1.k8s高可用集群说明
- Kubernetes Master 节点的高可用(HA)在没有云厂商LB的情况下通常有两种主流的实现方案:Keepalived + Nginx 或 Keepalived + HAProxy。这两种方案的核心目标都是通过负载均衡和 VIP(虚拟 IP)漂移实现多个 Master 节点的流量分发和故障转移。
- 我本来是想使用keepalived + nginx 做高可用的,但由于服务器有限且业务量不大,所以只使用keepalived 做VIP漂移,没有使用nginx做代理和负载均衡,但我会提供nginx的相关配置。
2.部署环境
- master至少部署3个节点,保证etcd是奇数节点,如果部署两个的话,在停掉一个master时,etcd是不可用的,那么api-server也不可用【重要!!!】
| IP地址 |
系统 |
内核 |
系统配置 |
角色 |
数据基础目录 |
| 172.16.1.23 |
|
|
|
VIP(keepalived) |
keepalived部署在3台master节点 |
| 172.16.1.20 |
CentOS7.8 |
5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 |
8核16G/100G |
master1 |
/data/ |
| 172.16.1.21 |
CentOS7.8 |
5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 |
8核16G/100G |
master2 |
/data/ |
| 172.16.1.24 |
CentOS7.8 |
5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 |
8核16G/100G |
master3 |
/data/ |
| 172.16.1.22 |
CentOS7.8 |
5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 |
8核16G/100G |
node1 |
/data/ |
| 172.16.1.xx |
CentOS7.8 |
5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 |
8核16G/100G |
node2 |
/data/ |
| 172.16.1.xx |
CentOS7.8 |
5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 |
8核16G/100G |
node3 |
/data/ |
3.初始化系统、内核升级、安装k8s组件
- 如果部署的是k8s HA高可用集群,只使用下边文档中的初始化部分,其余使用本文档,且所有的k8s节点都做同样初始化操作
https://www.cnblogs.com/Leonardo-li/p/18648449
4.编译kubeadm,修改证书授权时间
4.1 准备go环境
- go环境需要大于1.17,否则会报错,我这里用的是1.23
#下载go环境包
wget https://golang.google.cn/dl/go1.23.4.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar zxf go1.23.4.linux-amd64.tar.gz
mv go /usr/local/
#设置go环境变量
vim /etc/profile
#添加下面2行到文件末尾
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
export GOPATH=$HOME/go
#让环境变量生效
source /etc/profile
#测试go环境是否可用
go version
4.2 安装git
yum -y install git
4.3 kubeadm修改-编译
4.3.1 下载对应版本的kubernetes源码包,我这里是v1.23.17
git clone --depth 1 --branch v1.23.17 https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes.git
4.3.2 修改证书时间
cd kubernetes/
- 修改ca证书到100年,注释原代码(注释符号 // ),将代码里面的 *10 换成 *100
vim ./staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/util/cert/cert.go

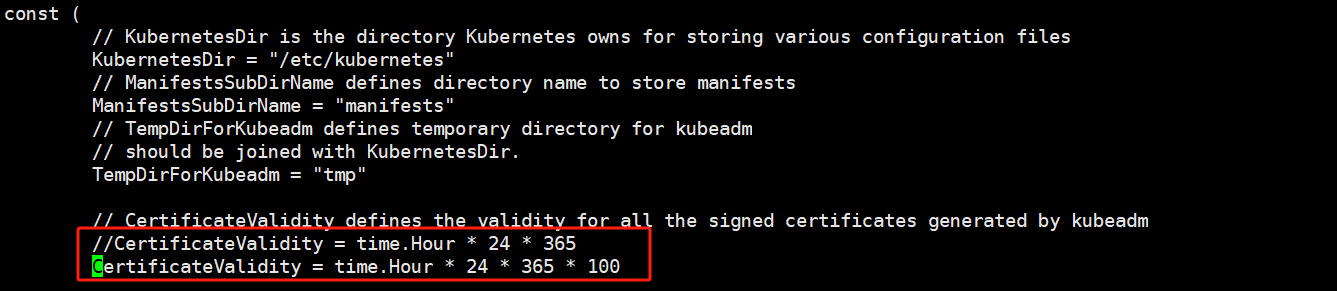
- 修改其他证书到100年,注释原代码(注释符号 // ),将代码里面的 24 * 365 改成 24 * 365 * 100
vim ./cmd/kubeadm/app/constants/constants.go
4.3.3 进行编译
make all WHAT=cmd/kubeadm GOFLAGS=-v
4.3.4 查看是否编译成功
ls _output/bin/kubeadm
4.3.5 拷贝到所有k8s机器,master和node
scp _output/bin/kubeadm root@172.16.1.20:/data/
scp _output/bin/kubeadm root@172.16.1.21:/data/
scp _output/bin/kubeadm root@172.16.1.24:/data/
scp _output/bin/kubeadm root@172.16.1.22:/data/
4.3.6 所以k8s节点备份kubeadm,并将新编译的kubeadm拷贝到相同目录
mv /usr/bin/kubeadm /usr/bin/kubeadm-old
mv /data/kubeadm /usr/bin/
5.部署keepalived
5.1 下载keepalived
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
yum -y install keepalived
5.2 keepalived配置
- master1 配置 keepalived.conf
[root@master1 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id LVS_DEVEL
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER # 设置为主节点
interface ens33 # 网络接口,根据实际情况修改
virtual_router_id 51 # VRRP 路由ID,主备节点必须相同
priority 100 # 优先级,主节点必须高于备份节点
advert_int 1 # VRRP通告间隔,单位秒
authentication {
auth_type PASS # 认证类型
auth_pass 1111 # 认证密码,主备节点必须相同
}
virtual_ipaddress {
172.16.1.23/22 # 虚拟IP地址,可以根据实际情况修改
}
}
