六Spring事务源码分析--9事务方法执行流程
六Spring事务源码分析--9事务方法执行流程
6.5.3 事务方法执行流程
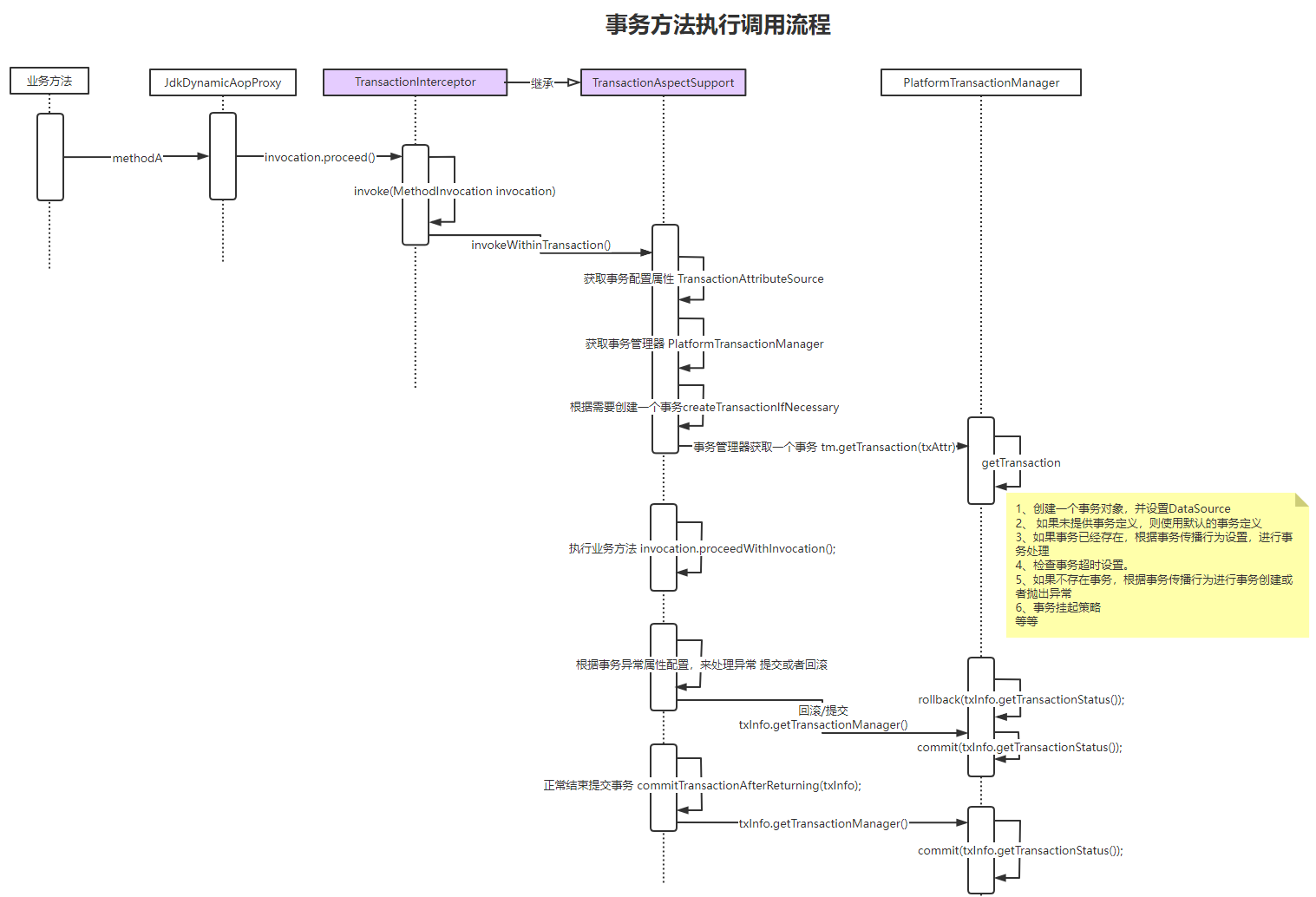
在AOP章节的调用逻辑中,执行业务方法methodA,会被JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke拦截执行,然后获取拦截器链,执行链式调用invocation.proceed。
当执行到事务拦截器TransactionInterceptor时:
//当前类在@Configuration配置类中被实例化
public class TransactionInterceptor extends TransactionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
//实例化,调用构造函数,传入PlatformTransactionManager(控制事务的开启、commit、rollback逻辑)、TransactionAttributeSource(负责事务属性的解析和缓存)
@Deprecated
public TransactionInterceptor(PlatformTransactionManager ptm, TransactionAttributeSource tas) {
setTransactionManager(ptm);
setTransactionAttributeSource(tas);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
//TAG1 invokeWithinTransaction--由父类实现
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new CoroutinesInvocationCallback() {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
//实现链式调用
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object getTarget() {
return invocation.getThis();
}
@Override
public Object[] getArguments() {
return invocation.getArguments();
}
});
}
TAG1 invokeWithinTransaction
该方法作用,是在完整事务中,调用被拦截的方法执行,定义了完整的事务开启、invocation.proceed、commit、rollback的逻辑。
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
//当前由aop切面驱动的当前线程事务信息transactionInfo持有者---可获取当前事务的status、attribute所有信息
private static final ThreadLocal<TransactionInfo> transactionInfoHolder =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current aspect-driven transaction");
@Nullable
private String transactionManagerBeanName;//事务管理器名称
@Nullable
private TransactionManager transactionManager; //事务管理器
@Nullable
private TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource; //事务属性解析源
@Nullable
private BeanFactory beanFactory; //spring中bean工厂类
/**………………………………invokeWithinTransaction方法定义事务执行所有逻辑,包括执行事务、commit/rollback…………………… */
//transactionInterceptor的父类,实现调用事务方法的具体逻辑
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// 如果transaction attribute 为 null, 那么method是non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
/** ………………………………………………………………………tas.getTransactionAttribute,在初始化中canApply已经被解析,存入缓存………………………………………………………………*/
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
//根据事务属性的getQualifier方法,决定事务管理器
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
/**……………………………………………………………………TransactionManager为ReactiveTransactionManager……………………………………………… */
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) {
boolean isSuspendingFunction = KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method);
boolean hasSuspendingFlowReturnType = isSuspendingFunction &&
COROUTINES_FLOW_CLASS_NAME.equals(new MethodParameter(method, -1).getParameterType().getName());
if (isSuspendingFunction && !(invocation instanceof CoroutinesInvocationCallback)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Coroutines invocation not supported: " + method);
}
CoroutinesInvocationCallback corInv = (isSuspendingFunction ? (CoroutinesInvocationCallback) invocation : null);
ReactiveTransactionSupport txSupport = this.transactionSupportCache.computeIfAbsent(method, key -> {
Class<?> reactiveType =
(isSuspendingFunction ? (hasSuspendingFlowReturnType ? Flux.class : Mono.class) : method.getReturnType());
ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(reactiveType);
