实验1
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> template<typename T> void output(const T &c); void test1(); void test2(); void test3(); int main() { std::cout<<"测试1:\n"; test1(); std::cout<<"\n测试2:\n"; test2(); std::cout<<"\n测试3:\n"; test3(); } template<typename T> void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i :c) std::cout<<i<<' '; std::cout<<'\n'; } void test1() { using namespace std; string s0{"0123456789"}; cout<<"s0="<<s0<<endl; string s1(s0); reverse(s1.begin(),s1.end()); cout<<"s1="<<s1<<endl; string s2(s0.size(),' '); reverse_copy(s0.begin(),s0.end(),s2.begin()); cout<<"s2="<<s2<<endl; } void test2() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0{2,0,4,9}; cout<<"v0: ";output(v0); vector<int>v1{v0}; reverse(v1.begin(),v1.end()); cout<<"v1: ";output(v1); vector<int>v2{v0}; reverse_copy(v0.begin(),v0.end(),v2.begin()); cout<<"v2: ";output(v2); } void test3(){ using namespace std; vector<int>v0{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; cout<<"v0: ";output(v0); vector<int>v1{v0}; rotate(v1.begin(),v1.begin()+1,v1.end()); cout<<"v1: ";output(v1); vector<int>v2{v0}; rotate(v2.begin(),v2.begin()+2,v2.end()); cout<<"v2: ";output(v2); vector<int>v3{v0}; rotate(v3.begin(),v3.end()-1,v3.end()); cout<<"v3: ";output(v3); vector<int>v4{v0}; rotate(v4.begin(),v4.end()-2,v4.end()); cout<<"v4: ";output(v4); }
运行结果:
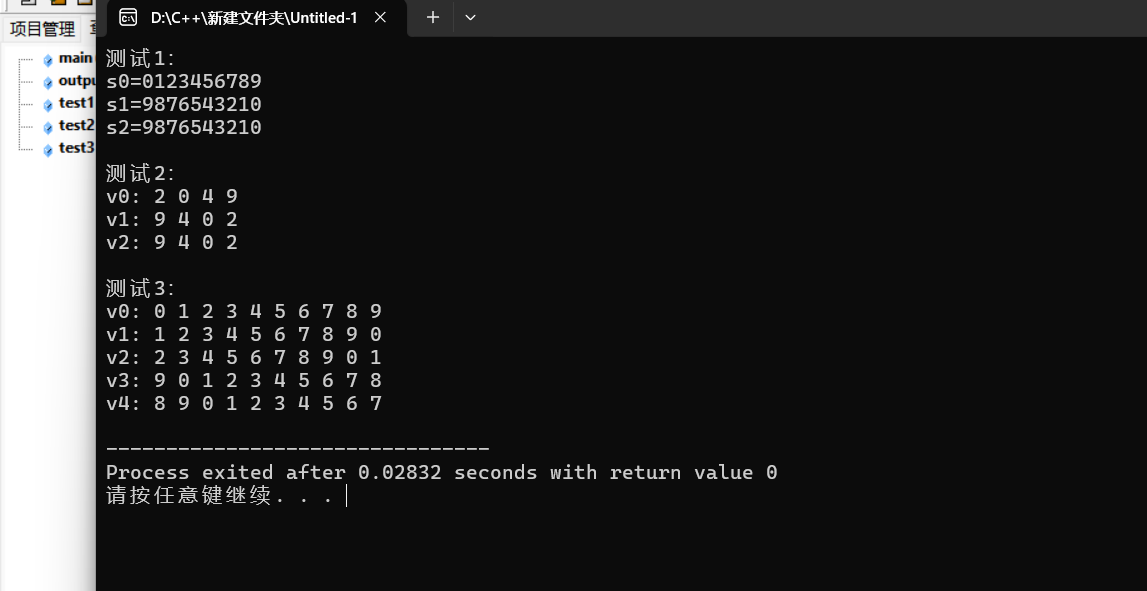
reverse用于将自身序列倒置,reverse_copy用于将序列倒置后复制到另一个目标区间
rotate可以将begin到end的序列往左或者往右循环移动指定位数
第一个和第3个表示序列区间的头和尾第2个参数左移是begin加()右移是end减()
2.实验任务2:
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> #include<numeric> #include<iomanip> #include<cstdlib> #include<ctime> template<typename T> void output(const T &c); int generate_random_number(); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { std::srand(std::time(0)); std::cout<<"测试1:\n"; test1(); std::cout<<"\n测试2:\n"; test2(); } template <typename T> void output(const T &c) { for (auto &i: