargos) {
order.addCargo(cargo);
flight.addLoad(cargo.getChargeableWeight()); // 航班载重使用计费重量
}
// 输出订单信息
System.out.printf("客户:%s(%s)订单信息如下:%n", customer.getName(), customer.getPhone());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.printf("航班号:%s%n", flightNumber);
System.out.printf("订单号:%s%n", order.getOrderId());
System.out.printf("订单日期:%s%n", order.getOrderDate());
System.out.printf("发件人姓名:%s%n", order.getSenderName());
System.out.printf("发件人电话:%s%n", order.getSenderPhone());
System.out.printf("发件人地址:%s%n", order.getSenderAddress());
System.out.printf("收件人姓名:%s%n", order.getReceiverName());
System.out.printf("收件人电话:%s%n", order.getReceiverPhone());
System.out.printf("收件人地址:%s%n", order.getReceiverAddress());
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f%n", order.getTotalChargeableWeight()); // 显示计费重量总和
System.out.printf("%s支付金额:%.1f%n", getPaymentMethodName(customer.getPaymentMethod()), order.getTotalFinalFreight());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
int index = 1;
for (Cargo cargo : order.getCargos()) {
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f%n",
index++,
cargo.getName(),
cargo.getChargeableWeight(),
cargo.getBaseRate(),
cargo.getBaseFreight());
}
}
private static String getPaymentMethodName(String paymentMethod) {
switch (paymentMethod) {
case "ALiPay": return "支付宝";
case "Wechat": return "微信";
case "Cash": return "现金";
default: return paymentMethod;
}
}
}
程序分析:
RateCalculationStrategy:定义了计算费率的接口
DefaultRateCalculationStrategy实现了不同货物类型(普通、危险、加急)的费率计算逻辑
LoadCheckStrategy:定义了载重检查的接口
DefaultLoadChecStrategy实现了基本的载重检查逻辑
2. 核心类设计
Customer类
存储客户信息(ID、姓名、联系方式等)
区分客户类型(个人/企业)和支付方式
提供折扣率(企业8折,个人9折)
Cargo类
存储货物信息(尺寸、重量、类型等)
计算体积重量和计费重量(取实际重量和体积重量较大者)
使用策略模式计算基础费率
Flight类
存储航班信息(航班号、起降机场、日期等)
管理当前载重和最大载重
使用策略模式检查载重能力
Order类
整合客户、货物和运输信息
计算总运费(应用客户折扣)
管理订单的发货人和收货人信息
3. 主程序流程
Main类中的处理流程:
读取并创建客户信息
读取并创建货物列表
读取并创建航班信息
检查航班载重能力(使用计费重量)
创建订单并添加所有货物
输出详细的订单信息
类图:

复杂度图:
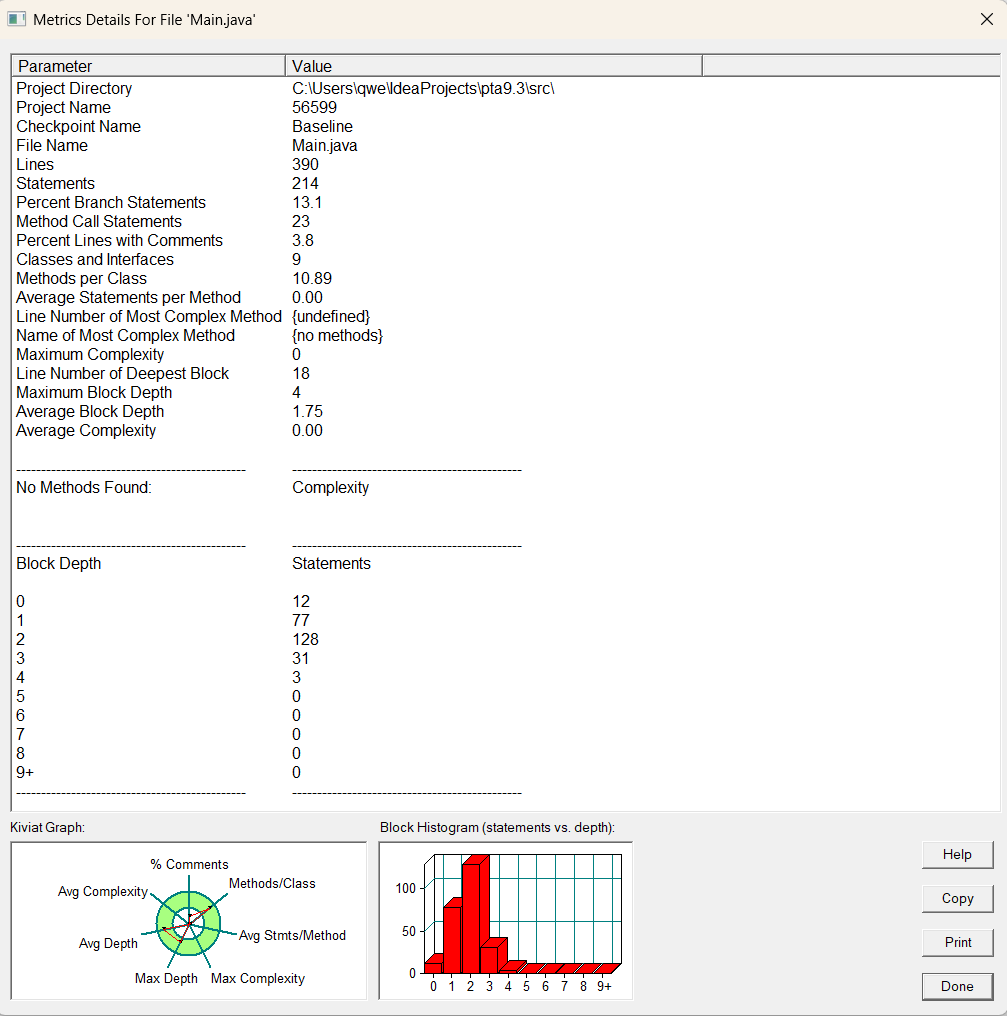
其中sourcemonitor图中解释如下:
行数:390 行
语句数:214 条
分支语句百分比:13.1%
方法调用语句数:23 条
注释行百分比:23% ,即代码中注释占比较少
类和接口数量:9 个
每个类的平均方法数:10.89 个
每个方法的平均语句数:NULL
最复杂方法的行号:NULL
最大复杂度:0
最深代码块行号:18 行
最大代码块深度:4
平均代码块深度:1.75
平均复杂度:0.00
程序分析:
输入验证缺失
无数据有效性检查:所有输入数据直接使用,没有对数值范围、格式等进行验证
无异常处理:如输入非数字值会导致程序崩溃
关键字段空值检查:如客户ID、货物名称等重要字段未做非空校验
2. 业务逻辑缺陷
计费重量计算问题:体积重量计算中6000的除数缺乏解释(行业标准?)