if (adapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply reactive transaction to non-reactive return type: " +
method.getReturnType());
}
return new ReactiveTransactionSupport(adapter);
});
InvocationCallback callback = invocation;
if (corInv != null) {
callback = () -> CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, corInv.getTarget(), corInv.getArguments());
}
Object result = txSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(method, targetClass, callback, txAttr, (ReactiveTransactionManager) tm);
if (corInv != null) {
Publisher<?> pr = (Publisher<?>) result;
return (hasSuspendingFlowReturnType ? KotlinDelegate.asFlow(pr) :
KotlinDelegate.awaitSingleOrNull(pr, corInv.getContinuation()));
}
return result;
}
/**………………………………………………………………………………………确定事务管理器类为PlatformTransactionManager…………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
//获取事务方法拦截点的字符串信息
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
//当事务属性为null
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) { //1
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
//TAG1.1 createTransactionIfNecessary
//创建一个完整的事务信息TransactionInfo,其有getTransaction、commit、rollback方法
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
//TAG1.2 invocation.proceedWithInvocation()
//事务方法是个around的advice,此处是执行拦截器链的操作,并最终调用目标类上的方法调用
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
//如果抛出异常ex
catch (Throwable ex) {
//TAG1.3 completeTransactionAfterThrowing
// target invocation exception
//完成抛出异常后的事务执行
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
//清理事务信息info
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
//TAG1.4 commitTransactionAfterReturning
//在执行结果返回后,commit事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
} //1
//如果事务属性不为null---CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager类型的事务管理器,不常用,代码忽略
else {
Object result;
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) ptm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
return retVal;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
}
TransactionAspectSupport中invokeWithinTransaction定义了事务执行的完整流程,执行如下逻辑:
1 获取TransactionAttributeSource,并获取事务属性TransactionAttribute
// 如果transaction attribute 为 null, 那么method是non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
/** ………………………………………………………………………tas.getTransactionAttribute,在初始化中canApply已经被解析,存入缓存………………………………………………………………*/
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
2 确定事务管理器TransactionManager
//根据事务属性的getQualifier方法,决定事务管理器
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
3 创建完整事务TransactionInfo(其内包括transactionAttribute、transactionStatus)
//TAG1.1 createTransactionIfNecessary
//创建一个完整的事务信息TransactionInfo,其有getTransaction、commit、rollback方法
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
4 链式调用,执行业务方法、以及其他拦截器
try {
//事务方法是个around的advice,此处是执行拦截器链的操作,并最终调用目标类上的方法调用
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
5 如果有异常(目标调用过程中的异常),根据事务配置的异常属性rollbackfor,处理commit或者rollback
//TAG1.2 completeTransactionAfterThrowing
// target invocation exception
//完成抛出异常后的事务执行
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
6 清理事务信息
finally {
//清理事务信息info
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
7 在调用结束,正常提交事务
//TAG1.3 commitTransactionAfterReturning
//在执行结果返回后,commit事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
