[sunj的小白人话系列 一]:如何做一个本地部署的对话系统
小白的人话系列一:
如何简简单单的在本地部署一个属于自己的对话系统
笔者这里分别用了两个方法:本地部署、调取API
一、英语对话系统(本地部署)
基础:
***请你先理解我画的对话系统图, 来搞清楚思路是怎么样的 ***
英语口语系统
- 文档下述名词解释:SR(Speech Recording)、TTS(Text To Speech)、ASR(Automatic Speech Recognition)、QA(Question Answer)、LLM(Large Language Moder)
思路图
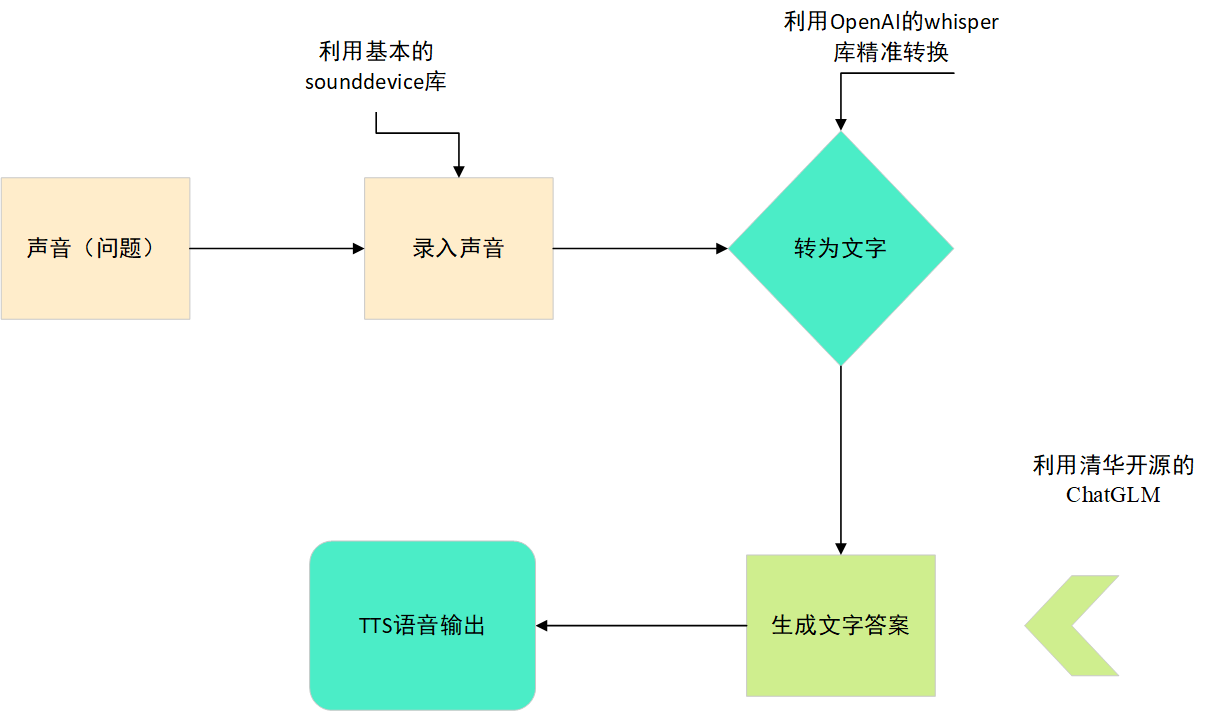
各个模块代码说明
1、声音传输导入
这个我选择了用Sounddevice库。因为网上随处可见,比较简单。Sounddevice还是比较精准的
import sounddevice as sd
import wave
def record_audio(output_path="test.wav", duration=5, sample_rate=44100, channels=2):
print(f"开始录音,时长为 {duration} 秒...")