c) std::cout<<i<<' '; std::cout<<"\n"; } int generate_random_number() { return std::rand()%101; } void test1() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0(10); generate(v0.begin(),v0.end(),generate_random_number); cout<<"v0: ";output(v0); vector<int>v1{v0}; sort(v1.begin(),v1.end()); cout<<"v1: ";output(v1); vector<int>v2{v0}; sort(v2.begin()+1,v2.end()-1); cout<<"v2: ";output(v2); } void test2() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0(10); generate(v0.begin(),v0.end(),generate_random_number); cout<<"v0: ";output(v0); auto min_iter=min_element(v0.begin(),v0.end()); auto max_iter=max_element(v0.begin(),v0.end()); cout<<"最小值: "<<*min_iter<<endl; cout<<"最大值:"<<*max_iter<<endl; auto ans=minmax_element(v0.begin(),v0.end()); cout<<"最小值:"<<*(ans.first)<<endl; cout<<"最大值: "<<*(ans.second)<<endl; double avg1=accumulate(v0.begin(),v0.end(),0.0)/v0.size(); cout<<"均值: "<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<avg1<<endl; sort(v0.begin(),v0.end()); double avg2=accumulate(v0.begin()+1,v0.end()-1,0.0)/(v0.size()-2); cout<<"去掉最大值,最小值之后,均值:"<<avg2<<endl; }
运行结果:
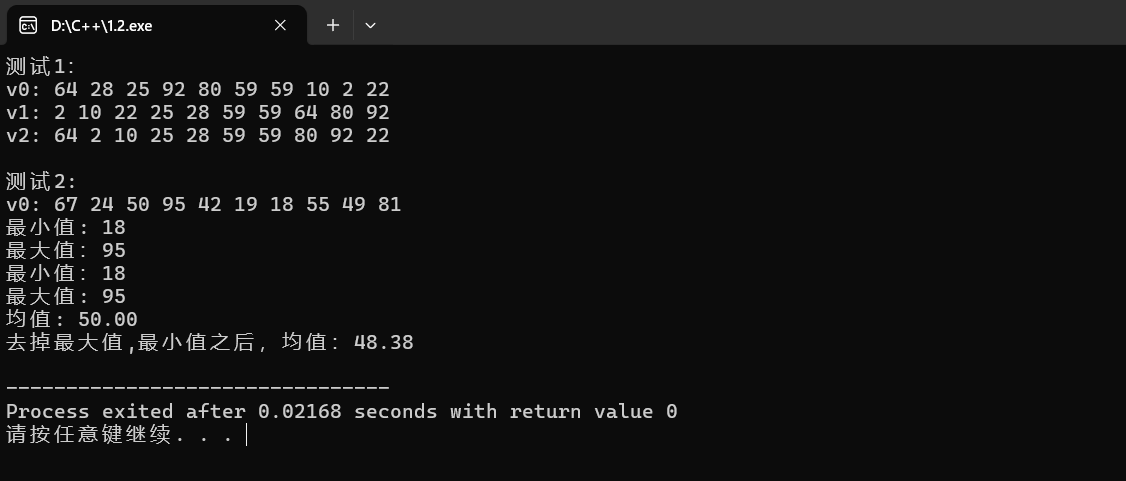
generate可以生成0到100的随机数填充进v0中
minmax_element有利于简化代码的量无需重复编写更加便利
遍历次数减少一倍
等效的两者都无参数且返回值都为int
实验任务3:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <cctype> unsigned char func(unsigned char c); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { std::cout << "测试1: 字符串大小写转换\n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n测试2: 字符变换\n"; test2(); } unsigned char func(unsigned char c) { if(c == 'z') return 'a'; if(c == 'Z') return 'A'; if(std::isalpha(c)) return static_cast<unsigned char>(c+1); return c; } void test1() { std::string s1("We'll be worth 20491"); std::cout << "s1 = " << s1 << '\n'; std::string s2; for(auto c: s1) s2 += std::tolower(c); std::cout << "s2 = " << s2 << '\n'; std::string s3; for(auto c: s1) s3 += std::toupper(c); std::cout << "s3 = " << s3 << '\n'; } void test2() { std::string s1("I love cosmos!"); std::cout << "s1 = " << s1 << '\n'; std::string s2(s1.size(), ' '); std::transform(s1.begin(), s1.end(), s2.begin(), func); std::cout << "s2 = " << s2 << '\n'; }