TAG1.1 createTransactionIfNecessary
TransactionAspectSupport
//TAG1.1 createTransactionIfNecessary
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// 如果事务没有命名
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
//设置joinpointIdentification为事务属性名称
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
//TAG1.1.1 PlatformTransactionManager.getTransaction
/**……………………………………………………………………attribute----transactionManager转换为---->transactionStatus…………………………………… */
//从transactionManager获取事务,返回status
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
//TAG1.1.2 prepareTransactionInfo
//通过attribute、status创建出一个完整的事务信息transactionInfo
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
protected TransactionInfo prepareTransactionInfo(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, String joinpointIdentification,
@Nullable TransactionStatus status) {
//构建TransactionInfo
TransactionInfo txInfo = new TransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
if (txAttr != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Getting transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
txInfo.newTransactionStatus(status);
}
//如果attribute为null,表示当前不存在事务
else {
// The TransactionInfo.hasTransaction() method will return false. We created it only
// to preserve the integrity of the ThreadLocal stack maintained in this class.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No need to create transaction for [" + joinpointIdentification +
"]: This method is not transactional.");
}
}
//无论是否存在事务,总是把transactionInfo设置到线程变量threadLocal上
txInfo.bindToThread();
return txInfo;
}
TAG1.1.1 PlatformTransactionManager.getTransaction(事务传播行为处理)
public interface PlatformTransactionManager extends TransactionManager {
//返回当前active的事务,或者根据事务传播行为,创建一个新的事务返回-----开启事务
/** (根据事务的传播行为,返回有效的事务或者创建一个新事务:--执行逻辑如下:
1 隔离级别、超时时间,应用在新建事务;
2 如果事务定义不被transactionManager支持,抛异常)
3 根据当前是否存在事务,分别根据不同的传播行为,创建事务对象(如required、never等)*/
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException;
getTransaction:
在事务管理器类AbstractPlatformTransactionManager中,getTransaction获取事务时,会处理不同的事务传播行为,例如当前存在事务,但调用方法事务传播级别为REQUIRES_NEW、PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED时,对当前事务进行挂起、恢复等操作,以此保证了当前数据库操作获取正确的Connection。
具体是在子事务提交的最后会将挂起的事务恢复,恢复时重新调用TransactionSynchronizationManager. bindResource设置之前的connection holder,这样再获取的连接就是被恢复的数据库连接, TransactionSynchronizationManager当前激活的连接只能是一个。
public abstract class AbstractPlatformTransactionManager implements PlatformTransactionManager, Serializable {
/**………………………………………………………………………………………………创建事务getTransaction……………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//事务管理器根据definition创建TransactionStatus(处理传播行为,创建事务)
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException {
//如果没有提供TransactionDefinition,使用默认事务定义
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
//TAG1.1.1.1 doGetTransaction
//由子类实现,DataSourceTransactionManager.doGetTransaction创建事务对象(里面包含事务资源,如connection)
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………………………处理当前存在事务的情况…………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) { //2
//TAG1.1.1.2 handleExistingTransaction
//根据传播行为propagation behavior,解决如何创建事务的逻辑,创建transactionStatus
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
} //2
// 检查新创建事务对象的超时时间,是否有效
if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());
}
