[本文出自天外归云的博客园]
Windows下Anaconda+Tensorflow环境部署
1. 安装Anaconda。
2. 开始菜单 > 所有程序 > Anaconda 3 (64-bit) > Anaconda Prompt > 执行命令:
conda create -n tensorflow python=3.5
至此创建了一个名字叫做tensorflow的虚拟环境,并指定了这个虚拟环境的python为3.5版本。
3. 激活虚拟环境,执行命令:
activate tensorflow
4. 安装CPU版本的tensorflow,执行命令:
pip install --ignore-installed --upgrade https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/windows/cpu/tensorflow-1.2.1-cp35-cp35m-win_amd64.whl
必须用这个whl结尾的https地址,用其他地址安装一会儿在python环境中import tensorflow都会报错。
至此环境部署完成。
使用方法
要运行一个tensorflow机器学习脚本,首先创建一个test.py文件,包含以下内容:
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf # Model parameters W = tf.Variable([.3], dtype=tf.float32) b = tf.Variable([-.3], dtype=tf.float32) # Model input and output x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) linear_model = W * x + b y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # loss loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(linear_model - y)) # sum of the squares # optimizer optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01) train = optimizer.minimize(loss) # training data x_train = [1, 2, 3, 4] y_train = [0, -1, -2, -3] # training loop init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess = tf.Session() sess.run(init) # reset values to wrong for i in range(1000): sess.run(train, {x: x_train, y: y_train}) # evaluate training accuracy curr_W, curr_b, curr_loss = sess.run([W, b, loss], {x: x_train, y: y_train}) print("W: %s b: %s loss: %s" % (curr_W, curr_b, curr_loss))
然后打开Anaconda Prompt,激活在我们刚才创建的tensorflow虚拟环境,并在其中执行上面的test.py文件,得到下面的运行结果:
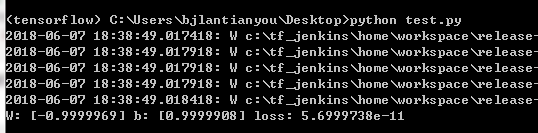
这就是tensorflow机器学习脚本在Anaconda Prompt中的使用方法。
数字识别实践
接下来详细解释下官方的HelloWord用例:
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data # 加载数据集,Label(标签)在one-hot编码后变成向量,所以在此读取数据集中的数据时指定了one_hot参数为true mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True) # 创建一个tensorflow的交互环境 sess = tf.InteractiveSession() # [None, 784]是shape,None代表不限条数的输入,784代表每条输入都是一个784维的向量 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # W的shape是[784, 10],784是特征的维数,10是类别数,每个特征都对应有10个类别 W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10])) # b的shape是[10],是个10维向量 b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) # 计算公式,其中matmul是tf.nn下面的矩阵乘法函数 y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b) # y_是真实的概率分布,即Label的one-hot编码,shape为[None, 10],None代表样本数不限,10代表每个样本对应的概率分布是一个10维向量 y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) # 损失函数(loss function)coss_entropy,reduce_sum求和,reduce_mean对每个batch数据结果求均值 cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1])) # 优化目标设定为cross_entropy,学习速率为0.5 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy) # 运行全局参数初始化器 tf.global_variables_initializer().run() # 迭代 for i in range(1000): # 每次从训练集中随机抽取100条样本构成一个mini-batch,他们的特征和标签分别存到batch_xs和batch_ys里 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) # 调用train_step对mini-batch中的样本进行训练 train_step.run({x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) # tf.equal对预测类别tf.argmax(y, 1)和实际类别tf.argmax(y_, 1)进行比较判断是否相等,tf.argmax函数从一个tensor中寻找最大值序号 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1)) # tf.cast()函数的作用是执行tensorflow 中张量数据类型转换 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) # 调用此方法将执行所有前面的操作,这些操作会生成产生此张量的操作所需的输入,这里是x和y_,分别是读取的图像特征和标签 print(accuracy.eval({x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels}))
运行结果如下:
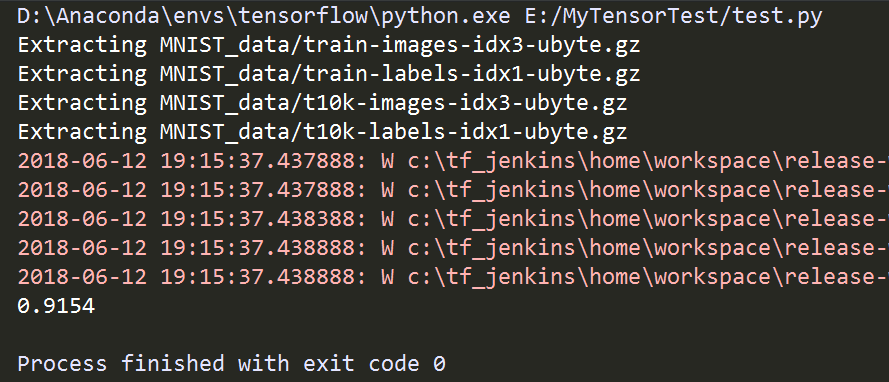
至此完成了训练,并求出了精准度。如果要用我们这次训练的模型来对数字进行识别,首先要保存本次训练的模型,然后再在本地读取数字图片数据并转化为模型可以接收的ndarray类型数据,用模型进行训练。那就要对上面的代码稍加改动。第一步,训练并保存模型,修改上面代码(number_recognition_train.py)如下,添加保存模型的过程:
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data import os # 加载数据集,Label(标签)在one-hot编码后变成向量,所以在此读取数据集中的数据时指定了one_hot参数为true mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True) # 创建一个tensorflow的交互环境 sess = tf.InteractiveSession() # [None, 784]是shape,None代表不限条数的输入,784代表每条输入都是一个784维的向量 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # W的shape是[784, 10],784是特征的维数,10是类别数,每个特征都对应有10个类别 W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10])) # b的shape是[10],是个10维向量 b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) # 计算公式,其中matmul是tf.nn下面的矩阵乘法函数 y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b) # y_是真实的概率分布,即Label的one-hot编码,shape为[None, 10],None代表样本数不限,10代表每个样本对应的概率分布是一个10维向量 y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) # 损失函数(loss function)coss_entropy,reduce_sum求和,reduce_mean对每个batch数据结果求均值 cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1])) # 优化目标设定为cross_entropy,学习速率为0.5 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy) # 运行全局参数初始化器 tf.global_variables_initializer().run() # 迭代 for i in range(1000): # 每次从训练集中随机抽取100条样本构成一个mini-batch,他们的特征和标签分别存到batch_xs和batch_ys里 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) # 调用train_step对mini-batch中的样本进行训练 train_step.run({x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) print("训练完成!") # 创建模型保存目录 model_dir = "models" model_name = "number_recognition" if not os.path.exists(model_dir): os.mkdir(model_dir) # 定义模型保存对象 saver = tf.train.Saver() # 保存模型 saver.save(sess, os.path.join(model_dir, model_name)) print("保存模型成功!") # tf.equal对预测类别tf.argmax(y, 1)和实际类别tf.argmax(y_, 1)进行比较判断是否相等,tf.argmax函数从一个tensor中寻找最大值序号 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1)) # tf.cast()函数的作用是执行tensorflow 中张量数据类型转换 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) # 调用此方法将执行所有前面的操作,这些操作会生成产生此张量的操作所需的输入,这里是x和y_,分别是读取的图像特征和标签 print("精准度:{}".format(accuracy.eval({x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels})))
运行之后,在当前目录下就会出现一个叫models的文件夹,其下会生成我们的模型文件:
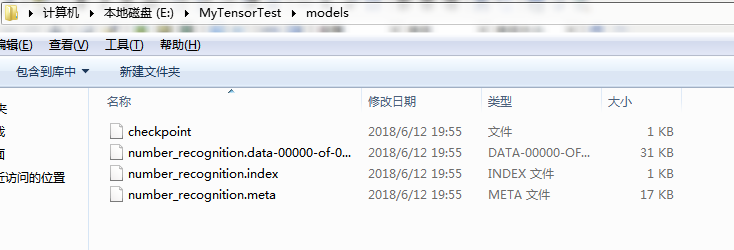
之后再写一个number_recognition_test.py文件,用我们已经保存到本地的模型对其他图片内容进行数字识别,内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python # 导入mnist数据库 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data", one_hot=True) import tensorflow as tf from PIL import Image import numpy as np # 读取mnist中的数据进行测试 def img_recognition_from_mnist(sess, y): # 从mnist中读取出一个测试图片 idx = 0 img = mnist.test.images[idx] print("type:{}".format(type(img))) print("img:{}".format(img)) print(list(img)) print(len(list(img))) # 根据模型计算结果 ret = sess.run(y, feed_dict={x: img.reshape(1, 784)}) # 显示测试结果 print("预测结果:{} 实际结果:{}".format((ret.argmax()), (mnist.test.labels[idx].argmax()))) # 读取本地图片转化为数据进行测试 def img_recognition_from_custom(image_path, sess, y): # 读取图片转成灰度格式 img = Image.open(image_path).convert('L') # resize的过程 img = img.resize((28, 28)) # 像素存入一维数组 arr = [1.0 - float(img.getpixel((j, i))) / 255.0 for i in range(28) for j in range(28)] # 转为ndarray类型并reshape np_arr = np.array(arr).reshape(1, 784) # 根据模型计算结果 ret = sess.run(y, feed_dict={x: np_arr}) # 显示预测结果 print("预测结果:{}".format((ret.argmax()))) if __name__ == '__main__': # 创建会话 sess = tf.Session() # 定义输入变量 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # 定义参数 W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10])) b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) # 定义模型和激励函数 y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b) # 定义模型保存对象 saver = tf.train.Saver([W, b]) # 恢复模型 saver.restore(sess, "models/number_recognition") print("恢复模型成功!") # img_recognition_from_mnist(sess, y) img_path = '7.jpg' img_recognition_from_custom(img_path, sess, y)
运行后发现预测结果是3,而实际图片中的数字是7:

看来这个训练集并不适合我的图片,需要自己来搞训练数据,再做一个训练集进行专门的训练。这个之后再说。
本文来自博客园,作者:天外归云,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/LanTianYou/p/9152255.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号