运行结果:
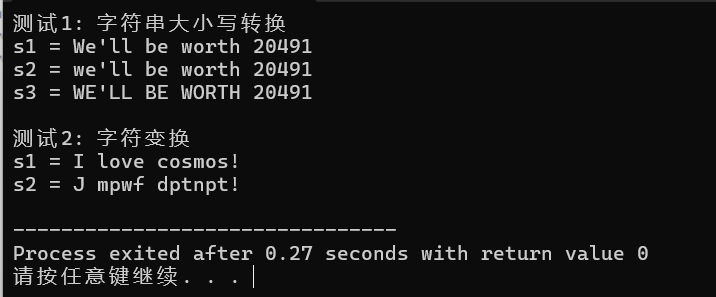
func的作用是将字符串中字母往后移一位若出现z或Z返回a或A
tolower将大写字母小写 小写字母与符号不变
toupper将小写字母大写 大写字母与符号不变
s1.begin表示进行操作的起始位置 s1.end表示进行操作的终止位置s2.begin 表示输出后起始位置 func表示进行的操作
如果修改s2变为s1相当于对s1进行覆盖破坏原来最开始的数据
实验任务4:
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<algorithm> bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s); bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s); int main() { using namespace std; string s; while(cin>>s) { cout<<boolalpha <<"区分大小写:"<<is_palindrome(s)<<"\n" <<"不区分大小写:"<<is_palindrome_ignore_case(s)<<"\n\n"; } } bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s) { int left=0; int right=s.length()-1; while(left<right) { if(s[right]!=s[left]) { return false; } right--; left++; } return true; } char lower(char s) { if(s>='A'&&s<='Z') { return s-'A'+'a'; } return s; } bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s) { int left=0,right=s.length()-1; while(left<right) { if(lower(s[left])!=lower(s[right])) { return false; } left++; right--; } return true; }
实验结果:
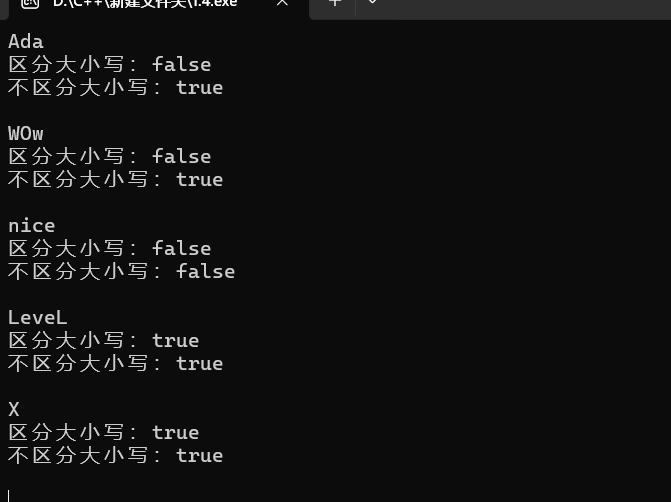
观察与思考:可以先将输入的字符串中空格部分填入相同字符然后对性的字符串进行判断
执行该操作的函数为:
void change(const std ::string &s) { int n=s.length(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(s[i]==' ') s[i]='a'; } }
实验任务5:
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<algorithm> std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2) { if (x == 0) { return "0"; } std::string result = ""; while (x > 0) { int remainder = x % n; x = x / n; char digit; if (remainder < 10) { digit = '0' + remainder; } else { digit = 'A' + (remainder - 10); } result = digit + result; } return result; } int main() { int x; while(std::cin >> x) { std::cout << "十进制:" << x << '\n' << "二进制:" << dec2n(x) << '\n' << "八进制:" << dec2n(x, 8) << '\n' << "十二进制:" << dec2n(x, 12) << '\n' << "十六进制:" << dec2n(x, 16) << '\n' << "三十二进制:" << dec2n(x, 32) << "\n\n"; } return 0; }