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………………………处理当前不存在事务的情况…………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//如果PROPAGATION_MANDATORY(必须在事务中执行),则抛异常
if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
//如果传播行为是REQUIRED、REQUIRES_NEW、NESTED,则创建新的事务
else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {//2
//因为不存在事务,所以不需要挂起当前资源
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);
}
try {
//TAG1.1.1.3 startTransaction
//开启新事务
return startTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
} //2
else { //2
//创建空事务:没有实际事务,但是任然可能同步
if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
} //2
}
spring的默认传播行为是REGUIRED--如果存在事务,使用当前;如果没有,创建事务。因此,这里我们只分析required传播行为的情况。
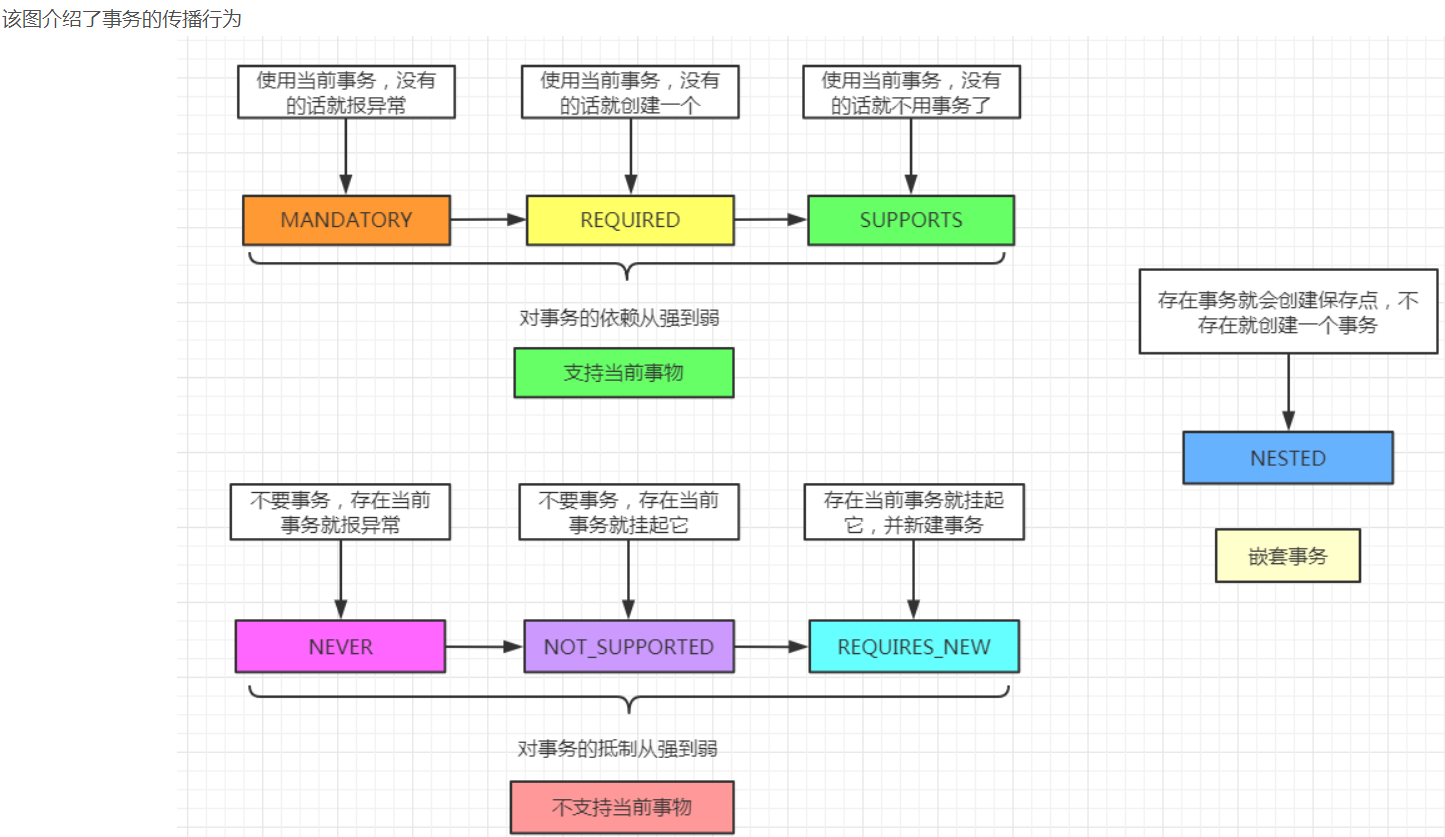
逻辑如下:

TAG1.1.1.1 doGetTransaction
创建用DataSource实现事务(借助数据库实现事务)的事务对象DataSourceTransactionObject,该对象创建并持有事务所需的connection。
DataSourceTransctionManager
@Override
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
//创建DataSource的事务对象
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
//TAG1.1.1.1.1 TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
return txObject;
}
/**
DataSourceTransactionManager调用该事务对象,代表一个connectionHolder
可以通过事务对象DataSourceTransactionObject设置当前事务RollbackOnly只回滚的属性
*/
private static class DataSourceTransactionObject extends JdbcTransactionObjectSupport {
private boolean newConnectionHolder;
private boolean mustRestoreAutoCommit;
public void setConnectionHolder(@Nullable ConnectionHolder connectionHolder, boolean newConnectionHolder) {
super.setConnectionHolder(connectionHolder);
this.newConnectionHolder = newConnectionHolder;
}
public boolean isNewConnectionHolder() {
return this.newConnectionHolder;
}
public void setMustRestoreAutoCommit(boolean mustRestoreAutoCommit) {
this.mustRestoreAutoCommit = mustRestoreAutoCommit;
}
public boolean isMustRestoreAutoCommit() {
return this.mustRestoreAutoCommit;
}
public void setRollbackOnly() {
getConnectionHolder().setRollbackOnly();
}
@Override
public boolean isRollbackOnly() {
return getConnectionHolder().isRollbackOnly();
}
@Override
public void flush() {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
TransactionSynchronizationUtils.triggerFlush();
}
}
}
事务管理器创建事务管理对象DataSourceTransactionObject,就持有数据库连接connection,并且可以设置事务的rollbackonly、判断是否是newconnection。
TAG1.1.1.1.1 TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource
TransactionSynchronizationManager
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………………………同步资源……………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//resource相当于一个(threadID,map(datasource,connectionHolder))的属性,这里用ThreadLocal保存
//key为DataSource,value为connectionHolder(保存当前threadID的connection)
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transactional resources");
/**……………………………………………………………………获取connection资源……………………………………………………………………………… */
@Nullable
public static Object getResource(Object key) {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
return doGetResource(actualKey);
}
@Nullable
private static Object doGetResource(Object actualKey) {
//初次调用,resource没有持有当前线程的map(DataSource,connectionHolder)
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
if (map == null) {
return null;
}
//如果当前存在事务,那么会从resource中获取当前线程对应的connectionHolder对象
Object value = map.get(actualKey);
// Transparently remove ResourceHolder that was marked as void(无效的)...