- master2 配置 keepalived.conf
[root@master2 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id LVS_DEVEL
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP # 设置为备份节点
interface ens33 # 确保使用正确的网络接口名称
virtual_router_id 51 # VRRP 路由ID,主备节点必须相同
priority 80 # 优先级,备份节点必须低于主节点
advert_int 1 # VRRP通告间隔,单位秒
authentication {
auth_type PASS # 认证类型
auth_pass 1111 # 认证密码,主备节点必须相同
}
virtual_ipaddress {
172.16.1.23/22 # 虚拟IP地址,与主节点相同
}
}
- master3 配置 keepalived.conf
[root@master3 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id LVS_DEVEL
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP # 设置为备份节点
interface ens33 # 确保使用正确的网络接口名称
virtual_router_id 51 # VRRP 路由ID,主备节点必须相同
priority 60 # 优先级,备份节点必须低于主节点
advert_int 1 # VRRP通告间隔,单位秒
authentication {
auth_type PASS # 认证类型
auth_pass 1111 # 认证密码,主备节点必须相同
}
virtual_ipaddress {
172.16.1.23/22 # 虚拟IP地址,与主节点相同
}
}
5.3 启动keepalived(3个节点)
systemctl restart keepalived
systemctl enable keepalived
5.4 补充nginx.conf代理和负载均衡配置,我这里暂时没有使用nginx,只使用了keepalived的VIP
#nginx.conf stream代理
stream {
upstream k8s_apiserver {
# 后端 Kubernetes Master 节点
server 172.16.1.21:6443; # Master1
server 172.16.1.22:6443; # Master2
server 172.16.1.24:6443; # Master3
}
server {
listen 6443; # 监听 6443 端口(TCP)
proxy_pass k8s_apiserver;
proxy_timeout 10s;
}
}
6.初始化k8s【master1】
6.1 编写kubeadm-config.yaml
- 172.16.4.177:8090/k8s12317/registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers 这是我的harbor私有仓库地址,是在之前离线下载镜像后推到自己的harbor的,具体参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/Leonardo-li/p/18648449
cat kubeadm-config.yaml
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: v1.23.17
imageRepository: 172.16.4.177:8090/k8s12317/registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
apiServer:
certSANs:
- "172.16.1.23" # VIP
- "172.16.1.20" # Master1 实际IP
- "172.16.1.21" # Master2 实际IP
- "172.16.1.24" # Master3 实际IP
- "127.0.0.1" # 本地回环
controlPlaneEndpoint: "172.16.1.23:6443" # VIP
networking:
serviceSubnet: 10.96.0.0/12 # 关键修正:serviceCIDR -> serviceSubnet
podSubnet: 10.244.0.0/16 # 确保与 Calico 配置匹配
--- ## 添加下面几行 添加ipvs模式,
apiVersion: kubeproxy.config.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubeProxyConfiguration
mode: ipvs
6.2 初始化master1
kubeadm init --config=kubeadm-config.yaml --upload-certs
master1初始化信息
[root@master1 kubeadm]# kubeadm init --config=kubeadm-config.yaml --upload-certs
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.23.17
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local master1] and IPs [10.96.0.1 172.16.1.20 172.16.1.23 172.16.1.21 172.16.1.24 127.0.0.1]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master1] and IPs [172.16.1.20 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master1] and IPs [172.16.1.20 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 15.008274 seconds
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.23" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
NOTE: The "kubelet-config-1.23" naming of the kubelet ConfigMap is deprecated. Once the UnversionedKubeletConfigMap feature gate graduates to Beta the default name will become just "kubelet-config". Kubeadm upgrade will handle this transition transparently.