实验结果: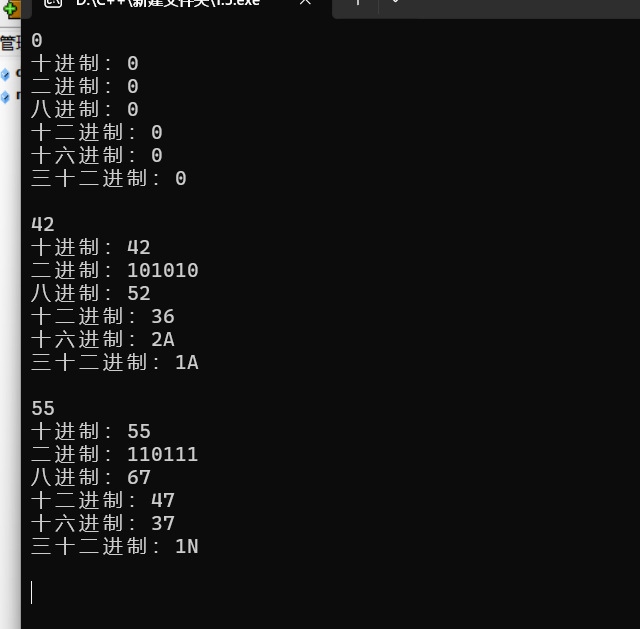
实验任务6:
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<algorithm> int main() { for(char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) { std::cout << c<<" "; } std::cout << std::endl; std::string result = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; for(int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) { std::cout << i; for(char c:result) { std::cout<<" "<<c; } std::cout << std::endl; std::rotate(result.begin(), result.begin() + 1, result.end()); } return 0; }
实验结果:
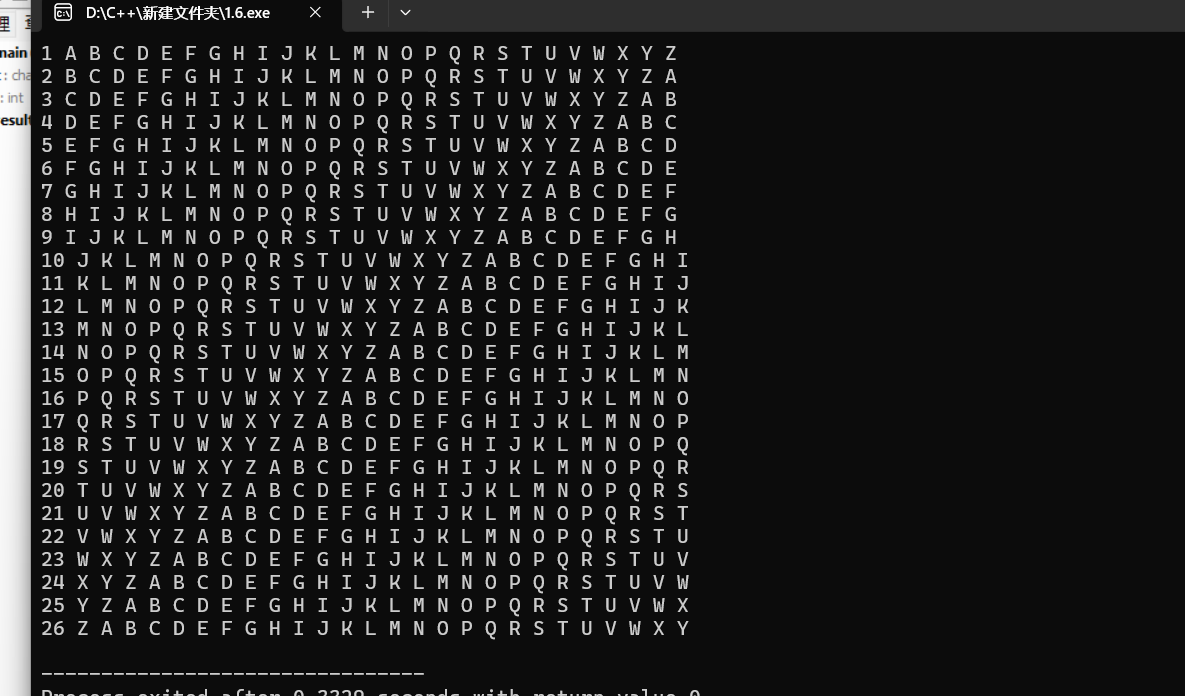
实验任务7
#include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; int generate_random_number() { return rand() % 10 + 1; } int main() { srand(time(0)); int correct_count = 0; const int total_questions = 10; for (int i = 1; i <= total_questions; i++) { int num1, num2, op, correct_answer, user_answer; char op_char; bool valid_question = false; while (!valid_question) { num1 = generate_random_number(); num2 = generate_random_number(); op = rand() % 4; switch (op) { case 0: op_char = '+'; correct_answer = num1 + num2; valid_question = true; break; case 1: if (num1 >= num2) { op_char = '-'; correct_answer = num1 - num2; valid_question = true; } break; case 2: op_char = '*'; correct_answer = num1 * num2; valid_question = true; break; case 3: if (num2 != 0 && num1 % num2 == 0) { op_char = '/'; correct_answer = num1 / num2; valid_question = true; } break; } } cout << num1 << " " << op_char << " " << num2 << " = "; cin >> user_answer; if (user_answer == correct_answer) { correct_count++; } cout << endl; } double accuracy = (static_cast<double>(correct_count) / total_questions) * 100; cout << "正确率: " << accuracy << "%\n"; return 0; }
实验结果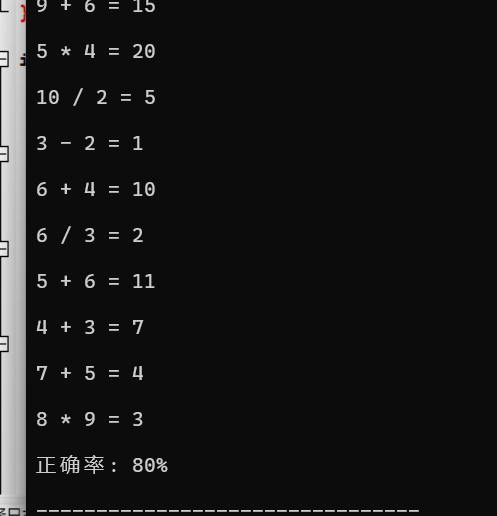



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号