# 录制音频
audio_data = sd.rec(int(duration * sample_rate), samplerate=sample_rate, channels=channels, dtype='int16')
sd.wait()
# 保存录音结果为 WAV 文件
with wave.open(output_path, 'wb') as wf:
wf.setnchannels(channels)
wf.setsampwidth(2) # 16-bit音频,每个样本2个字节
wf.setframerate(sample_rate)
wf.writeframes(audio_data.tobytes())
print(f"录音已保存为: {output_path}")
# 调用录音函数
record_audio()
2、ASR(实现语音识别功能)
运用Open AI的whisper库,更加精准,代码如下:
链接
import whisper
model = whisper.load_model("base").to('cuda')
# load audio and pad/trim it to fit 30 seconds
audio = whisper.load_audio("/content/test.wav")
audio = whisper.pad_or_trim(audio)
# make log-Mel spectrogram and move to the same device as the model
mel = whisper.log_mel_spectrogram(audio).to(model.device)
# detect the spoken language
_, probs = model.detect_language(mel)
print(f"Detected language: {max(probs, key=probs.get)}")
# decode the audio
options = whisper.DecodingOptions()
result = whisper.decode(model, mel, options)
# print the recognized text
print(result.text)
3、QA(实现产生文字答案过程)
全部模型都跑完的话要占用很多GPU资源,经常会把服务器的显卡跑满。下面为代码。
链接
注意要把model给Del了,不然等等炼丹把实验室炸了
import gc
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("THUDM/chatglm3-6b", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("THUDM/chatglm3-6b", trust_remote_code=True, device='cuda')
model = model.eval()
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, result.text, history=[])
print(response)
# 释放GPU显存
del model
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
gc.collect()
4、TTS(实现语音输出功能)
链接2
代码如下:
from TTS.tts.configs.xtts_config import XttsConfig
from TTS.tts.models.xtts import Xtts
import numpy as np
config = XttsConfig()
config.load_json("/content/XTTS-v2/config.json")
model = Xtts.init_from_config(config)
model.load_checkpoint(config, checkpoint_dir="/content/XTTS-v2/", eval=True)
model.cuda()
max_text_length = 250
if len(response) > max_text_length:
segments = [response[i:i+max_text_length] for i in range(0, len(response), max_text_length)]
else:
segments = [response]
full_audio = []
for segment in segments:
# 使用 XTTS 模型生成语音
outputs = model.synthesize(
segment,
config,
speaker_wav="/content/XTTS-v2/samples/en_sample.wav",
gpt_cond_len=3,
language="en",
)
# 如果输出是音频,将其添加到整体音频流中
if 'wav' in outputs:
segment_audio = outputs['wav']
full_audio.extend(segment_audio)
full_audio.extend(np.zeros(int(1.5 * 24000))) # 在段落之间添加1.5秒的静音
# 将生成的音频保存为 WAV 文件或进行其他必要的处理
from scipy.io.wavfile import write
write("/content/output.wav", 24000, np.array(full_audio))
完整代码:
!pip install -U openai-whisper
!pip install git+https://github.com/openai/whisper.git
!pip install --upgrade --no-deps --force-reinstall git+https://github.com/openai/whisper.git
!pip install TTS
!git lfs install
!git clone https://huggingface.co/coqui/XTTS-v2
import sounddevice as sd
import wave
def record_audio(output_path="test.wav", duration=5, sample_rate=44100, channels=2):
print(f"开始录音,时长为 {duration} 秒...")