[upload-certs] Storing the certificates in Secret "kubeadm-certs" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[upload-certs] Using certificate key:
6d3f1abc998f3ffd104a989aa4b5ff3ae622ccd1a9b0098d9b68ed4221820ac5
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master1 as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/master(deprecated) node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master1 as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: agitw8.fwghrey1nysrprf8
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
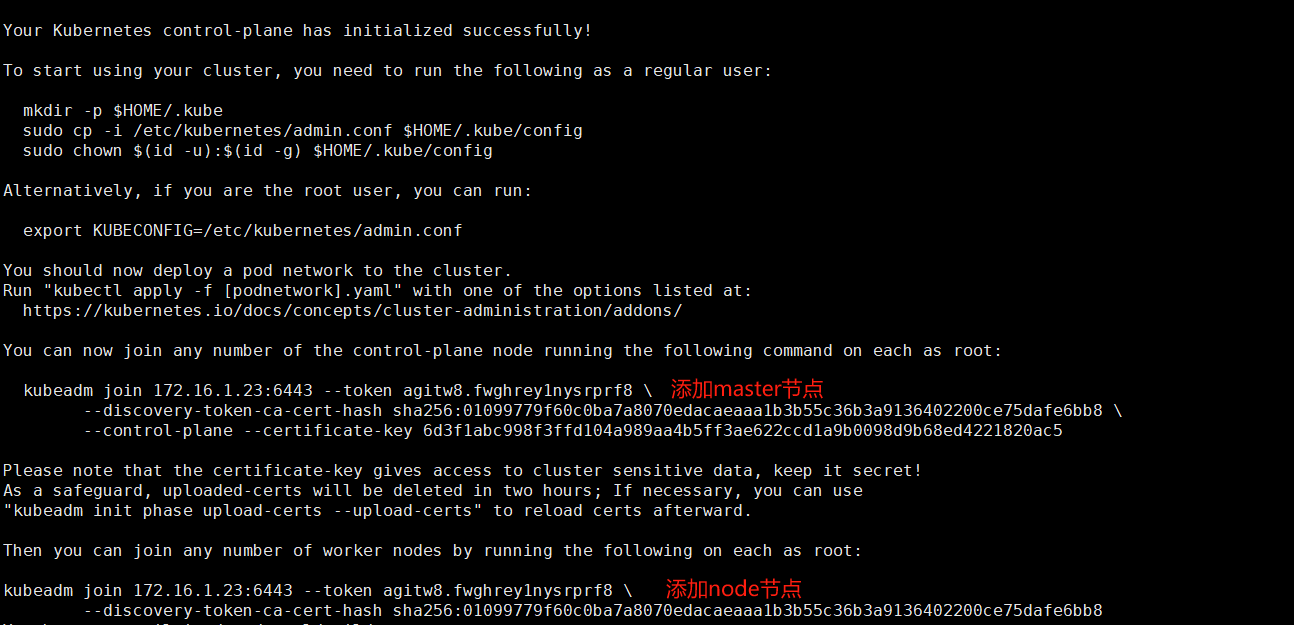
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of the control-plane node running the following command on each as root:
kubeadm join 172.16.1.23:6443 --token agitw8.fwghrey1nysrprf8 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:01099779f60c0ba7a8070edacaeaaa1b3b55c36b3a9136402200ce75dafe6bb8 \
--control-plane --certificate-key 6d3f1abc998f3ffd104a989aa4b5ff3ae622ccd1a9b0098d9b68ed4221820ac5
Please note that the certificate-key gives access to cluster sensitive data, keep it secret!
