C中单向链表之增删改查
C中单向链表之增删改查
// 链表(Linked List)是一种基础但至关重要的数据结构。它通过动态内存分配实现数据的非连续存储,解决了数组的固定长度和插入/删除低效的问题。无论是算法面试还是实际开发,链表都是高频考点和核心技能之一。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
// 单向链表(Singly Linked List)
typedef struct Node
{
int num;
char data[20];
struct Node *next;
Node(int x) : num(num), next(nullptr) {}
Node() {}
} STU, Node, *PNode;
// 链表创建(头插法)
PNode linked_create_head1()
{
int num, i = 0;
cout << "请输入节点数量:" << endl;
cin >> num;
PNode head = NULL;
PNode current = NULL;
while (i < num)
{
PNode temp;
PNode node = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("内存分配失败!\n");
exit(1);
}
memset(node, 0, sizeof(Node));
cout << "请输入第" << i << "节点data:" << endl;
cin >> node->data;
// 如果当前头节点为空,则将新节点作为头节点
if (head == NULL)
{
head = node;
}
else
{
node->next = head; // 将新节点的指针域指向head(老节点)
head = node; // 将新节点作为头节点
}
i++;
}
// 给节点编号
current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
current->num = i;
current = current->next;
}
return head;
}
// 链表创建(尾插法)
PNode linked_create_tail()
{
int num;
cout << "请输入节点数量:" << endl;
cin >> num;
PNode head = nullptr;
PNode tail = nullptr; // 记录尾节点
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
// 创建新节点
PNode node = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("内存分配失败!\n");
exit(1);
}
memset(node, 0, sizeof(Node));
cout << "请输入第" << i + 1 << "个节点data:" << endl;
cin >> node->data;
node->num = i; // 直接设置节点编号
// 如果是第一个节点
if (head == nullptr)
{
head = node;
tail = node;
node->next = nullptr;
}
else
{
// 将新节点连接到链表尾部
tail->next = node;
tail = node; // 更新尾节点
node->next = nullptr;
}
}
return head;
}
// 释放链表
void free_list(PNode head)
{
// 内存释放函数
// 当前节点指针
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << "链表为空" << endl;
return;
}
while (head != NULL)
{ // 遍历链表
PNode temp = head; // 临时保存当前节点
head = head->next; // 移动到下一个节点
free(temp); // 释放原节点内存
}
}
void print_list(PNode *head)
{
// 检查链表是否为空
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空\n");
return;
}
PNode current = *head; // 使用临时变量避免修改传入的 head 指针
// 遍历整个链表,包括最后一个节点
while (current) // 修改为 head 而不是 head->next
{
printf("当前节点为:%d,节点数据为%s\n", current->num, current->data);
current = current->next;
}
}
/*
task : 1.从指定位置插入节点
2.创建一个有序链表,根据value值排序
*/
void update_data(PNode head, int value)
{
PNode temp = head;
while (temp)
{
if (value == temp->num)
{
// 找到指定节点
// 先清空原始数据
memset(temp->data, 0, sizeof(temp->data));
cout << "请输入要更改的节点数据:" << endl;
cin >> temp->data;
cout << "节点数据更新成功" << endl;
printf("更改后的数据为%s\n", temp->data);
return;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
}
void insert_node(PNode head)
{
PNode temp = head;
PNode new_node = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (new_node == NULL)
{
printf("内存分配失败!\n");
exit(1);
}
memset(new_node, 0, sizeof(Node));
cout << "请输入插入节点的序号" << endl;
cin >> new_node->num;
cout << "请输入插入节点的数据" << endl;
cin >> new_node->data;
while (temp)
{
if (temp->num >= new_node->num)
{
if (temp->num == new_node->num)
{
new_node->next = temp; // 调整后续链表
}
temp->num = temp->num + 1; // 节点序号递增
}
temp = temp->next;
}
//设置前一位node的next为new_node
temp = head;
while (temp)
{
if ((temp->num) + 1 == new_node->num)
{
temp->next = new_node;
break; // 遍历链表找到插入的位置
}
}
}
int main()
{
PNode head;
head = linked_create_head1();
print_list(&head);
insert_node(head);
print_list(&head);
update_data(head, 1);
print_list(&head);
free_list(head);
return 0;
}
关于insert节点理解:
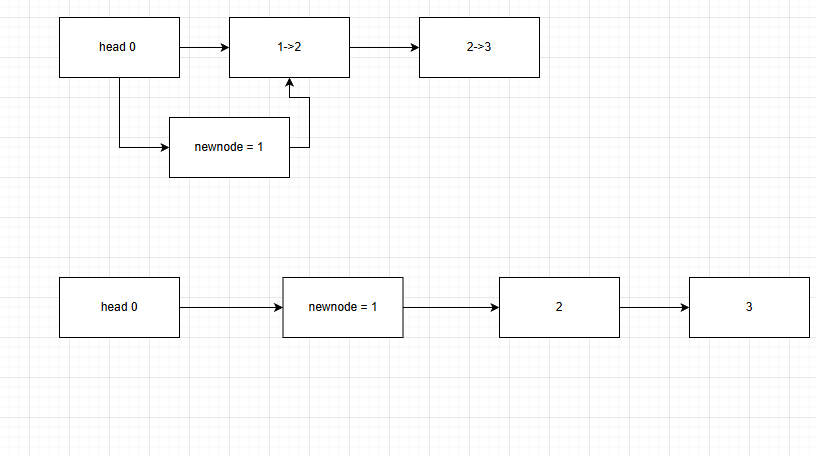
我们这里要想插入一个节点就得先找到它的序号前一位和后一位,所以我们将前一位node的next指向new_node,将new_node的next指向后一位node,将后几位node的序号各加一
本篇用于记录学习,如有问题欢迎指出
我要吃炸鸡


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号