rpn部分:
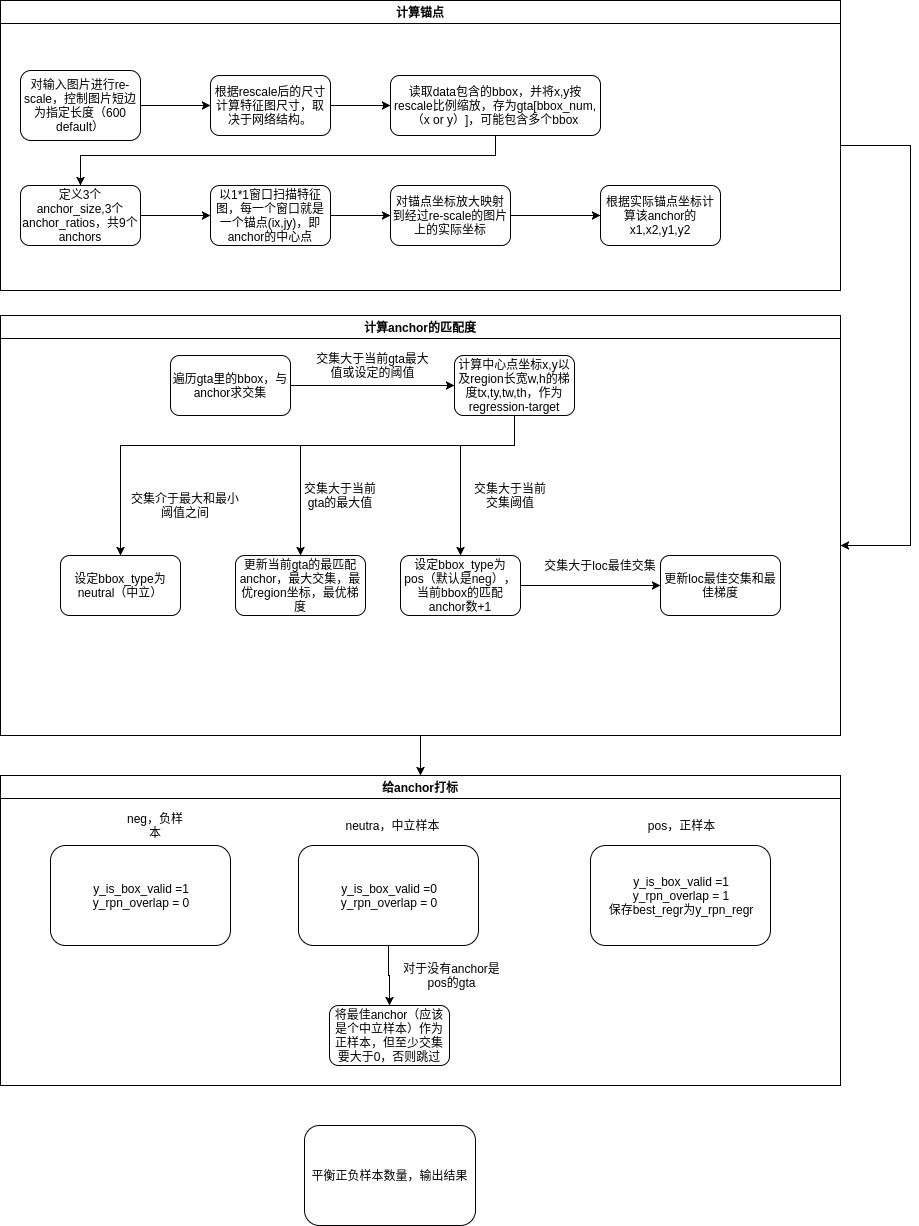
1 def calc_rpn(C, img_data, width, height, resized_width, resized_height, img_length_calc_function): 2 #C-配置信息;img_data-图片路径、bbox坐标、对应分类(一张图片可能有多个bbox) 3 #width, height-图片原尺寸;resized_width, resized_height-图片resize后的尺寸 4 #img_length_calc_function-一个方法,基于设置,从图片尺寸计算出网络之后的特征图尺寸 5 6 7 downscale = float(C.rpn_stride) 8 #下采样倍数 9 anchor_sizes = C.anchor_box_scales 10 anchor_ratios = C.anchor_box_ratios 11 num_anchors = len(anchor_sizes) * len(anchor_ratios) 12 #anchor的大小尺寸(3*3=9) 13 14 15 # calculate the output map size based on the network architecture 16 (output_width, output_height) = img_length_calc_function(resized_width, resized_height) 17 #计算出特征图尺寸 18 19 20 n_anchratios = len(anchor_ratios) 21 #n_anchratios-anchor的尺寸个数 22 23 24 # initialise empty output objectives 25 #以0初始化配置、参数 26 y_rpn_overlap = np.zeros((output_height, output_width, num_anchors)) 27 y_is_box_valid = np.zeros((output_height, output_width, num_anchors)) 28 y_rpn_regr = np.zeros((output_height, output_width, num_anchors * 4)) 29 30 31 num_bboxes = len(img_data['bboxes']) 32 33 34 num_anchors_for_bbox = np.zeros(num_bboxes).astype(int) 35 best_anchor_for_bbox = -1*np.ones((num_bboxes, 4)).astype(int) 36 best_iou_for_bbox = np.zeros(num_bboxes).astype(np.float32) 37 best_x_for_bbox = np.zeros((num_bboxes, 4)).astype(int) 38 best_dx_for_bbox = np.zeros((num_bboxes, 4)).astype(np.float32) 39 40 41 #将bbox的坐标分别通过缩放匹配到resize之后的特征图,记作gta,尺寸为(num_bboxes, 4) 42 # get the GT box coordinates, and resize to account for image resizing 43 gta = np.zeros((num_bboxes, 4)) 44 for bbox_num, bbox in enumerate(img_data['bboxes']): 45 # get the GT box coordinates, and resize to account for image resizing 46 gta[bbox_num, 0] = bbox['x1'] * (resized_width / float(width)) 47 gta[bbox_num, 1] = bbox['x2'] * (resized_width / float(width)) 48 gta[bbox_num, 2] = bbox['y1'] * (resized_height / float(height)) 49 gta[bbox_num, 3] = bbox['y2'] * (resized_height / float(height)) 50 51 # rpn ground truth 52 for anchor_size_idx in range(len(anchor_sizes)): 53 for anchor_ratio_idx in range(n_anchratios): 54 anchor_x = anchor_sizes[anchor_size_idx] * anchor_ratios[anchor_ratio_idx][0] 55 anchor_y = anchor_sizes[anchor_size_idx] * anchor_ratios[anchor_ratio_idx][1] 56 #计算ancohr的长宽。 