# 录制音频
audio_data = sd.rec(int(duration * sample_rate), samplerate=sample_rate, channels=channels, dtype='int16')
sd.wait()
# 保存录音结果为 WAV 文件
with wave.open(output_path, 'wb') as wf:
wf.setnchannels(channels)
wf.setsampwidth(2) # 16-bit音频,每个样本2个字节
wf.setframerate(sample_rate)
wf.writeframes(audio_data.tobytes())
print(f"录音已保存为: {output_path}")
# 调用录音函数
record_audio()
import whisper
model = whisper.load_model("base").to('cuda')
audio = whisper.load_audio("/content/test.wav")
audio = whisper.pad_or_trim(audio)
py
mel = whisper.log_mel_spectrogram(audio).to(model.device)
_, probs = model.detect_language(mel)
print(f"Detected language: {max(probs, key=probs.get)}")
options = whisper.DecodingOptions()
result = whisper.decode(model, mel, options)
print(result.text)
!git clone https://github.com/THUDM/ChatGLM3
!cd ChatGLM3
!pip install --upgrade numpy
!pip install --upgrade tensorflow
import gc
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
import random
random.seed(1)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("THUDM/chatglm3-6b", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("THUDM/chatglm3-6b", trust_remote_code=True, device='cuda')
model = model.eval()
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, result.text, history=[])
print(response)
# 释放GPU显存
del model
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
gc.collect()
from TTS.tts.configs.xtts_config import XttsConfig
from TTS.tts.models.xtts import Xtts
import numpy as np
config = XttsConfig()
config.load_json("/content/XTTS-v2/config.json")
model = Xtts.init_from_config(config)
model.load_checkpoint(config, checkpoint_dir="/content/XTTS-v2/", eval=True)
model.cuda()
max_text_length = 250
if len(response) > max_text_length:
segments = [response[i:i+max_text_length] for i in range(0, len(response), max_text_length)]
else:
segments = [response]
full_audio = []
for segment in segments:
# 使用 XTTS 模型生成语音
outputs = model.synthesize(
segment,
config,
speaker_wav="/content/XTTS-v2/samples/en_sample.wav",
gpt_cond_len=3,
language="en",
)
# 如果输出是音频,将其添加到整体音频流中
if 'wav' in outputs:
segment_audio = outputs['wav']
full_audio.extend(segment_audio)
full_audio.extend(np.zeros(int(1.5 * 24000))) # 在段落之间添加1.5秒的静音