As a safeguard, uploaded-certs will be deleted in two hours; If necessary, you can use
"kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs" to reload certs afterward.
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 172.16.1.23:6443 --token agitw8.fwghrey1nysrprf8 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:01099779f60c0ba7a8070edacaeaaa1b3b55c36b3a9136402200ce75dafe6bb8
- 初始化信息重要信息截取:1.拷贝配置文件到家目录(执行),2.添加master节点的命令(记录),3.添加node节点的命令 (记录)
- 将初始化后的管理员配置文件拷贝到家目录(命令直接从初始化信息中复制执行)
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
- 查看节点,此时还没有网络插件,所以状态为NotReady

7.初始化k8s【master2】
7.1 初始化master2,加入k8s集群
- 将【步骤6.2】中获取到的添加master节点的初始化命令复制-执行
kubeadm join 172.16.1.23:6443 --token agitw8.fwghrey1nysrprf8 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:01099779f60c0ba7a8070edacaeaaa1b3b55c36b3a9136402200ce75dafe6bb8 \
--control-plane --certificate-key 6d3f1abc998f3ffd104a989aa4b5ff3ae622ccd1a9b0098d9b68ed4221820ac5
master2初始化信息
[root@master2 data]# kubeadm join 172.16.1.23:6443 --token agitw8.fwghrey1nysrprf8 \
> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:01099779f60c0ba7a8070edacaeaaa1b3b55c36b3a9136402200ce75dafe6bb8 \
> --control-plane --certificate-key 6d3f1abc998f3ffd104a989aa4b5ff3ae622ccd1a9b0098d9b68ed4221820ac5
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -o yaml'
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks before initializing the new control plane instance
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[download-certs] Downloading the certificates in Secret "kubeadm-certs" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local master2] and IPs [10.96.0.1 172.16.1.21 172.16.1.23 172.16.1.20 172.16.1.24 127.0.0.1]
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master2] and IPs [172.16.1.21 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master2] and IPs [172.16.1.21 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Valid certificates and keys now exist in "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Using the existing "sa" key
[kubeconfig] Generating kubeconfig files
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[check-etcd] Checking that the etcd cluster is healthy
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
[etcd] Announced new etcd member joining to the existing etcd cluster
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for "etcd"
[etcd] Waiting for the new etcd member to join the cluster. This can take up to 40s
The 'update-status' phase is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Currently it performs no operation
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master2 as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/master(deprecated) node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master2 as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
This node has joined the cluster and a new control plane instance was created:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and approval was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
* Control plane (master) label and taint were applied to the new node.
* The Kubernetes control plane instances scaled up.
* A new etcd member was added to the local/stacked etcd cluster.
To start administering your cluster from this node, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Run 'kubectl get nodes' to see this node join the cluster.