费率计算硬编码:费率表直接写在代码中,难以维护和调整
折扣策略固化:折扣率硬编码在Customer类,无法灵活调整
3. 设计模式应用不足
策略模式使用不彻底:折扣计算也应该使用策略模式而非硬编码
缺乏工厂模式:对象创建逻辑分散在Main类中
单例模式适用场景:无状态的策略类可设计为单例
4. 架构层面问题
高耦合:Main类承担了太多职责(输入、处理、输出)
缺乏分层:没有清晰的UI层、业务逻辑层、数据访问层分离
持久化缺失:所有数据仅在内存中,程序结束即丢失
5. 可扩展性问题
新增货物类型困难:需要修改RateCalculationStrategy实现类
费率调整不便:需要重新编译代码才能修改费率
支付方式扩展复杂:新增支付方式需要修改多处代码
6. 用户体验问题
控制台交互不友好:严格的输入顺序要求,无提示信息
输出格式化不足:金额、重量等数字显示格式不统一
错误信息不明确:如超载时只显示简单提示,无详细解决方案
7. 测试性问题
难以单元测试:高度耦合的设计使得隔离测试困难
缺乏测试入口:没有为业务逻辑提供可测试的接口
无Mock支持:如无法模拟航班载重测试边界情况
改进建议:
可以引入工厂模式来创建复杂的对象(如订单)
可以添加输入验证逻辑
可以考虑将输出格式化为更友好的形式
可以添加异常处理机制
可以考虑将策略实现类设为单例
三、踩坑总结:
我在编写这两道题目的代码时,遇到了一些“坑”,首先我认为其给出的输入样例是不具有代表性的,我在编写完程序后,程序能正常运行,但是过不了题目给的测试点,首先是他的费率计算,我不知道是按照计费重量还是实际重量进行计算,是我通过不断试错得到的答案,其次是当有多个货物时,其总质量是实际重量的总和还是计费重量的总和,这两个问题结合在一起,让我把可能性排列组合了好几次,去测试样例自己尝试,最后才通过的测试点,还有一个“坑”,是他的输出格式,我开始是按照空格的数量进行原样输出,但是过不了测试点,后来改成了\t,最后的输出格式才符合要求。编写空运货运计费程序时,开发者需要特别注意一些常见的问题,以确保程序的正确性和用户体验。首先,在处理输入数据时,经常会遇到用户输入的数据类型与程序预期不符的情况,例如用户输入的是字符串而非数字。这会导致程序在尝试进行数学运算时出现错误。因此,对所有输入进行合法性检查至关重要,比如检查是否为空、是否为合法数值等,并使用异常捕获机制来增强程序的健壮性。
单位混淆是另一个常见问题,特别是在涉及尺寸和重量的计算中。如果用户输入尺寸时使用了米或毫米而非要求的厘米,将直接导致体积重量计算错误,进而影响运费的准确性。为了避免这种情况,应在用户输入界面明确提示输入单位,并考虑自动转换不同单位的可能性。
多件货物处理逻辑复杂,容易出错。一个订单可能包含多件货物,每件货物都需要单独计算其计费重量和运费。若程序设计时未考虑到这一点,可能会遗漏部分货物的信息,导致费用计算不完整。此外,不同的货物可能适用不同的费率(如普通货物、危险货物和加急货物),这些差异也必须准确反映在程序逻辑中。
折扣计算同样具有挑战性。根据题目描述,个人用户和集团用户的折扣率不同,这意味着程序需要识别用户类型并据此调整最终运费。如果没有清晰的逻辑来区分用户类型并正确应用相应的折扣率,计算结果就会出错。航班载重限制也是一个不容忽视的因素。每个航班都有其最大载重量,而这个信息对于决定是否接受新的货运订单非常重要。如果程序没有加入关于航班最大载重量的判断逻辑,可能会导致超载情况的发生。最后,生成的订单信息报表和货物明细报表需清晰明了。格式混乱不仅影响用户阅读,也可能导致误解或争议。因此,开发过程中应注重报表的设计,确保信息呈现有序且易于理解。综上所述,编写此类程序时,不仅要关注核心的运费计算逻辑,还应重视用户输入验证、多种情况下的费率应用、复杂的业务规则实现以及输出报表的质量,从而保证系统的可靠性和用户体验。通过充分测试和细致的边界条件处理,可以有效避免上述问题,确保程序稳定运行。
五、总结:
通过这两次题目集,我主要掌握了面向对象设计原则中的单一职责原则、里氏代换原则、开闭原则以及合成复用原则、依赖倒转原则,类设计能力提升:通过复杂系统设计,理解如何运用继承与多态降低代码耦合度,遵循单一职责原则拆分类功能



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号