if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) {
map.remove(actualKey);
// Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty...
if (map.isEmpty()) {
resources.remove();
}
value = null;
}
return value;
}
在第一次获取事务对象时,TransactionSynchronizationManager的同步资源connection目前为null;
如果不是第一次获取,即当前存在事务,那么会从resource中获取当前线程对应的connectionHolder对象
TAG1.1.1.2 handleExistingTransaction
处理当前存在事务的情况下,事务的创建流程。
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………………………处理当前存在事务的情况…………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) { //2
//TAG1.1.1.2 handleExistingTransaction
//根据传播行为propagation behavior,解决如何创建事务的逻辑,创建transactionStatus
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
} //2
首先,看如何根据事务对象transactionObject判断当前是否存在事务的逻辑
DataSourceTransactionManager
@Override
protected boolean isExistingTransaction(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
//当前txobject存在connectionHolder,且isTransactionActive
return (txObject.hasConnectionHolder() && txObject.getConnectionHolder().isTransactionActive());
}
然后,对存在事务的情况创建事务,进行分析
/**………………………………………………………………处理当前存在事务情况,根据事务传播行为,执行事务创建逻辑……………………………………………………………… */
private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction(
TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled)
throws TransactionException {
//never:以非事务运行,如果存在事务,抛异常
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'");
}
//NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务运行,如果有事务,则挂起
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction");
}
//挂起当前存在的事务
Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
//准备TransactionStatus,且newTransaction为false,且保存挂起资源suspendedResources
return prepareTransactionStatus(
definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
//REQUIRES_NEW总是开启新事务;如果存在事务,则将这个存在的事务挂起,然后开启新事务
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" +
definition.getName() + "]");
}
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
try {
//开启事务
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error beginEx) {
resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx);
throw beginEx;
}
}
//NESTED嵌套事务,创建一个嵌套事务
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
//判断是否允许嵌套实物
if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) {
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
"specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
}
//使用savepoint作为嵌套事务
if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) {
//创建DefaultTransactionStatus,标志位newTransaction为false
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
//创建事务,并持有savepoint
status.createAndHoldSavepoint();
return status;
}
else {
//嵌套的事务,通过被嵌套事务的begin、commit、rollback支持事务执行
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
//处理PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED.支持当前事务
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction");
}
if (isValidateExistingTransaction()) {
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) {
Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel()) {
Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants;
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " +
(currentIsolationLevel != null ?
isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) :
"(unknown)"));
}
}
if (!definition.isReadOnly()) {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is");
}
}
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
//准备事务状态status,设置newTransaction为false
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}

后面程序,处理当前不存在事务的逻辑:

TAG1.1.1.3 startTransaction(ST)
当前事务不存在的情况,且事务传播行为为required、required-new、nested时,需要创建新事务并开启。
AbstractTransactionPlatformManager
private TransactionStatus startTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction,
boolean debugEnabled, @Nullable SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources) {
//如果当前事务的TransactionSynchronization不为0,则表示是newSynchronization
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
//注意:这里新建的transactionStatus的newTransaction为true,只有true时才可以做实际的commit或者rollback
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
//ST1 doBegin
//开启事务,子类实现
doBegin(transaction, definition);
//ST2 prepareSynchronization
//初始化事务同步管理器TransactionSynchronizationManager,以及其内的同步事务器
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
注意transactionStatus的newTransaction设置
这里新建的transactionStatus的newTransaction为true,即新建的事务(没有嵌套或者其他情况)只有true时才可以做实际的commit或者rollback;如果为false,表示为其他情况,如嵌套,commit或者rollback,只是做位置标记(标志为需要commit或者rollback),需要进一步判断,再进行实际的commit或者rollback操作。
//ST1 doBegin
DataSourceTransactionManager
//开启事务--模板方法实现类中调用,具体实现在该处
@Override
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
Connection con = null;
try { //1
//如果txObject中没有connectionHolder
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) { //2
//ST1.1 obtainDataSource().getConnection
/** …………………………………………………………………………从DataSource新建connection…………………………………………………………………………*/
Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");
}
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
} //2
//将当前connection资源标记为与事务同步(表示当前connection资源已经被事务同步使用)
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
txObject.setReadOnly(definition.isReadOnly());
// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers,
// so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly
// configured the connection pool to set it already).