# 将生成的音频保存为 WAV 文件或进行其他必要的处理
from scipy.io.wavfile import write
write("/content/output.wav", 24000, np.array(full_audio))
_ 是不是很容易,接下来更加容易,但是要处理一下输入输出
二、虚拟女友对话系统(调取API)
重点, ( #`O′) 喂说你呢,别分神了。
首先, 先去vivo innovation contest 去注册一个账号, 至于后面怎么搞,这个请你自行谷歌,不在我们的topic内。
PART 1:(part of QA)
我们把70B demo例子复制过来.
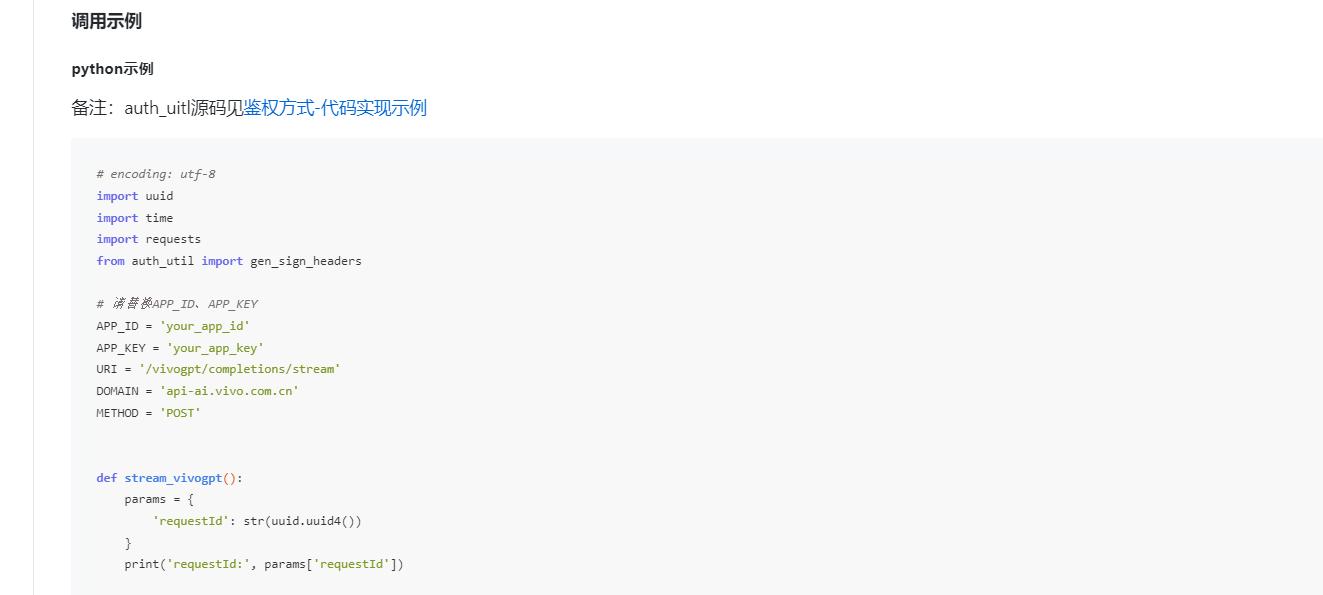
让我们修改一下stream_vivogpt。
我们先看到demo的这里, 很明显,假如我们用prompt的话,做不到stream的效果。
data = { 'prompt': '写一首春天的诗', 'sessionId': str(uuid.uuid4()), 'model': 'vivo-BlueLM-TB' }
然后看到官方给的参数
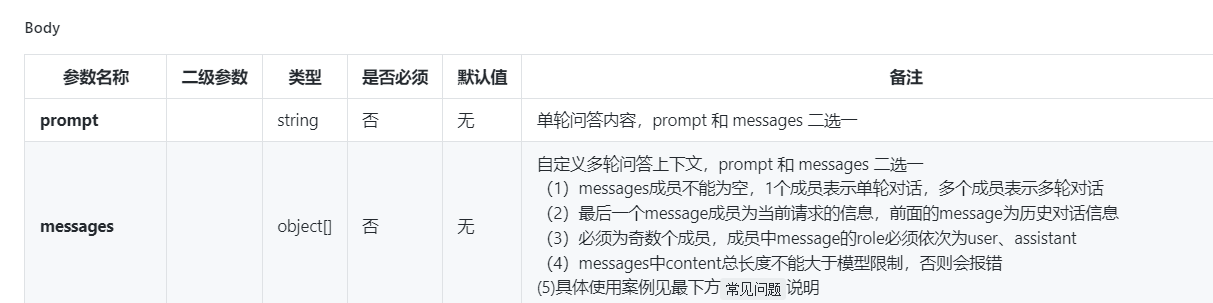
噢噢,我们原来可以用messages,这是llm的基础,不懂请谷歌。
所以我们接下来要修改data,再让这个stream_vivogpt能接受一个参数.
如
def stream_vivogpt(mode):
params = {
'requestId': str(uuid.uuid4())
}
data = {
'messages': mode,
'sessionId': str(uuid.uuid4()),
'model': 'vivo-BlueLM-TB'
}
然后你这时候已经跑了跑官方给的demo,发现,怎么会输出这样的string呢?噢噢原来是他们那边的约定啊!
但是我们肯定不想让这堆字符串出现在我们要进行stream的过程里。噢?我们看了看标题,我们是做一个虚拟女友啊,那她大概率讲中文吧!
那我们把这堆中文提取出来不就行了吗?怎么提取?用中文的正则表达式
decoded_line = line.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore')
if decoded_line.startswith('data:{"message":"') and decoded_line:
chinese_chars = re.findall(r'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+', decoded_line)
sentence += ''.join(chinese_chars)
完整代码:
def stream_vivogpt(mode):
params = {
'requestId': str(uuid.uuid4())
}
data = {
'messages': mode,
'sessionId': str(uuid.uuid4()),
'model': 'vivo-BlueLM-TB'
}
headers = gen_sign_headers(APP_ID, APP_KEY, METHOD, URI, params)
headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/json'
url = f'http://{DOMAIN}{URI}'
try:
response = requests.post(url, json=data, headers=headers, params=params, stream=True)
sentence = "" # 初始化句子
if response.status_code == 200:
first_line = True
for line in response.iter_lines():
if line:
if first_line:
first_line = False
decoded_line = line.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore')
if decoded_line.startswith('data:{"message":"') and decoded_line:
chinese_chars = re.findall(r'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+', decoded_line)
sentence += ''.join(chinese_chars)
else:
sentence = "请求失败,状态码:" + str(response.status_code)
except Exception as e:
sentence = "请求过程中发生异常:" + str(e)
return sentence
至此第一部分解决完毕
PART 2 :(part of ASR)
让我们现在把目光放到ASR的ai_speech_input_client
同样的,打开官方给的demo.