- 将初始化后的管理员配置文件拷贝到家目录(从初始化信息中复制执行)
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
- 查看节点信息,已经有两个master节点了,没有网络插件,状态为NotReady

8.初始化k8s【master3】
8.1 初始化master3,加入k8s集群
- 将【步骤6.2】中获取到的添加master节点的初始化命令复制-执行
kubeadm join 172.16.1.23:6443 --token agitw8.fwghrey1nysrprf8 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:01099779f60c0ba7a8070edacaeaaa1b3b55c36b3a9136402200ce75dafe6bb8 \
--control-plane --certificate-key 6d3f1abc998f3ffd104a989aa4b5ff3ae622ccd1a9b0098d9b68ed4221820ac5
master3初始化信息
[root@master3 ~]# kubeadm join 172.16.1.23:6443 --token agitw8.fwghrey1nysrprf8 \
> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:01099779f60c0ba7a8070edacaeaaa1b3b55c36b3a9136402200ce75dafe6bb8 \
> --control-plane --certificate-key 6d3f1abc998f3ffd104a989aa4b5ff3ae622ccd1a9b0098d9b68ed4221820ac5
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -o yaml'
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks before initializing the new control plane instance
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[download-certs] Downloading the certificates in Secret "kubeadm-certs" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local master3] and IPs [10.96.0.1 172.16.1.24 172.16.1.23 172.16.1.20 172.16.1.21 127.0.0.1]
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master3] and IPs [172.16.1.24 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master3] and IPs [172.16.1.24 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Valid certificates and keys now exist in "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Using the existing "sa" key
[kubeconfig] Generating kubeconfig files
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[check-etcd] Checking that the etcd cluster is healthy
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
[etcd] Announced new etcd member joining to the existing etcd cluster
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for "etcd"
[etcd] Waiting for the new etcd member to join the cluster. This can take up to 40s
The 'update-status' phase is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Currently it performs no operation
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master3 as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/master(deprecated) node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master3 as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
This node has joined the cluster and a new control plane instance was created:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and approval was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
* Control plane (master) label and taint were applied to the new node.
* The Kubernetes control plane instances scaled up.
* A new etcd member was added to the local/stacked etcd cluster.