if (con.getAutoCommit()) { //2
txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");
}
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………………………将connection的自动提交设置为false…………………………………………………………………………………………*/
con.setAutoCommit(false);
} //2
//如果当前事务definition为readonly,则将属性作为sql语句“SET TRANSACTION READ ONLY”,connection执行
prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);
//设置当前事务为活跃状态
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
// 如果是新建连接
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) { //2
//ST1.2 TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource
/**………………将datasource:connectionHolder存入TransactionSynchronizationManager的ThreadLocal中 ……………………*/
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(),txObject.getConnectionHolder());
} //2
} //1
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
//释放当前DataSource创建的connection
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);
}
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);
}
}
doBegin中,主要逻辑是
1 创建数据源连接DataSource.getConnection;
2 con.setAutoCommit(false);将connection自动提交设为false;
3 TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource;将datasource:connectionHolder存入TransactionSynchronizationManager的ThreadLocal中。保证一个线程的事务执行中,能够同意获取connection
//ST1.2 TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource
public static void bindResource(Object key, Object value) throws IllegalStateException {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Assert.notNull(value, "Value must not be null");
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
// set ThreadLocal Map if none found
if (map == null) {
map = new HashMap<>();
resources.set(map);
}
Object oldValue = map.put(actualKey, value);
// Transparently suppress a ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (oldValue instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) oldValue).isVoid()) {
oldValue = null;
}
if (oldValue != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Already value [" + oldValue + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] bound to thread");
}
}
//ST2 prepareSynchronization
对TransactionSynchronizationManager进行适当的初始化设置。
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
protected void prepareSynchronization(DefaultTransactionStatus status, TransactionDefinition definition) {
//如果为isNewSynchronization
if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(status.hasTransaction());
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(
definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT ?
definition.getIsolationLevel() : null);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(definition.isReadOnly());
//设置事务名称
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(definition.getName());
TransactionSynchronizationManager.initSynchronization();
}
}
TransactionSynchronizationManager
public static void initSynchronization() throws IllegalStateException {
if (isSynchronizationActive()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot activate transaction synchronization - already active");
}
//初始化TransactionSynchronizationManager上的事务同步器TransactionSynchronization容器
synchronizations.set(new LinkedHashSet<>());
}
TAG1.1.2 prepareTransactionInfo
将transactionStatus构造成为transactionInfo
TransactionAspectSupport
//TAG1.1 createTransactionIfNecessary
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// 如果事务没有命名
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
//设置joinpointIdentification为事务属性名称
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
//TAG1.1.1 PlatformTransactionManager.getTransaction---------------完成,返回status
/**……………………………………………………………………attribute----transactionManager转换为---->transactionStatus…………………………………… */
//从transactionManager获取事务,返回status
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
//TAG1.1.2 prepareTransactionInfo
//通过attribute、status创建出一个完整的事务信息transactionInfo
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
protected TransactionInfo prepareTransactionInfo(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, String joinpointIdentification,
@Nullable TransactionStatus status) {
//构建TransactionInfo
TransactionInfo txInfo = new TransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
if (txAttr != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Getting transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
txInfo.newTransactionStatus(status);
}
//如果attribute为null,表示当前不存在事务
else {
// The TransactionInfo.hasTransaction() method will return false. We created it only
// to preserve the integrity of the ThreadLocal stack maintained in this class.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No need to create transaction for [" + joinpointIdentification +
"]: This method is not transactional.");
}
}
//TAG1.1.2.1 txInfo.bindToThread()
//无论是否存在事务,总是把transactionInfo设置到线程变量threadLocal上
txInfo.bindToThread();
return txInfo;
}
此时,完成事物开启和创建,把transactionManager、transactionAttribute、事务名称(拦截点方法名称)等信息包装成TransactionInfo(包括完整的事务信息)。
TAG1.1.2.1 txInfo.bindToThread()
TransactionAspectSupport
//当前transactionInterceptor的线程对象ThreadLocal保存事务信息
private static final ThreadLocal<TransactionInfo> transactionInfoHolder =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current aspect-driven transaction");
//内部类TransactionInfo
private void bindToThread() {
// Expose current TransactionStatus, preserving any existing TransactionStatus
// for restoration after this transaction is complete.