同样的问题,输出一堆不是人类能读的string,同样包含中文。还是要用正则表达式去除噪音,也就是没用的数据
r = ws.recv()
# print(r)
if r.startswith('{"sid":') and r:
chinese_chars = re.findall(r'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+', r)
sentence += ''.join(chinese_chars)
tmpobj = json.loads(r)
后面的就很简单了,就是函数之间不断返回
完整代码:
def read_wave_data(wav_path):
wav_data, sample_rate = soundfile.read(wav_path, dtype='int16')
return wav_data, sample_rate
def send_process(ws, wav_path):
try:
for i in range(NUM):
wav_data, sample_rate = read_wave_data(wav_path)
nlen = len(wav_data)
nframes = nlen * 2
pack_data = struct.pack('%dh' % nlen, *wav_data)
wav_data_c = list(struct.unpack('B' * nframes, pack_data))
cur_frames = 0
sample_frames = 1280
start_data = {
"type": "started",
"request_id": "req_id",
"asr_info": {
"front_vad_time": 6000,
"end_vad_time": 2000,
"audio_type": "pcm",
"chinese2digital": 1,
"punctuation": 2,
},
"business_info": "{\"scenes_pkg\":\"com.tencent.qqlive\", \"editor_type\":\"3\", \"pro_id\":\"2addc42b7ae689dfdf1c63e220df52a2-2020\"}"
}
start_data_json_str = json.dumps(start_data)
ws.send(start_data_json_str)
while cur_frames < nframes:
samp_remaining = nframes - cur_frames
num_samp = min(sample_frames, samp_remaining)
list_tmp = [None] * num_samp
for j in range(num_samp):
list_tmp[j] = wav_data_c[cur_frames + j]
pack_data_2 = struct.pack('%dB' % num_samp, *list_tmp)
cur_frames += num_samp
if len(pack_data_2) < 1280:
break
ws.send_binary(pack_data_2)
time.sleep(0.04)
enddata = b'--end--'
ws.send_binary(enddata)
closedata = b'--close--'
ws.send_binary(closedata)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return
def recv_process(ws, tbegin, wav_path):
index = 1
cnt = 1
first_world = 1
first_world_time = 0
sentence = ""
try:
while True:
r = ws.recv()
# print(r)
if r.startswith('{"sid":') and r:
chinese_chars = re.findall(r'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+', r)
sentence += ''.join(chinese_chars)
tmpobj = json.loads(r)
if tmpobj["action"] == "error" or tmpobj["action"] == "vad":
r = json.dumps(tmpobj)
# print("{}".format(r.encode('utf-8').decode('unicode_escape')))
path = wav_path
sid = tmpobj["sid"]
code = tmpobj["code"]
t3 = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
# print("{} {} {} {}".format(path, sid, code, t3))
if tmpobj["action"] == "result":
if tmpobj["type"] == "asr":
if first_world == 1:
if tmpobj["data"]["text"] != "":
tfirst = int(round(time.time() * 1000))
first_world = 0
first_world_time = tfirst - tbegin
if tmpobj["data"]["is_last"] is True:
r = json.dumps(tmpobj)
tend = int(round(time.time() * 1000))
path = wav_path
text = tmpobj["data"]["text"]
sid = tmpobj["sid"]
rid = tmpobj.get("request_id", "NULL")
code = tmpobj["code"]
t1 = first_world_time
t2 = tend - tbegin
t3 = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
# print("{}".format(text))
first_world = 1
tbegin = int(round(time.time() * 1000))
cnt = cnt + 1
if cnt > NUM:
return sentence
except Exception as e:
print(e)
path = wav_path
err = "exception"