To start administering your cluster from this node, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Run 'kubectl get nodes' to see this node join the cluster.
- 将初始化后的管理员配置文件拷贝到家目录(从初始化信息中复制执行)
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
- 查看节点信息,已经有三个master节点了,没有网络插件,状态为NotReady

9.查看节点信息
- 由于没有安装calico网络插件,所以状态为NotReady
9.1 在master3查看节点信息
[root@master3 ~]# kubectl get node -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
master1 NotReady control-plane,master 23m v1.23.17 172.16.1.20 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
master2 NotReady control-plane,master 18m v1.23.17 172.16.1.21 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
master3 NotReady control-plane,master 2m52s v1.23.17 172.16.1.24 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
9.2 在master2查看节点信息
[root@master2 data]# kubectl get node -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
master1 NotReady control-plane,master 50m v1.23.17 172.16.1.20 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
master2 NotReady control-plane,master 44m v1.23.17 172.16.1.21 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
9.3 master1查看节点信息
[root@master1 ~]# kubectl get node -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
master1 NotReady control-plane,master 20m v1.23.17 172.16.1.20 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
master2 NotReady control-plane,master 15m v1.23.17 172.16.1.21 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
10.添加node节点到k8s集群(所有node节点执行)
10.1 将【步骤6.2】中获取到添加Node节点的初始化命令复制-执行
kubeadm join 172.16.1.23:6443 --token agitw8.fwghrey1nysrprf8 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:01099779f60c0ba7a8070edacaeaaa1b3b55c36b3a9136402200ce75dafe6bb8
node1注册到集群信息
[root@node1 ~]# kubeadm join 172.16.1.23:6443 --token agitw8.fwghrey1nysrprf8 \
> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:01099779f60c0ba7a8070edacaeaaa1b3b55c36b3a9136402200ce75dafe6bb8
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -o yaml'
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
10.2 查看node注册状态,在任意master执行(没有安装calico插件,所以状态不是Ready)
[root@master1 kubeadm]# kubectl get node -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
master1 NotReady control-plane,master 26m v1.23.17 172.16.1.20 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
master2 NotReady control-plane,master 21m v1.23.17 172.16.1.21 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
master3 NotReady control-plane,master 6m3s v1.23.17 172.16.1.24 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
node1 NotReady <none> 28s v1.23.17 172.16.1.22 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
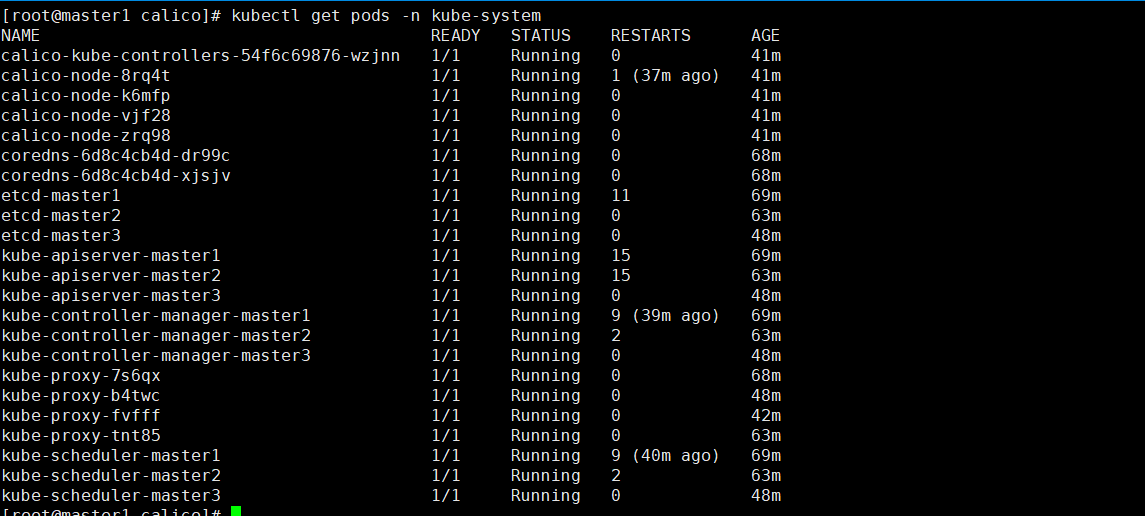
11.安装calico网络插件
https://www.cnblogs.com/Leonardo-li/p/18648449
[root@master1 calico]# kubectl get node -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