this.oldTransactionInfo = transactionInfoHolder.get();
transactionInfoHolder.set(this);
}
将TransactionInfo保存到当前transactionInterceptor的线程对象ThreadLocal,用以在当前事务线程中可以获取事务完整信息transactioninfo。
TAG1.2 invocation.proceedWithInvocation()
TransactionAspectSupport.invokeWithinTransaction
try {
//TAG1.2 invocation.proceedWithInvocation()
//事务方法是个around的advice,此处是执行拦截器链的操作,并最终调用目标类上的方法调用
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
//如果抛出异常ex
catch (Throwable ex) {
//TAG1.3 completeTransactionAfterThrowing
// target invocation exception
//完成抛出异常后的事务执行
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
//清理事务信息info
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
//TAG1.4 commitTransactionAfterReturning
//在执行结果返回后,commit事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
} //1
TAG1.2 completeTransactionAfterThrowing
TransactionAspectSupport
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
//如果事务信息info、status不为null
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) { //1
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
/** ………………………………………………………………………………………………如果事务属性不为空,且对当前异常ex进行回滚……………………………………………………………………………………*/
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
//TAG1.2.1 transactionManager.rollback
//调用事务管理器transactionmanager进行事务回滚rollback
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
} //2
//如果事务为空,或不对当前ex回滚,则执行commit(如果TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly()为true,仍旧进行回滚)
else { ///2
try {
//TAG1.2.2 transactionManager.commit
//调用事务管理器进行回滚
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
} //2
} //1
}
在拦截器链执行过程中,如果抛出异常ex,执行completeTransactionAfterThrowing,逻辑如下:
if(当前事务属性不为空&对当前ex回滚)
执行回滚逻辑rollback;
else(当前事务为null,或者不对当前ex回滚)
执行commit逻辑;---(如果TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly()为true,仍旧进行回滚)
TAG1.2.1 transactionManager.rollback(ROLL)
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
@Override
public final void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
//如果当前事务status.isCompleted,抛异常
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
//回滚
processRollback(defStatus, false);
}
private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status, boolean unexpected) {
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = unexpected;
try {
//ROLL1 triggerBeforeCompletion
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
/**……………………………………NESTED情况:tm.getTransaction时,当事务传播属性为nested时,可以通过设置savepoint的形式,创建事务…………………………………… */
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back transaction to savepoint");
//对于nested,回滚只是将status设置到savepoint点,不执行实际回滚
status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
}
/**………………………………………………………………………………只有newTransaction为true时,才会执行真正的回滚…………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//只有新事务才会回滚,因此只有最外层的事务才会回滚,而对于内层的事务,只是设置回滚标记
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback");
}
//ROLL2 doRollback
doRollback(status);
}
/**………………………………………………………………………………当前事务参与在一个更大的事务中…………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
else {
// Participating in larger transaction
if (status.hasTransaction()) {
if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - marking existing transaction as rollback-only");
}
//ROLL3 doSetRollbackOnly
//子事务,这里只是设置回滚标记(表示当前事务需要回滚)
doSetRollbackOnly(status);
}
else {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - letting transaction originator decide on rollback");
}
}
}
else {
logger.debug("Should roll back transaction but cannot - no transaction available");
}
// Unexpected rollback only matters here if we're asked to fail early
if (!isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = false;
}
}
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
//ROLL4 triggerAfterCompletion
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
throw ex;
}
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
// Raise UnexpectedRollbackException if we had a global rollback-only marker
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
finally {
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
当前方法rollback的主要逻辑如下:
private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status, boolean unexpected) {
//ROLL1 triggerBeforeCompletion
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
/**……………………………………NESTED情况:tm.getTransaction时,当事务传播属性为nested时,可以通过设置savepoint的形式,创建事务…………………………………… */
//对于nested,回滚只是将status设置到savepoint点,不执行实际回滚
status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
/**………………………………………………………………………………只有newTransaction为true时,才会执行真正的回滚…………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//只有新事务才会回滚,因此只有最外层的事务才会回滚,而对于内层的事务,只是设置回滚标记
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
//ROLL2 doRollback
doRollback(status);
}
/**………………………………………………………………………………当前事务参与在一个更大的事务中…………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//ROLL3 doSetRollbackOnly
//子事务,这里只是设置回滚标记(表示当前事务需要回滚)
doSetRollbackOnly(status);
//ROLL4 triggerAfterCompletion
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
//ROLL1 triggerBeforeCompletion
触发调用TransactionSynchronizationManager上的TransactionSynchronization集合,其会在事务执行过程的不同阶段调用before/after方法。
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
protected final void triggerBeforeCompletion(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {
TransactionSynchronizationUtils.triggerBeforeCompletion();
}
}
TransactionSynchronizationUtils
public static void triggerBeforeCompletion() {
//遍历TransactionSynchronizationManager上的getSynchronizations
for (TransactionSynchronization synchronization : TransactionSynchronizationManager.getSynchronizations()) {
try {
//执行事务同步器TransactionSynchronization不同阶段的before、after方法
synchronization.beforeCompletion();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.debug("TransactionSynchronization.beforeCompletion threw exception", ex);
}
}
}
//ROLL2 doRollback
DataSourceTransactionManager
@Override
protected void doRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]");
}
try {
//ROLL2.1 con.rollback()
//数据连接执行rollback
con.rollback();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw translateException("JDBC rollback", ex);
}
}
//ROLL2.1 con.rollback()
调用数据库连接对象connection,执行rollback。就是撤销当前事务在开启后所做的所有的更改,并释放该connection当前持有的数据库锁。
Connection
/**
* Undoes all changes made in the current transaction
* and releases any database locks currently held
* by this <code>Connection</code> object. This method should be
* used only when auto-commit mode has been disabled.