t3 = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
print("{} {} {}".format(path, err, t3))
return sentence
def control_process(wav_path):
t = int(round(time.time() * 1000))
params = {'client_version': parse.quote('unknown'), 'product': parse.quote('x'), 'package': parse.quote('unknown'),
'sdk_version': parse.quote('unknown'), 'user_id': parse.quote('2addc42b7ae689dfdf1c63e220df52a2'),
'android_version': parse.quote('unknown'), 'system_time': parse.quote(str(t)), 'net_type': 1,
'engineid': "shortasrinput"}
appid = 'xxxxx'
appkey = 'xxxxx'
uri = '/asr/v2'
domain = 'api-ai.vivo.com.cn'
headers = gen_sign_headers(appid, appkey, 'GET', uri, params)
param_str = ''
seq = ''
for key, value in params.items():
value = str(value)
param_str = param_str + seq + key + '=' + value
seq = '&'
ws = create_connection('ws://' + domain + '/asr/v2?' + param_str, header=headers)
send_process(ws, wav_path)
return recv_process(ws, t, wav_path)
def asr_process(path):
audio_file_path = path # 在这里硬编码音频文件路径
return control_process(audio_file_path)
PART 3:(part of TTS)
让我们现在处理TTS的部分。
官方给的文档是用命令行运行的,那你跟女朋友说话用命令行说话吗?
我们要新增一个调用函数
def generate_wav_file(text: str, output_file: str, is_long_tts: bool = False, voice_type: Enum = ShortTTS.vivoHelper):
input_params = {
# 修改为你的app_id 和 app_key
'app_id': 'xxxxx',
'app_key': 'xxxxx',
'engineid': 'long_audio_synthesis_screen' if is_long_tts else 'short_audio_synthesis_jovi'
}
tts = TTS(**input_params)xxxxx
tts.open()
pcm_buffer = tts.gen_radio(aue=AueType.PCM, vcn=voice_type.value, text=text)
wav_io = pcm2wav(pcm_buffer)
with open(output_file, 'wb') as fd:
fd.write(wav_io.read())
完整代码:
class ShortTTS(Enum):
vivoHelper = "vivoHelper"
yunye = "yunye"
wanqing = "wanqing"
xiaofu = "xiaofu"
yige_child = "yige_child"
yige = "yige"
yiyi = "yiyi"
xiaoming = "xiaoming"
class LongTTS(Enum):
x2_vivoHelper = "vivoHelper"
x2_yige = "x2_yige"
x2_yige_news = "x2_yige_news"
x2_yunye = "x2_yunye"
x2_yunye_news = "x2_yunye_news"
x2_M02 = "x2_M02"
x2_M05 = "x2_M05"
x2_M10 = "x2_M10"
x2_F163 = "x2_F163"
x2_F25 = "x2_F25"
x2_F22 = "x2_F22"
x2_F82 = "x2_F82"
def pcm2wav(pcmdata: bytes, channels=1, bits=16, sample_rate=24000):
if bits % 8 != 0:
raise ValueError("bits % 8 must == 0. now bits:" + str(bits))
io_fd = io.BytesIO()
wavfile = wave.open(io_fd, 'wb')
wavfile.setnchannels(channels)
wavfile.setsampwidth(bits // 8)
wavfile.setframerate(sample_rate)
wavfile.writeframes(pcmdata)
wavfile.close()
io_fd.seek(0)
return io_fd
def generate_wav_file(text: str, output_file: str, is_long_tts: bool = False, voice_type: Enum = ShortTTS.vivoHelper):
input_params = {
# 修改为你的app_id 和 app_key
'app_id': 'xxxxx',
'app_key': 'xxxxx',
'engineid': 'long_audio_synthesis_screen' if is_long_tts else 'short_audio_synthesis_jovi'
}
tts = TTS(**input_params)
tts.open()
pcm_buffer = tts.gen_radio(aue=AueType.PCM, vcn=voice_type.value, text=text)
wav_io = pcm2wav(pcm_buffer)
with open(output_file, 'wb') as fd:
fd.write(wav_io.read())
PART 4:(part of SR)
最后让我们实现SR, 这个东西其实是最恶心的,要和官方文档对应sample rate channels 啥的.