master1 Ready control-plane,master 31m v1.23.17 172.16.1.20 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
master2 Ready control-plane,master 26m v1.23.17 172.16.1.21 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
master3 Ready control-plane,master 10m v1.23.17 172.16.1.24 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
node1 Ready <none> 5m3s v1.23.17 172.16.1.22 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 5.4.278-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
12.k8s集群HA高可用验证
12.1 VIP和master节点状态查看
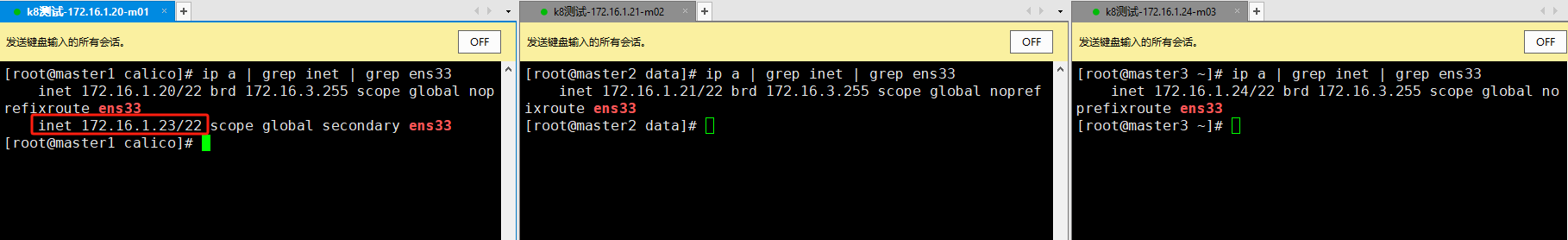
- VIP状态查看,可以看到此时的VIP(172.16.1.23)在master1(172.16.1.20)上。
12.2 高可用验证
- 此时的VIP在master1上,关闭master1服务器,查看VIP的漂移是否正常,发现VIP在master3上了
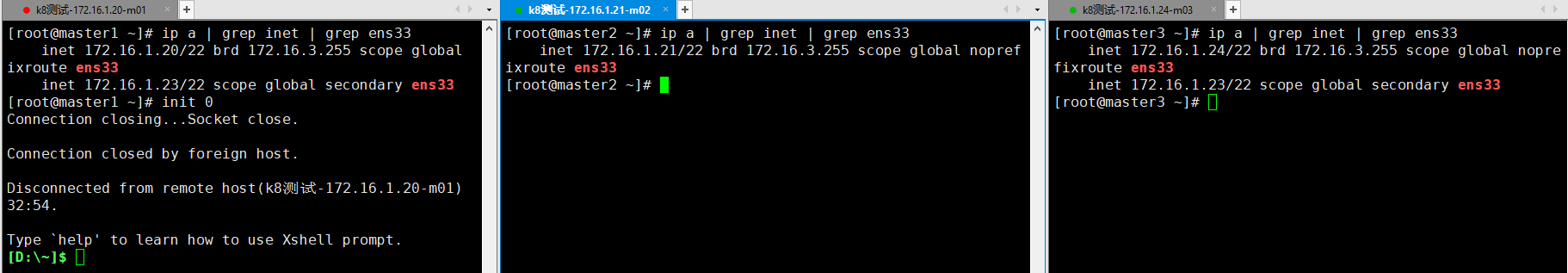
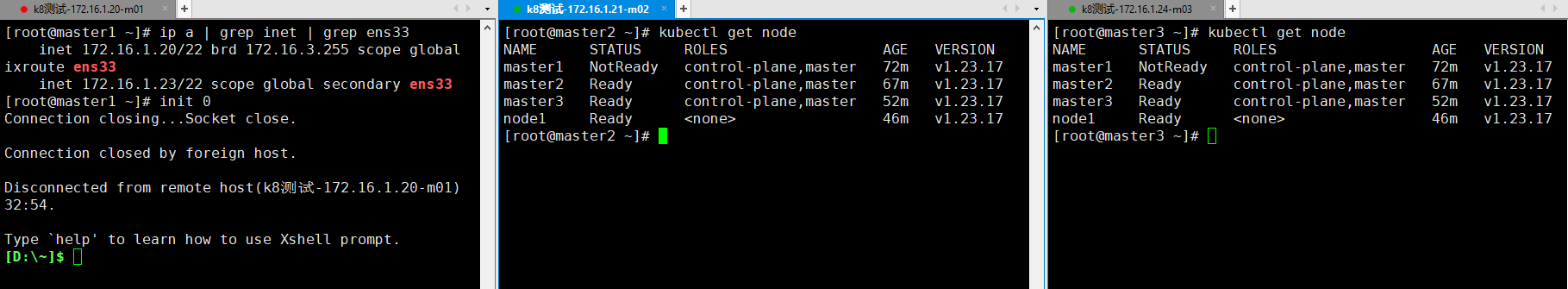
- 查看master2和master3控制层是否可用,发现是可以正常使用的
13.k8s永久证书确认
13.1 可以看到ca证书,还是其他业务使用的证书都是100年
kubeadm certs check-expiration
[root@master1 ~]# kubeadm certs check-expiration
[check-expiration] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[check-expiration] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -o yaml'
CERTIFICATE EXPIRES RESIDUAL TIME CERTIFICATE AUTHORITY EXTERNALLY MANAGED
admin.conf Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y ca no
apiserver Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y ca no
apiserver-etcd-client Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y etcd-ca no
apiserver-kubelet-client Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y ca no
controller-manager.conf Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y ca no
etcd-healthcheck-client Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y etcd-ca no
etcd-peer Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y etcd-ca no
etcd-server Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y etcd-ca no
front-proxy-client Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y front-proxy-ca no
scheduler.conf Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y ca no
CERTIFICATE AUTHORITY EXPIRES RESIDUAL TIME EXTERNALLY MANAGED
ca Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y no
etcd-ca Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y no
front-proxy-ca Mar 07, 2125 02:50 UTC 99y no
13.2 kubelet证书也是100年
openssl x509 -in /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet-client-current.pem -noout -dates
[root@master1 ~]# openssl x509 -in /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet-client-current.pem -noout -dates
notBefore=Mar 31 02:50:04 2025 GMT
notAfter=Mar 7 02:50:08 2125 GMT
14.参考文档
#高可用集群部署
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/l4qS_GnmEZ2BmQpO6VI3sQ
#永久证书创建
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/TRukdEGu0Nm_7wjqledrRg
#证书介绍
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/E1gc6pJGLzbgHCvbOd1nPQ














 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号