*
* @exception SQLException if a database access error occurs,
* this method is called while participating in a distributed transaction,
* this method is called on a closed connection or this
* <code>Connection</code> object is in auto-commit mode
* @see #setAutoCommit
*/
void rollback() throws SQLException;
//ROLL3 doSetRollbackOnly
DataSourceTransactionManager
@Override
protected void doSetRollbackOnly(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Setting JDBC transaction [" + txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection() +
"] rollback-only");
}
//设置事务对象为setRollbackOnly
txObject.setRollbackOnly();
}
DataSourceTransactionObject(内部类)
public void setRollbackOnly() {
//设置connectionHolder的属性setRollbackOnly
getConnectionHolder().setRollbackOnly();
}
仅仅设置connectionHolder的回滚标志。
//ROLL4 triggerAfterCompletion
逻辑同ROLL1
TAG1.2.2 transactionManager.commit(COMMIT)
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
@Override
public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………………………如果status设置了局部rollbackonly,依然回滚……………………………………………………………………………………………… */
if (defStatus.isLocalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Transactional code has requested rollback");
}
processRollback(defStatus, false);
return;
}
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………………………如果status设置了全局rollbackonly,依然回滚……………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//一般子事务会经过这里
if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Global transaction is marked as rollback-only but transactional code requested commit");
}
processRollback(defStatus, true);
return;
}
//事务提交(外层事务的提交,即newTransaction为true的)
processCommit(defStatus);
}
private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
try {
boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = false;
prepareForCommit(status);
//COMMIT1 triggerBeforeCommit
triggerBeforeCommit(status);
//COMMIT2 triggerBeforeCompletion
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
beforeCompletionInvoked = true;
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………………………NESTED:有savepoint的,这里释放savepoint……………………………………………………………………………………………… */
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
//释放savepoint
status.releaseHeldSavepoint();
}
/**…………………………………………………………………………status.isNewTransaction()只有新建的事务,才可以真正提交……………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//这里保证了外层的事务有commit和rollback的权力
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
//COMMIT3 doCommit
doCommit(status);
}
else if (isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
}
// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException if we have a global rollback-only
// marker but still didn't get a corresponding exception from commit.
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
catch (UnexpectedRollbackException ex) {
//COMMIT4 triggerAfterCompletion
// can only be caused by doCommit
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
throw ex;
}
catch (TransactionException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
if (isRollbackOnCommitFailure()) {
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
}
else {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
}
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
}
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
throw ex;
}
// Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there
// propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.
try {
//COMMIT5 triggerAfterCommit
triggerAfterCommit(status);
}
finally {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);
}
}
finally {
//COMMIT6 cleanupAfterCompletion
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
//COMMIT3 doCommit
DataSourceTransactionManager
@Override
protected void doCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Committing JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]");
}
try {
//COMMIT3.1 con.commit
con.commit();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw translateException("JDBC commit", ex);
}
}
//COMMIT3.1 con.commit
connection
/**
* Makes all changes made since the previous
* commit/rollback permanent and releases any database locks
* currently held by this <code>Connection</code> object.
* This method should be
* used only when auto-commit mode has been disabled.
*
* @exception SQLException if a database access error occurs,
* this method is called while participating in a distributed transaction,
* if this method is called on a closed connection or this
* <code>Connection</code> object is in auto-commit mode
* @see #setAutoCommit
*/
void commit() throws SQLException;
//COMMIT6 cleanupAfterCompletion--todo
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
private void cleanupAfterCompletion(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
status.setCompleted();
if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.clear();
}
//如果是新建事务(外层事务),直接回收连接资源
if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
doCleanupAfterCompletion(status.getTransaction());
}
//如果有挂起的资源,恢复之前资源
if (status.getSuspendedResources() != null) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Resuming suspended transaction after completion of inner transaction");
}
Object transaction = (status.hasTransaction() ? status.getTransaction() : null);
resume(transaction, (SuspendedResourcesHolder) status.getSuspendedResources());
}
}
TAG1.3 commitTransactionAfterReturning
TransactionAspectSupport
//TAG3 commitTransactionAfterReturning
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
//commit提交
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
}
这里会在业务流程执行完时,没有返回异常ex,且正确返回结果后,执行commit操作。后续commit提交如上所述。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号