57 # #anchor_ratios[anchor_ratio_idx]-size为idx的长宽 58 59 60 for ix in range(output_width): 61 # x-coordinates of the current anchor box 62 x1_anc = downscale * (ix + 0.5) - anchor_x / 2 63 x2_anc = downscale * (ix + 0.5) + anchor_x / 2 64 65 # ignore boxes that go across image boundaries 66 if x1_anc < 0 or x2_anc > resized_width: 67 continue 68 69 for jy in range(output_height): 70 71 72 # y-coordinates of the current anchor box 73 y1_anc = downscale * (jy + 0.5) - anchor_y / 2 74 y2_anc = downscale * (jy + 0.5) + anchor_y / 2 75 76 77 # ignore boxes that go across image boundaries 78 if y1_anc < 0 or y2_anc > resized_height: 79 continue 80 #-------------------------------------------------------------# 81 #将特征图每一点都作为锚点,通过downscale映射到图片的实际尺寸,再结合anchor的尺寸 82 #忽略超出图片范围的anchor 83 #得到大小、比例不一的多个锚框 84 85 86 #定义变量 87 # bbox_type indicates whether an anchor should be a target 88 #初始化bbox的类型为负样本 89 bbox_type = 'neg' 90 91 92 # this is the best IOU for the (x,y) coord and the current anchor 93 # note that this is different from the best IOU for a GT bbox 94 best_iou_for_loc = 0.0 95 96 97 #对锚框进行遍历: 98 for bbox_num in range(num_bboxes): 99 100 # get IOU of the current GT box and the current anchor box 101 #遍历gta里的bbox,与anchor求iou 102 curr_iou = iou([gta[bbox_num, 0], gta[bbox_num, 2], gta[bbox_num, 1], gta[bbox_num, 3]], [x1_anc, y1_anc, x2_anc, y2_anc]) 103 # calculate the regression targets if they will be needed 104 #若iou大于阈值或当前gta最大值 105 if curr_iou > best_iou_for_bbox[bbox_num] or curr_iou > C.rpn_max_overlap: 106 #计算gta和anchor的中心点坐标 107 #通过中心点坐标和bbox坐标,计算出x,y,w,h四个值的梯度值,用于后面的回归计算 108 cx = (gta[bbox_num, 0] + gta[bbox_num, 1]) / 2.0 109 cy = (gta[bbox_num, 2] + gta[bbox_num, 3]) / 2.0 110 cxa = (x1_anc + x2_anc)/2.0 111 cya = (y1_anc + y2_anc)/2.0 112 113 114 tx = (cx - cxa) / (x2_anc - x1_anc) 115 ty = (cy - cya) / (y2_anc - y1_anc) 116 tw = np.log((gta[bbox_num, 1] - gta[bbox_num, 0]) / (x2_anc - x1_anc)) 117 th = np.log((gta[bbox_num, 3] - gta[bbox_num, 2]) / (y2_anc - y1_anc)) 118 119 120 #对正样本进行操作 121 if img_data['bboxes'][bbox_num]['class'] != 'bg': 122 123 124 #所有对象都有anchor对应,所以追踪anchor就找到了对象 125 # all GT boxes should be mapped to an anchor box, so we keep track of which anchor box was best 126 # 如果iou>当前gta的最大值,更新当前gta的最匹配anchor,最大交集,最优region坐标,最优梯度 127 if curr_iou > best_iou_for_bbox[bbox_num]: 128 best_anchor_for_bbox[bbox_num] = [jy, ix, anchor_ratio_idx, anchor_size_idx] 129 best_iou_for_bbox[bbox_num] = curr_iou 130 best_x_for_bbox[bbox_num,:] = [x1_anc, x2_anc, y1_anc, y2_anc] 131 best_dx_for_bbox[bbox_num,:] = [tx, ty, tw, th] 132 133 134 # we set the anchor to positive if the IOU is >0.7 (it does not matter if there was another better box, it just indicates overlap) 135 #如果iou>0.7,bbox_type设为pos-正样本(默认是neg) 136 if curr_iou > C.rpn_max_overlap: 137 bbox_type = 