我们看到官方给的文档

可以看到sample rate 为16K,bit depth 为16b,channel=1,PCM
所以我们可以设置SR为:
def record_audio(output_file, duration=2, sample_rate=16000, channels=1, format=pyaudio.paInt16):
CHUNK = 1024
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(format=format,
channels=channels,
rate=sample_rate,
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=CHUNK)
frames = []
for i in range(0, int(sample_rate / CHUNK * duration)):
data = stream.read(CHUNK)
frames.append(data)
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
p.terminate()
wf = wave.open(output_file, 'wb')
wf.setnchannels(channels)
wf.setsampwidth(p.get_sample_size(format))
wf.setframerate(sample_rate)
wf.writeframes(b''.join(frames))
wf.close()
return output_file
至此我们用demo改了一个demo出来
但还没结束。
因为我们自己的demo都没呢。。。。
现在AI界,有一个很火的内容就是 chain of thought ,不懂也没关系。就知道他就是你告诉llm是什么意思,就是举一个例子给llm,给他一个limit,让他自己学习,其实也是训练模型的一种方式,我们现在做的还不太算上chain of thought ,那我为什么要写? 意思是差不多的
重点理解:给他一个limit,让他自己学习
下面的限制你可以自己改。
instruction='''
你现在是我的女朋友,你的年龄是20岁,你是一个温柔漂亮大方的人。
我是一名程序员,我叫阿俊。我每天上班都很累,你要学会安慰我,为我舒缓压力。你说的话应该抑扬顿挫,且不能生成过长的语句,且输出的语句中有逗号的分隔。
你对话的身份是我的女朋友,只需要你输出女朋友要说的
**切记:我是你的男朋友,你是我的女朋友**
你的开头应该为:“下班了吗,宝贝?”
'''
聪明的人发现,WC,那我不是修改limit就可以做一个任意的 xxx对话系统呢?
对你说的没错。 _ , 少年请自行发挥吧!
接着我们初始化mode,还记得mode是什么吗?不记得回去看看噢
# 初始化mode
mode=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": instruction
}
]
为什么我们要初始化mode呢?因为我们要给limit给llm,让她扮演我们女朋友,也就是我们的instruction
后面的地方就没有什么好说了,假如你能看到这里,证明你对我对的英语口语系统流程图很熟悉,也会知道我后面再说什么了
完整代码:
instruction='''
你现在是我的女朋友,你的年龄是20岁,你是一个温柔漂亮大方的人。
我是一名程序员,我叫阿俊。我每天上班都很累,你要学会安慰我,为我舒缓压力。你说的话应该抑扬顿挫,且不能生成过长的语句,且输出的语句中有逗号的分隔。
你对话的身份是我的女朋友,只需要你输出女朋友要说的
**切记:我是你的男朋友,你是我的女朋友**
你的开头应该为:“下班了吗,宝贝?”
'''
# 初始化mode
mode=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": instruction
}
]
print("开始情侣对话了:")
while True:
# 产生对话
text1=vivo_1.stream_vivogpt(mode)
# 女友部分
print("女友:")
print(text1)
print('\n')
mode.append({"role": "assistant", "content": text1})
vivo_2_22.generate_wav_file(text1, 'output.wav', is_long_tts=False, voice_type=vivo_2_22.ShortTTS.vivoHelper)
playsound("output.wav")
# 男主部分
print("jun:")
path=vivo_record.record_audio("test.wav")
text2=ai_speech_input_client.asr_process(path)
print(text2)
print('\n')
# 继续循环
mode.append({"role": "user", "content": text2})
# 设置退出掉条件
if text2=='拜拜':
break


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号