Unity中实现A*寻路
前言:最近没事儿没工作,计划每天写一篇博客,防止对Unity生疏,也可以记录学习的点点滴滴。
A*寻路在很多面试里都会问到,但实际工作中根本用不着自己写,网上有成熟的插件,不容易错还方便。
思路:我们将地块切成大小均匀的格子,格子分成普通(可通行)、起点、终点、阻挡类型(不可通行)。每次循环时,查找open列表中综合代价最低的为当前格子,查找当前格子的八个方向(也可以查找四个方向)的邻格,计算综合代价并加入到open列表中去,当前格子就加入到close列表里,并从open列表中移除。当open列表内容为空时,或者当前格子已经为结束点时,结束循环。F代表综合代价,也就是起始距离 + 结束距离 = 综合距离;H代表结束距离(忽视阻挡);G代表起始距离
示例:
第一步,先实现Cell对象
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; using System; public class Cell : MonoBehaviour, IComparable { private CellType m_type; public CellType myType { get => m_type; set { m_type = value; switch (m_type) { case CellType.Normal: SetColor(Color.white); break; case CellType.Start: SetColor(Color.green); break; case CellType.End: SetColor(Color.red); break; case CellType.Block: SetColor(Color.black); break; } } } public Vector2Int pos;//坐标 public int F, G, H;//综合代价、起始代价、结束代价 public Cell parent;//父物体,为方便查找上一个节点,类似链表 private MeshRenderer render; private void Awake() { render = GetComponent<MeshRenderer>(); } public void SetColor(Color color) { render.material.color = color; } /// <summary> /// 两个cell对象排序,需要实现icompareable接口,指定它俩对比,是指对比F /// </summary> /// <param name="obj"></param> /// <returns></returns> public int CompareTo(object obj) { Cell cell = (Cell)obj; if (cell.F > F) { return -1; } else if (cell.F == F) { return 0; } else { return 1; } } }
第二步,实现查找具体方法
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; /// <summary> /// 这就是格子类型 /// </summary> public enum CellType { Normal = 1, Start = 2, End = 3, Block = 4 } public class AStar : MonoBehaviour { /// <summary> /// 这是生成地图数据 /// </summary> public int[,] map = { {2, 1, 4, 1, 1 }, {1, 1, 4, 1, 1 }, {1, 1, 4, 1, 1 }, {1, 1, 4, 1, 1 }, {1, 1, 1, 1, 3 } }; /// <summary> /// 预制体 /// </summary> public GameObject prefab; /// <summary> /// 所有格子对象 /// </summary> private Cell[,] cells; /// <summary> /// 开始点坐标和结束点坐标 /// </summary> private Vector2Int startPos, endPos; /// <summary> /// open列表和close列表 /// </summary> private List<Cell> openList, closeList; /// <summary> /// 存储路径的栈 /// </summary> private Stack<Cell> path; private void Start() { cells = new Cell[map.GetLength(0), map.GetLength(1)]; openList = new List<Cell>(); closeList = new List<Cell>(); path = new Stack<Cell>(); //生成地图 Vector3 pos = Vector3.zero; for (int i = 0; i < map.GetLength(0); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < map.GetLength(1); j++) { pos.Set(i * 1.5f, 0, j * 1.5f); GameObject obj = GameObject.Instantiate<GameObject>(prefab); obj.transform.parent = transform; obj.transform.position = pos; Cell cell = obj.AddComponent<Cell>(); CellType temp = (CellType)map[i, j]; if (temp == CellType.Start) { startPos.Set(i, j); } else if (temp == CellType.End) { endPos.Set(i, j); } cell.myType = temp; cell.pos.Set(i, j); cells[i, j] = cell; } } } private void Update() { if (Input.GetMouseButton(0)) { Find(); StartCoroutine(Draw()); } } private void Find() { openList.Add(cells[startPos.x, startPos.y]); Cell currentCell = openList[0]; while (openList.Count > 0 && currentCell.myType != CellType.End) { //通过排序找到综合代价最小的 openList.Sort(); currentCell = openList[0]; //这里已经找到了 if (currentCell.myType == CellType.End) { while (currentCell.parent != null) { if (currentCell.parent.myType != CellType.Start) { path.Push(currentCell.parent); } currentCell = currentCell.parent; } return; } //查找八个邻格 for (int i = -1; i <= 1; i++) { for (int j = -1; j <= 1; j++) { //增量为0,代表这个坐标指自己,所以直接跳过 if (i == 0 && j == 0) { continue; } //如果想只获取四个方向的邻格,就需要排除增量i = 增量j的情况 //if (i == j) //{ // continue; //} int x = currentCell.pos.x + i; int y = currentCell.pos.y + j; if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= cells.GetLength(0) || y >= cells.GetLength(1) || cells[x,y].myType == CellType.Block || closeList.Contains(cells[x,y])) { //这里判断当前邻格的坐标是否合法?是否为阻塞格子?是否已经存在于close列表中? continue; } //重新计算起始距离,乘10为了方便计算。当前坐标的格子的起始距离 = CurrenCell的起始距离 + 当前坐标的格子与CurrenCell的距离 int g = (int)(currentCell.G + Mathf.Sqrt(Mathf.Abs(i) + Mathf.Abs(j))* 10); if (cells[x,y].G == 0 || g < cells[x,y].G) { //若当前坐标的格子并未被查找过,或者当前坐标的格子的起始代价大于新算的起始代价,则更新 cells[x, y].G = g; cells[x, y].parent = currentCell; } cells[x, y].H = (Mathf.Abs(x - endPos.x) + Mathf.Abs(y - endPos.y)) * 10;//计算结束距离 cells[x, y].F = cells[x, y].G + cells[x, y].H;//综合代价 if (!openList.Contains(cells[x,y])) { openList.Add(cells[x, y]); } } } openList.Remove(currentCell); closeList.Add(currentCell); if (openList.Count == 0) { //这里是指open列表都已经没有内容了,但是仍未查找到结束点,因此可认为无路可达 Debug.LogWarning("穷途末路"); } } } private IEnumerator Draw() { while (path.Count > 0) { Cell cell = path.Pop(); cell.SetColor(Color.blue); yield return new WaitForSeconds(0.2f); } } }
第三步,测试并查看正确性
这是八个方向的

这是四个方向的
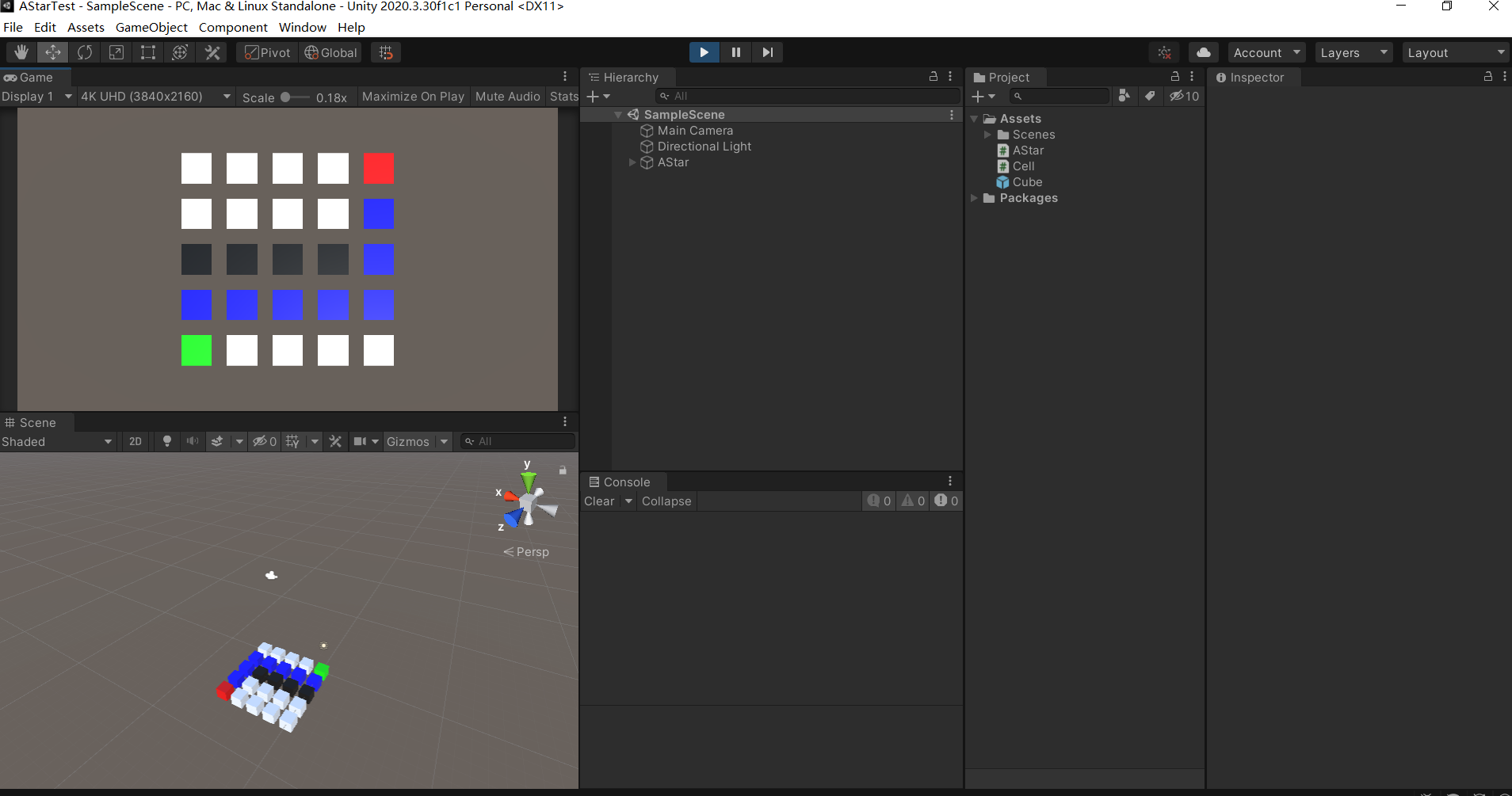
总结:
以前同事做推箱子的时候,就用过A*算法,还教过我,不过我当时并没懂,最近又挨着学了一次,发现还是自己动手牢靠,记得比较清晰。当时的我的误区在于,我以为close列表就是路径,其实close列表仅仅代表“这个格子我已经检查过啦,不必再检查了”,真正的路径是通过结束点,一步步获取它的parent直到起始点(起始点的parent为空),这样才是完整路径。还需要注意的是,我们每次循环都会对open列表排序,选择综合代价最小的格子,作为本次循环的“CurrentCell”,所以我们必须为Cell对象实现排序接口,指定排序是通过对比F综合代价。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号