'pos' 138 #当前bbox的匹配anchor数+1 139 num_anchors_for_bbox[bbox_num] += 1 140 141 142 #如果iou>当前best_iou_for_loc,则将best_regr设为当前的tx,ty,tw,th 143 # we update the regression layer target if this IOU is the best for the current (x,y) and anchor position 144 if curr_iou > best_iou_for_loc: 145 best_iou_for_loc = curr_iou 146 best_regr = (tx, ty, tw, th) 147 148 149 #如果iou介于最大和最小阈值之间,设定bbox_type为neutral(中立) 150 # if the IOU is >0.3 and <0.7, it is ambiguous and no included in the objective 151 if C.rpn_min_overlap < curr_iou < C.rpn_max_overlap: 152 # gray zone between neg and pos 153 if bbox_type != 'pos': 154 bbox_type = 'neutral' 155 156 157 158 159 # turn on or off outputs depending on IOUs 160 #根据type区分bbox 161 if bbox_type == 'neg': 162 #负样本 163 y_is_box_valid[jy, ix, anchor_ratio_idx + n_anchratios * anchor_size_idx] = 1 164 #有意义 165 y_rpn_overlap[jy, ix, anchor_ratio_idx + n_anchratios * anchor_size_idx] = 0 166 #不包含对象 167 elif bbox_type == 'neutral': 168 #中立 169 y_is_box_valid[jy, ix, anchor_ratio_idx + n_anchratios * anchor_size_idx] = 0 170 #无意义,不包含对象 171 y_rpn_overlap[jy, ix, anchor_ratio_idx + n_anchratios * anchor_size_idx] = 0 172 elif bbox_type == 'pos': 173 #正样本 174 y_is_box_valid[jy, ix, anchor_ratio_idx + n_anchratios * anchor_size_idx] = 1 175 y_rpn_overlap[jy, ix, anchor_ratio_idx + n_anchratios * anchor_size_idx] = 1 176 #有意义,包含对象 177 #(???体悟明咯,咩start啊) 178 start = 4 * (anchor_ratio_idx + n_anchratios * anchor_size_idx) 179 y_rpn_regr[jy, ix, start:start+4] = best_regr 180 181 182 # we ensure that every bbox has at least one positive RPN region 183 #每个bbox都至少要有一个pos的anchor,如果没有的话在中性anchor中挑最好的 184 for idx in range(num_anchors_for_bbox.shape[0]): 185 #如果没有bbox没有pos的anchor 186 if num_anchors_for_bbox[idx] == 0: 187 # no box with an IOU greater than zero ... 188 if best_anchor_for_bbox[idx, 0] == -1: 189 continue 190 y_is_box_valid[ 191 best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,0], best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,1], best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,2] + n_anchratios * 192 best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,3]] = 1 193 y_rpn_overlap[ 194 best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,0], best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,1], best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,2] + n_anchratios * 195 best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,3]] = 1 196 #(好似每个pos都有start、y_rpn_regr喔) 197 start = 4 * (best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,2] + n_anchratios * best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,3]) 198 y_rpn_regr[ 199 best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,0], best_anchor_for_bbox[idx,1], start:start+4] = best_dx_for_bbox[idx, :] 200 201 202 #用numpy大法进行anchor的回归 203 y_rpn_overlap = np.transpose(y_rpn_overlap, (2, 0, 1)) 204 y_rpn_overlap = np.expand_dims(y_rpn_overlap, axis=0) 205 206 207 y_is_box_valid = np.transpose(y_is_box_valid, (2, 0, 1)) 208 y_is_box_valid = np.expand_dims(y_is_box_valid, axis=0) 209 210 211 y_rpn_regr = np.transpose(y_rpn_regr, (2, 0, 1)) 212 y_rpn_regr = np.expand_dims(y_rpn_regr, axis=0) 213 214 215 pos_locs = np.where(np.logical_and(y_rpn_overlap[0, :, :, :] == 1, y_is_box_valid[0, :, :, :] == 1)) 216 neg_locs = np.where(np.logical_and(y_rpn_overlap[0, :, :, :] == 0, y_is_box_valid[0, :, :, :] == 1)) 217 218 219 num_pos = len(pos_locs[0]) 220 221 222 # one issue is that the RPN has many more negative than positive regions, so we turn off some of the negative 223 # regions. We also limit it to 256 regions. 224 #设定regions数量的最大值,并对正负样本均匀取样 225 num_regions = 256 226 227 228 if len(pos_locs[0]) > num_regions/2: 229 val_locs = random.sample(range(len(pos_locs[0])), len(pos_locs[0]) - num_regions/2) 230 y_is_box_valid[0, pos_locs[0][val_locs], pos_locs[1][val_locs], pos_locs[2][val_locs]] = 0 231 num_pos = num_regions/2 232 233 234 if len(neg_locs[0]) + num_pos > num_regions: 235 val_locs = random.sample(range(len(neg_locs[0])), len(neg_locs[0]) - num_pos) 236 y_is_box_valid[0, neg_locs[0][val_locs], neg_locs[1][val_locs], neg_locs[2][val_locs]] = 0 237 238 239 #得到二分类和回归的结果 240 y_rpn_cls = np.concatenate([y_is_box_valid, y_rpn_overlap], axis=1) 241 y_rpn_regr = np.concatenate([np.repeat(y_rpn_overlap, 4, axis=1), y_rpn_regr], axis=1) 242 243 244 return np.copy(y_rpn_cls), np.copy(y_rpn_regr)
rpn部分整合:
1 def rpn(base_layers,num_anchors): 2 3 4 x = Convolution2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu', kernel_initializer='normal', name='rpn_conv1')(base_layers) 5 6 7 # 通过1*1的卷积生成num_anchors数量的channel,每个channel包含特征图(w*h)个relu激活值,表明anchor是否有意义 8 #number_anchors=9(9种anchor) 9 x_class = Convolution2D(num_anchors, (1, 1), activation='sigmoid', kernel_initializer='uniform', name='rpn_out_class')(x) 10 x_regr = Convolution2D(num_anchors * 4, (1, 1), activation='linear', kernel_initializer='zero', name='rpn_out_regress')(x) 11 #x_class是原大小,深度为9(9种anchor的前/背景分类) 12 #x_regr是原大小,深度为9*4(9种anchor的坐标) 13 return [x_class, x_regr, base_layers]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号